人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.05
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
![]()
工具库:ivy - 机器学习统一框架
tags:[机器学习]
支持所有框架,目前支持 Jax,TensorFlow,PyTorch,MXNet 和 Numpy
‘ivy - The Unified Machine Learning Framework’
GitHub:http://github.com/unifyai/ivy
工具:pytest-memray - Python内存分析工具
tags:[内存分析]
‘pytest-memray - Memray is a memory profiler for Python’ by bloomberg
GitHub:http://github.com/bloomberg/pytest-memray
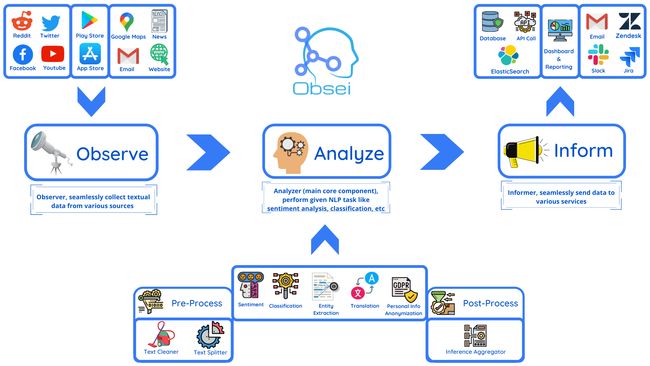
工具:Obsei - 面向文本分析的低代码自动化工具
tags:[低代码,自动化,文本分析]
‘Obsei: Observe, Analyze and Inform - Obsei is intended to be an automation tool for text analysis need.’ by Lalit Pagaria
GitHub:http://github.com/lalitpagaria/obsei
工具库:Frontend - COCO图片标注工具
tags:[数据标注,图片标注]
‘COCO Image Labelling Tool - Frontend (FE)’ by NAVER AI
GitHub:http://github.com/naver-ai/coco-annotation-tool
2.项目&代码
项目:90+个Python数据科学实战项目
tags:[数据科学]
《90+ Data Science Projects You Can Try with Python》by Aman Kharwal
Link:https://python.plainenglish.io/85-data-science-projects-c03c8750599e
项目:中文医学 知识图谱 CMeKG 工具代码及模型
tags:[医疗,知识图谱]
GitHub:http://github.com/king-yyf/CMeKG_tools
3.博文&分享
博文:在生产中部署机器学习模型的考虑因素
tags:[部署,机器学习]
《Considerations for Deploying Machine Learning Models in Production》by Jules S. Damji, Michael Galarnyk
Link:http://towardsdatascience.com/considerations-for-deploying-machine-learning-models-in-production-89d38d96cc23
免费书籍:高效深度学习
tags:[深度学习]
《Efficient Deep Learning》by Gaurav Menghani, Naresh Singh
Link:https://efficientdlbook.com/
4.数据&资源
资源:Made With ML - 机器学习项目(代码/博客文章等)分享社区
tags:[机器学习]
“Made With ML - Share what you’ve made with ML”
Link:https://madewithml.com/
资源:《计量经济学》博士课程资料
tags:[金融,经济,课程资料]
‘Econometrics - Slides for the PhD level course in Econometrics at the Tinbergen Institute, Amsterdam’ by Stanislav Avdeev
GitHub:http://github.com/stnavdeev/econometrics
资源:中国支持远程办公的部分公司
tags:[资讯]
GitHub:http://github.com/LinuxSuRen/remote-jobs-in-china
资源:半导体创业公司大列表
tags:[资讯]
‘awesome-semiconductor-startups - List of awesome semiconductor startups’ by Andreas Olofsson
GitHub:http://github.com/aolofsson/awesome-semiconductor-startups
资源:2022机器学习就业市场
tags:[就业,资讯]
《All Roads Lead to Rome: The Machine Learning Job Market in 2022》by Eric Jang
Link:https://evjang.com/2022/04/25/rome.html
5.研究&论文
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
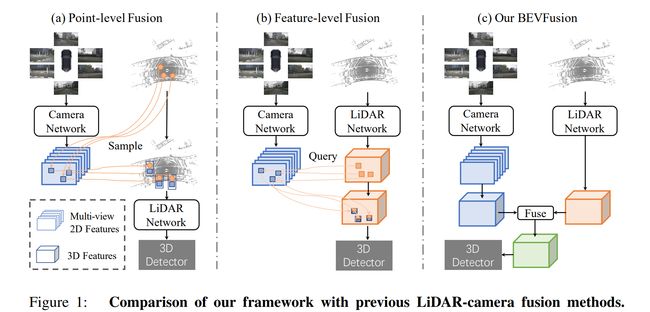
论文:BEVFusion: A Simple and Robust LiDAR-Camera Fusion Framework
论文标题:BEVFusion: A Simple and Robust LiDAR-Camera Fusion Framework
论文时间:27 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,Autonomous Driving,Object Detection,3D物体检测,自动驾驶,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.13790
代码实现:https://github.com/adlab-autodrive/bevfusion
论文作者:TingTing Liang, Hongwei Xie, Kaicheng Yu, Zhongyu Xia, Zhiwei Lin, Yongtao Wang, Tao Tang, Bing Wang, Zhi Tang
论文简介:Fusing the camera and LiDAR information has become a de-facto standard for 3D object detection tasks. / 融合相机和激光雷达信息已成为 3D 对象检测任务的事实标准。
