Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎完整版-基于Scrapy、Redis、elasticsearch和django打造一个完整的搜索引擎网站
Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎
基于Scrapy、Redis、elasticsearch和django打造一个完整的搜索引擎网站
https://github.com/mtianyan/ArticleSpider
未来是什么时代?是数据时代!数据分析服务、互联网金融,数据建模、自然语言处理、医疗病例分析……越来越多的工作会基于数据来做,而爬虫正是快速获取数据最重要的方式,相比其它语言,Python爬虫更简单、高效
一、基础知识学习:
1. 爬取策略的深度优先和广度优先
目录:
- 网站的树结构
- 深度优先算法和实现
- 广度优先算法和实现
网站url树结构分层设计:
- bogbole.com
- blog.bogbole.com
- python.bogbole.com
- python.bogbole.com/123
环路链接问题:
从首页到下面节点。
但是下面的链接节点又会有链接指向首页
所以:我们需要对于链接进行去重
1. 深度优先
2. 广度优先
跳过已爬取的链接
对于二叉树的遍历问题
深度优先(递归实现):
顺着一条路,走到最深处。然后回头
广度优先(队列实现):
分层遍历:遍历完儿子辈。然后遍历孙子辈
Python实现深度优先过程code:
def depth_tree(tree_node):
if tree_node is not None:
print (tree_node._data)
if tree_node._left is not None:
return depth_tree(tree_node.left)
if tree_node._right is not None:
return depth_tree(tree_node,_right)Python实现广度优先过程code:
def level_queue(root):
#利用队列实现树的广度优先遍历
if root is None:
return
my_queue = []
node = root
my_queue.append(node)
while my_queue:
node = my_queue.pop(0)
print (node.elem)
if node.lchild is not None:
my_queue.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild is not None:
my_queue.append(node.rchild)2. 爬虫网址去重策略
- 将访问过的url保存到数据库中
- 将url保存到set中。只需要O(1)的代价就可以查询到url
100000000*2byte*50个字符/1024/1024/1024 = 9G
- url经过md5等方法哈希后保存到set中,将url压缩到固定长度而且不重复
- 用bitmap方法,将访问过的url通过hash函数映射到某一位
- bloomfilter方法对bitmap进行改进,多重hash函数降低冲突
scrapy去重使用的是第三种方法:后面分布式scrapy-redis会讲解bloomfilter方法。
3. Python字符串编码问题解决:
- 计算机只能处理数字,文本转换为数字才能处理,计算机中8个bit作为一个字节,
所以一个字节能表示的最大数字就是255- 计算机是美国人发明的,所以一个字节就可以标识所有单个字符
,所以ASCII(一个字节)编码就成为美国人的标准编码- 但是ASCII处理中文明显不够,中文不止255个汉字,所以中国制定了GB2312编码
,用两个字节表示一个汉字。GB2312将ASCII也包含进去了。同理,日文,韩文,越来越多的国家为了解决这个问题就都发展了一套编码,标准越来越多,如果出现多种语言混合显示就一定会出现乱码- 于是unicode出现了,它将所有语言包含进去了。
- 看一下ASCII和unicode编码:
- 字母A用ASCII编码十进制是65,二进制 0100 0001
- 汉字”中” 已近超出ASCII编码的范围,用unicode编码是20013二进制是01001110 00101101
- A用unicode编码只需要前面补0二进制是 00000000 0100 0001
- 乱码问题解决的,但是如果内容全是英文,unicode编码比ASCII编码需要多一倍的存储空间,传输也会变慢。
- 所以此时出现了可变长的编码”utf-8” ,把英文:1字节,汉字3字节,特别生僻的变成4-6字节,如果传输大量的英文,utf8作用就很明显。
**读取文件,进行操作时转换为unicode编码进行处理** **保存文件时,转换为utf-8编码。以便于传输** 读文件的库会将转换为unicode *python2 默认编码格式为`ASCII`,Python3 默认编码为 `utf-8`*
#python3
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
s.encoding('utf-8')#python2
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
s = "我和你"
su = u"我和你"
~~s.encode("utf-8")#会报错~~
s.decode("gb2312").encode("utf-8")
su.encode("utf-8")二、伯乐在线爬取所有文章
1. 初始化文件目录
基础环境
- python 3.5.1
- JetBrains PyCharm 2016.3.2
- mysql+navicat
为了便于日后的部署:我们开发使用了虚拟环境。
pip install virtualenv
pip install virtualenvwrapper-win
安装虚拟环境管理
mkvirtualenv articlespider3
创建虚拟环境
workon articlespider3
直接进入虚拟环境
deactivate
退出激活状态
workon
知道有哪些虚拟环境注意:
默认workon的windows路径位于C:\Users\Administrator\Envs,建议将workon的虚拟列表路径改为非C盘,所以通过设置WORKON_HOME指定其他的路径,如我改为了:E:\Envs(不用再添加到path中)
如何创建指定python版本的虚拟环境:
virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python2.7 env在安装scrapy时:
如:pip install scrapy 时出现:error: Microsoft Visual C++ 14.0 is required. Get it with “Microsoft Visual C++ Build Tools”: http://landinghub.visualstudio.com/visual-cpp-build-tools
解决办法
方法一(前提你的网络够快): 安装 Microsoft visual c++ 14.0
https://964279924.ctfile.com/fs/1445568-239446865
或
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1q2Nj41Xk85CHHv7_zOhQIA 密码:qbba
方法二:https://www.jb51.net/article/125081.htm
通过在虚拟环境中
![]()
然后再安装scrapy就可以了:
![]()
scrapy项目初始化介绍
自行官网下载py35对应得whl文件进行pip离线安装
Scrapy 1.3.3
**命令行创建scrapy项目**
cd desktop
scrapy startproject ArticleSpider #在虚拟环境中输入**scrapy目录结构** scrapy借鉴了django的项目思想
scrapy.cfg:配置文件。setings.py:设置
SPIDER_MODULES = ['ArticleSpider.spiders'] #存放spider的路径
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'ArticleSpider.spiders'pipelines.py:
做跟数据存储相关的东西
middilewares.py:
自己定义的middlewares 定义方法,处理响应的IO操作
__init__.py:
项目的初始化文件。
items.py:
定义我们所要爬取的信息的相关属性。Item对象是种类似于表单,用来保存获取到的数据
**创建我们的spider**
cd ArticleSpider
scrapy genspider jobbole blog.jobbole.com可以看到直接为我们创建好的空项目里已经有了模板代码。如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class JobboleSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "jobbole"
allowed_domains = ["blog.jobbole.com"]
# start_urls是一个带爬的列表,
#spider会为我们把请求下载网页做到,直接到parse阶段
start_urls = ['http://blog.jobbole.com/']
def parse(self, response):
passscray在命令行启动某一个Spyder的命令:
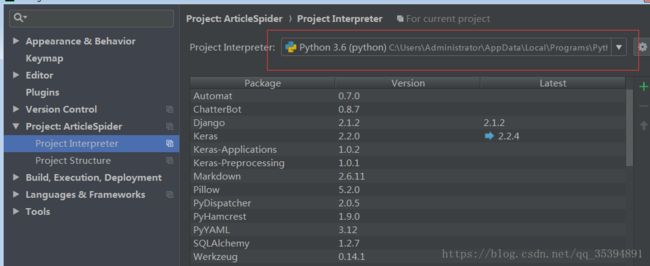
scrapy crawl jobbole注意:因为使用了虚拟环境,所以将项目导入pycharm时要将项目的project interpreter切换为虚拟环境下的python.exe
比如我的虚拟环境中的python.exe位于 E:\Envs\pyscrapy3\Scripts
**在windows报出错误** `ImportError: No module named ‘win32api’`
pip install pypiwin32#解决
**创建我们的调试工具类*** 在项目根目录里创建main.py 作为调试工具文件
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
__author__ = 'mtianyan'
__date__ = '2017/3/28 12:06'
from scrapy.cmdline import execute
import sys
import os
#将系统当前目录设置为项目根目录
#os.path.abspath(__file__)为当前文件所在绝对路径
#os.path.dirname为文件所在目录
#H:\CodePath\spider\ArticleSpider\main.py
#H:\CodePath\spider\ArticleSpider
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
#执行命令,相当于在控制台cmd输入改名了
execute(["scrapy", "crawl" , "jobbole"])**settings.py的设置不遵守reboots协议** `ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False` 在jobble.py打上断点:
def parse(self, response):
pass可以看到他返回的htmlresponse对象: 对象内部:
- body:网页内容
- _DEFAULT_ENCODING= ‘ascii’
- encoding= ‘utf-8’
可以看出scrapy已经为我们做到了将网页下载下来。而且编码也进行了转换.
