spring、springboot常用注解详解
缓存注解
@Cacheable 注解在方法上,表示该方法的返回结果是可以缓存的。也就是说,该方法的返回结果会放在缓存中,以便于以后使用相同的参数调用该方法时,会返回缓存中的值,而不会实际执行该方法。
@Override
@Cacheable({"menu", "menuById"})
public Menu findById(String id) {
Menu menu = this.getById(id);
if (menu != null){
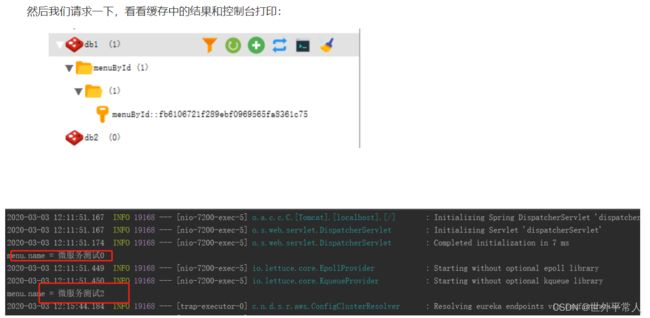
System.out.println("menu.name = " + menu.getName());
}
return menu;
}
---------
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Menu findById(@PathVariable("id")String id){
Menu menu0 = menuService.findById("fe278df654adf23cf6687f64d1549c0a");
Menu menu2 = menuService.findById("fb6106721f289ebf0969565fa8361c75");
return menu0;
}
可以多个key,结果

1、一个缓存名对应一个被注解的方法,但是一个方法可能传入不同的参数,那么结果也就会不同,这应该如何区分呢?
其实用传入的参数在作为key值拼接起来即可
有三种生成方案
1、spring自动生成的id #id
2、由参数生成的key
3、对象的hashCode()
代码如下:
/**一般是用这种方法*/
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"menuById"}, key = "#id")
public Menu findById(String id) {
Menu menu = this.getById(id);
if (menu != null){
System.out.println("menu.name = " + menu.getName());
}
return menu;
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"menuById"}, key = "'id-' + #menu.id")
public Menu findById(Menu menu) {
return menu;
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"menuById"}, key = "'hash' + #menu.hashCode()")
public Menu findByHash(Menu menu) {
return menu;
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"menuById"}, key = "#id", condition = "#conditionValue > 1")
public Menu findById(String id, Integer conditionValue) {
Menu menu = this.getById(id);
if (menu != null){
System.out.println("menu.name = " + menu.getName());
}
return menu;
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Menu findById(@PathVariable("id")String id){
Menu menu0 = menuService.findById("fe278df654adf23cf6687f64d1549c0a", 0);
Menu menu2 = menuService.findById("fb6106721f289ebf0969565fa8361c75", 2);
return menu0;
}
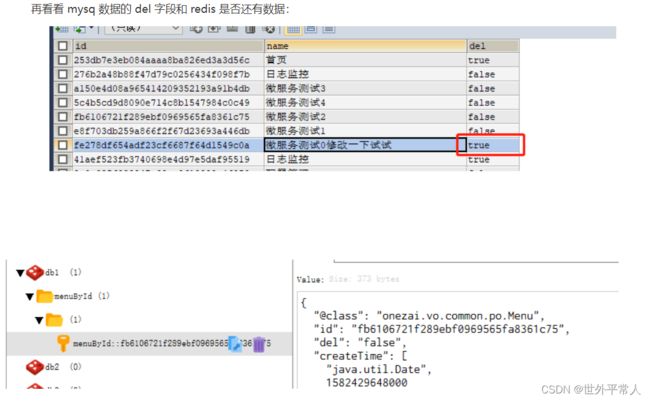
spring cache 也支持使用 @CacheEvict 来删除缓存
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "menuById", key = "#id")
public Boolean deleteById(String id) {
return this.removeById(id);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public Boolean deleteById(@PathVariable("id")String id){
return menuService.deleteById(id);
}
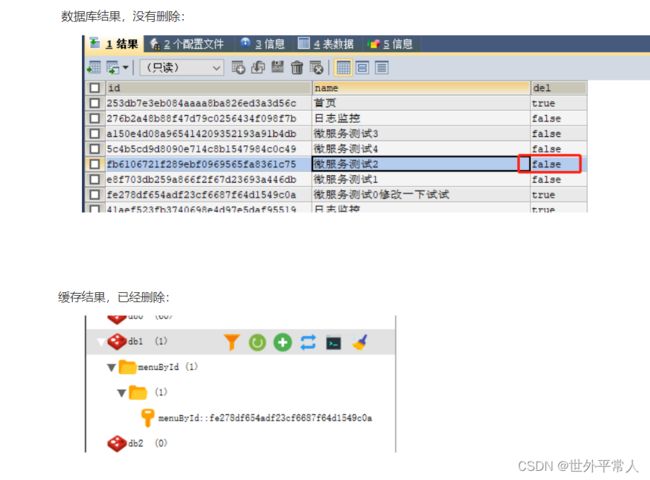
@CacheEvict有个属性beforeInvocation,默认是false,先执行方法(数据库),再操作缓存。
当值为true时,,先执行缓存,再操作方法(数据库)。
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "menuById", key = "#id", beforeInvocation = true)
public Boolean deleteById(String id) {
System.out.println("开始操作 db");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Boolean result = this.removeById(id);
System.out.println("db 操作结束");
return result;
}
2、@ConditionalOnMissingBean,它是修饰bean的一个注解,主要实现的是,当你的bean被注册之后,如果而注册相同类型的bean,就不会成功,它会保证你的bean只有一个,即你的实例只有一个,当你注册多个相同的bean时,会出现异常,以此来告诉开发人员
3、注解@BeanFactoryPostProcessor
接口与 BeanPostProcessor接口类似,可以对bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理;也就是spring ioc运行BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其他的bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它;如果业务需要,可以配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类,通过"order"控制执行次序(要实现Ordered接口)。
4、@ConditionalOnBean // 当给定的在bean存在时,则实例化当前Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean // 当给定的在bean不存在时,则实例化当前Bean
@ConditionalOnClass // 当给定的类名在类路径上存在,则实例化当前Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingClass // 当给定的类名在类路径上不存在,则实例化当前Bean