论文摘要:Fusing the camera and LiDAR information has become a de-facto standard for 3D object detection tasks. Current methods rely on point clouds from the LiDAR sensor as queries to leverage the feature from the image space. However, people discover that this underlying assumption makes the current fusion framework infeasible to produce any prediction when there is a LiDAR malfunction, regardless of minor or major. This fundamentally limits the deployment capability to realistic autonomous driving scenarios. In contrast, we propose a surprisingly simple yet novel fusion framework, dubbed BEVFusion, whose camera stream does not depend on the input of LiDAR data, thus addressing the downside of previous methods. We empirically show that our framework surpasses the state-of-the-art methods under the normal training settings. Under the robustness training settings that simulate various LiDAR malfunctions, our framework significantly surpasses the state-of-the-art methods by 15.7% to 28.9% mAP. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to handle realistic LiDAR malfunction and can be deployed to realistic scenarios without any post-processing procedure. The code is available at https://github.com/ADLab-AutoDrive/BEVFusion .
融合相机和激光雷达信息已成为 3D 对象检测任务的事实标准。当前的方法依赖于来自 LiDAR 传感器的点云作为查询来利用图像空间中的特征。然而,人们发现,这种基本假设使得当前的融合框架无法在发生 LiDAR 故障时做出任何预测,无论是轻微还是严重。这从根本上将部署能力限制在现实的自动驾驶场景中。相比之下,我们提出了一个令人惊讶的简单而新颖的融合框架,称为 BEVFusion,其相机流不依赖于 LiDAR 数据的输入,从而解决了以前方法的缺点。我们凭经验表明,我们的框架在正常训练设置下超越了最先进的方法。在模拟各种 LiDAR 故障的鲁棒性训练设置下,我们的框架显着超过了最先进的方法 15.7% 到 28.9% 的 mAP。据我们所知,我们是第一个处理现实 LiDAR 故障的人,并且可以在没有任何后处理程序的情况下部署到现实场景中。该代码可在 https://github.com/ADLab-AutoDrive/BEVFusion 获得。
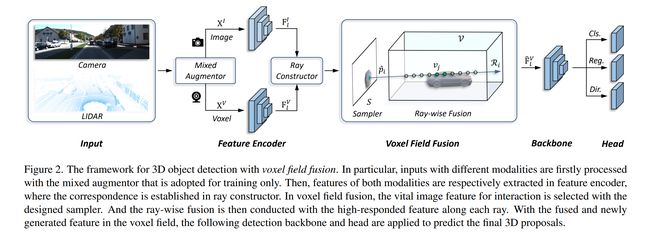
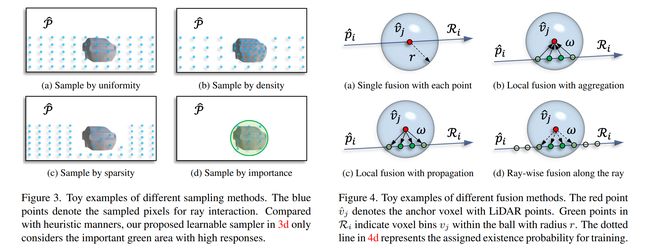
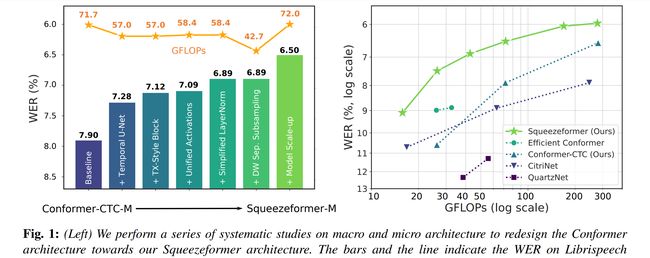
论文:Voxel Field Fusion for 3D Object Detection
论文标题:Voxel Field Fusion for 3D Object Detection
论文时间:31 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,Data Augmentation,Object Detection,3D物体检测,数据增强,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15938
代码实现:https://github.com/dvlab-research/vff
论文作者:Yanwei Li, Xiaojuan Qi, Yukang Chen, LiWei Wang, Zeming Li, Jian Sun, Jiaya Jia
论文简介:In this work, we present a conceptually simple yet effective framework for cross-modality 3D object detection, named voxel field fusion. / 在这项工作中,我们提出了一个概念上简单但有效的跨模态 3D 对象检测框架,称为体素场融合。
论文摘要:In this work, we present a conceptually simple yet effective framework for cross-modality 3D object detection, named voxel field fusion. The proposed approach aims to maintain cross-modality consistency by representing and fusing augmented image features as a ray in the voxel field. To this end, the learnable sampler is first designed to sample vital features from the image plane that are projected to the voxel grid in a point-to-ray manner, which maintains the consistency in feature representation with spatial context. In addition, ray-wise fusion is conducted to fuse features with the supplemental context in the constructed voxel field. We further develop mixed augmentor to align feature-variant transformations, which bridges the modality gap in data augmentation. The proposed framework is demonstrated to achieve consistent gains in various benchmarks and outperforms previous fusion-based methods on KITTI and nuScenes datasets. Code is made available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/VFF .