2. 提取伯乐在线内容
xpath的使用
xpath让你可以不懂前端html,不看html的详细结构,只需要会右键查看就能获取网页上任何内容。速度远超beautifulsoup。 目录:
1. xpath简介
2. xpath术语与语法
3. xpath抓取误区:javasrcipt生成html与html源文件的区别
4. xpath抓取实例
为什么要使用xpath?
- xpath使用路径表达式在xml和html中进行导航
- xpath包含有一个标准函数库
- xpath是一个w3c的标准
- xpath速度要远远超beautifulsoup。
**xpath节点关系**
- 父节点
*上一层节点* - 子节点
- 兄弟节点
*同胞节点* - 先辈节点
*父节点,爷爷节点* - 后代节点
*儿子,孙子*
xpath语法:
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| article | 选取所有article元素的所有子节点 |
| /article | 选取根元素article |
| article/a | 选取所有属于article的子元素的a元素 |
| //div | 选取所有div元素(不管出现在文档里的任何地方) |
| article//div | 选取所有属于article元素的后代的div元素,不管它出现在article之下的任何位置 |
| //@class | 选取所有名为class的属性 |
xpath语法-谓语:
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| /article/div[1 | 选取属于article子元素的第一个div元素 |
| /article/div[last()] | 选取属于article子元素的最后一个div元素 |
| /article/div[last()-1] | 选取属于article子元素的倒数第二个div元素 |
| //div[@color] | 选取所有拥有color属性的div元素 |
| //div[@color=’red’] | 选取所有color属性值为red的div元素 |
xpath语法:
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| /div/* | 选取属于div元素的所有子节点 |
| //* | 选取所有元素 |
| //div[@*] | 选取所有带属性的div 元素 |
| //div/a 丨//div/p | 选取所有div元素的a和p元素 |
| //span丨//ul | 选取文档中的span和ul元素 |
| article/div/p丨//span | 选取所有属于article元素的div元素的p元素以及文档中所有的 span元素 |
xpath抓取误区
firebugs插件
取某一个网页上元素的xpath地址
如:http://blog.jobbole.com/110287/
在标题处右键使用firebugs查看元素。
然后在2016 腾讯软件开发面试题(部分)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class JobboleSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "jobbole"
allowed_domains = ["blog.jobbole.com"]
start_urls = ['http://blog.jobbole.com/110287/']
def parse(self, response):
re_selector = response.xpath("/html/body/div[3]/div[3]/div[1]/div[1]/h1")
# print(re_selector)
pass调试debug可以看到
re_selector =(selectorlist)[]可以看到返回的是一个空列表,
列表是为了如果我们当前的xpath路径下还有层级目录时可以进行选取
空说明没取到值:
我们可以来chorme里观察一下
chorme取到的值
//*[@id="post-110287"]/div[1]/h1
chormexpath代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class JobboleSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "jobbole"
allowed_domains = ["blog.jobbole.com"]
start_urls = ['http://blog.jobbole.com/110287/']
def parse(self, response):
re_selector = response.xpath('//*[@id="post-110287"]/div[1]/h1')
# print(re_selector)
pass可以看出此时可以取到值
分析页面,可以发现页面内有一部html是通过JavaScript ajax交互来生成的,因此在f12检查元素时的页面结构里有,而xpath不对
xpath是基于html源代码文件结构来找的
xpath可以有多种多样的写法:
re_selector = response.xpath("/html/body/div[1]/div[3]/div[1]/div[1]/h1/text()")
re2_selector = response.xpath('//*[@id="post-110287"]/div[1]/h1/text()')
re3_selector = response.xpath('//div[@class="entry-header]/h1/text()')推荐使用id型。因为页面id唯一。
推荐使用class型,因为后期循环爬取可扩展通用性强。
通过了解了这些此时我们已经可以抓取到页面的标题,此时可以使用xpath利器照猫画虎抓取任何内容。只需要点击右键查看xpath。
开启控制台调试
scrapy shell http://blog.jobbole.com/110287/
完整的xpath提取伯乐在线字段代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
import re
class JobboleSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "jobbole"
allowed_domains = ["blog.jobbole.com"]
start_urls = ['http://blog.jobbole.com/110287/']
def parse(self, response):
#提取文章的具体字段
title = response.xpath('//div[@class="entry-header"]/h1/text()').extract_first("")
create_date = response.xpath("//p[@class='entry-meta-hide-on-mobile']/text()").extract()[0].strip().replace("·","").strip()
praise_nums = response.xpath("//span[contains(@class, 'vote-post-up')]/h10/text()").extract()[0]
fav_nums = response.xpath("//span[contains(@class, 'bookmark-btn')]/text()").extract()[0]
match_re = re.match(".*?(\d+).*", fav_nums)
if match_re:
fav_nums = match_re.group(1)
comment_nums = response.xpath("//a[@href='#article-comment']/span/text()").extract()[0]
match_re = re.match(".*?(\d+).*", comment_nums)
if match_re:
comment_nums = match_re.group(1)
content = response.xpath("//div[@class='entry']").extract()[0]
tag_list = response.xpath("//p[@class='entry-meta-hide-on-mobile']/a/text()").extract()
tag_list = [element for element in tag_list if not element.strip().endswith("评论")]
tags = ",".join(tag_list)
passcss选择器的使用:
# 通过css选择器提取字段
# front_image_url = response.meta.get("front_image_url", "") #文章封面图
title = response.css(".entry-header h1::text").extract_first()
create_date = response.css("p.entry-meta-hide-on-mobile::text").extract()[0].strip().replace("·","").strip()
praise_nums = response.css(".vote-post-up h10::text").extract()[0]
fav_nums = response.css(".bookmark-btn::text").extract()[0]
match_re = re.match(".*?(\d+).*", fav_nums)
if match_re:
fav_nums = int(match_re.group(1))
else:
fav_nums = 0
comment_nums = response.css("a[href='#article-comment'] span::text").extract()[0]
match_re = re.match(".*?(\d+).*", comment_nums)
if match_re:
comment_nums = int(match_re.group(1))
else:
comment_nums = 0
content = response.css("div.entry").extract()[0]
tag_list = response.css("p.entry-meta-hide-on-mobile a::text").extract()
tag_list = [element for element in tag_list if not element.strip().endswith("评论")]
tags = ",".join(tag_list)
pass3. 爬取所有文章
yield关键字
#使用request下载详情页面,下载完成后回调方法parse_detail()提取文章内容中的字段
yield Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url,post_url),callback=self.parse_detail)scrapy.http import Request下载网页
from scrapy.http import Request
Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url,post_url),callback=self.parse_detail)parse拼接网址应对herf内有可能网址不全
from urllib import parse
url=parse.urljoin(response.url,post_url)
parse.urljoin("http://blog.jobbole.com/all-posts/","http://blog.jobbole.com/111535/")
#结果为http://blog.jobbole.com/111535/class层级关系
next_url = response.css(".next.page-numbers::attr(href)").extract_first("")
#如果.next .pagenumber 是指两个class为层级关系。而不加空格为同一个标签twist异步机制
Scrapy使用了Twisted作为框架,Twisted有些特殊的地方是它是事件驱动的,并且比较适合异步的代码。在任何情况下,都不要写阻塞的代码。阻塞的代码包括:
- 访问文件、数据库或者Web
- 产生新的进程并需要处理新进程的输出,如运行shell命令
- 执行系统层次操作的代码,如等待系统队列
实现全部文章字段下载的代码:
def parse(self, response):
"""
1. 获取文章列表页中的文章url并交给scrapy下载后并进行解析
2. 获取下一页的url并交给scrapy进行下载, 下载完成后交给parse
"""
# 解析列表页中的所有文章url并交给scrapy下载后并进行解析
post_urls = response.css("#archive .floated-thumb .post-thumb a::attr(href)").extract()
for post_url in post_urls:
#request下载完成之后,回调parse_detail进行文章详情页的解析
# Request(url=post_url,callback=self.parse_detail)
print(response.url)
print(post_url)
yield Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url,post_url),callback=self.parse_detail)
#遇到href没有域名的解决方案
#response.url + post_url
print(post_url)
# 提取下一页并交给scrapy进行下载
next_url = response.css(".next.page-numbers::attr(href)").extract_first("")
if next_url:
yield Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url, post_url), callback=self.parse)全部文章的逻辑流程图
![]()
4. scrapy的items整合字段
数据爬取的任务就是从非结构的数据中提取出结构性的数据。
items 可以让我们自定义自己的字段(类似于字典,但比字典的功能更齐全)
在当前页,需要提取多个url
原始写法,extract之后则生成list列表,无法进行二次筛选:
post_urls = response.css("#archive .floated-thumb .post-thumb a::attr(href)").extract()改进写法:
post_nodes = response.css("#archive .floated-thumb .post-thumb a")
for post_node in post_nodes:
#获取封面图的url
image_url = post_node.css("img::attr(src)").extract_first("")
