《深度学习之PyTorch实战计算机视觉》第8章代码 图像风格迁移实战
《深度学习之PyTorch实战计算机视觉》第8章代码
代码
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, models
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.autograd import Variable
import copy
import time
transform = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Scale([224,224]),
transforms.ToTensor()
]
)
def loadimg(path = None):
img = Image.open(path)
if img.mode != "RGB":
img = img.convert('RGB')
img = transform(img)
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
return img
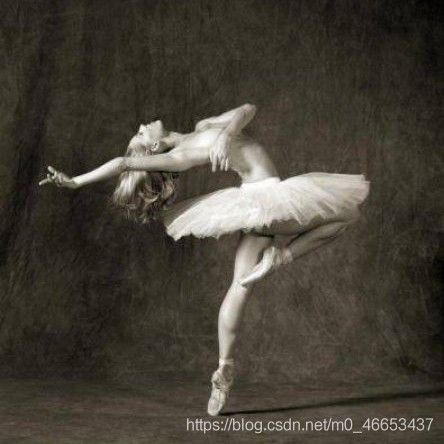
content_img = loadimg("images/3.jpg") #注意,images文件夹在当前文件夹的上一层文件夹中
#print("陈旭旗",content_img.shape)
content_img = Variable(content_img).cuda()#torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
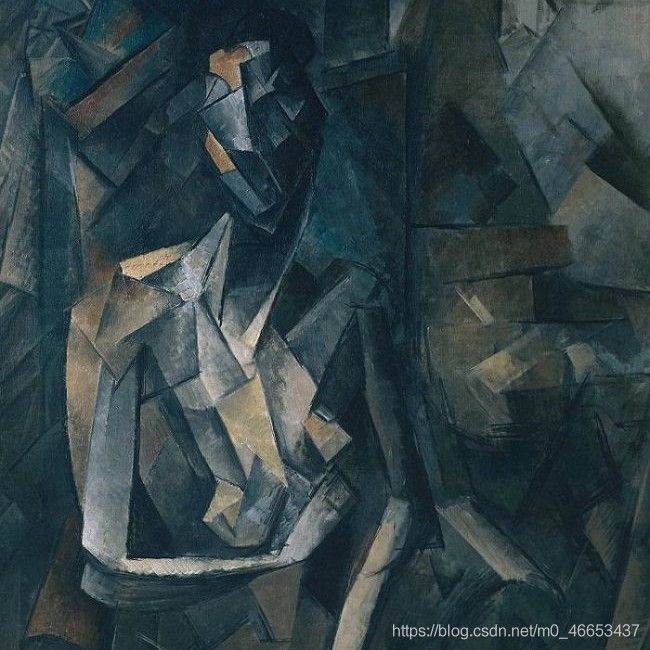
style_img = loadimg("images/8.jpg") #注意,images文件夹在当前文件夹的上一层文件夹中
style_img = Variable(style_img).cuda() #torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
print("陈旭旗",style_img.shape)
# plt.imshow(style_img.cpu().squeeze(0).numpy().transpose([1,2,0]))
# plt.show()
class Content_loss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight, target):
# target是通过卷积获取到的输入图像中的内容
# weight是我们设置的一个权重参数,用来控制内容和风格对最后合成图像的影响程度
super(Content_loss,self).__init__()
self.weight = weight
self.target = target.detach()*weight
# target.detach()用于对提取到的内容进行锁定,不需要进行梯度
self.loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()
def forward(self, input):# forward函数用于计算输入图像和内容图像之间的损失值
# input代表输入图像,
self.loss = self.loss_fn(input*self.weight, self.target)
return input
def backward(self):
# backward函数根据计算得到的损失值进行后向传播,并返回损失值
self.loss.backward(retain_graph = True)
# 每次 backward() 时,默认会把整个计算图free掉。一般情况下是
# 每次迭代,只需一次 forward() 和一次 backward() ,前向运算forward()
# 和反向传播backward()是成对存在的,一般一次backward()也是够用的。但
# 是不排除,由于自定义loss等的复杂性,需要一次forward(),多个不同loss的
# backward()来累积同一个网络的grad,来更新参数。于是,若在当前backward()后,
# 不执行forward() 而可以执行另一个backward(),需要在当前backward()时,
# 指定保留计算图,即backward(retain_graph)。
return self.loss
#实现的是格拉姆矩阵(Gram matrix)的功能
class Gram_matrix(torch.nn.Module):
# 我们通过卷积神经网络提取了风格图片的风格,这些风格其实是由数字组成的,数字的大小代表了
# 图片中风格的突出程度,而Gram矩阵是矩阵的内积运算,在运算过后输入到该矩阵的特征图中的大
# 的数字会变得更大,这就相当于图片的风格被放大了,放大的风格再参与损失计算,便能够对最后
# 的合成图片产生更大的影响。
def forward(self, input):
a,b,c,d = input.size()
feature = input.view(a*b, c*d)
gram = torch.mm(feature,feature.t()) #返回矩阵乘积
return gram.div(a*b*c*d)
class Style_loss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,weight,target):
super(Style_loss,self).__init__()
self.weight = weight
self.target = target.detach()*weight
self.loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()
self.gram = Gram_matrix()
def forward(self,input):
self.Gram = self.gram(input.clone())
self.Gram.mul_(self.weight)#原地操作,矩阵对应位相乘
self.loss = self.loss_fn(self.Gram,self.target)
return input
def backward(self):
self.loss.backward(retain_graph = True)