在这项工作中,我们提出了一个概念上简单但有效的跨模态 3D 对象检测框架,称为体素场融合。所提出的方法旨在通过将增强图像特征表示和融合为体素场中的射线来保持跨模态一致性。为此,可学习采样器首先设计用于从图像平面采样以点对射线方式投影到体素网格的重要特征,从而保持特征表示与空间上下文的一致性。此外,进行射线融合以将特征与构建的体素场中的补充上下文融合。我们进一步开发了混合增强器来对齐特征变体转换,从而弥合了数据增强中的模态差距。所提出的框架被证明可以在各种基准测试中实现一致的收益,并且优于以前在 KITTI 和 nuScenes 数据集上基于融合的方法。代码可在 https://github.com/dvlab-research/VFF 获得。
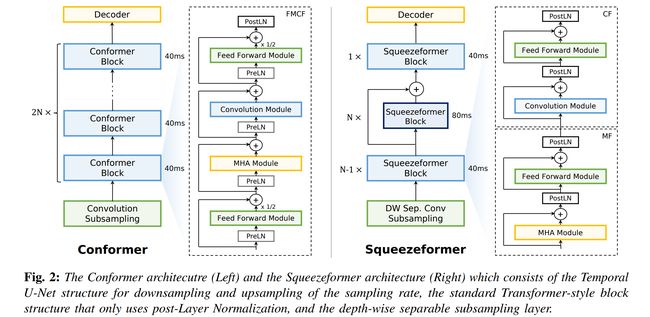
论文:Squeezeformer: An Efficient Transformer for Automatic Speech Recognition
论文标题:Squeezeformer: An Efficient Transformer for Automatic Speech Recognition
论文时间:2 Jun 2022
所属领域:Speech/语音
对应任务:Automatic Speech Recognition,Speech Recognition,自动语音识别,语音识别
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00888
代码实现:https://github.com/kssteven418/squeezeformer
论文作者:Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Albert Shaw, Nicholas Lee, Karttikeya Mangalam, Jitendra Malik, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer
论文简介:After reexamining the design choices for both the macro and micro-architecture of Conformer, we propose the Squeezeformer model, which consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art ASR models under the same training schemes. / 在重新检查了 Conformer 的宏观和微观架构的设计选择后,我们提出了 Squeezeformer 模型,该模型在相同的训练方案下始终优于最先进的 ASR 模型。
论文摘要:The recently proposed Conformer model has become the de facto backbone model for various downstream speech tasks based on its hybrid attention-convolution architecture that captures both local and global features. However, through a series of systematic studies, we find that the Conformer architecture’s design choices are not optimal. After reexamining the design choices for both the macro and micro-architecture of Conformer, we propose the Squeezeformer model, which consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art ASR models under the same training schemes. In particular, for the macro-architecture, Squeezeformer incorporates (i) the Temporal U-Net structure, which reduces the cost of the multi-head attention modules on long sequences, and (ii) a simpler block structure of feed-forward module, followed up by multi-head attention or convolution modules, instead of the Macaron structure proposed in Conformer. Furthermore, for the micro-architecture, Squeezeformer (i) simplifies the activations in the convolutional block, (ii) removes redundant Layer Normalization operations, and (iii) incorporates an efficient depth-wise downsampling layer to efficiently sub-sample the input signal. Squeezeformer achieves state-of-the-art results of 7.5%, 6.5%, and 6.0% word-error-rate on Librispeech test-other without external language models. This is 3.1%, 1.4%, and 0.6% better than Conformer-CTC with the same number of FLOPs. Our code is open-sourced and available online.
