【CVPR2020】3D目标检测论文汇总
文章目录
-
- 1. 3D目标检测——室外
-
-
- 1. Associate-3Ddet: Perceptual-to-Conceptual Association for 3D Point Cloud Object Detection
- 2. Structure Aware Single-stage 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud
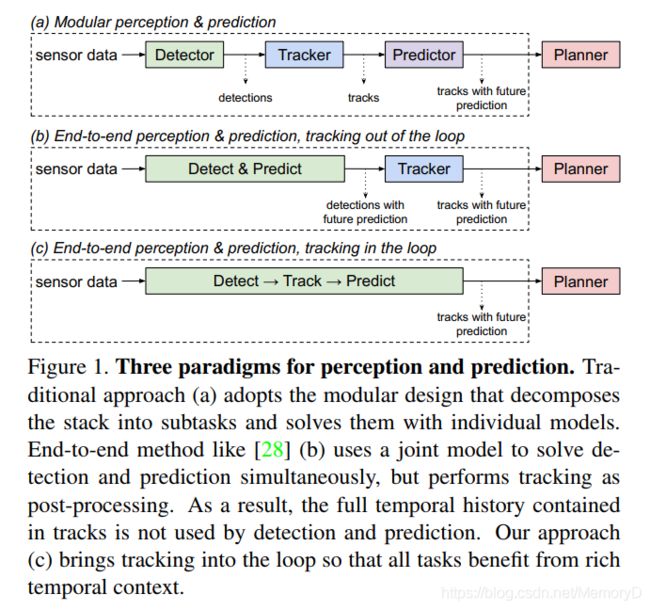
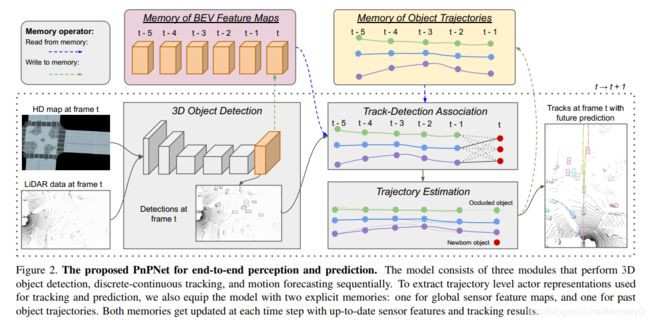
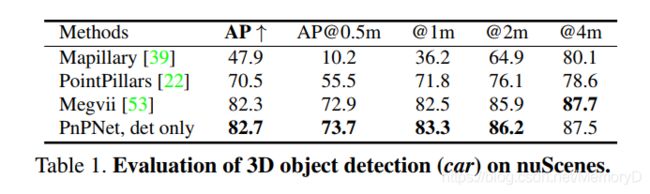
- 3. PnPNet: End-to-End Perception and Prediction with Tracking in the Loop
- 4. DOPS: Learning to Detect 3D Objects and Predict their 3D Shapes
- 5. Point-GNN: Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
- 6. PV-RCNN: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction for 3D Object Detection
- 7. Physically Realizable Adversarial Examples for LiDAR Object Detection
- 8. MotionNet: Joint Perception and Motion Prediction for Autonomous Driving Based on Bird’s Eye View Maps
- 9. 3DSSD: Point-based 3D Single Stage Object Detector
- 10. HVNet: Hybrid Voxel Network for LiDAR Based 3D Object Detection
- 11. LiDAR-based Online 3D Video Object Detection with Graph-based Message Passing and Spatiotemporal Transformer Attention
-
- 2. 3D目标检测增强技术
-
-
- 1. PointPainting: Sequential Fusion for 3D Object Detection
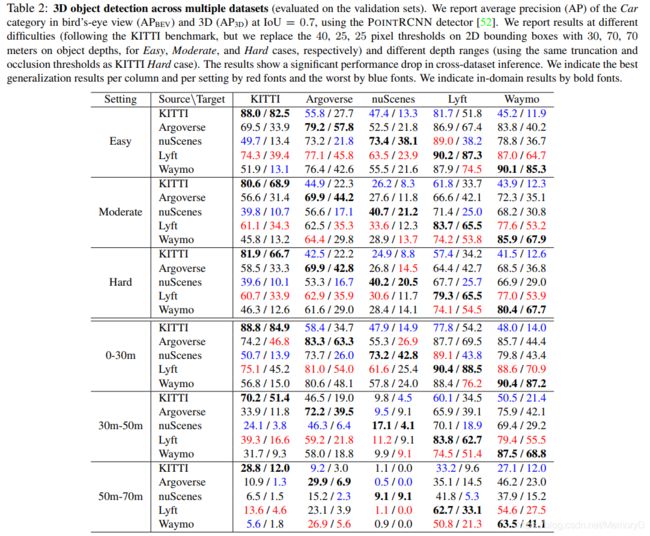
- 2. Train in Germany, Test in The USA: Making 3D Object Detectors Generalize
- 3. Learning to Evaluate Perception Models using Planner-Centric Metrics
- 4. What You See is What You Get: Exploiting Visibility for 3D Object Detection
-
- 3. 3D目标检测——室内
-
-
- 1. Density Based Clustering for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds
- 2. A Hierarchical Graph Network for 3D Object Detection on Point Clouds
- 3. ImVoteNet: Boosting 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds with Image Votes
- 4. MLCVNet: Multi-Level Context VoteNet for 3D Object Detection
- 5. SESS: Self-Ensembling Semi-Supervised 3D Object Detection
-
- 4. 单目3D目标检测
-
-
- 1. DSGN: Deep Stereo Geometry Network for 3D Object Detection
- 2. Learning Depth-Guided Convolutions for Monocular 3D Object Detection
- 3. End-to-End Pseudo-LiDAR for Image-Based 3D Object Detection
- 4. Disp R-CNN: Stereo 3D Object Detection via Shape Prior Guided Instance Disparity Estimation
-
1. 3D目标检测——室外
1. Associate-3Ddet: Perceptual-to-Conceptual Association for 3D Point Cloud Object Detection
-
摘要
Object detection from 3D point clouds remains a challenging task, though recent studies pushed the envelope with the deep learning techniques. Owing to the severe spatial occlusion and inherent variance of point density with the distance to sensors, appearance of a same object varies a lot in point cloud data. Designing robust feature representation against such appearance changes is hence the key issue in a 3D object detection method. In this paper, we innovatively propose a domain adaptation like approach to enhance the robustness of the feature representation. More specifically, we bridge the gap between the perceptual domain where the feature comes from a real scene and the conceptual domain where the feature is extracted from an augmented scene consisting of non-occlusion point cloud rich of detailed information. This domain adaptation approach mimics the functionality of the human brain when proceeding object perception. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our simple yet effective approach fundamentally boosts the performance of 3D point cloud object detection and achieves the state-of-the-art results.
尽管最近的研究推动了深度学习技术的发展,但从3D点云进行目标检测仍然是一项艰巨的任务。由于严重的空间遮挡、点密度以及传感器之间距离的固有差异,因此点云数据中同一对象的外观变化很大。因此,针对这种外观变化设计鲁棒的特征表示是3D目标检测方法中的关键问题。在本文中,我们创新地提出了一种类似域自适应的方法,以增强特征表示的鲁棒性。 更具体地说,我们弥合了以下两个域的差异:1)感知域:特征来自真实场景;2)概念域:特征提取自一个由丰富的详细信息的非遮挡点云组成的增强场景。在进行对象感知时,这种域适应方法可模仿人脑的功能。大量的实验表明,我们简单而有效的方法从根本上提高了3D点云目标检测的性能,并获得了SOTA的结果。
- 整体架构
-
论文: Associate-3Ddet: Perceptual-to-Conceptual Association for 3D Point Cloud Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/dleam/Associate-3Ddet
2. Structure Aware Single-stage 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud
-
摘要
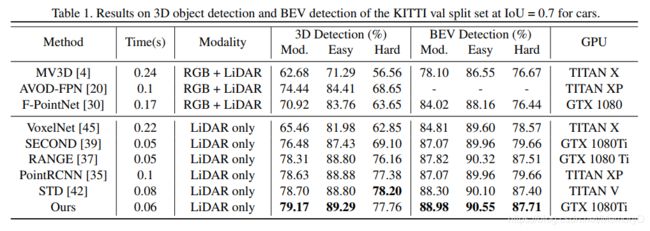
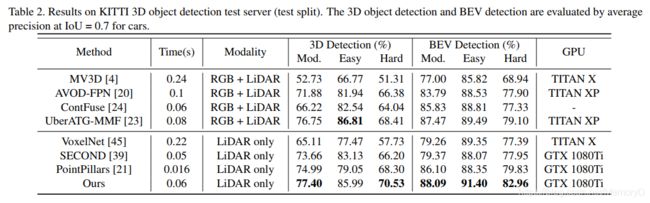
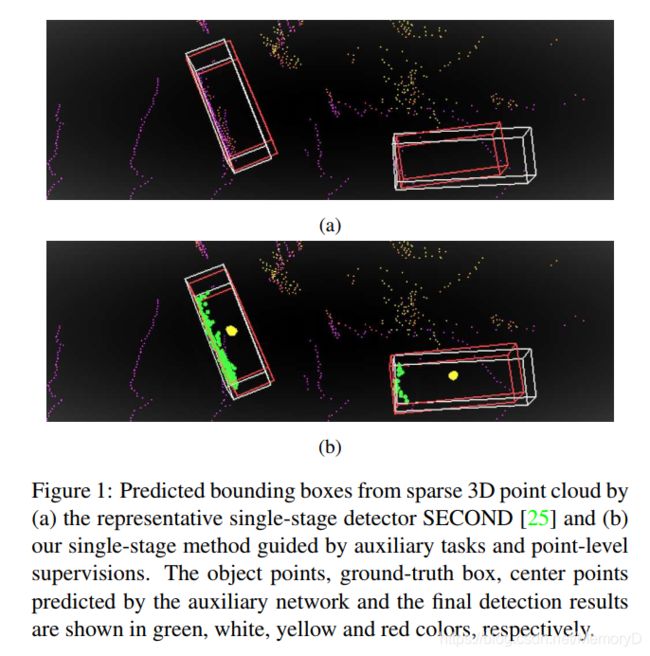
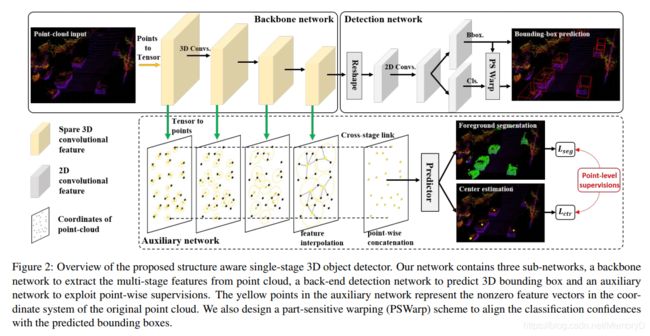
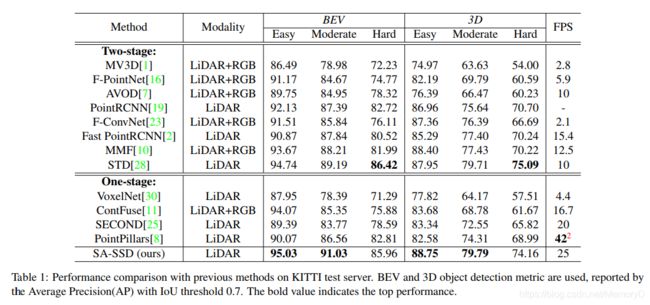
3D object detection from point cloud data plays an essential role in autonomous driving. Current single-stage detectors are efficient by progressively downscaling the 3D point clouds in a fully convolutional manner. However, the downscaled features inevitably lose spatial information and cannot make full use of the structure information of 3D point cloud, degrading their localization precision. In this work, we propose to improve the localization precision of single-stage detectors by explicitly leveraging the structure information of 3D point cloud. Specifically, we design an auxiliary network which converts the convolutional features in the backbone network back to point-level representations. The auxiliary network is jointly optimized, by two point-level supervisions, to guide the convolutional features in the backbone network to be aware of the object structure. The auxiliary network can be detached after training and therefore introduces no extra computation in the inference stage. Besides, considering that single-stage detectors suffer from the discordance between the predicted bounding boxes and corresponding classification confidences, we develop an efficient part-sensitive warping operation to align the confidences to the predicted bounding boxes. Our proposed detector ranks at the top of KITTI 3D/BEV detection leaderboards and runs at 25 FPS for inference.