post_url = post_node.css("::attr(href)").extract_first("")在下载网页的时候把获取到的封面图的url传给parse_detail的response
在下载网页时将这个封面url获取到,并通过meta将他发送出去。在callback的回调函数中接收该值
yield Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url,post_url),meta={"front_image_url":image_url},callback=self.parse_detail)
front_image_url = response.meta.get("front_image_url", "")urljoin的好处
如果你没有域名,我就从response里取出来,如果你有域名则我对你起不了作用了
**编写我们自定义的item并在jobboled.py中填充。
class JobBoleArticleItem(scrapy.Item):
title = scrapy.Field()
create_date = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
url_object_id = scrapy.Field()
front_image_url = scrapy.Field()
front_image_path = scrapy.Field()
praise_nums = scrapy.Field()
comment_nums = scrapy.Field()
fav_nums = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
tags = scrapy.Field()import之后实例化,实例化之后填充:
1. from ArticleSpider.items import JobBoleArticleItem
2. article_item = JobBoleArticleItem()
3. article_item["title"] = title
article_item["url"] = response.url
article_item["create_date"] = create_date
article_item["front_image_url"] = [front_image_url]
article_item["praise_nums"] = praise_nums
article_item["comment_nums"] = comment_nums
article_item["fav_nums"] = fav_nums
article_item["tags"] = tags
article_item["content"] = contentyield article_item将这个item传送到pipelines中
pipelines可以接收到传送过来的item
将setting.py中的pipeline配置取消注释
# Configure item pipelines
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.ArticlespiderPipeline': 300,
}当我们的item被传输到pipeline我们可以将其进行存储到数据库等工作
setting设置下载图片pipeline
ITEM_PIPELINES={
'scrapy.pipelines.images.ImagesPipeline': 1,
}H:\CodePath\pyEnvs\articlespider3\Lib\site-packages\scrapy\pipelines
里面有三个scrapy默认提供的pipeline
提供了文件,图片,媒体。
ITEM_PIPELINES是一个数据管道的登记表,每一项具体的数字代表它的优先级,数字越小,越早进入。
setting设置下载图片的地址
# IMAGES_MIN_HEIGHT = 100
# IMAGES_MIN_WIDTH = 100设置下载图片的最小高度,宽度。
新建文件夹images在
IMAGES_URLS_FIELD = "front_image_url"
project_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
IMAGES_STORE = os.path.join(project_dir, 'images')安装PILpip install pillow
定制自己的pipeline使其下载图片后能保存下它的本地路径
get_media_requests()接收一个迭代器对象下载图片
item_completed获取到图片的下载地址
![]()
继承并重写item_completed()
from scrapy.pipelines.images import ImagesPipeline
class ArticleImagePipeline(ImagesPipeline):
#重写该方法可从result中获取到图片的实际下载地址
def item_completed(self, results, item, info):
for ok, value in results:
image_file_path = value["path"]
item["front_image_path"] = image_file_path
return itemsetting中设置使用我们自定义的pipeline,而不是系统自带的
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.ArticlespiderPipeline': 300,
# 'scrapy.pipelines.images.ImagesPipeline': 1,
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.ArticleImagePipeline':1,
}![]()
图片url的md5处理
新建package utils
import hashlib
def get_md5(url):
m = hashlib.md5()
m.update(url)
return m.hexdigest()
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(get_md5("http://jobbole.com".encode("utf-8")))不确定用户传入的是不是:
def get_md5(url):
#str就是unicode了
if isinstance(url, str):
url = url.encode("utf-8")
m = hashlib.md5()
m.update(url)
return m.hexdigest()在jobbole.py中将url的md5保存下来
from ArticleSpider.utils.common import get_md5
article_item["url_object_id"] = get_md5(response.url)5. 数据保存到本地文件以及mysql中
保存到本地json文件
import codecs打开文件避免一些编码问题,自定义JsonWithEncodingPipeline实现json本地保存
class JsonWithEncodingPipeline(object):
#自定义json文件的导出
def __init__(self):
self.file = codecs.open('article.json', 'w', encoding="utf-8")
def process_item(self, item, spider):
#将item转换为dict,然后生成json对象,false避免中文出错
lines = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + "\n"
self.file.write(lines)
return item
#当spider关闭的时候
def spider_closed(self, spider):
self.file.close()setting.py注册pipeline
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.JsonWithEncodingPipeline': 2,
# 'scrapy.pipelines.images.ImagesPipeline': 1,
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.ArticleImagePipeline':1,
}scrapy exporters JsonItemExporter导出
scrapy自带的导出:
- 'CsvItemExporter',
- 'XmlItemExporter',
- 'JsonItemExporter'
from scrapy.exporters import JsonItemExporter
class JsonExporterPipleline(object):
#调用scrapy提供的json export导出json文件
def __init__(self):
self.file = open('articleexport.json', 'wb')
self.exporter = JsonItemExporter(self.file, encoding="utf-8", ensure_ascii=False)
self.exporter.start_exporting()
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.exporter.finish_exporting()
self.file.close()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.exporter.export_item(item)
return item设置setting.py注册该pipeline
'ArticleSpider.pipelines.JsonExporterPipleline ': 2- 1
保存到数据库(mysql)
数据库设计数据表,表的内容字段是和item一致的。数据库与item的关系。类似于django中model与form的关系。
日期的转换,将字符串转换为datetime
import datetime
try:
create_date = datetime.datetime.strptime(create_date, "%Y/%m/%d").date()
except Exception as e:
create_date = datetime.datetime.now().date()数据库表设计
![]()
- 三个num字段均设置不能为空,然后默认0.
- content设置为longtext
- 主键设置为url_object_id
数据库驱动安装pip install mysqlclient
Linux报错解决方案:
ubuntu:sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-dev
centos:sudo yum install python-devel mysql-devel
保存到数据库pipeline(同步)编写
import MySQLdb
class MysqlPipeline(object):
#采用同步的机制写入mysql
def __init__(self):
self.conn = MySQLdb.connect('127.0.0.1', 'root', 'password', 'article_spider', charset="utf8", use_unicode=True)
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
insert_sql = """
insert into jobbole_article(title, url, create_date, fav_nums)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)
"""
self.cursor.execute(insert_sql, (item["title"], item["url"], item["create_date"], item["fav_nums"]))
self.conn.commit()保存到数据库的(异步Twisted)编写
因为我们的爬取速度可能大于数据库存储的速度。异步操作。
设置可配置参数
seeting.py设置
MYSQL_HOST = "127.0.0.1"
MYSQL_DBNAME = "article_spider"
MYSQL_USER = "root"
MYSQL_PASSWORD = "123456"代码中获取到设置的可配置参数
twisted异步:
import MySQLdb.cursors
from twisted.enterprise import adbapi
#连接池ConnectionPool
# def __init__(self, dbapiName, *connargs, **connkw):
class MysqlTwistedPipline(object):
def __init__(self, dbpool):
self.dbpool = dbpool
@classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
dbparms = dict(
host = settings["MYSQL_HOST"],
db = settings["MYSQL_DBNAME"],
user = settings["MYSQL_USER"],
passwd = settings["MYSQL_PASSWORD"],
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor,
use_unicode=True,
)
#**dbparms-->("MySQLdb",host=settings['MYSQL_HOST']
dbpool = adbapi.ConnectionPool("MySQLdb", **dbparms)
return cls(dbpool)
def process_item(self, item, spider):
#使用twisted将mysql插入变成异步执行
query = self.dbpool.runInteraction(self.do_insert, item)
query.addErrback(self.handle_error, item, spider) #处理异常
def handle_error(self, failure, item, spider):
#处理异步插入的异常
print (failure)
def do_insert(self, cursor, item):
#执行具体的插入
#根据不同的item 构建不同的sql语句并插入到mysql中
insert_sql, params = item.get_insert_sql()
cursor.execute(insert_sql, params)
可选django.items
https://github.com/scrapy-plugins/scrapy-djangoitem
可以让我们保存的item直接变成django的models.
