Pytorch框架学习路径(一:张量简介与创建)
学习课程来自深度之眼。
文章目录
- 张量是什么?
- Variable数据类型
- 张量的创建
-
- Tensor创建一:直接创建
-
- torch.tensor创建张量
- torch.from_numpy创建张量
- Tensor创建二:依据数值创建
-
- torch.zeros()
- torch.zeros_like()和torch.ones()
- torch.full()
- Tensor创建三:依据概率创建
-
- torch.arange()
- torch.logspace()
- torch.logspace()
- torch.eye()
- torch.normal()
- 随机生成Tensor
- torch.randperm()
张量是什么?
Variable数据类型
理解Variable对理解张量是很有帮助的。
Variable是torch.autograd中的数据类型主要用于封装Tensor,让tensor能够进行自动求导。


张量的创建
Tensor创建一:直接创建
torch.tensor创建张量
| 1、通过torch.tensor创建张量 |
# =============================== example 1 ===============================
# 通过torch.tensor创建张量
#
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
print("ndarray的数据类型:", arr.dtype)
t_gpu = torch.tensor(arr, device='cuda') # 把数据从cpu转到gpu(这个过程需要一定的时间)
t = torch.tensor(arr)
print("t_gpu:{}\nt:{}".format(t_gpu, t))
# print(t)
torch.from_numpy创建张量
| 2、通过torch.from_numpy创建张量 |
# =============================== example 2 ===============================
# 通过torch.from_numpy创建张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
t = torch.from_numpy(arr)
print('1_1_1_'*20)
print("numpy array: ", arr)
print("tensor : ", t)
print('\n')
print('2_2_2_'*20)
print("修改arr")
arr[0, 0] = 0
print("numpy array: ", arr)
print("tensor : ", t)
print('\n')
print('3_3_3_' * 20)
print("修改tensor")
t[0, 0] = -1
print("numpy array: ", arr)
print("tensor : ", t)
OUT: 通过以下输出结果可以看出:从tor c h .f r om_ n u mp y 创建的te n sor于原n darr ay共享内存,当修改其中一个的数据,另外一个也将会被改动
1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_
numpy array: [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
tensor : tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_
修改arr
numpy array: [[0 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
tensor : tensor([[0, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_
修改tensor
numpy array: [[-1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6]]
tensor : tensor([[-1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
Tensor创建二:依据数值创建
torch.zeros()
| 3、通过torch.zeros创建全为0张量 |
# =============================== example 3 ===============================
# 通过torch.zeros创建张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
out_t = torch.tensor([1])
t = torch.zeros((3, 3), out=out_t)
print(t, '\n', out_t)
# print(id(t), id(out_t), id(t) == id(out_t))
print("t的内存地址 :{}\nout_t的内存地址 :{}\nt和out_t的内存地址是否相同 :{}".format(id(t), id(out_t), id(t) == id(out_t)))
OUT:
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
t的内存地址 :2703282791352
out_t的内存地址 :2703282791352
t和out_t的内存地址是否相同 :True
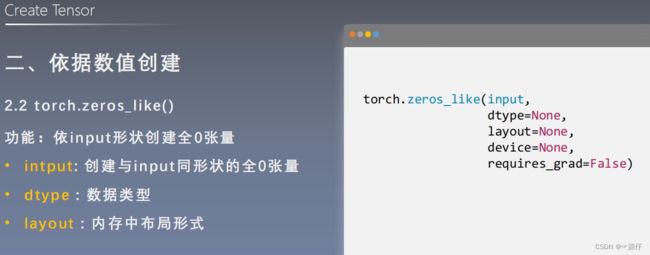
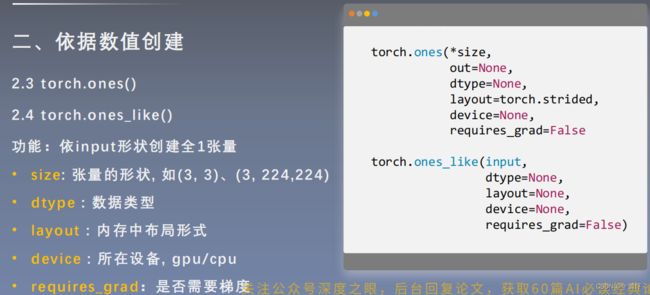
torch.zeros_like()和torch.ones()
torch.zeros_like()和torch.ones()这两种用法和torch.zeros()相同,不再举例说明。
torch.full()
| 4、通过torch.full创建全1张量 |