从点云数据检测3D目标在自动驾驶中起着至关重要的作用。当前的单级检测器以完全卷积的方式逐步缩小3D点云的尺寸,这非常有效。但是,缩小后的特征不可避免地会丢失空间信息,并且无法充分利用3D点云的结构信息,从而降低定位精度。在这项工作中,我们提出通过显式利用3D点云的结构信息来提高单级探测器的定位精度。具体来说,我们设计了一个辅助网络,该网络将骨干网中的卷积特征转换回点级(point-level)表示。辅助网络是通过两个点级别的监督共同优化的,以指导骨干网络中的卷积特征了解目标结构。辅助网络可以在训练后分离,因此在推理阶段不会引入额外的计算。 此外,考虑到单级检测器会遇到预测边界框与相应分类置信度之间的不一致的情况,我们开发了一种有效的部件敏感变形操作(part-sensitive warping operation),以将置信度与预测边界框对齐。我们提出的检测器排在KITTI 3D / BEV检测排行榜的顶部,以25 FPS的推理速度运行。
-
论文: Structure Aware Single-stage 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud
-
代码: https://github.com/skyhehe123/SA-SSD
3. PnPNet: End-to-End Perception and Prediction with Tracking in the Loop
-
摘要
We tackle the problem of joint perception and motion forecasting in the context of self-driving vehicles. Towards this goal we propose PnPNet, an end-to-end model that takes as input sequential sensor data, and outputs at each time step object tracks and their future trajectories. The key component is a novel tracking module that generates object tracks online from detections and exploits trajectory level features for motion forecasting. Specifically, the object tracks get updated at each time step by solving both the data association problem and the trajectory estimation problem. Importantly, the whole model is end-to-end trainable and benefits from joint optimization of all tasks. We validate PnPNet on two large-scale driving datasets, and show significant improvements over the state-of-the-art with better occlusion recovery and more accurate future prediction.
我们想要解决自动驾驶中的联合感知和运动预测问题。为了实现这一目标,我们提出了PnPNet,这是一个端到端模型,该模型将连续传感器数据作为输入,并在每个时间步长输出目标轨迹及其未来轨迹。关键组件是一个新颖的跟踪模块,该模块可根据检测结果在线生成目标跟踪轨迹,并利用轨迹级别的特征进行运动预测。具体而言,通过解决数据关联问题和轨迹估计问题,在每个时间步更新对象轨迹。 重要的是,整个模型是端到端可训练的,并且受益于所有任务的联合优化。我们在两个大型驾驶数据集上验证了PnPNet,并显示了与最新技术相比的显着改进,具有更好的遮挡恢复和更准确的未来预测。
-
论文: PnPNet: End-to-End Perception and Prediction With Tracking in the Loop
-
项目主页: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~sergio/publication/pnpnet/
4. DOPS: Learning to Detect 3D Objects and Predict their 3D Shapes
-
摘要
We propose DOPS, a fast single-stage 3D object detection method for LIDAR data. Previous methods often make domain-specific design decisions, for example projecting points into a bird-eye view image in autonomous driving scenarios. In contrast, we propose a general-purpose method that works on both indoor and outdoor scenes. The core novelty of our method is a fast, single-pass architecture that both detects objects in 3D and estimates their shapes. 3D bounding box parameters are estimated in one pass for every point, aggregated through graph convolutions, and fed into a branch of the network that predicts latent codes representing the shape of each detected object. The latent shape space and shape decoder are learned on a synthetic dataset and then used as supervision for the end-toend training of the 3D object detection pipeline. Thus our model is able to extract shapes without access to groundtruth shape information in the target dataset. During experiments, we find that our proposed method achieves stateof-the-art results by ∼5% on object detection in ScanNet scenes, and it gets top results by 3.4% in the Waymo Open Dataset, while reproducing the shapes of detected cars.
我们提出了DOPS,一种用于LIDAR数据的快速单阶段3D目标检测方法。先前的方法经常做出特定领域的设计决策,例如在自动驾驶场景中将点投影到鸟瞰图像中。相反,我们提出了一种适用于室内和室外场景的通用方法。我们方法的核心新颖之处在于快速的单次遍历(single-pass)体系结构,该体系结构既可以检测3D对象又可以估计其形状。 单次遍历对3D边界框参数的每个点进行估算,通过图卷积进行聚合,然后馈入网络的一个分支,该分支预测表示每个检测到的物体形状的潜在代码。在合成数据集上学习潜在的形状空间和形状解码器,然后将其用作3D目标检测管道的端到端训练的监督。 因此,我们的模型能够提取形状而无需访问目标数据集中的地面形状信息。在实验过程中,我们发现我们提出的方法在ScanNet场景中的目标检测方面,比SOTA结果提高了约5%,在Waymo Open Dataset中获得了比SOTA提高3.4%的最佳结果,同时再现了检测到的汽车的形状。

-
论文: DOPS: Learning to Detect 3D Objects and Predict Their 3D Shapes
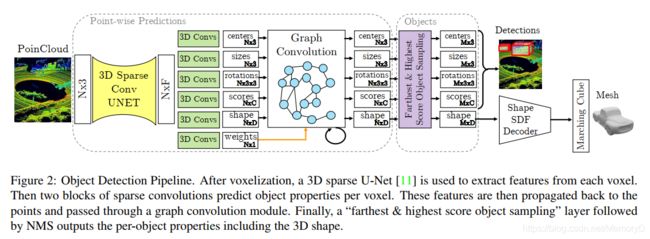
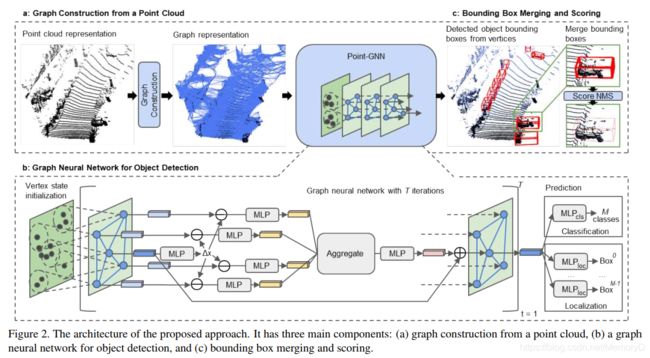
5. Point-GNN: Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
-
摘要
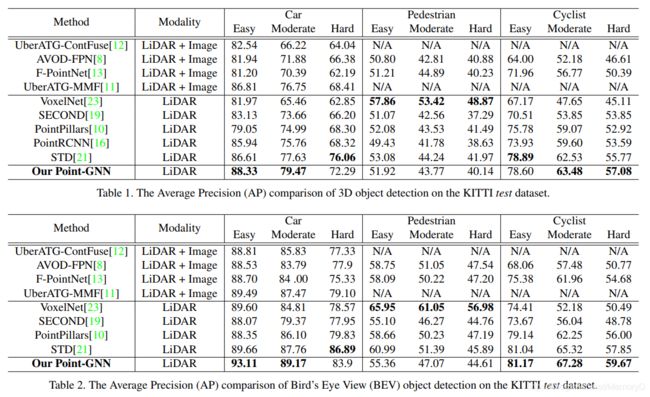
In this paper, we propose a graph neural network to detect objects from a LiDAR point cloud. Towards this end, we encode the point cloud efficiently in a fixed radius near-neighbors graph. We design a graph neural network, named Point-GNN, to predict the category and shape of the object that each vertex in the graph belongs to. In Point-GNN, we propose an auto-registration mechanism to reduce translation variance, and also design a box merging and scoring operation to combine detections from multiple vertices accurately. Our experiments on the KITTI benchmark show the proposed approach achieves leading accuracy using the point cloud alone and can even surpass fusion-based algorithms. Our results demonstrate the potential of using the graph neural network as a new approach for 3D object detection.