scrapy的itemloader来维护提取代码
itemloadr提供了一个容器,让我们配置某一个字段该使用哪种规则。
add_css add_value add_xpath
from scrapy.loader import ItemLoader
# 通过item loader加载item
front_image_url = response.meta.get("front_image_url", "") # 文章封面图
item_loader = ItemLoader(item=JobBoleArticleItem(), response=response)
item_loader.add_css("title", ".entry-header h1::text")
item_loader.add_value("url", response.url)
item_loader.add_value("url_object_id", get_md5(response.url))
item_loader.add_css("create_date", "p.entry-meta-hide-on-mobile::text")
item_loader.add_value("front_image_url", [front_image_url])
item_loader.add_css("praise_nums", ".vote-post-up h10::text")
item_loader.add_css("comment_nums", "a[href='#article-comment'] span::text")
item_loader.add_css("fav_nums", ".bookmark-btn::text")
item_loader.add_css("tags", "p.entry-meta-hide-on-mobile a::text")
item_loader.add_css("content", "div.entry")
#调用这个方法来对规则进行解析生成item对象
article_item = item_loader.load_item()
![]()
- 所有值变成了list
- 对于这些值做一些处理函数
item.py中对于item process处理函数
MapCompose可以传入函数对于该字段进行处理,而且可以传入多个
from scrapy.loader.processors import MapCompose
def add_mtianyan(value):
return value+"-mtianyan"
title = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(lambda x:x+"mtianyan",add_mtianyan),
)注意:此处的自定义方法一定要写在代码前面。
create_date = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(date_convert),
output_processor=TakeFirst()
)只取list中的第一个值。
自定义itemloader实现默认提取第一个
class ArticleItemLoader(ItemLoader):
#自定义itemloader实现默认提取第一个
default_output_processor = TakeFirst()list保存原值
def return_value(value):
return value
front_image_url = scrapy.Field(
output_processor=MapCompose(return_value)
)下载图片pipeline增加if增强通用性
class ArticleImagePipeline(ImagesPipeline):
#重写该方法可从result中获取到图片的实际下载地址
def item_completed(self, results, item, info):
if "front_image_url" in item:
for ok, value in results:
image_file_path = value["path"]
item["front_image_path"] = image_file_path
return item自定义的item带处理函数的完整代码
class JobBoleArticleItem(scrapy.Item):
title = scrapy.Field()
create_date = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(date_convert),
)
url = scrapy.Field()
url_object_id = scrapy.Field()
front_image_url = scrapy.Field(
output_processor=MapCompose(return_value)
)
front_image_path = scrapy.Field()
praise_nums = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(get_nums)
)
comment_nums = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(get_nums)
)
fav_nums = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(get_nums)
)
#因为tag本身是list,所以要重写
tags = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(remove_comment_tags),
output_processor=Join(",")
)
content = scrapy.Field()三、知乎网问题和答案爬取
1. 基础知识
session和cookie机制
cookie:
浏览器支持的存储方式
key-valuehttp无状态请求,两次请求没有联系
![]()
session的工作原理
(1)当一个session第一次被启用时,一个唯一的标识被存储于本地的cookie中。
(2)首先使用session_start()函数,从session仓库中加载已经存储的session变量。
(3)通过使用session_register()函数注册session变量。
(4)脚本执行结束时,未被销毁的session变量会被自动保存在本地一定路径下的session库中.
request模拟知乎的登录
http状态码
![]()
获取crsftoken
def get_xsrf():
#获取xsrf code
response = requests.get("https://www.zhihu.com",headers =header)
# # print(response.text)
# text =''
match_obj = re.match('.*name="_xsrf" value="(.*?)"', response.text)
if match_obj:
return (match_obj.group(1))
else:
return ""python模拟知乎登录代码:
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
import requests
try:
import cookielib
except:
import http.cookiejar as cookielib
import re
__author__ = 'mtianyan'
__date__ = '2017/5/23 16:42'
import requests
try:
import cookielib
except:
import http.cookiejar as cookielib
import re
session = requests.session()
session.cookies = cookielib.LWPCookieJar(filename="cookies.txt")
try:
session.cookies.load(ignore_discard=True)
except:
print ("cookie未能加载")
agent = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/53.0.2785.104 Safari/537.36"
header = {
"HOST":"www.zhihu.com",
"Referer": "https://www.zhizhu.com",
'User-Agent': agent
}
def is_login():
#通过个人中心页面返回状态码来判断是否为登录状态
inbox_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/question/56250357/answer/148534773"
response = session.get(inbox_url, headers=header, allow_redirects=False)
if response.status_code != 200:
return False
else:
return True
def get_xsrf():
#获取xsrf code
response = session.get("https://www.zhihu.com", headers=header)
response_text = response.text
#reDOTAll 匹配全文
match_obj = re.match('.*name="_xsrf" value="(.*?)"', response_text, re.DOTALL)
xsrf = ''
if match_obj:
xsrf = (match_obj.group(1))
return xsrf
def get_index():
response = session.get("https://www.zhihu.com", headers=header)
with open("index_page.html", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.text.encode("utf-8"))
print ("ok")
def get_captcha():
import time
t = str(int(time.time()*1000))
captcha_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/captcha.gif?r={0}&type=login".format(t)
t = session.get(captcha_url, headers=header)
with open("captcha.jpg","wb") as f:
f.write(t.content)
f.close()
from PIL import Image
try:
im = Image.open('captcha.jpg')
im.show()
im.close()
except:
pass
captcha = input("输入验证码\n>")
return captcha
def zhihu_login(account, password):
#知乎登录
if re.match("^1\d{10}",account):
print ("手机号码登录")
post_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/login/phone_num"
post_data = {
"_xsrf": get_xsrf(),
"phone_num": account,
"password": password,
"captcha":get_captcha()
}
else:
if "@" in account:
#判断用户名是否为邮箱
print("邮箱方式登录")
post_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/login/email"
post_data = {
"_xsrf": get_xsrf(),
"email": account,
"password": password
}
response_text = session.post(post_url, data=post_data, headers=header)
session.cookies.save()
# get_index()
# is_login()
# get_captcha()
zhihu_login("phone", "password")
zhihu_login("shouji", "mima")2. scrapy创建知乎爬虫登录
scrapy genspider zhihu www.zhihu.com- 1
因为知乎我们需要先进行登录,所以我们重写它的start_requests
def start_requests(self):
return [scrapy.Request('https://www.zhihu.com/#signin', headers=self.headers, callback=self.login)]
-
下载首页然后回调login函数。
-
login函数请求验证码并回调login_after_captcha函数.此处通过meta将post_data传送出去,后面的回调函数来用。
def login(self, response):
response_text = response.text
#获取xsrf。
match_obj = re.match('.*name="_xsrf" value="(.*?)"', response_text, re.DOTALL)
xsrf = ''
if match_obj:
xsrf = (match_obj.group(1))
if xsrf:
post_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/login/phone_num"
post_data = {
"_xsrf": xsrf,
"phone_num": "phone",
"password": "password",
"captcha": ""
}
import time
t = str(int(time.time() * 1000))
captcha_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/captcha.gif?r={0}&type=login".format(t)
#请求验证码并回调login_after_captcha.
yield scrapy.Request(captcha_url, headers=self.headers,
meta={"post_data":post_data}, callback=self.login_after_captcha)- login_after_captcha函数将验证码图片保存到本地,然后使用PIL库打开图片,肉眼识别后在控制台输入验证码值
然后接受步骤一的meta数据,一并提交至登录接口。回调check_login检查是否登录成功。
def login_after_captcha(self, response):
with open("captcha.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.body)
f.close()
from PIL import Image
try:
im = Image.open('captcha.jpg')
im.show()
im.close()
except:
pass
captcha = input("输入验证码\n>")
post_data = response.meta.get("post_data", {})
post_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/login/phone_num"
post_data["captcha"] = captcha
return [scrapy.FormRequest(
url=post_url,
formdata=post_data,
headers=self.headers,
callback=self.check_login
)]- check_login函数,验证服务器的返回数据判断是否成功
scrapy会对request的URL去重(RFPDupeFilter),加上dont_filter则告诉它这个URL不参与去重.
