Java数据结构之单链表(配图详解,简单易懂)
Java数据结构之单链表(配图详解,简单易懂)
文章目录
- Java数据结构之单链表(配图详解,简单易懂)
-
-
-
- 1.头插法:
- 2.尾插法:(难点在于如何找到尾巴)
- 3.打印链表:
- 4.求链表长度:
- 5.指定位置插入:(第一个节点的角标为0,单向链表不可逆,所以需要找到指定位置的前一个节点所在位置)
- 6.查询关键字:
- 7.删除第一次关键字:(因为单向链表的不可逆性,所以还是返回删除关键字的前一个位置)
- 8.删除所有关键字:(只通过一次遍历完成所有关键字的删除)
- 9.清空链表:
-
-
(本笔记主要介绍单向不带头节点非循环链表)
总结不易,希望uu们不要吝啬你们的哟(^U^)ノ~YO!!
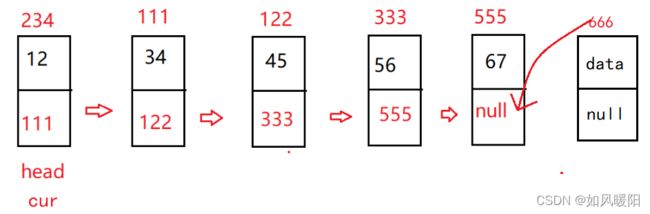
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的,看着这段文字抽象不,生硬不,那看看下边这幅图吧!
(●’◡’●)看到发哥脖子上这条大金链子了吗?其实数据结构中的链表就和发哥脖子上的金链子结构相似!!
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有多种链表结构:
单向、双向
带头、不带头
循环、非循环
下面是我围绕单向不带头非循环链表的一些分享心得!!!
其实发哥脖子上的链子,是由一节一节组成的,我们的单链表也是这样,每一个小节即为一个节点。
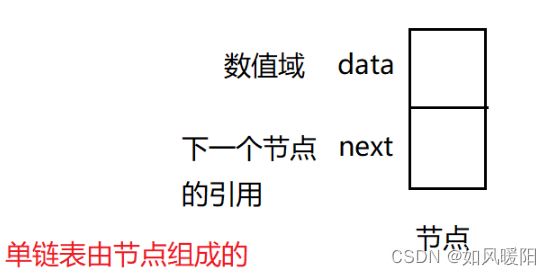
在一个节点内,不仅存放了数据,还存放了下一个数据的地址,这样一来,一个一个的节点就会串起来比如要把一组数据给存入其中,那么他的结构将会是这个样子.
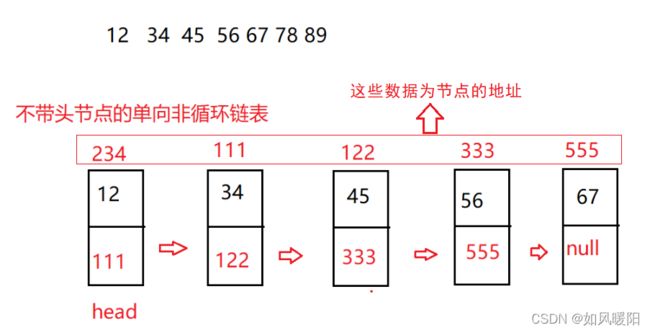
接下来我们就来通过代码实现这样一个结构:
首先先把链子上的一个个小环给造好,然后再串起来
class Node { //通过创建Node类,来实现一个节点的存在
public int data; //节点中存在数值data
public Node next;//节点中存在下一个节点的引用(地址),此处可能有疑问是next的类型,下面着重分享一下
/*就像我们在学习c语言指针部分内容时我们在定义指针变量的类型(所以说c生万物,其实都一样)
int a=10;
int*p=&a;
p存储的是a的地址,而p的类型是由a决定的,因为a是int型,所以指针变量p也是int型
,next内存储的是下一个节点的引用(地址),节点为Node型,所以next也应该是Node型
*/
public Node (int data){//构造方法,在实例化对象时给对象进行初始化
this.data=data;//this.next会被默认为null
}
接下来就是我们金链子的发光时刻了!
public class MyLinkedList {
public Node head;//head为对第一个节点的引用
public void addFirst(int data); //1.头插法
public void addLast(int data); //2.尾插法
public void display(); //3.打印单链表
public int size(); //4.得到单链表的长度
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data); //5.任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean contains(int key); //6.查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public void remove(int key); //7.删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key); //8.删除所有值为key的节点
public void clear();//9.清空链表
}
下边是我们一个个接口的实现.