# =============================== example 4 ===============================
# 通过torch.full创建全1张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.full((3, 3), 1.) # 1.6之后若不指定dtype,就需要传入浮点数
print(t)
OUT:
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
Tensor创建三:依据概率创建
torch.arange()
| 5、通过torch.arange创建等差数列张量 |
# =============================== example 5 ===============================
# 通过torch.arange创建等差数列张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.arange(2, 10, 2)
print(t)
OUT:
tensor([2, 4, 6, 8])
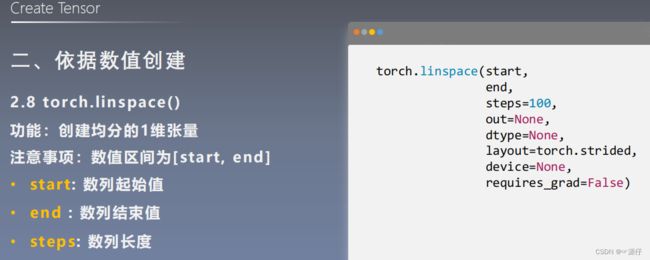
torch.logspace()
| 6、通过torch.linspace创建均分数列张量 |
# =============================== example 6 ===============================
# 通过torch.linspace创建均分数列张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
# t = torch.linspace(2, 10, 5)
t = torch.linspace(2, 10, 6)
print(t)
OUT:
tensor([ 2.0000, 3.6000, 5.2000, 6.8000, 8.4000, 10.0000])
torch.logspace()
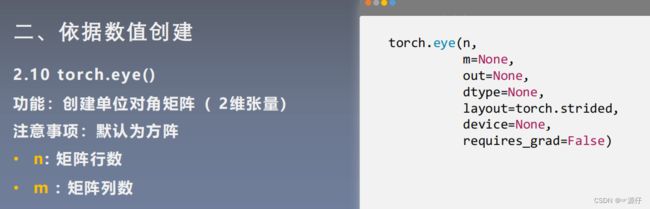
torch.eye()
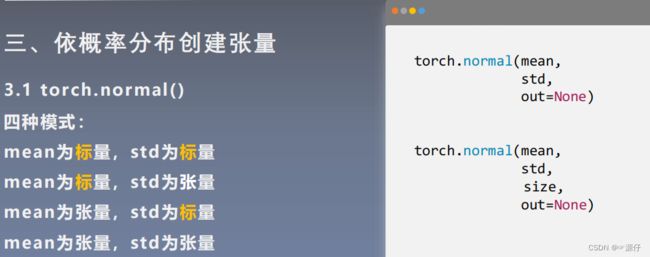
torch.normal()
| 7、通过torch.linspace创建均分数列张量 |
# =============================== example 7 ===============================
# 通过torch.normal创建正态分布张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
# mean:张量 std: 张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print('1_1_1_' * 20)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
# mean:标量 std: 标量
t_normal = torch.normal(0., 1., size=(4,))
print('2_2_2_' * 20)
print(t_normal)
# mean:张量 std: 标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = 1
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print('3_3_3_' * 20)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
OUT:
# =============================== example 7 ===============================
# 通过torch.normal创建正态分布张量
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
# mean:张量 std: 张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print('1_1_1_' * 20)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
# mean:标量 std: 标量
t_normal = torch.normal(0., 1., size=(4,))
print('2_2_2_' * 20)
print(t_normal)
# mean:张量 std: 标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = 1
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print('3_3_3_' * 20)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
OUT:
1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_
mean:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
std:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
tensor([1.6614, 2.5338, 3.1850, 6.4853])
2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_
tensor([-0.4519, -0.1661, -1.5228, 0.3817])
3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_
mean:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
std:1
tensor([-0.0276, 1.4369, 2.1077, 3.9417])
随机生成Tensor
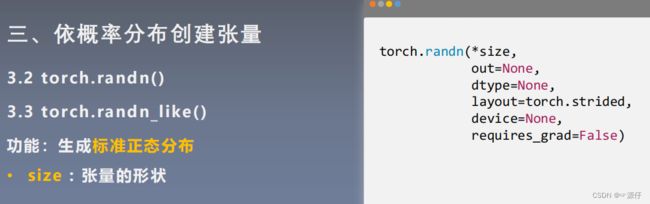
| 7、通过torch.rand和torch.randn随机生成张量 |
问题:torch.rand和torch.randn有什么区别?