在本文中,我们提出了一种图神经网络来检测LiDAR点云中的物体。为此,我们在固定半径的近邻图中有效地编码了点云。我们设计了一个图神经网络,称为Point-GNN,以预测图中每个顶点所属的对象的类别和形状。在Point-GNN中,我们提出了一种自动注册机制来减少平移差异,并且还设计了一种框合并和计分操作,以准确地组合来自多个顶点的检测。 我们在KITTI基准上进行的实验表明,所提出的方法仅使用点云即可达到领先的准确性,甚至可以超越基于融合的算法。我们的结果证明了使用图神经网络作为3D目标检测的新方法的潜力。

-
论文:Point-GNN: Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
-
代码: https://github.com/WeijingShi/Point-GNN
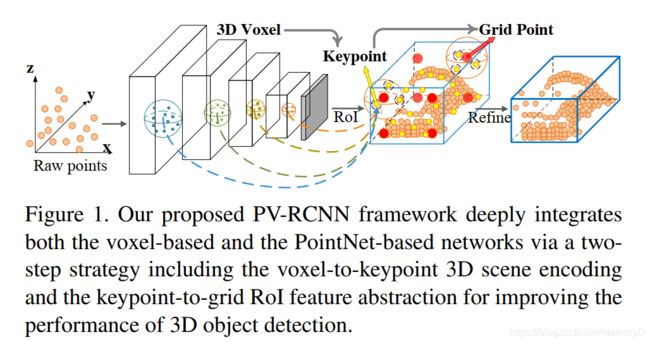
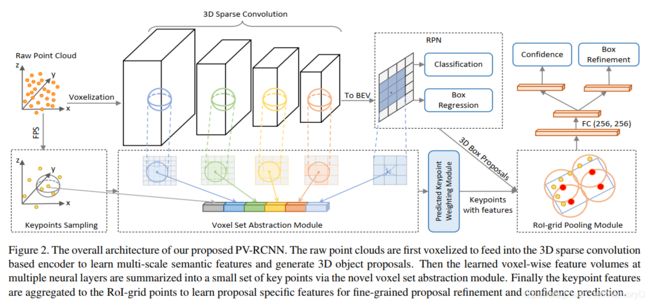
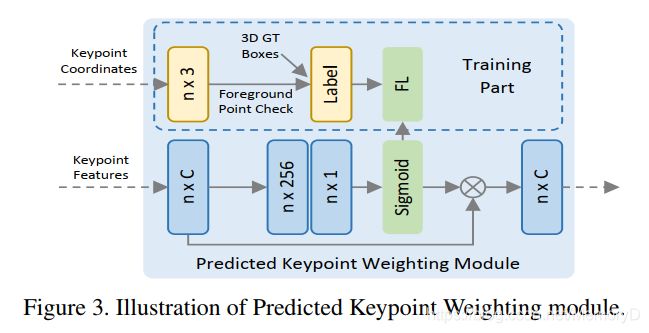
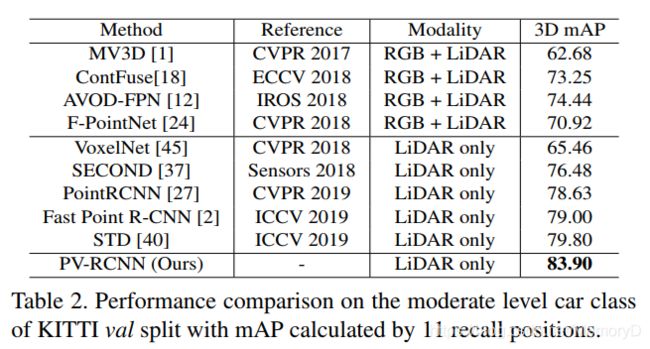
6. PV-RCNN: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction for 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
We present a novel and high-performance 3D object detection framework, named PointVoxel-RCNN (PV-RCNN), for accurate 3D object detection from point clouds. Our proposed method deeply integrates both 3D voxel Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and PointNet-based set abstraction to learn more discriminative point cloud features. It takes advantages of efficient learning and high-quality proposals of the 3D voxel CNN and the flexible receptive fields of the PointNet-based networks. Specifically, the proposed framework summarizes the 3D scene with a 3D voxel CNN into a small set of keypoints via a novel voxel set abstraction module to save follow-up computations and also to encode representative scene features. Given the highquality 3D proposals generated by the voxel CNN, the RoIgrid pooling is proposed to abstract proposal-specific features from the keypoints to the RoI-grid points via keypoint set abstraction. Compared with conventional pooling operations, the RoI-grid feature points encode much richer context information for accurately estimating object confidences and locations. Extensive experiments on both the KITTI dataset and the Waymo Open dataset show that our proposed PV-RCNN surpasses state-of-the-art 3D detection methods with remarkable margins.
我们提出了一种新颖的高性能3D对象检测框架,名为PointVoxel-RCNN(PV-RCNN),用于从点云中进行精确的3D对象检测。我们提出的方法将3D体素卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于PointNet的集合抽象方法进行了深度集成,以学习更多判别性点云特征。它利用了3D体素CNN的高效学习和高质量候选区域以及基于PointNet的网络的灵活感受域的优势。具体而言,提出的框架通过新颖的体素集合抽象模块将具有3D体素CNN的3D场景汇总为一小组关键点,以节省后续计算并对代表性的场景特征进行编码。给定体素CNN生成的高质量3D候选区域,使用RoI网格池化,通过关键点集合抽象,将特定候选区域的特征从关键点抽象到RoI网格点。与传统的池化操作相比,RoI网格特征点对更丰富的上下文信息进行了编码,以准确地估计对象的置信度和位置。 在KITTI数据集和Waymo Open数据集上进行的大量实验表明,我们提出的PV-RCNN以显着的优势超越了最新的3D检测方法。
-
论文:PV-RCNN: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction for 3D Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet
7. Physically Realizable Adversarial Examples for LiDAR Object Detection
-
摘要
Modern autonomous driving systems rely heavily on deep learning models to process point cloud sensory data; meanwhile, deep models have been shown to be susceptible to adversarial attacks with visually imperceptible perturbations. Despite the fact that this poses a security concern for the self-driving industry, there has been very little exploration in terms of 3D perception, as most adversarial attacks have only been applied to 2D flat images. In this paper, we address this issue and present a method to generate universal 3D adversarial objects to fool LiDAR detectors. In particular, we demonstrate that placing an adversarial object on the rooftop of any target vehicle to hide the vehicle entirely from LiDAR detectors with a success rate of 80%. We report attack results on a suite of detectors using various input representation of point clouds. We also conduct a pilot study on adversarial defense using data augmentation. This is one step closer towards safer self-driving under unseen conditions from limited training data.
现代自动驾驶系统严重依赖于深度学习模型来处理点云感官数据。同时,已经证明,深层模型容易受到视觉上无法察觉的干扰的对抗攻击。尽管这对自动驾驶行业构成了安全隐患,但大多数对抗性攻击仅应用于2D平面图像,而在3D感知方面的探索很少。在本文中,我们解决了这个问题,并提出了一种生成通用3D对抗对象的方法来欺骗LiDAR检测器。特别是,我们证明了在任何目标车辆的车顶上放置一个对抗物体,有80%的成功率使车辆完全对LiDAR探测器隐藏。 我们使用点云的各种输入表示形式,在一组检测器上报告攻击结果。我们还使用数据增强技术进行对抗性防御的初步研究。这是在看不见的条件下,使用有限的训练数据,朝着更安全的自动驾驶迈出的一步。

-
论文: Physically Realizable Adversarial Examples for LiDAR Object Detection
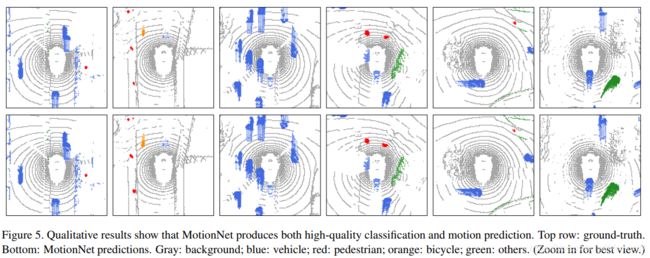
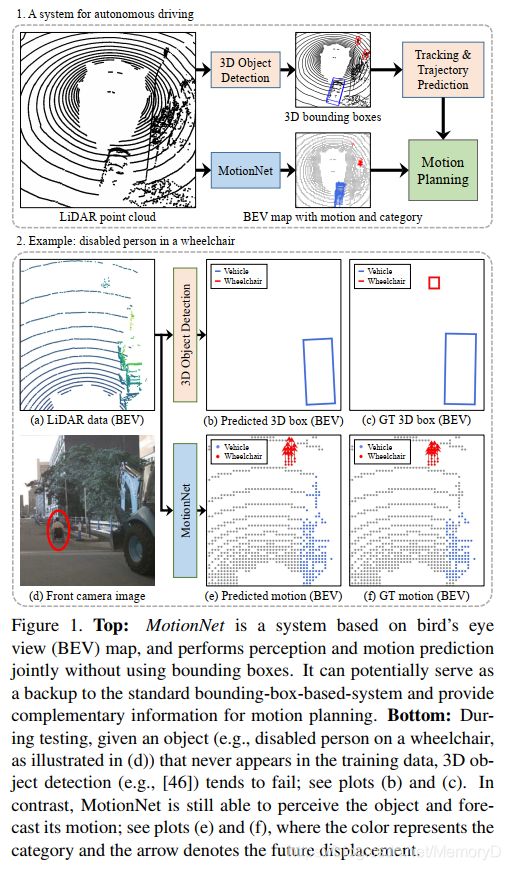
8. MotionNet: Joint Perception and Motion Prediction for Autonomous Driving Based on Bird’s Eye View Maps
-
摘要
The ability to reliably perceive the environmental states, particularly the existence of objects and their motion behavior, is crucial for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose an efficient deep model, called MotionNet, to jointly perform perception and motion prediction from 3D point clouds. MotionNet takes a sequence of LiDAR sweeps as input and outputs a bird’s eye view (BEV) map, which encodes the object category and motion information in each grid cell. The backbone of MotionNet is a novel spatiotemporal pyramid network, which extracts deep spatial and temporal features in a hierarchical fashion. To enforce the smoothness of predictions over both space and time, the training of MotionNet is further regularized with novel spatial and temporal consistency losses. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method overall outperforms the state-of-the-arts, including the latest scene-flow- and 3D-object-detection-based methods. This indicates the potential value of the proposed method serving as a backup to the bounding-box-based system, and providing complementary information to the motion planner in autonomous driving.
