遗传算法求解TSP问题-python实现
遗传算法求解TSP问题
1. TSP问题简介
旅行商人要拜访n个城市,并最终回到出发城市,要求每个城市只能拜访一次,优化目标是最小化路程之和。
2. 例子求解结果
20个城市坐标:(88, 16),(42, 76),(5, 76),(69, 13),(73, 56),(100, 100),(22, 92),(48, 74),(73, 46),(39, 1),(51, 75),(92, 2),(101, 44),(55, 26),(71, 27),(42, 81),(51, 91),(89, 54),(33, 18),(40, 78)
结果路径图和迭代效果如下:
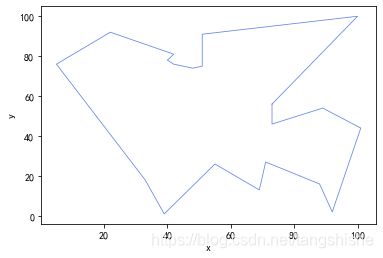
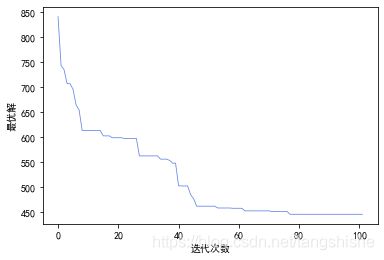
3. 遗传算法设计
自然数编码、锦标赛选择、顺序交叉、基本位变异、一对一生存者竞争。python编程。算法详细情况可参考Geatpy进化算法介绍 (Geatpy也是一个实用的Python遗传算法工具箱)
3.1 适应度函数
def calFitness(line,dis_matrix):
dis_sum = 0
dis = 0
for i in range(len(line)):
if i<len(line)-1:
dis = dis_matrix.loc[line[i],line[i+1]]#计算距离
dis_sum = dis_sum+dis
else:
dis = dis_matrix.loc[line[i],line[0]]
dis_sum = dis_sum+dis
return round(dis_sum,1)
3.2 锦标赛选择
def tournament_select(pops,popsize,fits,tournament_size):
new_pops,new_fits = [],[]
while len(new_pops)<len(pops):
tournament_list = random.sample(range(0,popsize),tournament_size)
tournament_fit = [fits[i] for i in tournament_list]
#转化为df方便索引
tournament_df = pd.DataFrame([tournament_list,tournament_fit]).transpose().sort_values(by=1).reset_index(drop=True)
#选出获胜者
fit = tournament_df.iloc[0,1]
pop = pops[int(tournament_df.iloc[0,0])]
new_pops.append(pop)
new_fits.append(fit)
return new_pops,new_fits
3.3 顺序交叉
def crossover(popsize,parent1_pops,parent2_pops,pc):
child_pops = []
for i in range(popsize):
#初始化
child = [None]*len(parent1_pops[i])
parent1 = parent1_pops[i]
parent2 = parent2_pops[i]
if random.random() >= pc:
child = parent1.copy()#随机生成一个(或者随机保留父代中的一个)
random.shuffle(child)
else:
#parent1
start_pos = random.randint(0,len(parent1)-1)
end_pos = random.randint(0,len(parent1)-1)
if start_pos>end_pos:
tem_pop = start_pos
start_pos = end_pos
end_pos = tem_pop
child[start_pos:end_pos+1] = parent1[start_pos:end_pos+1].copy()
# parent2 -> child
list1 = list(range(end_pos+1,len(parent2)))
list2 = list(range(0,start_pos))
list_index = list1+list2
j = -1
for i in list_index:
for j in range(j+1,len(parent2)):
if parent2[j] not in child:
child[i] = parent2[j]
break
child_pops.append(child)
return child_pops
3.4 基本位变异
随机选出两个位置进行交换
def mutate(pops,pm):
pops_mutate = []
for i in range(len(pops)):
pop = pops[i].copy()
#随机多次成对变异
t = random.randint(1,5)
count = 0
while count < t:
if random.random() < pm:
mut_pos1 = random.randint(0,len(pop)-1)
mut_pos2 = random.randint(0,len(pop)-1)
if mut_pos1 != mut_pos2:
tem = pop[mut_pos1]
pop[mut_pos1] = pop[mut_pos2]
pop[mut_pos2] = tem
pops_mutate.append(pop)
count +=1
return pops_mutate
#另一种实现方式
# def mutate(pops,pm):
# pops_mutate = []
# for i in range(len(pops)):
# pop = pops[i].copy()
# for j in range(len(pop)):
# if random.random() < pm:
# mut_pos = random.randint(0,len(pop)-1)
# if j != mut_pos:
# tem = pop[j]
# pop[j] = pop[mut_pos]
# pop[mut_pos] = tem
# pops_mutate.append(pop)
# return pops_mutate
3.5 主函数
import math
import random
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pylab import mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 添加这条可以让图形显示中文
#画路径图
def draw_path(line,CityCoordinates):
x,y= [],[]
for i in line:
Coordinate = CityCoordinates[i]
x.append(Coordinate[0])
y.append(Coordinate[1])
x.append(x[0])
y.append(y[0])
plt.plot(x, y,'r-', color='#4169E1', alpha=0.8, linewidth=0.8)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
#参数
CityNum = 20#城市数量
MinCoordinate = 0#二维坐标最小值
MaxCoordinate = 101#二维坐标最大值
#GA参数
generation = 100 #迭代次数
popsize = 100 #种群大小
tournament_size = 5 #锦标赛小组大小
pc = 0.95 #交叉概率
pm = 0.1 #变异概率
#随机生成城市数据,城市序号为0,1,2,3...
