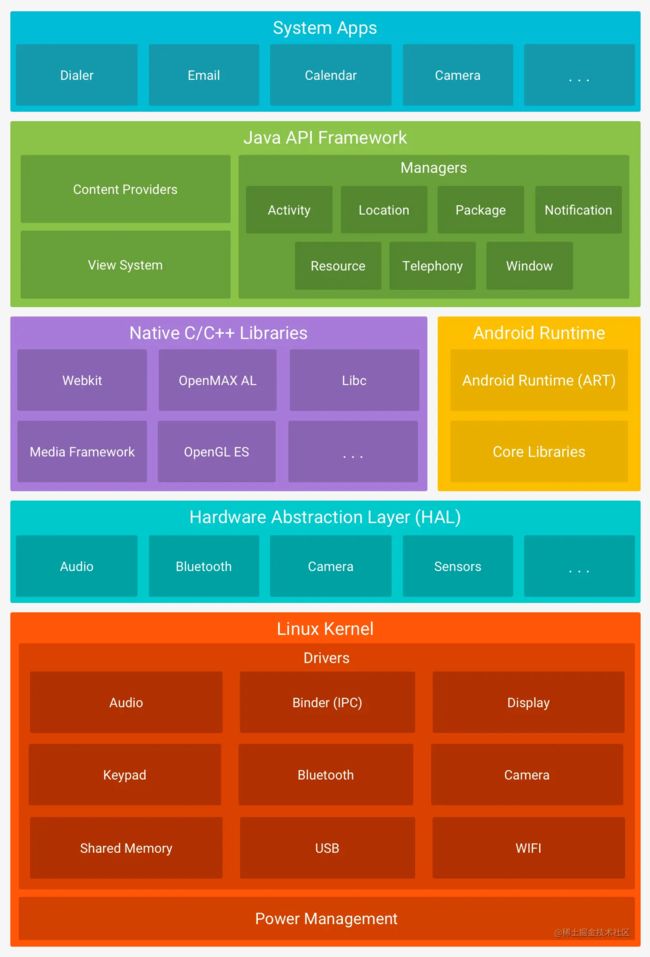
源码解读之 Android App应用是如何启动的?
前言
作为多年的 Android 开发,写了不少应用,但是一个App到底是怎么启动起来的?你要说桌面点一下就启动了,那也对。但是它的启动过程呢?带着这样的疑问,咱们来一步步学习。
Android 启动过程
一般在任何平台上,都会逐步加载和执行以下组件:
- Boot loader
- U-boot (optional)
- Kernel
- Android
Android进程有以下顺序:
- Init
- Zygote
- System Server
- Service Manager
- Other Daemons and processes
- Applications
具体情况如下图,这两幅图结合起来比较有意思:
-
Boot ROM:当电源按下时,引导芯片代码会从预定义的地方(固化在ROM)开始执行,加载引导程序BootLoader到RAM,然后执行。(这一步由"芯片厂商"负责设计和实现)
-
Boot loader:Bootloader开始执行,首先负责完成硬件的初始化,引导操作系统启动。(这一步由"设备厂商"负责设计和实现)
-
Kernel:Linux 内核是 Android 的核心,负责进程创建、进程间通信、设备驱动程序、文件系统管理等。 Android 在主流内核上应用自定义补丁来支持 Android 运行所需的某些功能,如唤醒锁等。内核可以作为未压缩图像或压缩图像加载。在加载时,它挂载根文件系统(通常作为内核命令行参数传递)并启动用户空间中的第一个应用程序。(这一步则是Android内核开发过程中需要涉及的地方)
-
Android:Android系统以及各大Linux的发行版,他们的Linux内核部分启动过程都是差不多的,他们之间最大的区别就在于init程序的不同,因为init程序决定了系统在启动过程中,究竟会启动哪些守护进程和服务,以及呈现出怎样的一个用户UI界面。
因此,init程序是分析Android启动过程中最核心的程序。
-
init 和 init.rc:启动内核时执行的第一个用户空间应用程序是位于根文件夹中的 init 可执行文件。该进程解析称为"init.rc"脚本的启动脚本。这是用一种专为 android 设计的语言编写的,用于启动所有必要的进程、守护程序和服务,以便 android 正常运行。它提供了各种类型的执行时间,例如 early-init、on-boot、on-post-fs 等。(用户空间的鼻祖)
-
Demons and Services:init 进程创建了各种守护进程和进程,如 rild、vold、mediaserver、adb 等,每个进程负责自己的功能。这些进程的描述不在本文的范围内。相反,我们将更多地讨论"Zygote"进程。
-
Service Manager:Service Manager进程 管理系统中运行的所有Service。创建的每个服务都会在此进程中注册自己,并且此信息供其他进程/应用程序将来参考。
-
Zygote:Zygote 是启动时创建的第一个 init 进程之一。术语"合子"是基于生物学"形成的初始细胞分裂产生后代"。类似地,"zygote in android"初始化 Dalivik VM(ART) 和 fork 以创建多个实例来支持每个 android 进程。它有助于在 VM 实例之间使用共享代码,从而减少内存占用和加载时间,非常适合嵌入式系统。Zygote 除了在服务器套接字上安装侦听器外,还预加载了稍后在 Android 应用程序中使用的类和资源。完成后,系统服务器启动。
-
System Server:SystemServer 进程启动 Android 中可用的所有服务。
本文咱们重点从 init 开始到应用启动。
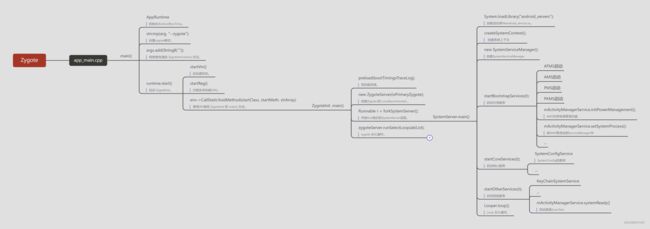
1、Zygote是什么
在Android系统里面,zygote是一个进程的名字。Android是基于Linux System的,当你的手机开机的时候,Linux的内核加载完成之后就会启动一个叫"init"的进程。在Linux System里面,所有的进程都是由init进程fork出来的,我们的zygote进程也不例外。
Zygote是一个虚拟机进程,同时也是一个虚拟机实例的孵化器,每当系统要求执行一个Android应用程序,Zygote就会fork(分裂)出一个子进程来执行该应用程序。
1.1 app_main.cpp
frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
在Zygote启动后就会执行 app_main.cpp。不管是C/c++/java,他们的入口就是 main(),就跟看到 Activity 咱们直接找 onCreate() 方法一样。
1.1.1 main()
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
...
//注释1:初始化AppRuntime(AndroidRunTime)
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
...
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
//注释2:设置zygote模式
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
}
...
}
Vector args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
...
} else {
// 我们处于 zygote 模式。
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
// 注释3:在 zygote 模式下,将参数传递给 ZygoteInit.main() 方法。