可靠地感知环境状态的能力,尤其是目标是否存在及其运动行为,对于自动驾驶至关重要。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个有效的深度模型,称为MotionNet,以同时执行3D点云的感知和运动预测。 MotionNet将LiDAR扫描序列作为输入,并输出鸟瞰(BEV)图,该图对每个网格单元中的对象类别和运动信息进行编码。 MotionNet的骨干是一个新颖的时空金字塔网络,它以分层方式提取深层的时空特征。 为了在时间和空间上增强预测的平滑性,对MotionNet的训练进行了进一步的调整,使其具有新颖的时空一致性损失。大量实验表明,该方法总体上优于最新技术,包括基于最新场景流和3D目标检测的方法。这表明了所提出方法的潜在价值,可作为基于边界框的系统的备份,并为自动驾驶中的运动计划器提供补充信息。
-
论文:MotionNet: Joint Perception and Motion Prediction for Autonomous Driving Based on Bird’s Eye View Maps
-
代码: https://www.merl.com/research/license#MotionNet
9. 3DSSD: Point-based 3D Single Stage Object Detector
-
摘要
Prevalence of voxel-based 3D single-stage detectors contrast with underexplored point-based methods. In this paper, we present a lightweight point-based 3D single stage object detector 3DSSD to achieve decent balance of accuracy and efficiency. In this paradigm, all upsampling layers and the refinement stage, which are indispensable in all existing point-based methods, are abandoned. We instead propose a fusion sampling strategy in downsampling process to make detection on less representative points feasible. A delicate box prediction network, including a candidate generation layer and an anchor-free regression head with a 3D center-ness assignment strategy, is developed to meet the demand of high accuracy and speed. Our 3DSSD paradigm is an elegant single-stage anchor-free one. We evaluate it on widely used KITTI dataset and more challenging nuScenes dataset. Our method outperforms all state-of-the-art voxelbased single-stage methods by a large margin, and even yields comparable performance with two-stage point-based methods, with amazing inference speed of 25+ FPS, 2⇥ faster than former state-of-the-art point-based methods.
基于体素的3D单级检测器的流行与基于点的未充分开发方法形成对比。在本文中,我们提出了一种轻量级的基于点的3D单级目标检测器3DSSD,以实现准确性和效率的良好平衡。在这个方法中,所有现有的基于点的方法都必不可少的所有上采样层和细化阶段都将被放弃。相反,我们在下采样过程中提出了一种融合采样策略,以使在代表性较小的点上进行检测变得可行。为了满足高精度和高速度的需求,开发了一种精巧的边界框预测网络,其中包括候选生成层和使用3D中心度分配策略的anchor-free回归头。 我们的3DSSD方法是一种优雅的单阶段anchor-free模式。我们在广泛使用的KITTI数据集和更具挑战性的nuScenes数据集上对其进行评估。我们的方法在很大程度上领先于所有基于体素的单阶段方法,甚至可以与两阶段基于点的方法产生可比的性能,惊人的推理速度为25+ FPS,比以前最先进的基于点的方法快2两倍。
-
论文:3DSSD: Point-based 3D Single Stage Object Detector
-
代码: https://github.com/tomztyang/3DSSD
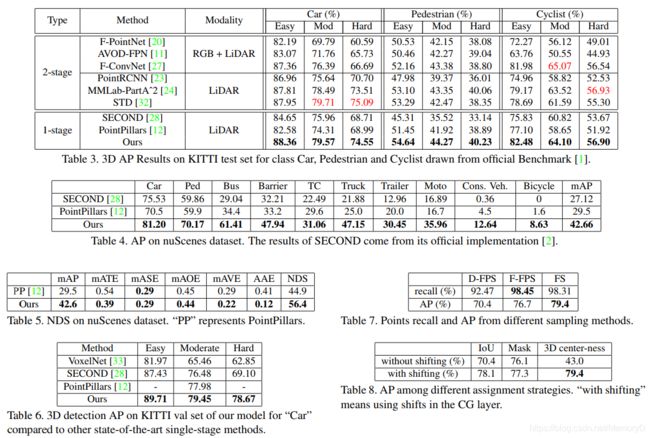
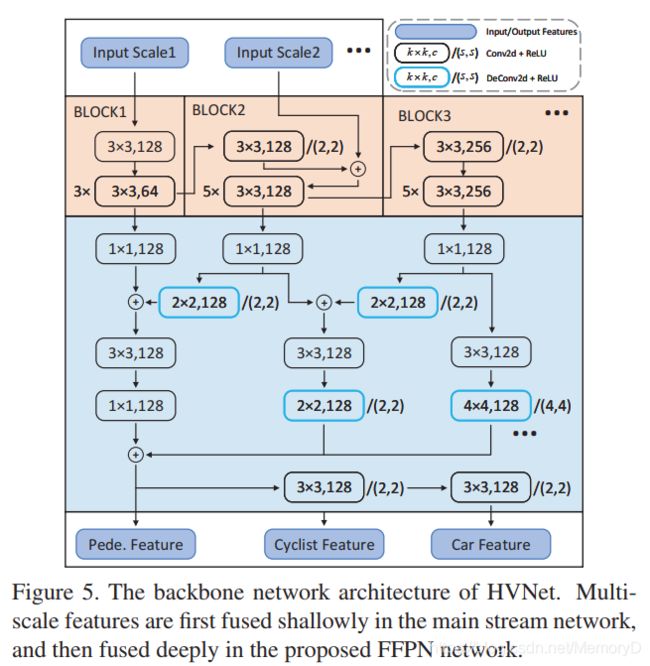
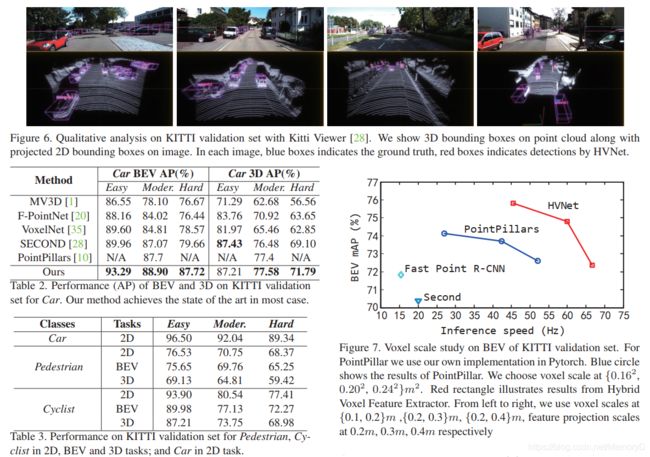
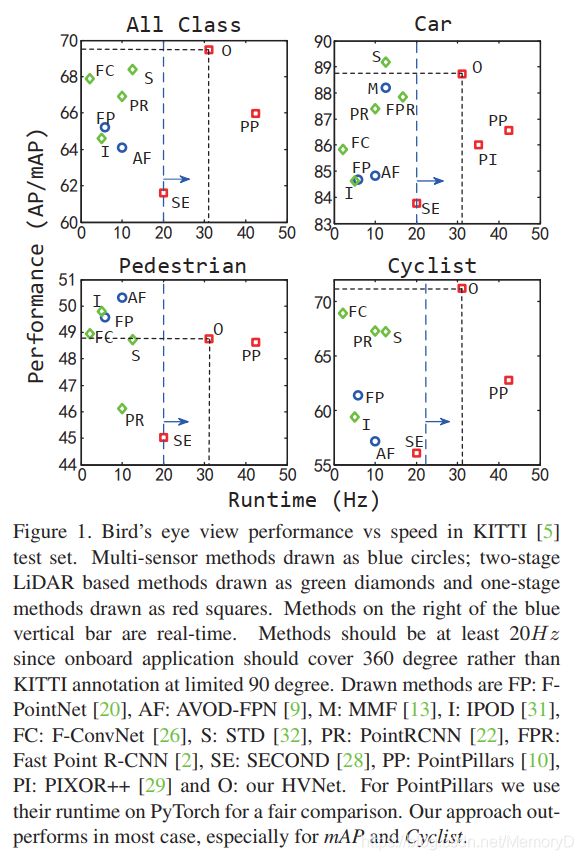
10. HVNet: Hybrid Voxel Network for LiDAR Based 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
We present Hybrid Voxel Network (HVNet), a novel onestage unified network for point cloud based 3D object detection for autonomous driving. Recent studies show that 2D voxelization with per voxel PointNet style feature extractor leads to accurate and efficient detector for large 3D scenes. Since the size of the feature map determines the computation and memory cost, the size of the voxel becomes a parameter that is hard to balance. A smaller voxel size gives a better performance, especially for small objects, but a longer inference time. A larger voxel can cover the same area with a smaller feature map, but fails to capture intricate features and accurate location for smaller objects. We present a Hybrid Voxel network that solves this problem by fusing voxel feature encoder (VFE) of different scales at point-wise level and project into multiple pseudo-image feature maps. We further propose an attentive voxel feature encoding that outperforms plain VFE and a feature fusion pyramid network to aggregate multi-scale information at feature map level. Experiments on the KITTI benchmark show that a single HVNet achieves the best mAP among all existing methods with a real time inference speed of 31Hz.