最近提出的 Conformer 模型已成为各种下游语音任务的事实上的主干模型,基于其捕获局部和全局特征的混合注意力卷积架构。然而,通过一系列系统的研究,我们发现Conformer架构的设计选择并不是最优的。在重新检查了 Conformer 的宏观和微观架构的设计选择后,我们提出了 Squeezeformer 模型,该模型在相同的训练方案下始终优于最先进的 ASR 模型。特别是,对于宏架构,Squeezeformer 结合了(i)Temporal U-Net 结构,这降低了长序列上的多头注意力模块的成本,以及(ii)前馈模块的更简单的块结构,紧随其后的是多头注意力或卷积模块,而不是 Conformer 中提出的 Macaron 结构。此外,对于微架构,Squeezeformer (i) 简化了卷积块中的激活,(ii) 删除了冗余的层归一化操作,以及 (iii) 结合了有效的深度下采样层以有效地对输入信号进行子采样。在没有外部语言模型的情况下,Squeezeformer 在 Librispeech test-other 上实现了 7.5%、6.5% 和 6.0% word-error-rate的前沿一流结果。这比具有相同 FLOP 数量的 Conformer-CTC 好 3.1%、1.4% 和 0.6%。我们的代码是开源的,可以在github获取。
论文:Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation
论文标题:Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation
论文时间:24 Feb 2021
所属领域:Playing Games/游戏
对应任务:Image Generation,Text to image generation,Text-to-Image Generation,Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation,图像生成,文本到图像生成,文本到图像生成,零样本文本到图像生成
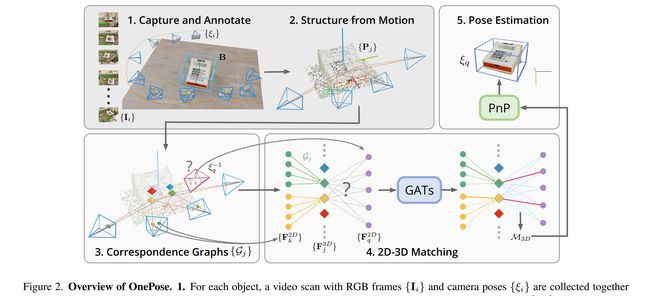
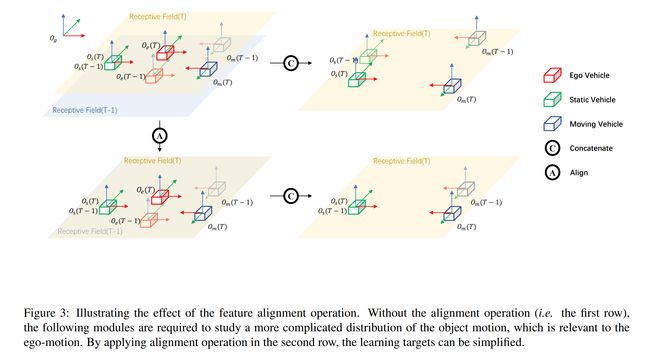
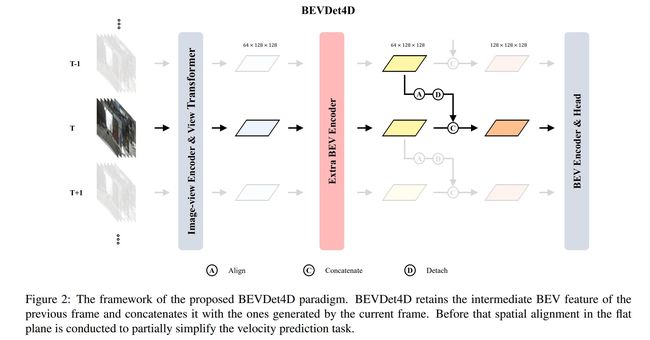
论文地址: 代码实现:https://github.com/openai/DALL-E , https://github.com/lucidrains/DALLE-pytorch , https://github.com/borisdayma/dalle-mini , https://github.com/kakaobrain/rq-vae-transformer , https://github.com/xyzforever/bevt 论文作者:Aditya Ramesh, Mikhail Pavlov, Gabriel Goh, Scott Gray, Chelsea Voss, Alec Radford, Mark Chen, Ilya Sutskever 论文简介:Text-to-image generation has traditionally focused on finding better modeling assumptions for training on a fixed dataset. / 文本到图像的生成传统上专注于为固定数据集的训练寻找更好的建模假设。 论文摘要:Text-to-image generation has traditionally focused on finding better modeling assumptions for training on a fixed dataset. These assumptions might involve complex architectures, auxiliary losses, or side information such as object part labels or segmentation masks supplied during training. We describe a simple approach for this task based on a transformer that autoregressively models the text and image tokens as a single stream of data. With sufficient data and scale, our approach is competitive with previous domain-specific models when evaluated in a zero-shot fashion. 文本到图像的生成传统上专注于为固定数据集的训练寻找更好的建模假设。这些假设可能涉及复杂的架构、辅助损失或辅助信息,例如训练期间提供的对象部分标签或分割掩码。我们描述了一种基于转换器的简单方法,该转换器将文本和图像标记自回归建模为单个数据流。凭借足够的数据和规模,我们的方法在以零样本方式评估时与以前的特定领域模型具有竞争力。 论文标题:OnePose: One-Shot Object Pose Estimation without CAD Models 论文时间:24 May 2022 所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉 对应任务:6D Pose Estimation,Graph Attention,Pose Estimation,Visual Localization,6D姿势估计,图形注意,姿势估计,视觉定位 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12257 代码实现:https://github.com/zju3dv/OnePose 论文作者:Jiaming Sun, ZiHao Wang, Siyu Zhang, Xingyi He, Hongcheng Zhao, Guofeng Zhang, Xiaowei Zhou 论文简介:We propose a new method named OnePose for object pose estimation. / 我们提出了一种名为 OnePose 的新方法来进行物体姿态估计。 论文摘要:We propose a new method named OnePose for object pose estimation. Unlike existing instance-level or category-level methods, OnePose does not rely on CAD models and can handle objects in arbitrary categories without instance- or category-specific network training. OnePose draws the idea from visual localization and only requires a simple RGB video scan of the object to build a sparse SfM model of the object. Then, this model is registered to new query images with a generic feature matching network. To mitigate the slow runtime of existing visual localization methods, we propose a new graph attention network that directly matches 2D interest points in the query image with the 3D points in the SfM model, resulting in efficient and robust pose estimation. Combined with a feature-based pose tracker, OnePose is able to stably detect and track 6D poses of everyday household objects in real-time. We also collected a large-scale dataset that consists of 450 sequences of 150 objects. 