if (startSystemServer) {
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
//PROP_VALUE_MAX = 92;
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
...
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
if (zygote) {
//注释4:调用 AndroidRuntime.start() 方法
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
...
} else {
...
}
}
注释1:初始化 AppRuntime ,其实就是 AndroidRuntime(ART)。
注释2:设置zygote模式。
注释3:将参数传递给 ZygoteInit.main() 方法。
注释4:启动 ZygoteInit 。这里的 ZygoteInit 就是 zygote 进程的启动类。这个下面讲到。咱们先看看AndroidRuntime 的 start() 方法。
1.2 AndroidRuntime.cpp
frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
Android 虚拟机
1.2.1 start()
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector& options, bool zygote)
{
...
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
//注释1:启动虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote, primary_zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
//注释2:注册安卓功能(JNI)
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
...
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
...
/*
* 启动虚拟机。 该线程成为VM的主线程,直到VM退出才会返回。
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
...
} else {
...
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
...
} else {
//注释3
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
}
}
...
}
复制代码
注释1:启动VM(虚拟机)
注释2:注册安卓功能(JNI)
注释3:便用JNI调用 Zygotelnit 的 main() 方法。这里的 Zygotelnit 是class文件,也就是说从这里开始就进入java领域喽。
JNI:连接 native(C/C++) 层 和 java 层的桥梁。
1.3 ZygoteInit.java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
/**
* zygote 进程的启动类。
*/
public class ZygoteInit {
...
}
复制代码
这是 Zygote 进程的入口点。 它创建 Zygote 服务,加载资源,并处理与准备分叉到应用程序的过程相关的其他任务。
1.3.1 main()
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static void main(String[] argv) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
try {
...
boolean startSystemServer = false;
//argv:用于指定 Zygote 配置的命令行参数。
...
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
//注释1:预加载资源。
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
}
...
//注释2:创建Zygote 的 LocalServerSocket 。
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
if (startSystemServer) {
//注释3:开始fork我们的SystemServer进程。
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
...
}
...
// 注释4:zygote 永久循环。
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
...
} finally {
if (zygoteServer != null) {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
}
...
}
复制代码
注释1:预加载资源。
注释2:创建Zygote 的 LocalServerSocket 。
注释3:开始 fork 我们的 SystemServer 进程。
注释4:zygote 永久循环。
这里咱们看看 forkSystemServer() ;
1.3.2 forkSystemServer()
/**
* Prepare the arguments and forks for the system server process.