一个均匀分布,一个是标准正态分布。
# =============================== example 7 ===============================
# torch.rand和torch.randn
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
# rand(*size, out=None, dtype=None)
t1 = torch.rand(2, 3)
print('1_1_1_' * 20)
print("t1:{}\nt1.type:{}".format(t1, t1.type()))
# randn(*size, out=None, dtype=None)
# randn_like(input, dtype=None)
t2 = torch.randn(2, 3)
t3 = torch.randn_like(t1)
print('\n')
print('2_2_2_' * 20)
print("t2:{}\nt2.type:{}".format(t2, t2.type()))
print("t3:{}\nt3.type:{}".format(t3, t3.type()))
# randint(low=0, high, size, out=None, dtype=None)
# randint_like(input, low=0, high, dtype=None)
# 整数范围[low, high)
t4 = torch.randint(1, 4, (2, 3, 2)) # 形状写成[2,3,2]也行
t5 = torch.randint_like(t1, 4)
print('\n')
print('3_3_3_' * 20)
print("t4:{}\nt4.type:{}".format(t4, t4.type()))
print("t5:{}\nt5.type:{}".format(t5, t5.type()))
OUT:
1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_1_
t1:tensor([[0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031],
[0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999]])
t1.type:torch.FloatTensor
2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_2_
t2:tensor([[ 0.5636, 1.1431, 0.8590],
[ 0.7056, -0.3406, -1.2720]])
t2.type:torch.FloatTensor
t3:tensor([[-1.1948, 0.0250, -0.7627],
[ 1.3969, -0.3245, 0.2879]])
t3.type:torch.FloatTensor
3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_3_
t4:tensor([[[3, 3],
[1, 1],
[2, 1]],
[[3, 1],
[3, 3],
[1, 3]]])
t4.type:torch.LongTensor
t5:tensor([[1., 3., 3.],
[1., 2., 1.]])
t5.type:torch.FloatTensor
torch.randperm()
# =============================== example 9 ===============================
# torch.randperm()
flag = True
# flag = False
if flag:
# torch中没有random.shuffle
# y = torch.randperm(n) y是把1到n这些数随机打乱得到的一个数字序列
import torch
# randperm(n, out=None, dtype=torch.int64)-> LongTensor
idx = torch.randperm(3)
a = torch.Tensor(4, 2)
print("a: {}".format(a))
print("\nidx: {}\nidx.type: {}".format(idx, idx.type()))
print("\na[idx]: {}".format(a[idx]))
OUT:
a: tensor([[-1.9488e-07, -3.3273e+20],
[-1.9488e-07, 5.3236e+21],
[-1.9488e-07, -1.6909e+16],
[-1.9488e-07, 3.1477e+25]])
idx: tensor([1, 2, 0])
idx.type: torch.LongTensor
a[idx]: tensor([[-1.9488e-07, 5.3236e+21],
[-1.9488e-07, -1.6909e+16],
[-1.9488e-07, -3.3273e+20]])