我们提出了一种名为 OnePose 的新方法来进行对象姿态估计。与现有的实例级或类别级方法不同,OnePose 不依赖 CAD 模型,并且可以处理任意类别中的对象,而无需实例或类别特定的网络训练。 OnePose 从视觉定位中汲取思想,只需要对对象进行简单的 RGB 视频扫描,即可构建对象的稀疏 SfM 模型。然后,将该模型注册到具有通用特征匹配网络的新查询图像。为了缓解现有视觉定位方法的缓慢运行时间,我们提出了一种新的图注意力网络,该网络直接将查询图像中的 2D 兴趣点与 SfM 模型中的 3D 点进行匹配,从而实现高效且稳健的姿态估计。结合基于特征的姿势跟踪器,OnePose 能够实时稳定地检测和跟踪日常家居对象的 6D 姿势。我们还收集了一个包含 150 个对象的 450 个序列的大规模数据集。 论文标题:Improved Vector Quantized Diffusion Models 论文时间:31 May 2022 所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉 对应任务:Denoising,Image Generation,去噪,图像生成 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.16007 代码实现:https://github.com/microsoft/vq-diffusion 论文作者:Zhicong Tang, Shuyang Gu, Jianmin Bao, Dong Chen, Fang Wen 论文简介:When trained on ImageNet, we dramatically improve the FID score from 11. 89 to 4. 83, demonstrating the superiority of our proposed techniques. / 在 ImageNet 上训练时,我们将 FID 分数从 11. 89 显着提高到 4. 83,证明了我们提出的技术的优越性。 论文摘要:Vector quantized diffusion (VQ-Diffusion) is a powerful generative model for text-to-image synthesis, but sometimes can still generate low-quality samples or weakly correlated images with text input. We find these issues are mainly due to the flawed sampling strategy. In this paper, we propose two important techniques to further improve the sample quality of VQ-Diffusion. 1) We explore classifier-free guidance sampling for discrete denoising diffusion model and propose a more general and effective implementation of classifier-free guidance. 2) We present a high-quality inference strategy to alleviate the joint distribution issue in VQ-Diffusion. Finally, we conduct experiments on various datasets to validate their effectiveness and show that the improved VQ-Diffusion suppresses the vanilla version by large margins. We achieve an 8.44 FID score on MSCOCO, surpassing VQ-Diffusion by 5.42 FID score. When trained on ImageNet, we dramatically improve the FID score from 11.89 to 4.83, demonstrating the superiority of our proposed techniques. 矢量量化扩散(VQ-Diffusion)是一种用于文本到图像合成的强大生成模型,但有时仍然可能生成低质量样本或与文本输入相关的弱图像。我们发现这些问题主要是由于有缺陷的抽样策略造成的。在本文中,我们提出了两种重要的技术来进一步提高 VQ-Diffusion 的样本质量。 1)我们探索了离散去噪扩散模型的无分类指导抽样,并提出了一种更通用、更有效的无分类指导实现。 2)我们提出了一种高质量的推理策略来缓解 VQ-Diffusion 中的联合分布问题。最后,我们对各种数据集进行了实验以验证它们的有效性,并表明改进的 VQ-Diffusion 大大抑制了原始版本的问题。我们在 MSCOCO 上获得了 8.44 FID 分数,超过了 VQ-Diffusion 5.42 FID 分数。在 ImageNet 上训练时,我们将 FID 分数从 11.89 显着提高到 4.83,证明了我们提出的技术的优越性。 论文标题:Optimizing Relevance Maps of Vision Transformers Improves Robustness 论文时间:2 Jun 2022 所属领域:计算机视觉 对应任务:图像识别,模型理解,图像分类 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01161 代码实现:https://github.com/hila-chefer/robustvit 论文作者:Hila Chefer, Idan Schwartz, Lior Wolf 论文简介:It has been observed that visual classification models often rely mostly on the image background, neglecting the foreground, which hurts their robustness to distribution changes. / 据观察,视觉分类模型通常主要依赖于图像背景,而忽略了前景,这损害了它们对分布变化的鲁棒性。 论文摘要:It has been observed that visual classification models often rely mostly on the image background, neglecting the foreground, which hurts their robustness to distribution changes. To alleviate this shortcoming, we propose to monitor the model’s relevancy signal and manipulate it such that the model is focused on the foreground object. This is done as a finetuning step, involving relatively few samples consisting of pairs of images and their associated foreground masks. Specifically, we encourage the model’s relevancy map (i) to assign lower relevance to background regions, (ii) to consider as much information as possible from the foreground, and (iii) we encourage the decisions to have high confidence. When applied to Vision Transformer (ViT) models, a marked improvement in robustness to domain shifts is observed. Moreover, the foreground masks can be obtained automatically, from a self-supervised variant of the ViT model itself; therefore no additional supervision is required. 