LeetCode | 图
文章目录
-
-
-
- 785. Is Graph Bipartite? (判断二分图)
- 210. Course Schedule II (课程表II)
- 1059. All Paths from Source Lead to Destination (Medium)
- 1135. Connecting Cities With Minimum Cost 最小生成树
-
-
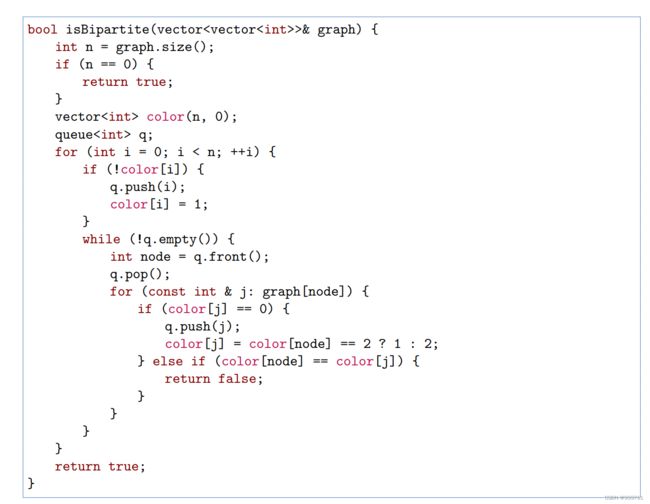
785. Is Graph Bipartite? (判断二分图)
-
思路:染色算法
我们用 0 表示未检查的节点,用 1 和 2 表示两种不同的颜色。由于二分图的性质,连边的两个点必然染不同的颜色,所以从0开始,给他染颜色1,然后给邻点染颜色2,在从邻点遍历,染不同的染色。如果出现邻点与这个点有相同颜色,就不是二分图,false。

-
深度搜索
注意:图中可能含有多个连通域,所以我们需要判断是否存在顶点未被访问,若存在则从它开始再进行一轮 dfs 染色。
具体:在cur顶点时,遍历所有邻点,如果邻点颜色与cur相同,矛盾返回false。如果邻点未被染色,则把这个点染成与cur不同的,再遍历这个邻点的邻点。
注意,需要遍历完所有cur的邻点才能得出cur与他邻点是否不同色的结论,即我们需要引入一个flag变量,如果仅仅找到一个未染色点,然后判断周围点的颜色,再看返回值,这个返回值作为Cur这个节点的返回值,这样是过于简单的,因为可能还存在其他未染色节点。
class Solution {
public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) {
ArrayList<ArrayList> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visited = new int[graph.length];
boolean ans = true;
//注意:可能有多个连通分支,对每个连通分支遍历是否为二分图
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
visited[i] = 1;
ans = ans &&dfs(graph,visited,i);
}
}
return ans;
}
boolean dfs(int[][] graph, int[] visted, int cur){
int c = visted[cur];
boolean flag = true;
for(int j=0; j<graph[cur].length;j++){
if(visted[graph[cur][j]]==c) return false;
if(visted[graph[cur][j]]==0) {
visted[graph[cur][j]]= c==1? 2:1;
flag &= dfs(graph,visted,graph[cur][j]);
}
}
return flag;
}
}
- 广度优先搜索
也就是先搜0这个点的所有邻点,放入栈中,把邻点染成与0这个点不同的颜色,然后再遍历0的邻点的邻点,依次类推
210. Course Schedule II (课程表II)
- 具体思路
首先,建立有向图,[a,b]表示修a前要先修b,这时我们要让b指向a,把b加入a的列表中。拿prerequisites = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]举例,我们建立的list列表edges就为[ [ ], [0], [0], [1,2]],表示修0的时候不用修别的,修1的时候要修0,修2的时候要修0,修3的时候要修1和2
接着,我们建立indeg表示每门课的先修课程数目(即入度),则indeg=[0,1,1,2]
其次,我们找到入度为0的点课0,把他加入队列,然后遍历有向图edges,把有先修0的课程入度减1,如果这时候有课程入度变为0,即说明前面的已经先修完了,所以可以加入队列,然后再遍历先修课为这门新入度为0的课的,入度再减去一
class Solution {
// 存储有向图
List<List<Integer>> edges;
// 存储每个节点的入度
int[] indeg;
// 存储答案
int[] result;
// 答案下标
int index;
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
edges = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
edges.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
indeg = new int[numCourses];
result = new int[numCourses];
index = 0;
for (int[] info : prerequisites) {
edges.get(info[1]).add(info[0]);
++indeg[info[0]];
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// 将所有入度为 0 的节点放入队列中
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if (indeg[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 从队首取出一个节点