*
* @return A {@code Runnable} that provides an entrypoint into system_server code in the child
* process; {@code null} in the parent.
*/
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
...
//命令行来启动SystemServer
//ZygoteInit.main(String argv[])里面的argv 跟这个类似
String[] args = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
+ "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010,3011",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
//处理与 zygote spawner 相关的 args 的参数解析。
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs;
int pid;
try {
ZygoteCommandBuffer commandBuffer = new ZygoteCommandBuffer(args);
try {
parsedArgs = ZygoteArguments.getInstance(commandBuffer);
} catch (EOFException e) {
throw new AssertionError("Unexpected argument error for forking system server", e);
}
commandBuffer.close();
...
//请求 fork 系统服务器进程
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
复制代码
这里启动了一个 system server 。下面咱们就看看他。
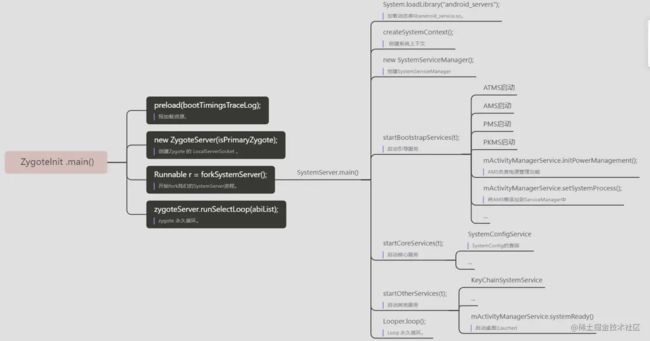
2、SystemServer
system server 也就是 SystemServer。SystemServer也是一个进程,包括ActivityTaskManagerService、ActivityManagerService、PackageManagerService、WindowManagerService等92种服务。
Android Framework里面两大非常重要的进程:
-
SystemServer进程。
-
Zygote进程。
2.1 SystemServer.java
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
public final class SystemServer {
...
}
复制代码
2.1.1 main()
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
public SystemServer() {
// Check for factory test mode.
mFactoryTestMode = FactoryTest.getMode();
...
}
复制代码
下面 咱们看看 run () 里面都用什么?
2.1.2 run()
private void run() {
try {
...
// 注释1:加载动态库libandroid_service.so。
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// 注释2:创建系统上下文。
createSystemContext();
// 调用每个进程的主线模块初始化。
ActivityThread.initializeMainlineModules();
// 注释3:创建 SystemServiceManager。
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// 为可并行化的 init 任务准备线程池
SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();
...
} finally {
}
// 注释4:Start services。
try {
//下面咱们看看这个三个方法启动什么服务
startBootstrapServices(t);
startCoreServices(t);
startOtherServices(t);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
...
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
...
// 注释5:Loop 永久循环。
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
复制代码
注释1:加载动态库libandroid_service.so。
注释2:创建系统上下文。
注释3:创建 SystemServiceManager。
注释4:启动服务(startBootstrapServices、startCoreServices、startOtherServices)
注释5:Loop 永久循环。
2.1.3 createSystemContext()
private void createSystemContext() {
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
}
复制代码
初始化系统上下文对象mSystemContext,并设置默认的主题,mSystemContext实际上是一个Context(ContextImpl)对象。
调用ActivityThread.systemMain()的时候,会调用ActivityThread.attach(true),而在attach()里面,则创建了Application对象,并调用了Application.onCreate()。
2.1.4 startBootstrapServices()
/**
* 启动系统引导服务,因为这些服务之间有复杂的相互依赖关系,所以都放在了这个方法里面。
*/
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
final String TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG = "ReadingSystemConfig";
SystemServerInitThreadPool.submit(SystemConfig::getInstance, TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG);
// PlatformCompat Service 由 ActivityManagerService, PackageManagerService 和 其他服务做使用
PlatformCompat platformCompat = new PlatformCompat(mSystemContext);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.PLATFORM_COMPAT_SERVICE, platformCompat);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.PLATFORM_COMPAT_NATIVE_SERVICE,
new PlatformCompatNative(platformCompat));
AppCompatCallbacks.install(new long[0]);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(FileIntegrityService.class);
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UriGrantsManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
startMemtrackProxyService();
// StartActivityManager
ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
//初始化 ActivityManagerService
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
mWindowManagerGlobalLock = atm.getGlobalLock();
mDataLoaderManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
DataLoaderManagerService.class);
mIncrementalServiceHandle = startIncrementalService();
t.traceEnd();
//初始化PowerManagerService(电源服务),需要提前启动,因为其他服务需要它。
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ThermalManagerService.class);
// 电源管理已经开启,ActivityManagerService负责电源管理功能
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RecoverySystemService.Lifecycle.class);
...