据观察,视觉分类模型通常主要依赖于图像背景,而忽略了前景,这损害了它们对分布变化的鲁棒性。为了缓解这个缺点,我们建议监控模型的相关性信号并对其进行操作,使模型专注于前景对象。这是作为微调步骤完成的,涉及相对较少的样本,这些样本由成对的图像及其相关的前景蒙版组成。具体来说,我们鼓励模型的相关性图 (i) 将较低的相关性分配给背景区域,(ii) 考虑尽可能多的来自前景的信息,以及 (iii) 我们鼓励决策具有高置信度。当应用于 Vision Transformer (ViT) 模型时,可以观察到域转移的鲁棒性显着提高。此外,可以从 ViT 模型本身的自我监督变体中自动获得前景蒙版;因此不需要额外的监督。 论文标题:Group R-CNN for Weakly Semi-supervised Object Detection with Points 论文时间:12 May 2022 所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉 对应任务:Object Detection,Representation Learning,Semi-Supervised Object Detection,目标检测,表示学习,半监督目标检测,物体检测 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05920 代码实现:https://github.com/jshilong/grouprcnn 论文作者:Shilong Zhang, Zhuoran Yu, Liyang Liu, Xinjiang Wang, Aojun Zhou, Kai Chen 论文简介:The core of this task is to train a point-to-box regressor on well-labeled images that can be used to predict credible bounding boxes for each point annotation. / 这项任务的核心是在标记良好的图像上训练一个点到框回归器,该回归器可用于预测每个点注释的可信边界框。 论文摘要:We study the problem of weakly semi-supervised object detection with points (WSSOD-P), where the training data is combined by a small set of fully annotated images with bounding boxes and a large set of weakly-labeled images with only a single point annotated for each instance. The core of this task is to train a point-to-box regressor on well-labeled images that can be used to predict credible bounding boxes for each point annotation. We challenge the prior belief that existing CNN-based detectors are not compatible with this task. Based on the classic R-CNN architecture, we propose an effective point-to-box regressor: Group R-CNN. Group R-CNN first uses instance-level proposal grouping to generate a group of proposals for each point annotation and thus can obtain a high recall rate. To better distinguish different instances and improve precision, we propose instance-level proposal assignment to replace the vanilla assignment strategy adopted in the original R-CNN methods. As naive instance-level assignment brings converging difficulty, we propose instance-aware representation learning which consists of instance-aware feature enhancement and instance-aware parameter generation to overcome this issue. Comprehensive experiments on the MS-COCO benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Specifically, Group R-CNN significantly outperforms the prior method Point DETR by 3.9 mAP with 5% well-labeled images, which is the most challenging scenario. The source code can be found at https://github.com/jshilong/GroupRCNN 我们研究了带点的弱半监督目标检测(WSSOD-P)问题,其中训练数据由一小部分带边界框的完全注释图像和一大组仅带边界框的弱标记图像组合而成。为每个实例注释一个点。该任务的核心是在标记良好的图像上训练一个点到框回归器,该回归器可用于预测每个点注释的可信边界框。我们挑战了现有的基于 CNN 的检测器与该任务不兼容的先验信念。基于经典的 R-CNN 架构,我们提出了一种有效的点到框回归器:Group R-CNN。 Group R-CNN首先使用实例级proposal grouping为每个点注释生成一组proposal,从而可以获得较高的召回率。为了更好地区分不同的实例并提高精度,我们提出实例级提案分配来代替原始 R-CNN 方法中采用的普通分配策略。由于原始版本的实例级分配带来了收敛困难,我们提出了实例感知表示学习,它包括实例感知特征增强和实例感知参数生成来克服这个问题。 MS-COCO 基准的综合实验证明了我们方法的有效性。具体来说,在最具挑战性的场景下,Group R-CNN 以3.9 mAP,5% 的良好标记图像显著优于先前的方法 Point DETR。源代码可以在https://github.com/jshilong/GroupRCNN找到 论文标题:Learning to Untangle Genome Assembly with Graph Convolutional Networks 论文时间:1 Jun 2022 所属领域:生物科技,基因科技 对应任务:图神经网络 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00668 代码实现:https://github.com/lvrcek/gnnome-assembly 论文作者:Lovro Vrček, Xavier Bresson, Thomas Laurent, Martin Schmitz, Mile Šikić 论文简介:In this work, we explore a different approach to the central part of the genome assembly task that consists of untangling a large assembly graph from which a genomic sequence needs to be reconstructed. / 在这项工作中,我们探索了一种不同的方法来处理基因组组装任务的核心部分,该任务包括解开需要重建基因组序列的大型组装图。 