Java SPI解析与应用场景
什么是Java SPI?
SPI的全名为:Service Provider Interface。在java.util.ServiceLoader的文档里有比较详细的介绍。简单的总结下 Java SPI 机制的思想。我们系统里抽象的各个模块,往往有很多不同的实现方案,比如日志模块的方案,xml解析模块、jdbc模块的方案等。面向的对象的设计里,我们一般推荐模块之间基于接口编程,模块之间不对实现类进行硬编码。一旦代码里涉及具体的实现类,就违反了可拔插的原则,如果需要替换一种实现,就需要修改代码。为了实现在模块装配的时候能不在程序里动态指明,这就需要一种服务发现机制。
Java SPI 就是提供这样的一个机制:为某个接口寻找服务实现的机制。有点类似IOC的思想,就是将装配的控制权移到程序之外,在模块化设计中这个机制尤其重要Java SPI 的具体约定为:当服务的提供者,提供了服务接口的一种实现之后,在jar包的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名,并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。基于这样一个约定就能很好的找到服务接口的实现类,而不需要再代码里制定。jdk提供服务实现查找的一个工具类:java.util.ServiceLoader。
Java SPI使用demo
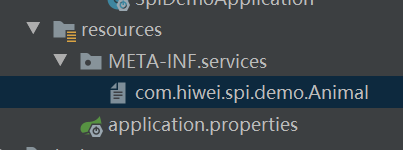
- 定义一个接口:
package com.hiwei.spi.demo;
public interface Animal {
void speak();
}
- 创建两个实现类:
package com.hiwei.spi.demo;
public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("喵喵喵!");
}
}
package com.hiwei.spi.demo;
public class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("汪汪汪!");
}
}
com.hiwei.spi.demo.Cat
com.hiwei.spi.demo.Dog
- 使用
package com.hiwei.spi;
import com.hiwei.spi.demo.Animal;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
public class SpiDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
//会根据文件找到对应的实现类
ServiceLoader<Animal> load = ServiceLoader.load(Animal.class);
//执行实现类方法
for (Animal animal : load) {
animal.speak();
}
}
}
执行结果:
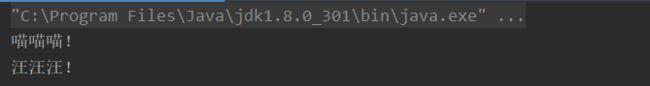
上面我们可以看到java spi会帮助我们找到接口实现类。那么实际生产中怎么使用呢?
将上面的代码打成jar,然后在其它项目中引入,同样的目录下创建文件,并写上自己实现类的路径:
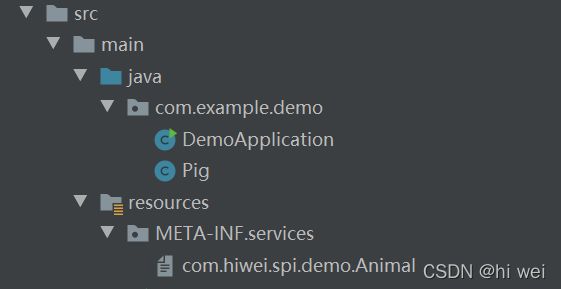
本项目实现类:
package com.example.demo;
import com.hiwei.spi.demo.Animal;
public class Pig implements Animal {
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("哼哼哼!");
}
}
代码中,我们调用jar中的main方法:
package com.example.demo;
import com.hiwei.spi.SpiDemoApplication;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpiDemoApplication.main(args);
}
}
执行结果:
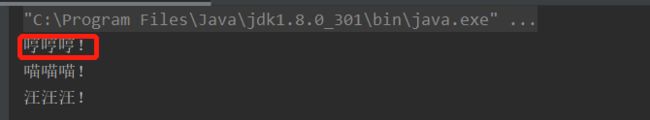
可以看见自定义的实现类也被执行了。在实际生产中,我们就可以使用java spi面向接口编程,实现可插拔。
SPI在JDBC中的应用
以最新的mysql-connector-java-8.0.27.jar为例
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.27version>
dependency>
在使用JDBC连接数据库时,只需要使用:
DriverManager.getConnection("url", "username", "password");
DriverManager有静态方法:
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
看下loadInitialDrivers()方法,其中有:
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
//获取Driver.class的实现类
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
可以看见,会根据java spi获取Driver.class的实现类,可以在mysql-connector-java-8.0.27.jar下面看到,定义的文件:

程序会根据文件找到对应的实现类,并连接数据库。
SPI在sharding-jdbc中的应用
sharding-jdbc是一款用于分库分表的中间件,在数据库分布式场景中,对于主键生成要保证唯一性,主键生成策略有很多种实现。sharding-jsbc在主键生成上就使用了SPI进行扩展。
下面看下sharding-jdbc源码在主键生成上是怎么应用的:
源码中的 ShardingRule.class主要封装分库分表的策略规则,包括主键生成。看下createDefaultKeyGenerator方法:
//生成默认主键生成策略
private ShardingKeyGenerator createDefaultKeyGenerator(final KeyGeneratorConfiguration keyGeneratorConfiguration) {
//SPI服务发现
ShardingKeyGeneratorServiceLoader serviceLoader = new ShardingKeyGeneratorServiceLoader();
return containsKeyGeneratorConfiguration(keyGeneratorConfiguration)
? serviceLoader.newService(keyGeneratorConfiguration.getType(), keyGeneratorConfiguration.getProperties()) : serviceLoader.newService();
}
继续看ShardingKeyGeneratorServiceLoader(),有静态代码块注册:
static {
//SPI: 加载主键生成策略
NewInstanceServiceLoader.register(ShardingKeyGenerator.class);
}
看下register方法:
public static <T> void register(final Class<T> service) {
//服务发现
for (T each : ServiceLoader.load(service)) {
registerServiceClass(service, each);
}
}
看到这,真相大白,就是应用java spi机制。
我们再看下resources目录下:
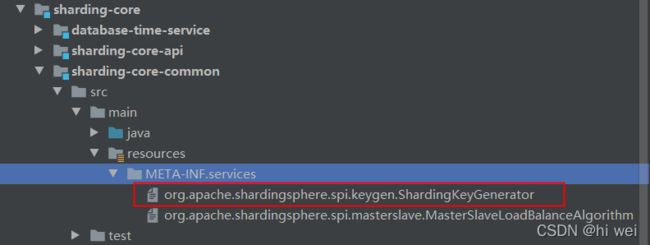
可以看到有对应接口命名的文件,文件内容:

有两个实现,分别是雪花算法和UUID,这也对应了sharding-jdbc的提供的两种生成策略。我们在使用sharding-jdbc时,也可以自定义策略,便于扩展。
sharding-jdbc对于SPI的使用点还有很多,这里就不一一列举了。对于SPI机制,我们在工作中也可以实际应用,提升程序的可扩展性。
扩展
以上是Java SPI的解析。其实SPI机制在很多地方都有用到,只是以不同的形式应用,具体的实现略有不同。例如dubbo中也有类似的spi机制;springboot的自动装配,也使用了spi机制:
springboot自动装配:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.hiwei.valve.ValveAutoConfiguration
- springboot的扫描文件,装配对应的类:
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
//加载文件中的类
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的值:

SPI在Java开发中是个很重要的设计,所以我们一定要熟练掌握。