我们提出了混合体素网络(HVNet),这是一种用于自动驾驶的基于点云的3D目标检测的新型单级统一网络。最近的研究表明,使用每个体素PointNet样式特征提取器进行2D体素化可以为大型3D场景提供准确高效的检测器。由于特征图的大小决定了计算和存储成本,因此体素的大小成为难以平衡的参数。较小的体素尺寸可提供更好的性能,尤其是对于小物体,但推理时间更长。较大的体素可以使用较小的特征图覆盖相同的区域,但无法捕获较小物体的复杂特征和准确位置。我们提出了一种混合体素网络,通过在点水平上融合不同比例的体素特征编码器(VFE)并投影到多个伪图像特征图中,可以解决此问题。 我们进一步提出了一种 attentive 的体素特征编码,其性能优于普通VFE和特征融合金字塔网络,可在特征图级别聚合多尺度信息。在KITTI基准上进行的实验表明,单个HVNet在所有现有方法中实现最佳的mAP,并且实时推断速度为31Hz。
-
论文:HVNet: Hybrid Voxel Network for LiDAR Based 3D Object Detection
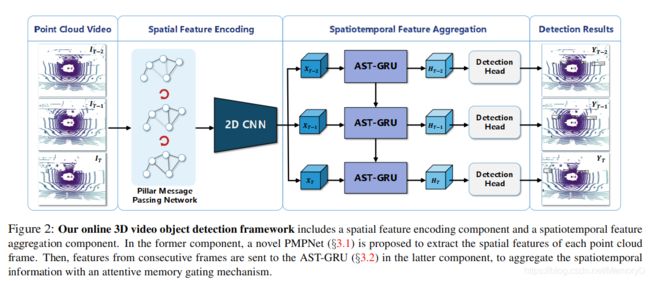
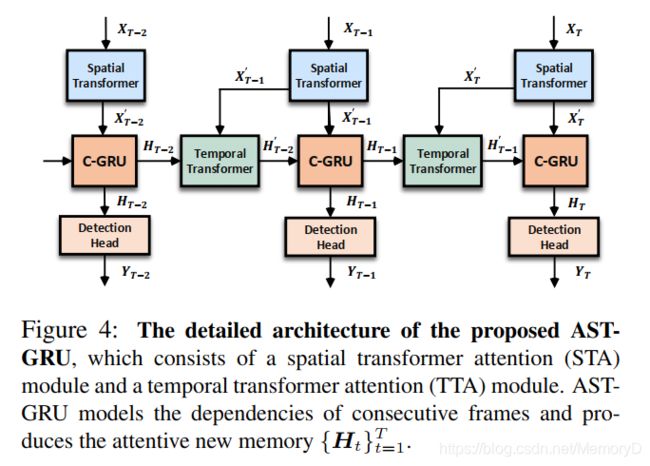
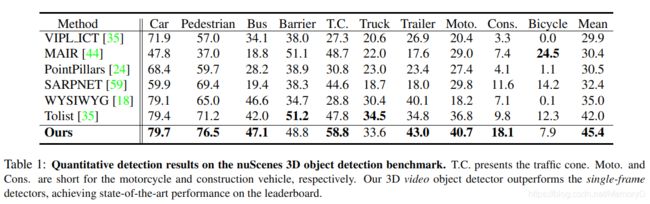
11. LiDAR-based Online 3D Video Object Detection with Graph-based Message Passing and Spatiotemporal Transformer Attention
-
摘要
Existing LiDAR-based 3D object detectors usually focus on the single-frame detection, while ignoring the spatiotemporal information in consecutive point cloud frames. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end online 3D video object detector that operates on point cloud sequences. The proposed model comprises a spatial feature encoding component and a spatiotemporal feature aggregation component. In the former component, a novel Pillar Message Passing Network (PMPNet) is proposed to encode each discrete point cloud frame. It adaptively collects information for a pillar node from its neighbors by iterative message passing, which effectively enlarges the receptive field of the pillar feature. In the latter component, we propose an Attentive Spatiotemporal Transformer GRU (AST-GRU) to aggregate the spatiotemporal information, which enhances the conventional ConvGRU with an attentive memory gating mechanism. AST-GRU contains a Spatial Transformer Attention (STA) module and a Temporal Transformer Attention (TTA) module, which can emphasize the foreground objects and align the dynamic objects, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed 3D video object detector achieves state-of-the-art performance on the large-scale nuScenes benchmark.
现有的基于LiDAR的3D目标检测器通常专注于单帧检测,而忽略了连续点云帧中的时空信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种在点云序列上运行的端到端在线3D视频目标检测器。所提出的模型包括空间特征编码组件和时空特征聚集组件。在前一个组件中,提出了一种新颖的支柱消息传递网络(PMPNet)对每个离散点云帧进行编码。它通过迭代消息传递来自适应地从其相邻节点收集有关支柱节点的信息,从而有效地扩大了支柱要素的接收范围。在后一个组件中,我们提出了一个时空时变变压器GRU(AST-GRU)来聚合时空信息,从而通过注意性存储器门控机制增强了传统的ConvGRU。 AST-GRU包含一个空间转换注意(STA)模块和一个时间转换注意(TTA)模块,它们可以分别强调前景对象并对齐动态对象。实验结果表明,提出的3D视频目标检测器在大规模nuScenes基准上达到了最新的性能。
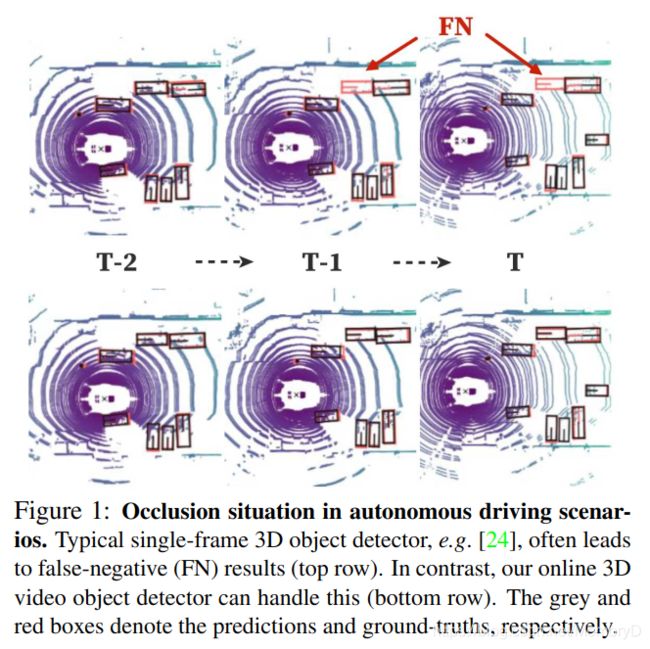
-
论文:LiDAR-based Online 3D Video Object Detection with Graph-based Message Passing and Spatiotemporal Transformer Attention
-
代码: https://github.com/yinjunbo/3DVID
2. 3D目标检测增强技术
这几篇论文没有提出一个自己的检测框架,而是提出一些数据处理之类的技术,可以增强一些现有方法的性能。
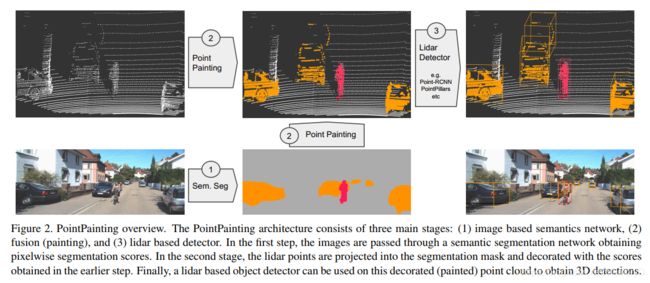
1. PointPainting: Sequential Fusion for 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
Camera and lidar are important sensor modalities for robotics in general and self-driving cars in particular. The sensors provide complementary information offering an opportunity for tight sensor-fusion. Surprisingly, lidar-only methods outperform fusion methods on the main benchmark datasets, suggesting a gap in the literature. In this work, we propose PointPainting: a sequential fusion method to fill this gap. PointPainting works by projecting lidar points into the output of an image-only semantic segmentation network and appending the class scores to each point. The appended (painted) point cloud can then be fed to any lidaronly method. Experiments show large improvements on three different state-of-the art methods, Point-RCNN, VoxelNet and PointPillars on the KITTI and nuScenes datasets. The painted version of PointRCNN represents a new state of the art on the KITTI leaderboard for the bird’s-eye view detection task. In ablation, we study how the effects of Painting depends on the quality and format of the semantic segmentation output, and demonstrate how latency can be minimized through pipelining.