1.头插法:
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node=new Node(data);//我们先把要插的数据造成链表再进行插入
if(this.head==null) {//一个数据也没有时,其实就是直接存入一个数据
this.head=node;//然后将head指向我们刚刚创建的节点
return;//完成后记得直接返回
}
node.next=this.head;//注意两者不能颠倒顺序(自己可以尝试一下如果颠倒链表将接不上),节点都是先连接才能保证链表的连接
this.head=node;
}
2.尾插法:(难点在于如何找到尾巴)
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node=new Node(data);
if(this.head==null) {//如果链表为空,直接插入
this.head=node;
return;
}
Node cur=this.head;//创建cur用来表示目前节点
while(cur.next!=null)//设置循环让cur往后走,当cur到最后一个节点时停止循环
{
cur=cur.next;//cur后移
}
cur.next=node;//最后一个节点接上尾巴
}
3.打印链表:
public void disPlay() {
Node cur=this.head;
while (cur!=null) {//设置循环遍历链表 完成打印
System.out.println(cur.data+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
}
4.求链表长度:
public int size() {
int count=0;
Node cur=this.head;
while (cur!=null) {//遍历链表,求出长度,返回长度
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
5.指定位置插入:(第一个节点的角标为0,单向链表不可逆,所以需要找到指定位置的前一个节点所在位置)
private Node searchIndex(int index) {//封装一个方法用来找指定位置
if(index<0||index>this.size())//判断位置合法性
{
throw new RuntimeException("index位置不合法");
}
Node cur=this.head;
int count=0;
while (count!=index-1)//找到指定位置的前一个位置,返回这个节点
{
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if(index==0) {//空链表直接插
this.addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index==this.size()) {//this.size()返回链表长度,位置为最后,直接调用尾插法
this.addLast(data);
return;
}
Node cur=searchIndex(index);//返回目标位置的前一个位置的节点
Node node=new Node(data);//为该数据创立节点
node.next=cur.next;//以下两步完成连接,一般都是先接上后边,如果这两步顺序调换,则无法完成连接
cur.next=node;
}
6.查询关键字:
public boolean contains(int key) {
if(this.head==null)//空链表直接返回false
return false;
Node cur=this.head;//cur完成遍历,查询链表中是否存在关键字key
while (cur!=null) {
if(cur.data==key)
return true;
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;//完成遍历后没有找到,返回false
}
7.删除第一次关键字:(因为单向链表的不可逆性,所以还是返回删除关键字的前一个位置)
private Node searchDeleteAhead(int key) {
Node cur=this.head;
while (cur.next!=null) {//遍历链表找寻关键字
if(cur.next.data==key) {//找到则返回关键字的前一个节点的引用
return cur;
}else {
cur=cur.next;//否则继续往后走
}
}
return null;//没找到返回空
}
public void removeKey(int key) {
if(this.head==null) {//空链表直接返回
return;
}
if(this.head.data==key) {//第一个节点单独考虑,因为需要返回关键字的前一个节点,若头结点为关键字则没有前一个节点,直接将头节点删除即可
this.head=this.head.next;
return;
}
Node ahead=searchDeleteAhead(key);
if(ahead==null) {
System.out.println("无该节点!");
}else {
ahead.next=ahead.next.next;//前节点的next=被删节点的next完成删除
}
}
8.删除所有关键字:(只通过一次遍历完成所有关键字的删除)
public void removeAllKeys(int key) {
//因为删除一个节点需要前一个节点的连接,所以需要建立两个节点完成整个工程
Node ahead=this.head;//前一个节点
Node cur=ahead.next;//后一个节点(在cur中判断data是否与key相等),两个节点从头开始往后遍历
while (cur!=null) {//当cur为空时完成遍历
if(cur.data==key) {//在cur中判断data是否与key相等,如果相等则删除
ahead.next=cur.next;//先完成连接
cur=cur.next;//连接完成后cur后移继续判断该cur.data是否为关键字,ahead不用动(因为已经删除该节点以后,只需cur后移,ahead仍为cur的前一个节点)
}else {//如果不相等,则两者均后移
ahead=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(this.head.data==key) {//最后考虑头节点,如果相等再完成删除
this.head=this.head.next;
}
}
解释一下为什么最后考虑头节点
if(this.head.data==key) {
this.head=this.head.next;
}
while (del!=null) {
if(del.data==key) {
ahead.next=del.next;
del=del.next;
}else {
ahead=del;
del=del.next;
}
}
如图所示,再先删除头节点以后,直接跳过了ahead.data的考虑,所以把头节点放在最后考虑,如果相等删除即可。
9.清空链表:
public void clear() {
this.head=null;
}
(可别小看这一行代码,其实它完成了整个链表的清空)
JVM在回收内存时,当该对象没有人在引用它的时候,这个对象才会被回收,当把this.head置为空时,也就相当于没有对象引用第一个头节点了(其实就像多米诺骨牌后边就全掉了),第一个被回收,后边也就都被回收了
总结不易,希望uu们不要吝啬你们的哟(^U^)ノ~YO!!