源码中的startrequest:
def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
yield self.make_requests_from_url(url)我们将原本的start_request的代码放在了现在重写的,回调链最后的check_login
def check_login(self, response):
#验证服务器的返回数据判断是否成功
text_json = json.loads(response.text)
if "msg" in text_json and text_json["msg"] == "登录成功":
for url in self.start_urls:
yield scrapy.Request(url, dont_filter=True, headers=self.headers)![]()
3. 知乎数据表设计
![]()
上图为知乎答案版本1
![]()
上图为知乎答案版本2
设置数据表字段
| 问题字段 | 回答字段 |
|---|---|
| zhihu_id | zhihu_id |
| topics | url |
| url | question_id |
| title | author_id |
| content | content |
| answer_num | parise_num |
| comments_num | comments_num |
| watch_user_num | create_time |
| click_num | update_time |
| crawl_time | crawl_time |
![]()
![]()
知乎url分析
点具体问题下查看更多。
可获得接口:
https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/questions/25914034/answers?include=data%5B%2A%5D.is_normal%2Cis_collapsed%2Ccollapse_reason%2Cis_sticky%2Ccollapsed_by%2Csuggest_edit%2Ccomment_count%2Ccan_comment%2Ccontent%2Ceditable_content%2Cvoteup_count%2Creshipment_settings%2Ccomment_permission%2Cmark_infos%2Ccreated_time%2Cupdated_time%2Creview_info%2Crelationship.is_authorized%2Cis_author%2Cvoting%2Cis_thanked%2Cis_nothelp%2Cupvoted_followees%3Bdata%5B%2A%5D.author.follower_count%2Cbadge%5B%3F%28type%3Dbest_answerer%29%5D.topics&limit=20&offset=43&sort_by=default
重点参数:offset=43isend = truenext![]()
href=”/question/25460323”
all_urls = [parse.urljoin(response.url, url) for url in all_urls]- 1
- 从首页获取所有a标签。如果提取的url中格式为 /question/xxx 就下载之后直接进入解析函数parse_question
如果不是question页面则直接进一步跟踪。
def parse(self, response):
"""
提取出html页面中的所有url 并跟踪这些url进行一步爬取
如果提取的url中格式为 /question/xxx 就下载之后直接进入解析函数
"""
all_urls = response.css("a::attr(href)").extract()
all_urls = [parse.urljoin(response.url, url) for url in all_urls]
#使用lambda函数对于每一个url进行过滤,如果是true放回列表,返回false去除。
all_urls = filter(lambda x:True if x.startswith("https") else False, all_urls)
for url in all_urls:
match_obj = re.match("(.*zhihu.com/question/(\d+))(/|$).*", url)
if match_obj:
# 如果提取到question相关的页面则下载后交由提取函数进行提取
request_url = match_obj.group(1)
yield scrapy.Request(request_url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse_question)
else:
# 如果不是question页面则直接进一步跟踪
yield scrapy.Request(url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse)- 进入parse_question函数处理
**创建我们的item
item要用到的方法ArticleSpider\utils\common.py:
def extract_num(text):
#从字符串中提取出数字
match_re = re.match(".*?(\d+).*", text)
if match_re:
nums = int(match_re.group(1))
else:
nums = 0
return numssetting.py中设置SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
SQL_DATE_FORMAT = "%Y-%m-%d"
使用:
from ArticleSpider.settings import SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT- 1
知乎的问题 item
class ZhihuQuestionItem(scrapy.Item):
#知乎的问题 item
zhihu_id = scrapy.Field()
topics = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
answer_num = scrapy.Field()
comments_num = scrapy.Field()
watch_user_num = scrapy.Field()
click_num = scrapy.Field()
crawl_time = scrapy.Field()
def get_insert_sql(self):
#插入知乎question表的sql语句
insert_sql = """
insert into zhihu_question(zhihu_id, topics, url, title, content, answer_num, comments_num,
watch_user_num, click_num, crawl_time
)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(content), answer_num=VALUES(answer_num), comments_num=VALUES(comments_num),
watch_user_num=VALUES(watch_user_num), click_num=VALUES(click_num)
"""
zhihu_id = self["zhihu_id"][0]
topics = ",".join(self["topics"])
url = self["url"][0]
title = "".join(self["title"])
content = "".join(self["content"])
answer_num = extract_num("".join(self["answer_num"]))
comments_num = extract_num("".join(self["comments_num"]))
if len(self["watch_user_num"]) == 2:
watch_user_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][0])
click_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][1])
else:
watch_user_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][0])
click_num = 0
crawl_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
params = (zhihu_id, topics, url, title, content, answer_num, comments_num,
watch_user_num, click_num, crawl_time)
return insert_sql, params知乎问题回答item
class ZhihuAnswerItem(scrapy.Item):
#知乎的问题回答item
zhihu_id = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
question_id = scrapy.Field()
author_id = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
parise_num = scrapy.Field()
comments_num = scrapy.Field()
create_time = scrapy.Field()
update_time = scrapy.Field()
crawl_time = scrapy.Field()
def get_insert_sql(self):
#插入知乎question表的sql语句
insert_sql = """
insert into zhihu_answer(zhihu_id, url, question_id, author_id, content, parise_num, comments_num,
create_time, update_time, crawl_time
) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(content), comments_num=VALUES(comments_num), parise_num=VALUES(parise_num),
update_time=VALUES(update_time)
"""
create_time = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(self["create_time"]).strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
update_time = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(self["update_time"]).strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
params = (
self["zhihu_id"], self["url"], self["question_id"],
self["author_id"], self["content"], self["parise_num"],
self["comments_num"], create_time, update_time,
self["crawl_time"].strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT),
)
return insert_sql, params有了两个item之后,我们继续完善我们的逻辑
def parse_question(self, response):
#处理question页面, 从页面中提取出具体的question item
if "QuestionHeader-title" in response.text:
#处理新版本
match_obj = re.match("(.*zhihu.com/question/(\d+))(/|$).*", response.url)
if match_obj:
question_id = int(match_obj.group(2))
item_loader = ItemLoader(item=ZhihuQuestionItem(), response=response)
item_loader.add_css("title", "h1.QuestionHeader-title::text")
item_loader.add_css("content", ".QuestionHeader-detail")
item_loader.add_value("url", response.url)
item_loader.add_value("zhihu_id", question_id)
item_loader.add_css("answer_num", ".List-headerText span::text")
item_loader.add_css("comments_num", ".QuestionHeader-actions button::text")
item_loader.add_css("watch_user_num", ".NumberBoard-value::text")
item_loader.add_css("topics", ".QuestionHeader-topics .Popover div::text")
question_item = item_loader.load_item()
else:
#处理老版本页面的item提取
match_obj = re.match("(.*zhihu.com/question/(\d+))(/|$).*", response.url)
if match_obj:
question_id = int(match_obj.group(2))
item_loader = ItemLoader(item=ZhihuQuestionItem(), response=response)
# item_loader.add_css("title", ".zh-question-title h2 a::text")
item_loader.add_xpath("title", "//*[@id='zh-question-title']/h2/a/text()|//*[@id='zh-question-title']/h2/span/text()")
item_loader.add_css("content", "#zh-question-detail")
item_loader.add_value("url", response.url)
item_loader.add_value("zhihu_id", question_id)
item_loader.add_css("answer_num", "#zh-question-answer-num::text")
item_loader.add_css("comments_num", "#zh-question-meta-wrap a[name='addcomment']::text")
# item_loader.add_css("watch_user_num", "#zh-question-side-header-wrap::text")
item_loader.add_xpath("watch_user_num", "//*[@id='zh-question-side-header-wrap']/text()|//*[@class='zh-question-followers-sidebar']/div/a/strong/text()")
item_loader.add_css("topics", ".zm-tag-editor-labels a::text")
question_item = item_loader.load_item()
yield scrapy.Request(self.start_answer_url.format(question_id, 20, 0), headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse_answer)
yield question_item处理问题回答提取出需要的字段
def parse_answer(self, reponse):
#处理question的answer
ans_json = json.loads(reponse.text)
is_end = ans_json["paging"]["is_end"]
next_url = ans_json["paging"]["next"]
#提取answer的具体字段
for answer in ans_json["data"]:
answer_item = ZhihuAnswerItem()
answer_item["zhihu_id"] = answer["id"]
answer_item["url"] = answer["url"]
answer_item["question_id"] = answer["question"]["id"]
answer_item["author_id"] = answer["author"]["id"] if "id" in answer["author"] else None
answer_item["content"] = answer["content"] if "content" in answer else None
answer_item["parise_num"] = answer["voteup_count"]
answer_item["comments_num"] = answer["comment_count"]
answer_item["create_time"] = answer["created_time"]
answer_item["update_time"] = answer["updated_time"]
answer_item["crawl_time"] = datetime.datetime.now()
yield answer_item
if not is_end:
yield scrapy.Request(next_url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse_answer)知乎提取字段流程图:
![]()
深度优先:
1. 提取出页面所有的url,并过滤掉不需要的url
2. 如果是questionurl就进入question的解析
3. 把该问题的爬取完了然后就返回初始解析
将item写入数据库
pipelines.py错误处理
插入时错误可通过该方法监控
def handle_error(self, failure, item, spider):
#处理异步插入的异常
print (failure)改造pipeline使其变得更通用
原本具体硬编码的pipeline
def do_insert(self, cursor, item):
#执行具体的插入
insert_sql = """
insert into jobbole_article(title, url, create_date, fav_nums)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)
"""
cursor.execute(insert_sql, (item["title"], item["url"], item["create_date"], item["fav_nums"]))改写后的:
def do_insert(self, cursor, item):
#根据不同的item 构建不同的sql语句并插入到mysql中
insert_sql, params = item.get_insert_sql()
cursor.execute(insert_sql, params)可选方法一:
if item.__class__.__name__ == "JobBoleArticleItem":
#执行具体的插入
insert_sql = """