摄像头和激光雷达是普通机器人(尤其是自动驾驶汽车)机器人技术的重要传感器形式。传感器提供补充信息,为紧密的传感器融合提供了机会。令人惊讶的是,仅使用激光雷达的方法在主要基准数据集上要好于融合方法,这表明文献中存在空白。在本工作中,我们提出了PointPainting:一个用于填补这个空白的时序融合方法。PointPainting的工作方式是,将激光雷达点投影到仅使用图像的语义分割网络的输出中,并将类分数附加到每个点。 然后可以将附加过的(painted)点云馈送到任何 lidar-only 方法。实验表明,在KITTI和nuScenes数据集上,我们的方法对三种不同的最新方法(Point-RCNN,VoxelNet和PointPillars)有重大改进。PointRCNN的painted版本是KITTI排行榜上用于鸟瞰检测任务的SOTA水平。在消融研究中,我们研究 painting 的效果如何取决于语义分段输出的质量和格式,并演示如何通过流水线将等待时间最小化。
-
论文:PointPainting: Sequential Fusion for 3D Object Detection
2. Train in Germany, Test in The USA: Making 3D Object Detectors Generalize
-
摘要
In the domain of autonomous driving, deep learning has substantially improved the 3D object detection accuracy for LiDAR and stereo camera data alike. While deep networks are great at generalization, they are also notorious to overfit to all kinds of spurious artifacts, such as brightness, car sizes and models, that may appear consistently throughout the data. In fact, most datasets for autonomous driving are collected within a narrow subset of cities within one country, typically under similar weather conditions. In this paper we consider the task of adapting 3D object detectors from one dataset to another. We observe that na¨ıvely, this appears to be a very challenging task, resulting in drastic drops in accuracy levels. We provide extensive experiments to investigate the true adaptation challenges and arrive at a surprising conclusion: the primary adaptation hurdle to overcome are differences in car sizes across geographic areas. A simple correction based on the average car size yields a strong correction of the adaptation gap. Our proposed method is simple and easily incorporated into most 3D object detection frameworks. It provides a first baseline for 3D object detection adaptation across countries, and gives hope that the underlying problem may be more within grasp than one may have hoped to believe.
在自动驾驶领域,深度学习已大大提高了LiDAR和立体相机数据的3D目标检测精度。虽然深层网络的泛化能力很强,但它们也臭名昭著,无法适应所有杂散的伪像,例如亮度,汽车尺寸和模型,这些伪像可能在整个数据中始终出现。实际上,大多数自动驾驶数据集,通常都是在相似的天气条件下,在一个国家的一小部分城市内收集的。在本文中,我们考虑了将3D目标检测器从一个数据集中迁移到另一个数据集的任务。我们观察到,这似乎是一个非常具有挑战性的任务,迁移数据集导致准确性水平急剧下降。我们提供了广泛的实验来调查迁移数据集的真正挑战是什么,并得出令人惊讶的结论:迁移数据集要克服的主要障碍是各个地理区域的汽车尺寸差异。基于平均汽车尺寸的简单校正会对迁移数据集提供巨大的帮助。我们提出的方法简单易行,可以轻松地集成到大多数3D目标检测框架中。它为各国进行3D目标检测的适应性提供了第一个基准,并给出了希望,潜在的问题比人们可能愿意相信的更多。
-
论文:Train in Germany, Test in The USA: Making 3D Object Detectors Generalize
-
代码: https://github.com/cxy1997/3D_adapt_auto_driving
3. Learning to Evaluate Perception Models using Planner-Centric Metrics
-
摘要
Variants of accuracy and precision are the gold-standard by which the computer vision community measures progress of perception algorithms. One reason for the ubiquity of these metrics is that they are largely task-agnostic; we in general seek to detect zero false negatives or positives. The downside of these metrics is that, at worst, they penalize all incorrect detections equally without conditioning on the task or scene, and at best, heuristics need to be chosen to ensure that different mistakes count differently. In this paper, we propose a principled metric for 3D object detection specifically for the task of self-driving. The core idea behind our metric is to isolate the task of object detection and measure the impact the produced detections would induce on the downstream task of driving. Without hand-designing it to, we find that our metric penalizes many of the mistakes that other metrics penalize by design. In addition, our metric downweighs detections based on additional factors such as distance from a detection to the ego car and the speed of the detection in intuitive ways that other detection metrics do not. For human evaluation, we generate scenes in which standard metrics and our metric disagree and find that humans side with our metric 79% of the time.
各种各样的准确性和精确度是计算机视觉社区衡量感知算法进展的黄金标准。这些指标无处不在的原因之一是它们在很大程度上与任务无关。我们通常寻求检测零个假阴性或阳性。这些指标的缺点是,最坏的情况下,所有不正确的检测均会受到惩罚,而不会考虑到任务或场景的不同,因此需要选择启发式方法以确保不同的错误的计数方式不同。 在本文中,我们针对3D目标检测提出了一种原则性的度量标准,专门用于自动驾驶任务。我们度量标准的核心思想是隔离目标检测任务,并度量所产生的检测将对下游驾驶任务产生的影响。无需手动设计,我们的指标就会惩罚许多错误,而在其他指标中需要人为设计。 此外,我们的指标会根据其他因素(例如检测目标到自我汽车的距离以及检测速度)以直观的方式来权衡检测结果,这是其他检测指标无法做到的。为了进行人工评估,我们生成了一些场景,在这些场景中,标准指标和我们的指标不一致,并且发现人类在79%的时间内都支持我们的指标。

-
论文:Learning to Evaluate Perception Models Using Planner-Centric Metrics
-
代码: https://nv-tlabs.github.io/detection-relevance
4. What You See is What You Get: Exploiting Visibility for 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
Recent advances in 3D sensing have created unique challenges for computer vision. One fundamental challenge is finding a good representation for 3D sensor data. Most popular representations (such as PointNet) are proposed in the context of processing truly 3D data (e.g. points sampled from mesh models), ignoring the fact that 3D sensored data such as a LiDAR sweep is in fact 2.5D. We argue that representing 2.5D data as collections of (x, y, z) points fundamentally destroys hidden information about freespace. In this paper, we demonstrate such knowledge can be efficiently recovered through 3D raycasting and readily incorporated into batch-based gradient learning. We describe a simple approach to augmenting voxel-based networks with visibility: we add a voxelized visibility map as an additional input stream. In addition, we show that visibility can be combined with two crucial modifications common to state-of-the-art 3D detectors: synthetic data augmentation of virtual objects and temporal aggregation of LiDAR sweeps over multiple time frames. On the NuScenes 3D detection benchmark, we show that, by adding an additional stream for visibility input, we can significantly improve the overall detection accuracy of a state-of-the-art 3D detector.
3D感测的最新进展为计算机视觉带来了独特的挑战。一个基本挑战是找到3D传感器数据的良好表示形式。在处理真正的3D数据(例如从网格模型采样的点)的背景下提出了最流行的表示形式(例如PointNet),而忽略了诸如LiDAR扫描等3D传感数据实际上为2.5D的事实。我们认为将2.5D数据表示为 ( x , y , z ) (x, y, z) (x,y,z) 的点集会从根本上破坏有关自由空间的隐藏信息。在本文中,我们证明了此类知识可以通过3D射线检测有效地恢复,并且可以轻松地并入基于批次的梯度学习中。我们描述了一种使用可见性去增强基于体素的网络的简单方法:我们添加一个体素化的可见性图作为附加的输入流。 此外,我们展示了可见性可以与最新3D检测器的两项关键修改相结合:虚拟对象的合成数据增强和LiDAR扫描在多个时间范围内的时间聚合。在NuScenes 3D检测基准上,我们展示出,通过将可见性添加为额外的输入流,我们可以显着提高最新3D检测器的整体检测精度。
-
论文:What You See is What You Get: Exploiting Visibility for 3D Object Detection
-
项目主页: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~peiyunh/wysiwyg/
-
代码: https://github.com/peiyunh/wysiwyg
3. 3D目标检测——室内
1. Density Based Clustering for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds
-
摘要
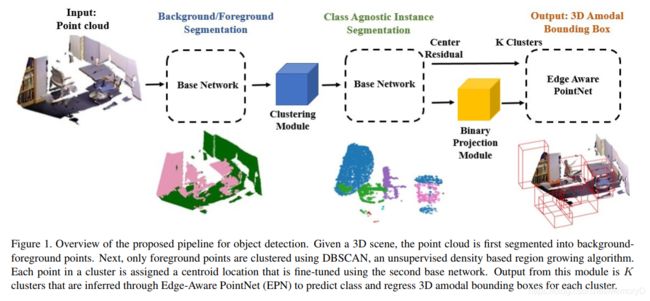
Current 3D detection networks either rely on 2D object proposals or try to directly predict bounding box parameters from each point in a scene. While former methods are dependent on performance of 2D detectors, latter approaches are challenging due to the sparsity and occlusion in point clouds, making it difficult to regress accurate parameters. In this work, we introduce a novel approach for 3D object detection that is significant in two main aspects: a) cascaded modular approach that focuses the receptive field of each module on specific points in the point cloud, for improved feature learning and b) a class agnostic instance segmentation module that is initiated using unsupervised clustering. The objective of a cascaded approach is to sequentially minimize the number of points running through the network. While three different modules perform the tasks of background-foreground segmentation, class agnostic instance segmentation and object detection, through individually trained point based networks. We also evaluate bayesian uncertainty in modules, demonstrating the over all level of confidence in our prediction results. Performance of the network is evaluated on the SUN RGB-D benchmark dataset, that demonstrates an improvement as compared to state-of-the-art methods.