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
// Package manager isn't started yet; need to use SysProp not hardware feature
if (SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.enable_sidekick_graphics", false)) {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WEAR_SIDEKICK_SERVICE_CLASS);
}
// 初始化DisplayManagerService(显示管理器)
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
// Start the package manager.
try {
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
} finally {
}
// 现在PackageManagerService已经启动,注册 dex 加载报告器来捕获系统服务加载的任何 dex 文件。
// 这些 dex 文件将由 BackgroundDexOptService 优化。
SystemServerDexLoadReporter.configureSystemServerDexReporter(mPackageManagerService);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
...
//将AMS等添加到ServiceManager中
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
if (!mOnlyCore) {
boolean disableOtaDexopt = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_otadexopt",
false);
if (!disableOtaDexopt) {
try {
OtaDexoptService.main(mSystemContext, mPackageManagerService);
} catch (Throwable e) {
} finally {
}
}
}
...
mSensorServiceStart = SystemServerInitThreadPool.submit(() -> {
TimingsTraceAndSlog traceLog = TimingsTraceAndSlog.newAsyncLog();
startSensorService();
}, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
// startBootstrapServices
}
复制代码
改动比较大的地方:
-
ActivityTaskManagerService(ATMS):负责管理除Activity和进程,包括生命周期和状态切换。
-
ActivityManagerService(AMS):AMN的子类,负责管理三大组件(除Activity)和进程,包括生命周期和状态切换。AMS因为要和ui交互,所以极其复杂,涉及window。
ActivityTaskManagerService:把 Activity 相关的内容从 ActivityManagerService 剥离出来而产生的。
PowerManagerService(PMS):电源管理服务。
PackageManagerService(PKMS):包管理服务,不叫PMS是为了和电源管理服务区分开。
2.1.5 startCoreServices()
/**
* 启动核心服务。
*/
private void startCoreServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
// Service for system config
mSystemServiceManager.startService(SystemConfigService.class);
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
...
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LooperStatsService.Lifecycle.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ROLLBACK_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(NativeTombstoneManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BugreportManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(GpuService.class);
// startCoreServices
}
复制代码
2.1.6 startOtherServices()
/**
* 启动其他服务。
*/
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
final Context context = mSystemContext;
VibratorService vibrator = null;
DynamicSystemService dynamicSystem = null;
IStorageManager storageManager = null;
NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
IpSecService ipSecService = null;
VpnManagerService Manager = null;
VcnManagementService vcnManagement = null;
NetworkStatsService networkStats = null;
NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicy = null;
NsdService serviceDiscovery = null;
WindowManagerService wm = null;
SerialService serial = null;
NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdater = null;
InputManagerService inputManager = null;
TelephonyRegistry telephonyRegistry = null;
ConsumerIrService consumerIr = null;
MmsServiceBroker mmsService = null;
HardwarePropertiesManagerService hardwarePropertiesService = null;
PacProxyService pacProxyService = null;
...
// 现在便可以开始启动三方APP应用(如Launcher启动桌面)
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
...
}, t);
// startOtherServices
}
复制代码
经过上面这些步骤,我们调用调用createSystemContext()创建系统上下文的时候,也已经完成了mSystemContext和ActivityThread的创建。
ATMS、AMS、WMS、PKMS等对象已经创建好了,并且完成了成员变量初始化。
注意:这是系统进程开启时的流程,在这之后,会开启系统的
Launcher程序,完成系统界面的加载与显示。
在Android的框架设计中,服务器端指的就是所有App共用的系统服务,比如我们这里提到的ATMS、AMS、WMS、PKMS等等,这些基础的系统服务是被所有的App公用的。
3、Launcher是什么
在Android系统中,应用程序是由Launcher启动起来的,其实,Launcher本身也是一个应用程序,其它的应用程序安装后,就会Launcher的界面上出现一个相应的图标,点击这个图标时,Launcher就会对应的应用程序启动起来。
当然也可以在 其他应用 启动应用。但是本质上都是调用startActivity()。
3.1 LauncherActivity.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LauncherActivity.java
/**
* Displays a list of all activities which can be performed
* for a given intent. Launches when clicked.
*
* @deprecated Applications can implement this UI themselves using
* {@link androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView} and
* {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#queryIntentActivities(Intent, int)}
*/
@Deprecated
public abstract class LauncherActivity extends ListActivity {
...
@Override
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
Intent intent = intentForPosition(position);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
复制代码
小结
附送整图一张
关于 startActivity() 有了解的可以直接看看。本篇内容太多我自己看着都闹心。没看过的关注走一波,详细内容会在下一篇: ❤️ Android startActivity源码分析 ❤️中讲解。