insert into jobbole_article(title, url, create_date, fav_nums)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)
"""
cursor.execute(insert_sql, (item["title"], item["url"], item["create_date"], item["fav_nums"]))推荐方法:
把sql语句等放到item里面:
jobboleitem类内部方法
def get_insert_sql(self):
insert_sql = """
insert into jobbole_article(title, url, create_date, fav_nums)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(fav_nums)
"""
params = (self["title"], self["url"], self["create_date"], self["fav_nums"])
return insert_sql, params知乎问题:
def get_insert_sql(self):
#插入知乎question表的sql语句
insert_sql = """
insert into zhihu_question(zhihu_id, topics, url, title, content, answer_num, comments_num,
watch_user_num, click_num, crawl_time
)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(content), answer_num=VALUES(answer_num), comments_num=VALUES(comments_num),
watch_user_num=VALUES(watch_user_num), click_num=VALUES(click_num)
"""
zhihu_id = self["zhihu_id"][0]
topics = ",".join(self["topics"])
url = self["url"][0]
title = "".join(self["title"])
content = "".join(self["content"])
answer_num = extract_num("".join(self["answer_num"]))
comments_num = extract_num("".join(self["comments_num"]))
if len(self["watch_user_num"]) == 2:
watch_user_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][0])
click_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][1])
else:
watch_user_num = int(self["watch_user_num"][0])
click_num = 0
crawl_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
params = (zhihu_id, topics, url, title, content, answer_num, comments_num,
watch_user_num, click_num, crawl_time)
return insert_sql, params知乎回答:
def get_insert_sql(self):
#插入知乎回答表的sql语句
insert_sql = """
insert into zhihu_answer(zhihu_id, url, question_id, author_id, content, parise_num, comments_num,
create_time, update_time, crawl_time
) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(content), comments_num=VALUES(comments_num), parise_num=VALUES(parise_num),
update_time=VALUES(update_time)
"""
create_time = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(self["create_time"]).strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
update_time = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(self["update_time"]).strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT)
params = (
self["zhihu_id"], self["url"], self["question_id"],
self["author_id"], self["content"], self["parise_num"],
self["comments_num"], create_time, update_time,
self["crawl_time"].strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT),
)
return insert_sql, params第二次爬取到相同数据,更新数据
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content=VALUES(content), answer_num=VALUES(answer_num), comments_num=VALUES(comments_num),
watch_user_num=VALUES(watch_user_num), click_num=VALUES(click_num)调试技巧
if match_obj:
#如果提取到question相关的页面则下载后交由提取函数进行提取
request_url = match_obj.group(1)
yield scrapy.Request(request_url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse_question)
#方便调试
break
else:
#方便调试
pass
#如果不是question页面则直接进一步跟踪
#方便调试
# yield scrapy.Request(url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse) #方便调试
# yield question_item错误排查
[key error] title
pipeline中debug定位到哪一个item的错误。
四、通过CrawlSpider对招聘网站拉钩网进行整站爬取
推荐工具cmder
http://cmder.net/
下载full版本,使我们在windows环境下也可以使用linux部分命令。
配置path环境变量
1. 设计拉勾网的数据表结构
![]()
2. 初始化拉钩网项目并解读crawl源码
scrapy genspider --list
查看可使用的初始化模板
ailable templates:
- basic
- crawl
- csvfeed
- xmlfeed
scrapy genspider -t crawl lagou www.lagou.comcmd与pycharm不同,mark root
setting.py 设置目录
crawl模板
class LagouSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'lagou'
allowed_domains = ['www.lagou.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.lagou.com/']
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'Items/'), callback='parse_item', follow=True),
)
def parse_item(self, response):
i = {}
#i['domain_id'] = response.xpath('//input[@id="sid"]/@value').extract()
#i['name'] = response.xpath('//div[@id="name"]').extract()
#i['description'] = response.xpath('//div[@id="description"]').extract()
return i源码阅读剖析
https://doc.scrapy.org/en/1.3/topics/spiders.html#crawlspider
提供了一些可以让我们进行简单的follow的规则,link,迭代爬取
rules:
规则,crawel spider读取并执行
parse_start_url(response):
example:
rules是一个可迭代对象,里面有Rule实例->LinkExtractor的分析allow=('category\.php', ), callback='parse_item',
allow允许的url模式。callback,要回调的函数名。
因为rules里面没有self,无法获取到方法。
import scrapy
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
class MySpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'example.com'
allowed_domains = ['example.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.example.com']
rules = (
# Extract links matching 'category.php' (but not matching 'subsection.php')
# and follow links from them (since no callback means follow=True by default).
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('category\.php', ), deny=('subsection\.php', ))),
# Extract links matching 'item.php' and parse them with the spider's method parse_item
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('item\.php', )), callback='parse_item'),
)
def parse_item(self, response):
self.logger.info('Hi, this is an item page! %s', response.url)
item = scrapy.Item()
item['id'] = response.xpath('//td[@id="item_id"]/text()').re(r'ID: (\d+)')
item['name'] = response.xpath('//td[@id="item_name"]/text()').extract()
item['description'] = response.xpath('//td[@id="item_description"]/text()').extract()
return item 分析拉勾网模板代码
1. 将http加上s
2. 重命名parse_item为我们自定义的parse_job
3. 点击class LagouSpider(CrawlSpider):的CrawlSpider,进入crawl源码
4. class CrawlSpider(Spider):可以看出它继承于spider
5. 入口:def start_requests(self):
6. alt+左右方向键,不同代码跳转
7. 5->之后默认parse CrawlSpider里面有parse函数。但是这次我们不能向以前一样覆盖
Crawl.py核心函数parse。
parse函数调用_parse_response
def parse(self, response):
return self._parse_response(response, self.parse_start_url, cb_kwargs={}, follow=True)_parse_response
- 判断是否有callback即有没有self.parse_start_url
- 我们可以重载parse_start_url加入自己的处理
- 把参数传递给函数,并调用process_results函数
_parse_response函数
def _parse_response(self, response, callback, cb_kwargs, follow=True):
if callback:
cb_res = callback(response, **cb_kwargs) or ()
cb_res = self.process_results(response, cb_res)
for requests_or_item in iterate_spider_output(cb_res):
yield requests_or_item
if follow and self._follow_links:
for request_or_item in self._requests_to_follow(response):
yield request_or_itemparse_start_url的return值将会被process_results方法接收处理
如果不重写,因为返回为空,然后就相当于什么都没做
def process_results(self, response, results):
return results点击followlink
def set_crawler(self, crawler):
super(CrawlSpider, self).set_crawler(crawler)
self._follow_links = crawler.settings.getbool('CRAWLSPIDER_FOLLOW_LINKS', True)如果setting中有这个参数,则可以进一步执行到parse
_requests_to_follow
1. 判断传入的是不是response,如果不是直接returns
2. 针对当前response设置一个空set,去重
3. 把self的rules通过enumerate变成一个可迭代对象
4. 跳转rules详情
5. 拿到link通过link_extractor.extract_links抽取出具体的link
6. 执行我们的process_links
7. link制作完成发起Request,回调_response_downloaded函数
8. 然后执行parse_respose
def _requests_to_follow(self, response):
if not isinstance(response, HtmlResponse):
return
seen = set()
for n, rule in enumerate(self._rules):
links = [lnk for lnk in rule.link_extractor.extract_links(response)
if lnk not in seen]
if links and rule.process_links:
links = rule.process_links(links)
for link in links:
seen.add(link)
r = Request(url=link.url, callback=self._response_downloaded)
r.meta.update(rule=n, link_text=link.text)
yield rule.process_request(r)_compile_rules
- 在我们初始化时会调用_compile_rules
copy.copy(r) for r in self.rules]将我们的rules进行一个copy- 调用回调函数get_method。
- 调用rules里面我们定义的process_links
- 调用rules里面我们定义的process_request
def _compile_rules(self):
def get_method(method):
if callable(method):
return method
elif isinstance(method, six.string_types):
return getattr(self, method, None)
self._rules = [copy.copy(r) for r in self.rules]
for rule in self._rules:
rule.callback = get_method(rule.callback)
rule.process_links = get_method(rule.process_links)
rule.process_request = get_method(rule.process_request) self.process_links = process_links
self.process_request = process_request
可以通过在rules里面传入我们自己的处理函数,实现对url的自定义。
达到负载均衡,多地不同ip访问。
_response_downloaded
通过rule取到具体的rule
调用我们自己的回调函数
def _response_downloaded(self, response):
rule = self._rules[response.meta['rule']]
return self._parse_response(response, rule.callback, rule.cb_kwargs, rule.follow)- allow :符合这个url我就爬取
- deny : 符合这个url规则我就放弃
- allow_domin : 这个域名下的我才处理
- allow_domin : 这个域名下的我不处理
- restrict_xpaths:进一步限定xpath
self, allow=(), deny=(), allow_domains=(), deny_domains=(), restrict_xpaths=(),
tags=('a', 'area'), attrs=('href',), canonicalize=True,
unique=True, process_value=None, deny_extensions=None, restrict_css=()extract_links
如果有restrict_xpaths,他会进行读取执行
def extract_links(self, response):
base_url = get_base_url(response)
if self.restrict_xpaths:
docs = [subdoc
for x in self.restrict_xpaths
for subdoc in response.xpath(x)]
else:
docs = [response.selector]
all_links = []
for doc in docs:
links = self._extract_links(doc, response.url, response.encoding, base_url)
all_links.extend(self._process_links(links))
return unique_list(all_links)get_base_url:
urllib.parse.urljoin替我们拼接好url
def get_base_url(text, baseurl='', encoding='utf-8'):
"""Return the base url if declared in the given HTML `text`,
relative to the given base url.