当前的3D检测网络要么依赖于2D对象建议,要么尝试根据场景中的每个点直接预测边界框参数。虽然前一种方法取决于2D检测器的性能,但后一种方法由于点云中的稀疏性和遮挡性而具有挑战性,从而难以回归准确的参数。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新颖的3D目标检测方法,该方法在两个主要方面都具有重要意义:a)级联模块化方法,该方法将每个模块的接收场集中在点云中的特定点上,以改进特征学习; b)a使用无监督群集启动的类不可知实例分段模块。级联方法的目的是顺序地减少通过网络运行的点的数量。尽管三个不同的模块通过单独训练的基于点的网络执行背景-前景分割,类不可知实例分割和目标检测的任务。我们还评估了模块中的贝叶斯不确定性,证明了我们对预测结果的整体置信度。在SUN RGB-D基准数据集上评估了网络的性能,这证明了与最新方法相比的改进。
-
论文: Density Based Clustering for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds
2. A Hierarchical Graph Network for 3D Object Detection on Point Clouds
-
摘要
3D object detection on point clouds finds many applications. However, most known point cloud object detection methods did not adequately accommodate the characteristics (e.g., sparsity) of point clouds, and thus some key semantic information (e.g., shape information) is not well captured. In this paper, we propose a new graph convolution (GConv) based hierarchical graph network (HGNet) for 3D object detection, which processes raw point clouds directly to predict 3D bounding boxes. HGNet effectively captures the relationship of the points and utilizes the multilevel semantics for object detection. Specially, we propose a novel shape-attentive GConv (SA-GConv) to capture the local shape features, by modelling the relative geometric positions of points to describe object shapes. An SA-GConv based U-shape network captures the multi-level features, which are mapped into an identical feature space by an improved voting module and then further utilized to generate proposals. Next, a new GConv based Proposal Reasoning Module reasons on the proposals considering the global scene semantics, and the bounding boxes are then predicted. Consequently, our new framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods on two large-scale point cloud datasets, by ∼4% mean average precision (mAP) on SUN RGB-D and by ∼3% mAP on ScanNet-V2.
点云上的3D目标检测有许多应用。但是,大多数已知的点云目标检测方法不能充分适应点云的特性(例如,稀疏性),因此不能很好地捕获一些关键语义信息(例如,形状信息)。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的基于图卷积(GConv)的层次图网络(HGNet)用于3D目标检测,该网络直接处理原始点云以预测3D边界框。 HGNet有效地捕获了点之间的关系,并利用多级语义进行目标检测。特别是,我们提出了一种新颖的形状专注GConv(SA-GConv),通过对点的相对几何位置进行建模以描述对象形状来捕获局部形状特征。基于SA-GConv的U形网络捕获了多层特征,这些多层特征通过改进的投票模块映射到相同的特征空间中,然后进一步用于生成提案。接下来,一个新的基于GConv的提议推理模块基于考虑全局场景语义的提议原因,然后预测边界框。因此,我们的新框架在两个大型点云数据集上的性能优于最新方法,在SUN RGB-D上平均平均精度(mAP)约4%,在ScanNet-V2上平均mAP约3%。
-
论文: A Hierarchical Graph Network for 3D Object Detection on Point Clouds
3. ImVoteNet: Boosting 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds with Image Votes
-
摘要
3D object detection has seen quick progress thanks to advances in deep learning on point clouds. A few recent works have even shown state-of-the-art performance with just point clouds input (e.g. VOTENET). However, point cloud data have inherent limitations. They are sparse, lack color information and often suffer from sensor noise. Images, on the other hand, have high resolution and rich texture. Thus they can complement the 3D geometry provided by point clouds. Yet how to effectively use image information to assist point cloud based detection is still an open question. In this work, we build on top of VOTENET and propose a 3D detection architecture called IMVOTENET specialized for RGB-D scenes. IMVOTENET is based on fusing 2D votes in images and 3D votes in point clouds. Compared to prior work on multi-modal detection, we explicitly extract both geometric and semantic features from the 2D images. We leverage camera parameters to lift these features to 3D. To improve the synergy of 2D-3D feature fusion, we also propose a multi-tower training scheme. We validate our model on the challenging SUN RGB-D dataset, advancing state-of-the-art results by 5.7 mAP. We also provide rich ablation studies to analyze the contribution of each design choice.
得益于点云上深度学习的进步,3D目标检测取得了快速进展。最近的一些工作仅使用点云输入甚至获得了最好的性能(例如VOTENET)。但是,点云数据具有固有的局限性。它们稀疏,缺少颜色信息,并且经常遭受传感器噪声的影响。另一方面,图像具有高分辨率和丰富的纹理。因此,它们可以补充点云提供的3D几何形状。然而,如何有效地使用图像信息来辅助基于点云的检测仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在这项工作中,我们以VOTENET为基础,并提出了一种称为IMVOTENET的3D检测架构,专门用于RGB-D场景。 IMVOTENET基于融合图像中的2D投票和点云中的3D投票。与以前的多模式检测工作相比,我们从2D图像中显式提取了几何特征和语义特征。我们利用相机参数将这些功能提升为3D。为了提高2D-3D特征融合的协同作用,我们还提出了一种多塔训练方案。我们在具有挑战性的SUN RGB-D数据集上验证了模型,将最新结果提高了5.7 mAP。我们还提供丰富的消融研究,以分析每种设计选择的贡献。
-
论文: ImVoteNet: Boosting 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds with Image Votes
4. MLCVNet: Multi-Level Context VoteNet for 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
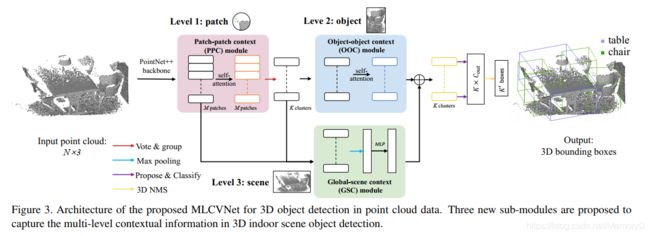
In this paper, we address the 3D object detection task by capturing multi-level contextual information with the selfattention mechanism and multi-scale feature fusion. Most existing 3D object detection methods recognize objects individually, without giving any consideration on contextual information between these objects. Comparatively, we propose Multi-Level Context VoteNet (MLCVNet) to recognize 3D objects correlatively, building on the state-of-the-art VoteNet. We introduce three context modules into the voting and classifying stages of VoteNet to encode contextual information at different levels. Specifically, a Patch-to-Patch Context (PPC) module is employed to capture contextual information between the point patches, before voting for their corresponding object centroid points. Subsequently, an Object-to-Object Context (OOC) module is incorporated before the proposal and classification stage, to capture the contextual information between object candidates. Finally, a Global Scene Context (GSC) module is designed to learn the global scene context. We demonstrate these by capturing contextual information at patch, object and scene levels. Our method is an effective way to promote detection accuracy, achieving new state-of-the-art detection performance on challenging 3D object detection datasets, i.e., SUN RGBD and ScanNet.
在本文中,我们通过利用自注意力机制和多尺度特征融合捕获多级上下文信息来解决3D目标检测任务。大多数现有的3D目标检测方法可以单独识别对象,而无需考虑这些对象之间的上下文信息。相比之下,我们提出了多级上下文投票网(MLCVNet),以基于最新的投票网来关联地识别3D对象。我们在VoteNet的投票和分类阶段引入了三个上下文模块,以在不同级别上对上下文信息进行编码。具体地,在投票给它们对应的对象质心点之前,采用补丁到补丁上下文(PPC)模块来捕获点补丁之间的上下文信息。随后,在提议和分类阶段之前合并了对象到对象上下文(OOC)模块,以捕获对象候选对象之间的上下文信息。最后,设计了一个全局场景上下文(GSC)模块来学习全局场景上下文。我们通过在补丁,对象和场景级别捕获上下文信息来演示这些内容。我们的方法是提高检测精度,在具有挑战性的3D目标检测数据集(即SUN RGBD和ScanNet)上实现最新技术检测性能的有效方法。
-
论文: MLCVNet: Multi-Level Context VoteNet for 3D Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/NUAAXQ/MLCVNet
5. SESS: Self-Ensembling Semi-Supervised 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
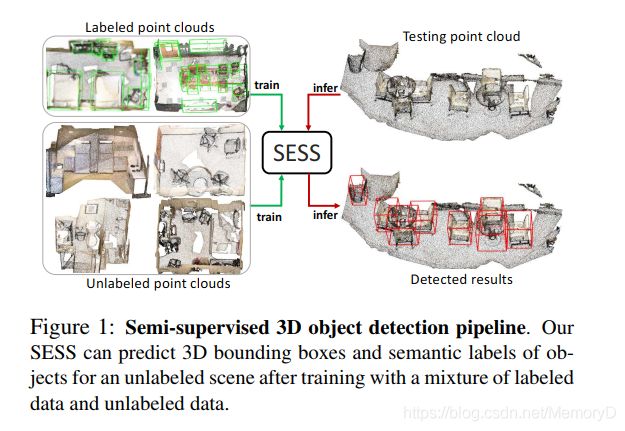
The performance of existing point cloud-based 3D object detection methods heavily relies on large-scale highquality 3D annotations. However, such annotations are often tedious and expensive to collect. Semi-supervised learning is a good alternative to mitigate the data annotation issue, but has remained largely unexplored in 3D object detection. Inspired by the recent success of self-ensembling technique in semi-supervised image classification task, we propose SESS, a self-ensembling semi-supervised 3D object detection framework. Specifically, we design a thorough perturbation scheme to enhance generalization of the network on unlabeled and new unseen data. Furthermore, we propose three consistency losses to enforce the consistency between two sets of predicted 3D object proposals, to facilitate the learning of structure and semantic invariances of objects. Extensive experiments conducted on SUN RGB-D and ScanNet datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SESS in both inductive and transductive semi-supervised 3D object detection. Our SESS achieves competitive performance compared to the state-of-the-art fully-supervised method by using only 50% labeled data.