int u = queue.poll();
// 放入答案中
result[index++] = u;
for (int v: edges.get(u)) {
--indeg[v];
// 如果相邻节点 v 的入度为 0,就可以选 v 对应的课程了
if (indeg[v] == 0) {
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
if (index != numCourses) {
return new int[0];
}
return result;
}
}
Python版本:
class Solution(object):
def findOrder(self, numCourses, prerequisites):
dic = {}
inp = {}
res = []
s = set()
# 每个点对应的先修map
for i in range(len(prerequisites)):
edge = prerequisites[i]
if edge[0] not in dic.keys():
dic[edge[0]] = [edge[1]]
else:
dic[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
for key in dic.keys():
inp[key] = len(dic[key])
# 队列遍历
stack = []
for i in range(numCourses):
if i not in dic.keys():
stack.append(i)
while(len(stack)>0):
cur = stack.pop(0)
res.append(cur)
s.add(cur)
for key in dic.keys():
if cur in dic[key]:
inp[key] -= 1
if inp[key]==0 and key not in s:
s.add(key)
stack.append(key)
if len(res)!=numCourses:
return []
else:
return res
1059. All Paths from Source Lead to Destination (Medium)
判断是否所有路径都能从source到Destination ,是的话返回true
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:false
说明:节点 1 和节点 2 都可以到达,但也会卡在那里。
注意判断是否陷入了环路。
具体做法:
-
首先,建立vistied列表,记录是否遍历过。并建立m表,记录每个点指向的下一个点是什么。例如edges = [[0,1],[0,2]],则
m=[ [1,2], [ ], [ ] ],如果destination 还会指向下一个点,则返回False -
接着,dfs遍历。遍历到cur时,如果cur没有下一个点,且cur不是终点则返回false;否则,for循环遍历cur的下一个点,如果下个点访问过了,则返回false(因为有环),没遍历过,则标记为遍历了,然后看下一个点能否走到终点。最后再回溯,再遍历另外的下一个点
class Solution {
public:
bool leadsToDestination(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
vector<vector<int>> m(n);
for(auto& e : edges)
m[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
if(!m[destination].empty())
return false;//终点后面还有路径
return dfs(m,visited,source,destination);
}
bool dfs(vector<vector<int>>& m, vector<bool>& visited, int cur, int destination)
{
if(m[cur].size()==0 && cur != destination)
return false;//到达一个终点,但不是目标点
for(int next : m[cur])//往下走
{
if(visited[next])//访问过了
return false;//有环
visited[next] = true;//访问
if(!dfs(m, visited, next, destination))
return false;
visited[next] = false;//回溯
}
return true;
}
};
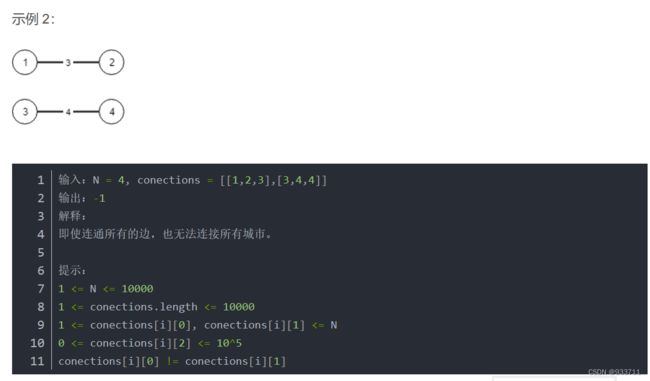
1135. Connecting Cities With Minimum Cost 最小生成树
每个城市之间的连接有费用,现在返回连通所有城市的最小费用,如果非连通图,可以返回-1
有两种算法,一个是Kruskal,一个是Prim
- Kruskal算法
将边的权值排序,小的先遍历,用并查集检查两个顶点是否合并了,没有合并则将该边加入生成树
PS:也可以使用优先队列实现(相当于排序)
具体做法:
class Solution {
public:
int find(int x) //不断向上找,直到找到下标和元素相同的点;不理解背后原因的,可以学习下树的数组表示发。
{
while(x != p[x]) x = p[x];
return x;
}
int minimumCost(int N, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
int ans = 0;
int point_num = 0;
//sort重定义比较是重载的<号,为真则不交换,否则交换。
//基于上述原则,对cmp返回对应的true or false
auto cmp = [](vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){return a[2] < b[2];};
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
p.push_back(i);
}
sort(connections.begin(), connections.end(), cmp);//按cost值排序,采用贪心算法
for (auto conn : connections) {
int px = find(conn[0]),py = find(conn[1]);
if(px != py) { //如果该边所在的两个节点不在同一个集合
p[px] = py; //合并集合
ans += conn[2];
point_num++;
//对于无向图的话,至少需要n-1条边可以使得图是联通的;
//如果对于有向图的话,至少需要n条边才可以使得图是联通的
if(point_num == N - 1){
return ans;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private:
vector<int> p; //集合关系表,用一个数组来描述N个节点的集合关系;等同于树的数组表示方法。
};
- prim算法
prim算法核心思想
1)以某一个点为起点(通常为数组的第一个点)。以“点”为参照物,从该点所在“集合”的边当中依次选择cost最小的边去连接一个“新的”节点。
2)在一个结合新(要注意是新的,否则会死循环)加入一个节点后,将会扩大原有的集合,而该集合所连接的边和点都会发生变化。针对这类问题,选择小顶堆作为数据结构。
3)当该集合中有N个点时,所有的点都已经被访问过了。
class Solution {
public:
int minimumCost(int N, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
//重载priority_queue的比较函数,priority_queue默认是大顶堆,重载的是<号
//默认情况下如果左边参数大于右边参数,则说明左边形参的优先级低于右边形参,会将左边的放到后面
//构建小顶堆时,我们实现一个>号的判断即可,大于返回true,优先级低,被放到后面,则小的会放前面
struct cmp {
bool operator () (const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b) {
return a[2] > b[2];
}
};
int selected = 0, ans = 0;
//构建点和cost的集合关系,本质是个三维数组,第一维是起点,二维是<终点、开销>
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> edgs(N+1,vector<pair<int,int>>());
//构建小顶堆,将最合适的点放在最前面
priority_queue<vector<int>,vector<vector<int>>,cmp> pq;
vector<int> visit(N+1, 0);
//初始化边集合
for(auto re : connections){
edgs[re[0]].push_back(make_pair(re[1],re[2]));
edgs[re[1]].push_back(make_pair(re[0],re[2]));
}
//本次选择1为起点,如果1点没有变,则1永远是孤岛。本次选择1为起点
if(edgs[1].size() == 0){
return -1;
}
selected = 1;
visit[1] = true;
//起点1所在的边放入小顶堆
for(int i = 0;i < edgs[1].size(); ++i){
pq.push(vector<int>({1,edgs[1][i].first,edgs[1][i].second}));
}
//遍历小顶堆
while(!pq.empty()) {
auto curr = pq.top();pq.pop();
if(!visit[curr[1]]){
visit[curr[1]] = true;
ans += curr[2];
//依次取出cost最小的边所在的点加入集合
for(auto e : edgs[curr[1]]){
pq.push(vector<int>({curr[1],e.first,e.second}));
}
selected++;
if(selected == N){ //如果N个节点都在时,则结束循环
return ans;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};