If no base url is found, the given `baseurl` is returned.
"""
text = to_unicode(text, encoding)
m = _baseurl_re.search(text)
if m:
return moves.urllib.parse.urljoin(
safe_url_string(baseurl),
safe_url_string(m.group(1), encoding=encoding)
)
else:
return safe_url_string(baseurl)编写rule规则
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=("zhaopin/.*",)), follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=("gongsi/j\d+.html",)), follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'jobs/\d+.html'), callback='parse_job', follow=True),
)3. 设计lagou的items
需要用到的方法
from w3lib.html import remove_tags
def remove_splash(value):
#去掉工作城市的斜线
return value.replace("/","")
def handle_jobaddr(value):
addr_list = value.split("\n")
addr_list = [item.strip() for item in addr_list if item.strip()!="查看地图"]
return "".join(addr_list)定义好的item
class LagouJobItem(scrapy.Item):
#拉勾网职位信息
title = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
url_object_id = scrapy.Field()
salary = scrapy.Field()
job_city = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(remove_splash),
)
work_years = scrapy.Field(
input_processor = MapCompose(remove_splash),
)
degree_need = scrapy.Field(
input_processor = MapCompose(remove_splash),
)
job_type = scrapy.Field()
publish_time = scrapy.Field()
job_advantage = scrapy.Field()
job_desc = scrapy.Field()
job_addr = scrapy.Field(
input_processor=MapCompose(remove_tags, handle_jobaddr),
)
company_name = scrapy.Field()
company_url = scrapy.Field()
tags = scrapy.Field(
input_processor = Join(",")
)
crawl_time = scrapy.Field()
重写的itemloader
设置默认只提取第一个
class LagouJobItemLoader(ItemLoader):
#自定义itemloader
default_output_processor = TakeFirst()4. 提取字段值并存入数据库
def parse_job(self, response):
#解析拉勾网的职位
item_loader = LagouJobItemLoader(item=LagouJobItem(), response=response)
item_loader.add_css("title", ".job-name::attr(title)")
item_loader.add_value("url", response.url)
item_loader.add_value("url_object_id", get_md5(response.url))
item_loader.add_css("salary", ".job_request .salary::text")
item_loader.add_xpath("job_city", "//*[@class='job_request']/p/span[2]/text()")
item_loader.add_xpath("work_years", "//*[@class='job_request']/p/span[3]/text()")
item_loader.add_xpath("degree_need", "//*[@class='job_request']/p/span[4]/text()")
item_loader.add_xpath("job_type", "//*[@class='job_request']/p/span[5]/text()")
item_loader.add_css("tags", '.position-label li::text')
item_loader.add_css("publish_time", ".publish_time::text")
item_loader.add_css("job_advantage", ".job-advantage p::text")
item_loader.add_css("job_desc", ".job_bt div")
item_loader.add_css("job_addr", ".work_addr")
item_loader.add_css("company_name", "#job_company dt a img::attr(alt)")
item_loader.add_css("company_url", "#job_company dt a::attr(href)")
item_loader.add_value("crawl_time", datetime.now())
job_item = item_loader.load_item()
return job_item获得的拉勾网item数据![]()
5. items中添加get_insert_sql实现存入数据库
def get_insert_sql(self):
insert_sql = """
insert into lagou_job(title, url, url_object_id, salary, job_city, work_years, degree_need,
job_type, publish_time, job_advantage, job_desc, job_addr, company_name, company_url,
tags, crawl_time) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE salary=VALUES(salary), job_desc=VALUES(job_desc)
"""
params = (
self["title"], self["url"], self["url_object_id"], self["salary"], self["job_city"],
self["work_years"], self["degree_need"], self["job_type"],
self["publish_time"], self["job_advantage"], self["job_desc"],
self["job_addr"], self["company_name"], self["company_url"],
self["job_addr"], self["crawl_time"].strftime(SQL_DATETIME_FORMAT),
)
return insert_sql, params五、爬虫与反爬虫
1. 基础知识
如何使我们的爬虫不被禁止掉
爬虫:
自动获取数据的程序,关键是批量的获取
反爬虫:
使用技术手段防止爬虫程序的方法
误伤:
反爬虫技术将普通用户识别为爬虫,效果再好也不能用
学校,网吧,出口的公网ip只有一个,所以禁止ip不能用。
ip动态分配。a爬封b
成本:
反爬虫人力和机器成本
拦截:
拦截率越高,误伤率越高
反爬虫的目的:
![]()
爬虫与反爬虫的对抗过程:
![]()
使用检查可以查看到价格,而查看网页源代码无法查看到价格字段。
scrapy下载到的网页时网页源代码。
js(ajax)填充的动态数据无法通过网页获取到。
2. scrapy架构及源码介绍
![]()
![]()
- 我们编写的spider,然后yield一个request发送给engine
- engine拿到什么都不做然后给scheduler
- engine会生成一个request给engine
- engine拿到之后通过downloadermiddleware 给downloader
- downloader再发送response回来给engine。
- engine拿到之后,response给spider。
- spider进行处理,解析出item & request,
- item->给itempipeline;如果是request,跳转步骤二
path:articlespider3\Lib\site-packages\scrapy\core
- engine.py:
- scheduler.py
-
downloader
-
item
- pipeline
- spider
engine.py:重要函数schedule
- enqueue_request:把request放scheduler
- _next_request_from_scheduler:从调度器拿。
def schedule(self, request, spider):
self.signals.send_catch_log(signal=signals.request_scheduled,
request=request, spider=spider)
if not self.slot.scheduler.enqueue_request(request):
self.signals.send_catch_log(signal=signals.request_dropped,
request=request, spider=spider)articlespider3\Lib\site-packages\scrapy\core\downloader\handlers
支持文件,ftp,http下载(https).