CityCoordinates = [(random.randint(MinCoordinate,MaxCoordinate),random.randint(MinCoordinate,MaxCoordinate)) for i in range(CityNum)]
# CityCoordinates = [(88, 16),(42, 76),(5, 76),(69, 13),(73, 56),(100, 100),(22, 92),(48, 74),(73, 46),(39, 1),(51, 75),(92, 2),(101, 44),(55, 26),(71, 27),(42, 81),(51, 91),(89, 54),(33, 18),(40, 78)]#随机生成的例子
#计算城市之间的距离
dis_matrix = pd.DataFrame(data=None,columns=range(len(CityCoordinates)),index=range(len(CityCoordinates)))
for i in range(len(CityCoordinates)):
xi,yi = CityCoordinates[i][0],CityCoordinates[i][1]
for j in range(len(CityCoordinates)):
xj,yj = CityCoordinates[j][0],CityCoordinates[j][1]
dis_matrix.iloc[i,j] = round(math.sqrt((xi-xj)**2+(yi-yj)**2),2)
iteration = 0
#初始化,随机构造
pops = [random.sample([i for i in list(range(len(CityCoordinates)))],len(CityCoordinates)) for j in range(popsize)]
#计算适应度
fits = [None]*popsize
for i in range(popsize):
fits[i] = calFitness(pops[i],dis_matrix)
#保留当前最优
best_fit = min(fits)
best_pop = pops[fits.index(best_fit)]
print('初代最优值 %.1f' % (best_fit))
best_fit_list = []
best_fit_list.append(best_fit)
while iteration <= generation:
#锦标赛赛选择
pop1,fits1 = tournament_select(pops,popsize,fits,tournament_size)
pop2,fits2 = tournament_select(pops,popsize,fits,tournament_size)
#交叉
child_pops = crossover(popsize,pop1,pop2,pc)
#变异
child_pops = mutate(child_pops,pm)
#计算子代适应度
child_fits = [None]*popsize
for i in range(popsize):
child_fits[i] = calFitness(child_pops[i],dis_matrix)
#一对一生存者竞争
for i in range(popsize):
if fits[i] > child_fits[i]:
fits[i] = child_fits[i]
pops[i] = child_pops[i]
if best_fit>min(fits):
best_fit = min(fits)
best_pop = pops[fits.index(best_fit)]
best_fit_list.append(best_fit)
print('第%d代最优值 %.1f' % (iteration, best_fit))
iteration += 1
#路径顺序
print(best_pop)
#路径图
draw_path(best_pop,CityCoordinates)
#迭代图
iters = list(range(len(best_fit_list)))
plt.plot(iters, best_fit_list, 'r-', color='#4169E1', alpha=0.8, linewidth=0.8)
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
TSP系列目录
| 智能优化算法类别 | 启发式算法求解TSP问题系列博文 |
|---|---|
| 进化算法 | 遗传算法求解TSP问题 |
| 仿人智能优化算法 | 禁忌搜索算法求解TSP问题 |
| 仿自然优化算法 | 模拟退火算法求解TSP问题 |
| 群智能优化算法 | 蚁群算法求解TSP问题 |
| 群智能优化算法 | 粒子群算法求解TSP问题 |
| 总结篇 | 五种常见启发式算法求解TSP问题 |
| 改进篇 | 遗传-粒子群算法&遗传-禁忌搜索算法求解TSP问题 |
记录学习过程,欢迎指正