Minimax 算法中的 Alpha Beta 剪枝
就像我们在之前的文章中讨论的那样,硬编码的 AI 可以用来创建一个聪明的对手,你可以挑战经典的井字游戏!
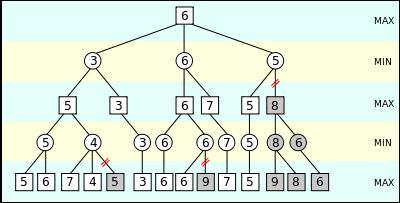
但是,该算法仍然可以进一步优化。但我们如何做到这一点?Alpha Beta Pruning 是一种搜索算法,它试图减少由 minimax 算法在其搜索树中评估的集线器数量。它是一种对抗性搜索算法,通常用于两人游戏(井字游戏、国际象棋、围棋等)的机器游戏。
当观察到不少于一个概率最终比以前分析的举动更令人遗憾时,它就停止完全评估一个举动。此类举动无需进一步评估。当连接到标准的极小极大树时,它会恢复与极小极大树无法区分的移动,但会修剪掉不会以任何方式、形状或形式影响官方结论的分支!
你一定在想这个数字到底意味着什么。好吧,它显示了算法如何忽略在我们的游戏动作中并不真正需要的子树。该算法保持了两个品质,alpha 和 beta,它们分别说明了扩展玩家所保证的基本分数和限制玩家所保证的最大分数。起初 alpha 是负无穷大,而 beta 是肯定无穷大,即两个玩家以他们最可怕的分数开始。在任何时候,限制玩家 (beta) 保证的最极端分数都不会像扩展玩家 (alpha) 保证的基本分数一样多(即 beta <= alpha),增强玩家不需要考虑这个中心的亲戚,因为他们永远不会真正参与进来。
算法
笔记 :
-
Alpha Beta Pruning 不是一种新算法,实际上是一种优化!
-
Alpha是最大化者目前在该水平或以上可以保证的最佳值。
-
Beta是最小化器当前可以保证在该级别或以上的最佳值。
当然,我们使用井字游戏作为参考示例!
def minimax(depth, player, alpha, beta)
if gameover or depth == 0
return calculated_score
end
children = all legal moves for player
if player is AI (maximizing player)
for each child
score = minimax(depth - 1, opponent, alpha, beta)
if (score > alpha)
alpha = score
end
if alpha >= beta
break
end
return alpha
end
else #player is minimizing player
best_score = +infinity
for each child
score = minimax(depth - 1, player, alpha, beta)
if (score < beta)
beta = score
end
if alpha >= beta
break
end
return beta
end
end
end
#then you would call it like
minimax(2, computer, -inf, +inf)
复杂
- 最坏情况性能:
O(|E|) = O(b^(d/2)) - 最坏情况空间复杂度:
O(|V|) = O(b * d)
实现
- Next Best Move Guesser - Python
交互式控制台游戏- Python
import numpy as np
import sys
from copy import copy
rows = 3
cols = 3
board = np.zeros((rows,cols))
inf = float("inf")
neg_inf = float("-inf")
def printBoard():
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if board[i, j] == 0:
sys.stdout.write(' _ ')
elif board[i, j] == 1:
sys.stdout.write(' X ')
else:
sys.stdout.write(' O ')
print ''
# The heuristic function which will be evaluating board's position for each of the winning POS
heuristicTable = np.zeros((rows+1, cols+1))
numberOfWinningPositions = rows + cols + 2
for index in range(rows+1):
heuristicTable[index, 0] = 10**index
heuristicTable[0, index] =-10**index
winningArray = np.array([[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8], [0, 3, 6], [1, 4, 7], [2, 5, 8], [0, 4, 8], [2, 4, 6]])
def utilityOfState(state):
stateCopy = copy(state.ravel())
heuristic = 0
for i in range(numberOfWinningPositions):
maxp = 0
minp = 0
for j in range(rows):
if stateCopy[winningArray[i,j]] == 2:
maxp += 1
elif stateCopy[winningArray[i,j]] == 1:
minp += 1
heuristic += heuristicTable[maxp][minp]
