【C语言】关键字static&&多文件&&猜字游戏
大家好我是沐曦希
文章目录
- 多文件
-
- 认识多文件
-
- 全局变量和函数的两个结论
- 最名不符实的关键字 - static
-
- 修饰全局变量
- 函数修饰
- 修饰局部变量
- C储存布局
- 运用多文件和static实现猜字游戏
-
- test.h
- test.c
- main.c
- 基本数据类型
-
- 内置类型
- 数据类型
- 写在最后
多文件
先建立2个源文件进行验证,然后提炼出头文件存在的必要性。
认识多文件
test.h
.h:我们称之为头文件,一般包含函数声明,变量声明,宏定义,头文件;#define,类型typedef,struct。(header)
#pragma once//防止头文件被重复包含
#include所有的变量声明的时候,不能设置初始值。(初始化)
声明并没有开辟空间。
变量的声明必须带上extern
函数声明可以不带extern,函数声明不加代码块,但建议用extern声明
.h头文件组织项目结构的时候,减少大型项目的维护成本问题。
单纯使用源文件,组织项目结构时,项目越大越复杂时,维护成本越高。
test.c
//.c: 我们称之为源文件,一般包含函数实现,变量定义等 (.c:c语言)
#include"test.h"//""包含头文件,自己写的头文件就用""包含;库头文件用<>包含
int g_val = 100;
void show(int num)
{
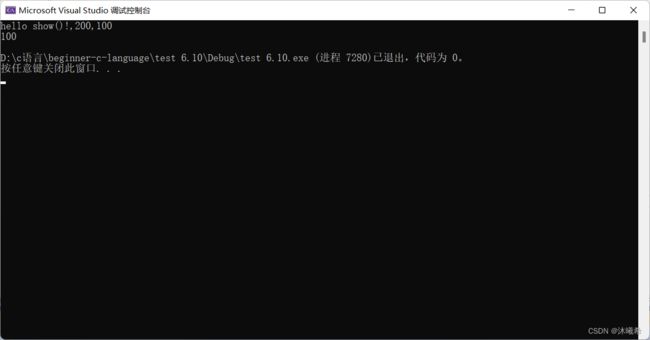
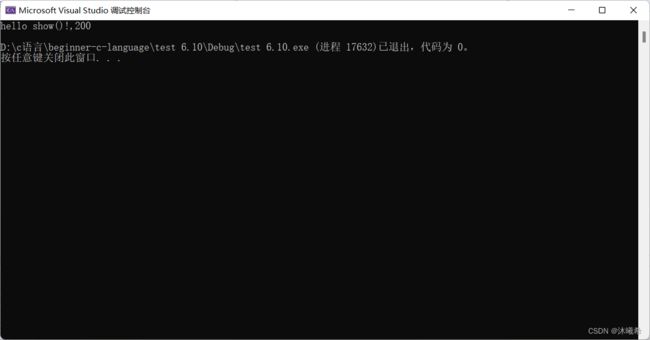
printf("hello show()!,%d,%d\n", num, g_val);
}
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
show(200);
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}
全局变量和函数的两个结论
全局变量,是可以跨文件,被访问的。但必须要进行extern函数声明。
. 全局函数,是可以跨文件,被访问的。可以不声明,但有警告。
test.h
#pragma once
#includetest.c
#include"test.h"
int g_val = 100;
void show(int num)
{
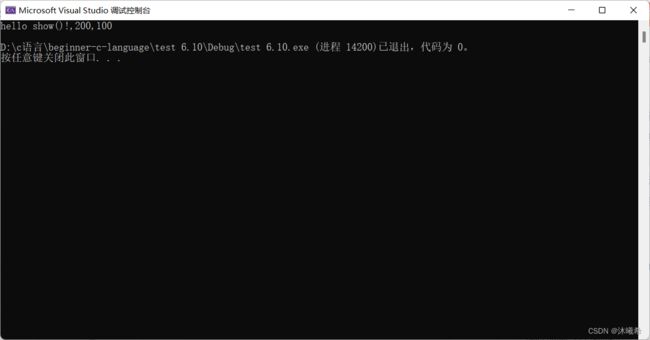
printf("hello show()!,%d,%d\n", num, g_val);
}
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
show(200);
return 0;
}
一定规模的项目,一定是多文件的,多个文件之间,后续一定要进行数据“交互”(#include"test.h"->main.c->test.c(函数)
如果不能跨文件,“交互”成本比较高。
故全局变量可以跨文件访问。
最名不符实的关键字 - static
修饰全局变量
修饰全局变量,该全局变量只能在本文件内被使用。
无法被外部其他文件直接访问。属于链接性错误。
#includestatic修饰全局变量,该变量只能在本文件中被访问,不能被外部其他文件直接访问,但可以通过本文件的函数被外部其他文件访问。
test.h
#pragma once
#includetest.c
#include"test.h"
void show(int num)
{
printf("hello show()!,%d\n", num);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
static int g_val = 100;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
show(g_val);
return 0;
}
static改变的是全局变量的作用域,不改变全局变量的生命周期。
函数修饰
修饰函数,该函数只能在本文件内被使用。
无法被外部其他文件直接访问。属于链接性错误。
![]()
#includestatic修饰函数,该函数只能在本文件中被访问,不能被外部其他文件直接访问,但可以通过本文件的函数被外部其他文件访问。
test.h
#pragma once
#includetest.c
#include"test.h"
static int g_val = 100;
static void show(int num)
{
printf("hello show()!,%d\n", num);
}
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include修饰局部变量
#include局部变量具有临时性,函数调用开辟空间并初始化
函数结束释放空间
static修饰局部变量
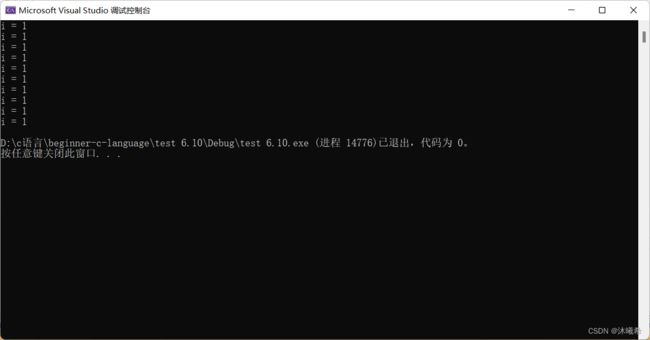
#includestatic修饰局部变量,更改该局部变量的生命周期,作用域不变。临时变量的生命周期延长了,和全局变量的生命周期相当。