论文摘要:A quest to determine the complete sequence of a human DNA from telomere to telomere started three decades ago and was finally completed in 2021. This accomplishment was a result of a tremendous effort of numerous experts who engineered various tools and performed laborious manual inspection to achieve the first gapless genome sequence. However, such method can hardly be used as a general approach to assemble different genomes, especially when the assembly speed is critical given the large amount of data. In this work, we explore a different approach to the central part of the genome assembly task that consists of untangling a large assembly graph from which a genomic sequence needs to be reconstructed. Our main motivation is to reduce human-engineered heuristics and use deep learning to develop more generalizable reconstruction techniques. Precisely, we introduce a new learning framework to train a graph convolutional network to resolve assembly graphs by finding a correct path through them. The training is supervised with a dataset generated from the resolved CHM13 human sequence and tested on assembly graphs built using real human PacBio HiFi reads. Experimental results show that a model, trained on simulated graphs generated solely from a single chromosome, is able to remarkably resolve all other chromosomes. Moreover, the model outperforms hand-crafted heuristics from a state-of-the-art \textit{de novo} assembler on the same graphs. Reconstructed chromosomes with graph networks are more accurate on nucleotide level, report lower number of contigs, higher genome reconstructed fraction and NG50/NGA50 assessment metrics. 确定人类 DNA 从端粒到端粒的完整序列的探索始于 30 年前,最终于 2021 年完成。这一成就是众多专家付出巨大努力的结果,他们设计了各种工具并进行了费力的人工检查实现第一个无间隙基因组序列。然而,这种方法几乎不能用作组装不同基因组的通用方法,尤其是当组装速度对于大量数据至关重要时。在这项工作中,我们探索了一种不同的方法来处理基因组组装任务的核心部分,包括解开需要重建基因组序列的大型组装图。我们的主要动机是减少人工设计的启发式方法,并使用深度学习来开发更通用的重建技术。准确地说,我们引入了一个新的学习框架来训练图卷积网络,通过找到正确的路径来解析装配图。训练使用从解析的 CHM13 人类序列生成的数据集进行监督,并在使用真实人类 PacBio HiFi 读取构建的装配图上进行测试。实验结果表明,在仅从单个染色体生成的模拟图上训练的模型能够显著解析所有其他染色体。此外,该模型在相同的图上优于来自最先进的de novo汇编器的手工启发式算法。使用图形网络重建的染色体在核苷酸水平上更准确,报告的重叠群数量更少,基因组重建分数和 NG50/NGA50 评估指标更高。 论文标题:Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training 论文时间:28 Oct 2021 所属领域:深度学习 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.14883 代码实现:https://github.com/hpcaitech/colossalai 论文作者:Zhengda Bian, Hongxin Liu, Boxiang Wang, Haichen Huang, Yongbin Li, Chuanrui Wang, Fan Cui, Yang You 论文简介:The Transformer architecture has improved the performance of deep learning models in domains such as Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. / Transformer 架构提高了深度学习模型在计算机视觉和自然语言处理等领域的性能。 论文摘要:The Transformer architecture has improved the performance of deep learning models in domains such as Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. Together with better performance come larger model sizes. This imposes challenges to the memory wall of the current accelerator hardware such as GPU. It is never ideal to train large models such as Vision Transformer, BERT, and GPT on a single GPU or a single machine. There is an urgent demand to train models in a distributed environment. However, distributed training, especially model parallelism, often requires domain expertise in computer systems and architecture. It remains a challenge for AI researchers to implement complex distributed training solutions for their models. In this paper, we introduce Colossal-AI, which is a unified parallel training system designed to seamlessly integrate different paradigms of parallelization techniques including data parallelism, pipeline parallelism, multiple tensor parallelism, and sequence parallelism. Colossal-AI aims to support the AI community to write distributed models in the same way as how they write models normally. This allows them to focus on developing the model architecture and separates the concerns of distributed training from the development process. The documentations can be found at [https://www.colossalai.org](https://www.colossalai.org) and the source code can be found at https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI. Transformer 架构提高了深度学习模型在计算机视觉和自然语言处理等领域的性能。