现有基于点云的3D目标检测方法的性能在很大程度上依赖于大规模高质量3D注释。但是,这样的注释通常很乏味并且收集起来很昂贵。半监督学习是缓解数据注释问题的一种不错的选择,但在3D目标检测中仍未得到充分研究。受到最近在半监督图像分类任务中自组装技术的成功的启发,我们提出了自组装半监督3D目标检测框架SESS。具体而言,我们设计了一种彻底的扰动方案,以增强网络在未标记和新的看不见的数据上的泛化能力。此外,我们提出了三个一致性损失,以加强两组预测的3D对象建议之间的一致性,从而有助于学习对象的结构和语义不变性。在SUN RGB-D和ScanNet数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了SESS在感应式和感应式半监督3D目标检测中的有效性。与最新的完全监督方法相比,我们的SESS仅使用50%的标记数据即可实现竞争优势。
-
论文: SESS: Self-Ensembling Semi-Supervised 3D Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/Na-Z/sess
4. 单目3D目标检测
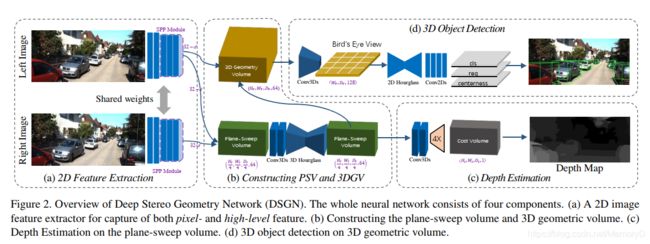
1. DSGN: Deep Stereo Geometry Network for 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
Most state-of-the-art 3D object detectors heavily rely on LiDAR sensors because there is a large performance gap between image-based and LiDAR-based methods. It is caused by the way to form representation for the prediction in 3D scenarios. Our method, called Deep Stereo Geometry Network (DSGN), significantly reduces this gap by detecting 3D objects on a differentiable volumetric representation – 3D geometric volume, which effectively encodes 3D geometric structure for 3D regular space. With this representation, we learn depth information and semantic cues simultaneously. For the first time, we provide a simple and effective one-stage stereo-based 3D detection pipeline that jointly estimates the depth and detects 3D objects in an endto-end learning manner. Our approach outperforms previous stereo-based 3D detectors (about 10 higher in terms of AP) and even achieves comparable performance with several LiDAR-based methods on the KITTI 3D object detection leaderboard.
由于基于图像的方法与基于LiDAR的方法之间存在较大的性能差距,因此大多数最先进的3D目标检测器都严重依赖LiDAR传感器。这是由在3D场景中形成表示预测的方式引起的。我们的方法称为深度立体几何网络(DSGN),它通过在可区分的体积表示形式(3D几何体)上检测3D对象,从而显着缩小了这一差距,该3D几何体有效地为3D规则空间编码了3D几何结构。通过这种表示,我们可以同时学习深度信息和语义提示。我们首次提供了一种简单有效的基于立体声的单阶段3D检测管道,该管道可以以端到端的学习方式联合估算深度并检测3D对象。我们的方法优于以前的基于立体声的3D检测器(在AP方面要高出约10个),甚至可以在KITTI 3D目标检测排行榜上与几种基于LiDAR的方法取得可比的性能。
-
论文: DSGN: Deep Stereo Geometry Network for 3D Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/chenyilun95/DSGN
2. Learning Depth-Guided Convolutions for Monocular 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
3D object detection from a single image without LiDAR is a challenging task due to the lack of accurate depth information. Conventional 2D convolutions are unsuitable for this task because they fail to capture local object and its scale information, which are vital for 3D object detection. To better represent 3D structure, prior arts typically transform depth maps estimated from 2D images into a pseudo-LiDAR representation, and then apply existing 3D point-cloud based object detectors. However, their results depend heavily on the accuracy of the estimated depth maps, resulting in suboptimal performance. In this work, instead of using pseudo-LiDAR representation, we improve the fundamental 2D fully convolutions by proposing a new local convolutional network (LCN), termed Depth-guided Dynamic-Depthwise-Dilated LCN (D4LCN), where the filters and their receptive fields can be automatically learned from image-based depth maps, making different pixels of different images have different filters. D4LCN overcomes the limitation of conventional 2D convolutions and narrows the gap between image representation and 3D point cloud representation. Extensive experiments show that D4LCN outperforms existing works by large margins. For example, the relative improvement of D4LCN against the state-of-theart on KITTI is 9.1% in the moderate setting. D4LCN ranks 1st on KITTI monocular 3D object detection benchmark at the time of submission (car, December 2019).
由于缺乏准确的深度信息,从没有LiDAR的单个图像进行3D目标检测是一项艰巨的任务。常规2D卷积不适合此任务,因为它们无法捕获本地对象及其比例信息,这对于3D目标检测至关重要。为了更好地表示3D结构,现有技术通常将根据2D图像估计的深度图转换为伪LiDAR表示,然后应用现有的基于3D点云的目标检测器。但是,它们的结果在很大程度上取决于估计的深度图的准确性,从而导致性能欠佳。在这项工作中,我们不使用伪LiDAR表示,而是通过提出一个新的局部卷积网络(LCN)(称为深度引导动态深度扩展LCN(D4LCN))来改进基本的2D全卷积,其中滤波器及其接收器字段可以从基于图像的深度图自动学习,从而使不同图像的不同像素具有不同的滤镜。 D4LCN克服了常规2D卷积的局限性,缩小了图像表示和3D点云表示之间的差距。大量实验表明,D4LCN在很大程度上优于现有作品。例如,在中等水平下,D4LCN相对于KITTI的最新水平的相对改进为9.1%。在提交时(汽车,2019年12月),D4LCN在KITTI单目3D目标检测基准上排名第一。
-
整体架构
- 论文: Learning Depth-Guided Convolutions for Monocular 3D Object Detection
- 代码: https://github.com/dingmyu/D4LCN
3. End-to-End Pseudo-LiDAR for Image-Based 3D Object Detection
-
摘要
Reliable and accurate 3D object detection is a necessity for safe autonomous driving. Although LiDAR sensors can provide accurate 3D point cloud estimates of the environment, they are also prohibitively expensive for many settings. Recently, the introduction of pseudo-LiDAR (PL) has led to a drastic reduction in the accuracy gap between methods based on LiDAR sensors and those based on cheap stereo cameras. PL combines state-of-the-art deep neural networks for 3D depth estimation with those for 3D object detection by converting 2D depth map outputs to 3D point cloud inputs. However, so far these two networks have to be trained separately. In this paper, we introduce a new framework based on differentiable Change of Representation (CoR) modules that allow the entire PL pipeline to be trained end-to-end. The resulting framework is compatible with most state-of-the-art networks for both tasks and in combination with PointRCNN improves over PL consistently across all benchmarks — yielding the highest entry on the KITTI image-based 3D object detection leaderboard at the time of submission.
可靠,准确的3D目标检测是安全自动驾驶的必要条件。尽管LiDAR传感器可以提供对环境的准确3D点云估计,但对于许多设置而言,它们的价格也过高。最近,伪LiDAR(PL)的引入已大大缩小了基于LiDAR传感器的方法与基于廉价立体相机的方法之间的精度差距。 PL通过将2D深度图输出转换为3D点云输入,将用于3D深度估计的最新深度神经网络与用于3D目标检测的深度神经网络相结合。但是,到目前为止,这两个网络必须分别进行培训。在本文中,我们介绍了一个基于差异表示形式(CoR)模块的新框架,该框架允许对整个PL管道进行端到端培训。最终的框架与大多数最新的网络兼容,可同时完成所有任务,并且与PointRCNN相比,在所有基准测试中均不断提高PL的性能-提交时在KITTI基于图像的3D目标检测排行榜上获得最高排名。
-
论文: End-to-End Pseudo-LiDAR for Image-Based 3D Object Detection
-
代码: https://github.com/mileyan/pseudo-LiDAR_e2e
4. Disp R-CNN: Stereo 3D Object Detection via Shape Prior Guided Instance Disparity Estimation
-
摘要
In this paper, we propose a novel system named Disp R-CNN for 3D object detection from stereo images. Many recent works solve this problem by first recovering a point cloud with disparity estimation and then apply a 3D detector. The disparity map is computed for the entire image, which is costly and fails to leverage category-specific prior. In contrast, we design an instance disparity estimation network (iDispNet) that predicts disparity only for pixels on objects of interest and learns a category-specific shape prior for more accurate disparity estimation. To address the challenge from scarcity of disparity annotation in training, we propose to use a statistical shape model to generate dense disparity pseudo-ground-truth without the need of LiDAR point clouds, which makes our system more widely applicable. Experiments on the KITTI dataset show that, even when LiDAR ground-truth is not available at training time, Disp R-CNN achieves competitive performance and outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by 20% in terms of average precision.
在本文中,我们提出了一种名为Disp R-CNN的新颖系统,用于从立体图像中检测3D对象。许多最近的工作通过首先使用视差估计恢复点云,然后应用3D检测器来解决此问题。对于整个图像计算视差图,这是昂贵的并且不能利用特定于类别的先验。相比之下,我们设计了一个实例视差估计网络(iDispNet),该网络仅预测感兴趣对象上像素的视差,并在获得特定类别的形状之前进行更准确的视差估计。为了解决训练中视差标注的稀缺性带来的挑战,我们建议使用统计形状模型来生成密集的视差伪地面真相,而无需使用LiDAR点云,这使得我们的系统更广泛地适用。在KITTI数据集上进行的实验表明,即使在训练时没有LiDAR地面真相时,Disp R-CNN仍可实现竞争性能,并且在平均精度方面要比以前的最新方法高出20%。
-
论文: Disp R-CNN: Stereo 3D Object Detection via Shape Prior Guided Instance Disparity Estimation
-
代码: https://github.com/zju3dv/disprcnn