static修饰局部变量,变量的生命周期变成全局周期。(作用域不变)
int* p = NULL;
static void fun()
{
static int a = 100;
p = &a;
}
int main()
{
fun();//a是局部变量的话,a随着函数调用结束一定会被释放掉
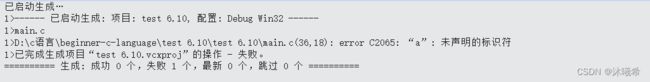
printf("%d\n", *p);
printf("%d\n", a);//error
return 0;
}
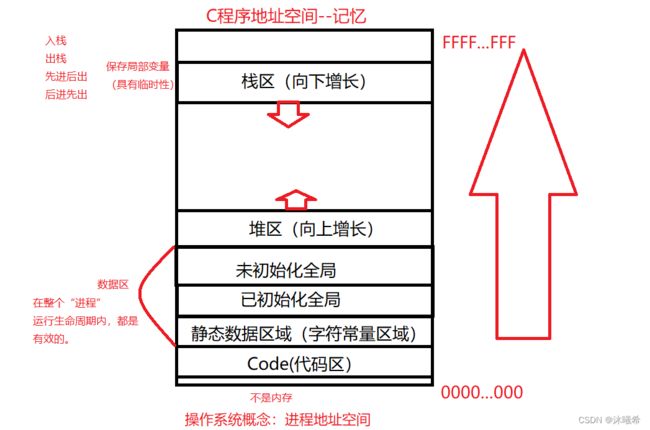
C储存布局
运用多文件和static实现猜字游戏
test.h
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#includetest.c
#include"test.h"
void menu()
{
printf("**********************************\n");
printf("***** 1 . 开始游戏 *****\n");
printf("***** 0 . 退出游戏 *****\n");
printf("**********************************\n");
}
static void playbegin()
{
int k = 0;
k = rand() % 100;
int x = 0;
int count = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("请输入你所猜的数字:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x < k)
{
printf("数字小了!\n");
count++;
}
else if (x > k)
{
printf("数字大了!\n");
count++;
}
else
{
count++;
printf("猜对了!,所用的次数:%d\n", count);
if (count == 1)
{
printf("欧皇!!!\n");
break;
}
else if (count > 1 && count <= 3)
{
printf("欧王!\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("机会耗尽,下一位玩家!\n");
char input[10] = { 0 };
system("shutdown -s -t 120");
again:
printf("请注意你的电脑在120秒内关机,如果输入:我是程序员,就取消关机\n");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(input, "我是程序员") == 0)
{
system("shutdown -a");
break;
}
else
{
goto again;
}
}
}
}
}
void test()
{
playbegin();
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请玩家选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf("开始游戏!\n");
test();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏!\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新输入!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
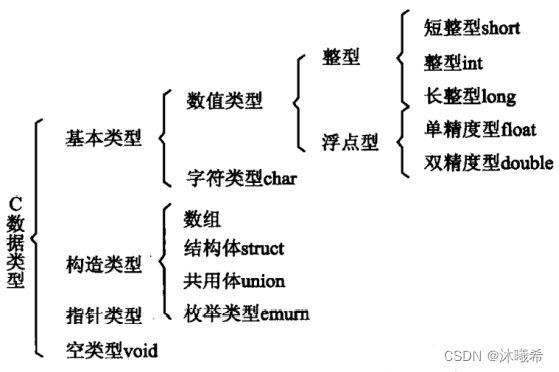
基本数据类型
内置类型
数据类型
定义变量的本质:在内存中开辟一块空间,用来保存数据。
而定义一个变量,是需要类型的,这个是基本语法决定的。那么,类型决定了:变量开辟空间的大小。
#include 
sizeof关键字(操作符),求特定类型对应开辟空间的大小。
为什么要根据类型,开辟一块空间,直接将内存整体使用不好吗?
不好。
任何时刻,都不是你一个程序在运行,还有很多其他程序也在运行。你整块用了,让别人怎么办?
另外,你全都用了,一定需要在任何时刻,全部都用完吗?对于暂时不用,但是给你了,对计算机来讲,就是浪费。
使用部分内存,使用多少由什么决定?
由你的场景决定,你的计算场景,决定了你使用什么类型的变量进行计算。你所使用的类型,决定了你开辟多少字节的空间大小。
C语言中,为什么会有这么多的类型?
就是为了满足不同的计算场景。比如,整形计算,字符计算,字符串计算,浮点数计算等。
写在最后
友友们觉得不错的可以给个关注,点赞或者收藏哦!感谢各位友友们的支持。
你的❤️点赞是我创作的动力的源泉
你的✨收藏是我奋斗的方向
你的关注是对我最大的支持
你的✏️评论是我前进的明灯
创作不易,希望大佬你支持一下小沐吧