伴随着更好的性能而来的是更大的模型尺寸。这对当前 GPU 等加速器硬件的内存墙提出了挑战。在单个 GPU 或单个机器上训练 Vision Transformer、BERT 和 GPT 等大型模型从来都不是理想的选择。迫切需要在分布式环境中训练模型。然而,分布式训练,尤其是模型并行性,通常需要计算机系统和架构方面的领域专业知识。人工智能研究人员为他们的模型实施复杂的分布式训练解决方案仍然是一个挑战。在本文中,我们介绍 Colossal-AI,它是一个统一的并行训练系统,旨在无缝集成不同范式的并行化技术,包括数据并行、管道并行、多张量并行和序列并行。 Colossal-AI 旨在支持 AI 社区以与他们通常编写模型的方式相同的方式编写分布式模型。这使他们能够专注于开发模型架构,并将分布式训练的关注点与开发过程分开。文档可以在 https://www.colossalai.org 找到,源代码可以在 [https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI]( https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI)。 论文标题:BEVDet4D: Exploit Temporal Cues in Multi-camera 3D Object Detection 论文时间:31 Mar 2022 所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉 对应任务:3D Object Detection,Object Detection,3D物体检测,物体检测 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.17054 代码实现:https://github.com/HuangJunJie2017/BEVDet 论文作者:JunJie Huang, Guan Huang 论文简介:Single frame data contains finite information which limits the performance of the existing vision-based multi-camera 3D object detection paradigms. / 单帧数据包含有限的信息,这限制了现有基于视觉的多相机 3D 对象检测范例的性能。 论文摘要:Single frame data contains finite information which limits the performance of the existing vision-based multi-camera 3D object detection paradigms. For fundamentally pushing the performance boundary in this area, a novel paradigm dubbed BEVDet4D is proposed to lift the scalable BEVDet paradigm from the spatial-only 3D space to the spatial-temporal 4D space. We upgrade the naive BEVDet framework with a few modifications just for fusing the feature from the previous frame with the corresponding one in the current frame. In this way, with negligible additional computing budget, we enable BEVDet4D to access the temporal cues by querying and comparing the two candidate features. Beyond this, we simplify the task of velocity prediction by removing the factors of ego-motion and time in the learning target. As a result, BEVDet4D with robust generalization performance reduces the velocity error by up to -62.9%. This makes the vision-based methods, for the first time, become comparable with those relied on LiDAR or radar in this aspect. On challenge benchmark nuScenes, we report a new record of 54.5% NDS with the high-performance configuration dubbed BEVDet4D-Base, which surpasses the previous leading method BEVDet-Base by +7.3% NDS. 单帧数据包含有限的信息,限制了现有的基于视觉的多相机 3D 对象检测范例的性能。为了从根本上推动该领域的性能边界,提出了一种名为 BEVDet4D 的新范式,将可扩展的 BEVDet 范式从仅空间的 3D 空间提升到时空 4D 空间。我们升级了朴素的 BEVDet 框架,并进行了一些修改,只是为了将前一帧的特征与当前帧中的相应特征融合。通过这种方式,在可忽略的额外计算预算的情况下,我们使 BEVDet4D 能够通过查询和比较两个候选特征来访问时间线索。除此之外,我们通过去除学习目标中的自我运动和时间因素来简化速度预测的任务。结果,具有强大泛化性能的 BEVDet4D 将速度误差降低了高达 -62.9%。这使得基于视觉的方法在这方面第一次可以与依赖激光雷达或雷达的方法相媲美。在挑战基准 nuScenes 上,我们使用名为 BEVDet4D-Base 的高性能配置报告了 54.5% NDS 的新纪录,超过了之前的领先方法 BEVDet-Base +7.3% NDS。 我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
论文:OnePose: One-Shot Object Pose Estimation without CAD Models
论文:Improved Vector Quantized Diffusion Models
论文:Optimizing Relevance Maps of Vision Transformers Improves Robustness
论文:Group R-CNN for Weakly Semi-supervised Object Detection with Points
论文:Learning to Untangle Genome Assembly with Graph Convolutional Networks
论文:Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training
论文:BEVDet4D: Exploit Temporal Cues in Multi-camera 3D Object Detection