return heuristic
def minimax(state,alpha,beta,maximizing,depth,maxp,minp):
if depth==0:
return utilityOfState(state),state
rowsLeft,columnsLeft=np.where(state==0)
returnState=copy(state)
if rowsLeft.shape[0]==0:
return utilityOfState(state),returnState
if maximizing==True:
utility=neg_inf
for i in range(0,rowsLeft.shape[0]):
nextState=copy(state)
nextState[rowsLeft[i],columnsLeft[i]]=maxp
#print 'in max currently the Nextstate is ',nextState,'\n\n'
Nutility,Nstate=minimax(nextState,alpha,beta,False,depth-1,maxp,minp)
if Nutility > utility:
utility=Nutility
returnState=copy(nextState)
if utility>alpha:
alpha=utility
if alpha >=beta :
#print 'pruned'
break;
#print 'for max the best move is with utility ',utility,' n state ',returnState
return utility,returnState
else:
utility=inf
for i in range(0,rowsLeft.shape[0]):
nextState=copy(state)
nextState[rowsLeft[i],columnsLeft[i]]=minp
#print 'in min currently the Nextstate is ',nextState,'\n\n'
Nutility,Nstate=minimax(nextState,alpha,beta,True,depth-1,maxp,minp)
if Nutility < utility:
utility=Nutility
returnState=copy(nextState)
if utility< beta:
beta=utility
if alpha >=beta :
#print 'pruned'
break;
return utility,returnState
def checkGameOver(state):
stateCopy=copy(state)
value=utilityOfState(stateCopy)
if value >=1000:
return 1
return -1
def main():
num=input('enter player num (1st or 2nd) ')
value=0
global board
for turn in range(0,rows*cols):
if (turn+num)%2==1: #make the player go first, and make the user player as 'X'
r,c=[int(x) for x in raw_input('Enter your move ').split(' ')]
board[r-1,c-1]=1
printBoard()
value=checkGameOver(board)
if value==1:
print 'U win.Game Over'
sys.exit()
print '\n'
else: #its the computer's turn make the PC always put a circle'
#right now we know the state if the board was filled by the other player
state=copy(board)
value,nextState=minimax(state,neg_inf,inf,True,2,2,1)
board=copy(nextState)
printBoard()
print '\n'
value=checkGameOver(board)
if value==1:
print 'PC wins.Game Over'
sys.exit()
print 'Its a draw'
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
应用
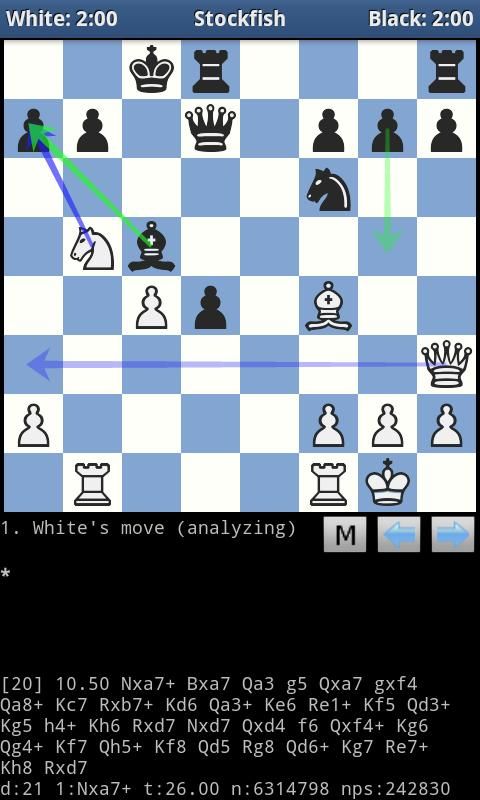
它的主要应用是在国际象棋游戏中。Stockfish(国际象棋)是一个 C++ 开源国际象棋程序,实现了 Alpha Beta 剪枝算法。Stockfish 是一个成熟的实现,被评为当今最强大的国际象棋引擎之一,它在 2016 年和 2017 年赢得了顶级国际象棋引擎锦标赛就证明了这一点。
需要注意的一件更有趣的事情是,alpha-beta 剪枝的实现通常可以通过它们是“软故障”还是“硬故障”来描述。伪代码说明了故障软变化。使用 fail-soft alpha-beta,alphabeta 函数可能返回的值 (v) 超过(v < α 或 v > β)由其函数调用参数设置的 α 和 β 边界。相比之下,fail-hard alpha-beta 将其函数返回值限制在 α 和 β 的包含范围内。