return self.loss
use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
cnn = models.vgg16(pretrained=True).features
#print(cnn)
#print(models.vgg16(pretrained=True))
if use_gpu:
cnn = cnn.cuda()
model = copy.deepcopy(cnn)
content_losses = []
style_losses = []
conten_weight = 1
style_weight = 1000
new_model = torch.nn.Sequential()
gram = Gram_matrix()
if use_gpu:
new_model = new_model.cuda()
gram = gram.cuda()
content_layer = ["Conv_3"]
style_layer = ["Conv_1","Conv_2","Conv_3","Conv_4"]
index = 1
# print("cxq陈旭旗")
# print(list(model)[:8])
# print("cxq陈旭旗")
# cxq = 0
for layer in list(model)[:8]:
if isinstance(layer, torch.nn.Conv2d):
name = "Conv_"+str(index)
new_model.add_module(name, layer)
if name in content_layer: #["Conv_3"]
target = new_model(content_img).clone()
content_loss = Content_loss(conten_weight,target)
new_model.add_module("content_loss_"+str(index),content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
if name in style_layer: #["Conv_1","Conv_2","Conv_3","Conv_4"]
target = new_model(style_img).clone()
target = gram(target)
style_loss = Style_loss(style_weight, target)
new_model.add_module("style_loss_"+str(index), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
if isinstance(layer, torch.nn.ReLU):
name = "Relu_"+str(index)
new_model.add_module(name,layer)
index = index+1
if isinstance(layer, torch.nn.MaxPool2d):
name = "MaxPool_"+str(index)
new_model.add_module(name, layer)
# cxq +=1
# if cxq == 9:
# print(new_model)
# print(new_model)
# print("陈旭旗content_losses:\n")
# print(content_losses)
# print("\n\n\n陈旭旗style_losses:\n")
# print(style_losses)
input_img = content_img.clone()#torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
parameter = torch.nn.Parameter(input_img.data)#含义是将一个固定不可训练的tensor转换成可以训练的类型parameter
optimizer = torch.optim.LBFGS([parameter])
epoch_n = 300
epoch = 0
time_open = time.time()
while epoch <= epoch_n:
def closure():
optimizer.zero_grad()
style_score = 0
content_score = 0
parameter.data.clamp_(0,1)#torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
new_model(parameter)
for sl in style_losses:
style_score += sl.backward()
for cl in content_losses:
content_score += cl.backward()
global epoch
epoch += 1
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print("Epoch:{} Style Loss: {:4f} Content Loss:{:4f}".format(
epoch,
style_score.item(),
content_score.item()
)
)
return style_score+content_score
optimizer.step(closure)
time_end = time.time() - time_open
print("程序运行时间:{}秒...".format(int(time_end)))
plt.figure("内容图像")
plt.imshow(content_img.data.cpu().squeeze(0).numpy().transpose([1,2,0]))
plt.figure("风格图像")
plt.imshow(style_img.data.cpu().squeeze(0).numpy().transpose([1,2,0]))
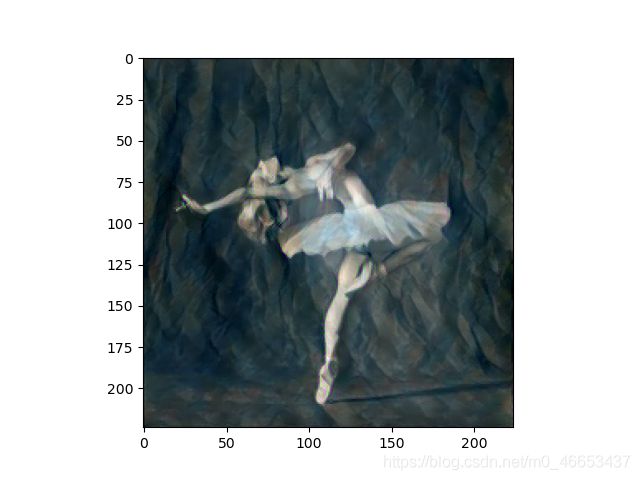
plt.figure("风格迁移图像")
plt.imshow(parameter.data.cpu().squeeze(0).numpy().transpose([1,2,0]))
plt.show()