后期定制middleware:
- spidermiddlewire
- downloadmiddlewire
django和scrapy结构类似
3. scrapy的两个重要类:request和response
类似于django httprequest
yield Request(url=parse.urljoin(response.url, post_url))- 1
request参数:
class Request(object_ref):
def __init__(self, url, callback=None, method='GET', headers=None, body=None,
cookies=None, meta=None, encoding='utf-8', priority=0,
dont_filter=False, errback=None):cookies:
Lib\site-packages\scrapy\downloadermiddlewares\cookies.py
cookiejarkey = request.meta.get("cookiejar")- priority: 优先级,影响调度顺序
- dont_filter:我的同样的request不会被过滤
- errback:错误时的回调函数
https://doc.scrapy.org/en/1.2/topics/request-response.html?highlight=response
errback example:
class ErrbackSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "errback_example"
start_urls = [
"http://www.httpbin.org/", # HTTP 200 expected
"http://www.httpbin.org/status/404", # Not found error
"http://www.httpbin.org/status/500", # server issue
"http://www.httpbin.org:12345/", # non-responding host, timeout expected
"http://www.httphttpbinbin.org/", # DNS error expected
]
def start_requests(self):
for u in self.start_urls:
yield scrapy.Request(u, callback=self.parse_httpbin,
errback=self.errback_httpbin,
dont_filter=True)
def parse_httpbin(self, response):
self.logger.info('Got successful response from {}'.format(response.url))
# do something useful here...
def errback_httpbin(self, failure):
# log all failures
self.logger.error(repr(failure))
# in case you want to do something special for some errors,
# you may need the failure's type:
if failure.check(HttpError):
# these exceptions come from HttpError spider middleware
# you can get the non-200 response
response = failure.value.response
self.logger.error('HttpError on %s', response.url)
elif failure.check(DNSLookupError):
# this is the original request
request = failure.request
self.logger.error('DNSLookupError on %s', request.url)
elif failure.check(TimeoutError, TCPTimedOutError):
request = failure.request
self.logger.error('TimeoutError on %s', request.url)response类
def __init__(self, url, status=200, headers=None, body=b'', flags=None, request=None):
self.headers = Headers(headers or {})response的参数:
request:yield出来的request,会放在response,让我们知道它是从哪里来的
4. 自行编写随机更换useagent
- setting中设置
user_agent_list = [
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:51.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/51.0',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/53.0.2785.104 Safari/537.36',
]然后在代码中使用。
from settings import user_agent_list
import random
random_index =random.randint(0,len(user_agent_list))
random_agent = user_agent_list[random_index]
'User-Agent': random_agent import random
random_index = random.randint(0, len(user_agent_list))
random_agent = user_agent_list[random_index]
self.headers["User-Agent"] = random_agent
yield scrapy.Request(request_url, headers=self.headers, callback=self.parse_question)但是问题:每个request之前都得这样做。
5. middlewire配置及编写fake UseAgent代理池
取消DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES的注释状态
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'ArticleSpider.middlewares.MyCustomDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
}articlespider3\Lib\site-packages\scrapy\downloadermiddlewares\useragent.py
class UserAgentMiddleware(object):
"""This middleware allows spiders to override the user_agent"""
def __init__(self, user_agent='Scrapy'):
self.user_agent = user_agent
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
o = cls(crawler.settings['USER_AGENT'])
crawler.signals.connect(o.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
return o
def spider_opened(self, spider):
self.user_agent = getattr(spider, 'user_agent', self.user_agent)
def process_request(self, request, spider):
if self.user_agent:
request.headers.setdefault(b'User-Agent', self.user_agent)重要方法process_request
**配置默认useagent为none
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'ArticleSpider.middlewares.MyCustomDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
'scrapy.downloadermiddlewares.useragent.UserAgentMiddleware': None
}使用fakeuseragentpip install fake-useragent
settinf.py设置随机模式RANDOM_UA_TYPE = "random"
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
class RandomUserAgentMiddlware(object):
#随机更换user-agent
def __init__(self, crawler):
super(RandomUserAgentMiddlware, self).__init__()
self.ua = UserAgent()
self.ua_type = crawler.settings.get("RANDOM_UA_TYPE", "random")
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
return cls(crawler)
def process_request(self, request, spider):
def get_ua():
return getattr(self.ua, self.ua_type)
request.headers.setdefault('User-Agent', get_ua())6. 使用西刺代理创建ip代理池保存到数据库*
ip动态变化:重启路由器等
ip代理的原理:
不直接发送自己真实ip,而使用中间代理商(代理服务器),那么服务器不知道我们的ip也就不会把我们禁掉
setting.py设置
“
class RandomProxyMiddleware(object):
#动态设置ip代理
def process_request(self, request, spider):
request.meta["proxy"] = "http://111.198.219.151:8118"使用西刺代理创建代理池保存到数据库
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
__author__ = 'mtianyan'
__date__ = '2017/5/24 16:27'
import requests
from scrapy.selector import Selector
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host="127.0.0.1", user="root", passwd="password", db="article_spider", charset="utf8")
cursor = conn.cursor()
def crawl_ips():
#爬取西刺的免费ip代理
headers = {"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:52.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/52.0"}
for i in range(1568):
re = requests.get("http://www.xicidaili.com/nn/{0}".format(i), headers=headers)
selector = Selector(text=re.text)
all_trs = selector.css("#ip_list tr")
ip_list = []
for tr in all_trs[1:]:
speed_str = tr.css(".bar::attr(title)").extract()[0]
if speed_str:
speed = float(speed_str.split("秒")[0])
all_texts = tr.css("td::text").extract()
ip = all_texts[0]
port = all_texts[1]
proxy_type = all_texts[5]
ip_list.append((ip, port, proxy_type, speed))
for ip_info in ip_list:
cursor.execute(
"insert proxy_ip(ip, port, speed, proxy_type) VALUES('{0}', '{1}', {2}, 'HTTP')".format(
ip_info[0], ip_info[1], ip_info[3]
)
)
conn.commit()
class GetIP(object):
def delete_ip(self, ip):
#从数据库中删除无效的ip
delete_sql = """
delete from proxy_ip where ip='{0}'
""".format(ip)
cursor.execute(delete_sql)
conn.commit()
return True
def judge_ip(self, ip, port):
#判断ip是否可用
http_url = "http://www.baidu.com"
proxy_url = "http://{0}:{1}".format(ip, port)
try:
proxy_dict = {
"http":proxy_url,
}
response = requests.get(http_url, proxies=proxy_dict)
except Exception as e:
print ("invalid ip and port")
self.delete_ip(ip)
return False
else:
code = response.status_code
if code >= 200 and code < 300:
print ("effective ip")
return True
else:
print ("invalid ip and port")
self.delete_ip(ip)
return False
def get_random_ip(self):
#从数据库中随机获取一个可用的ip
random_sql = """
SELECT ip, port FROM proxy_ip
ORDER BY RAND()
LIMIT 1
"""
result = cursor.execute(random_sql)
for ip_info in cursor.fetchall():
ip = ip_info[0]
port = ip_info[1]
judge_re = self.judge_ip(ip, port)
if judge_re:
return "http://{0}:{1}".format(ip, port)
else:
return self.get_random_ip()
# print (crawl_ips())
if __name__ == "__main__":
get_ip = GetIP()
get_ip.get_random_ip()使用scrapy_proxies创建ip代理池
pip install scrapy_proxies
收费,但是简单
https://github.com/scrapy-plugins/scrapy-crawlera
tor隐藏。
http://www.theonionrouter.com/
7. 通过云打码实现验证码的识别
http://www.yundama.com/
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
__author__ = 'mtianyan'
__date__ = '2017/6/24 16:48'
import json
import requests
class YDMHttp(object):
apiurl = 'http://api.yundama.com/api.php'
username = ''
password = ''
appid = ''
appkey = ''
def __init__(self, username, password, appid, appkey):
self.username = username
self.password = password
self.appid = str(appid)
self.appkey = appkey
def balance(self):
data = {'method': 'balance', 'username': self.username, 'password': self.password, 'appid': self.appid, 'appkey': self.appkey}
response_data = requests.post(self.apiurl, data=data)
ret_data = json.loads(response_data.text)
if ret_data["ret"] == 0:
print ("获取剩余积分", ret_data["balance"])
return ret_data["balance"]
else:
return None
def login(self):
data = {'method': 'login', 'username': self.username, 'password': self.password, 'appid': self.appid, 'appkey': self.appkey}
response_data = requests.post(self.apiurl, data=data)
ret_data = json.loads(response_data.text)
if ret_data["ret"] == 0:
print ("登录成功", ret_data["uid"])
return ret_data["uid"]
else:
return None
def decode(self, filename, codetype, timeout):
data = {'method': 'upload', 'username': self.username, 'password': self.password, 'appid': self.appid, 'appkey': self.appkey, 'codetype': str(codetype), 'timeout': str(timeout)}
files = {'file': open(filename, 'rb')}
response_data = requests.post(self.apiurl, files=files, data=data)
ret_data = json.loads(response_data.text)
if ret_data["ret"] == 0:
print ("识别成功", ret_data["text"])
return ret_data["text"]
else:
return None
def ydm(file_path):
username = ''
# 密码
password = ''
# 软件ID,开发者分成必要参数。登录开发者后台【我的软件】获得!
appid =
# 软件密钥,开发者分成必要参数。登录开发者后台【我的软件】获得!
appkey = ''
# 图片文件
filename = 'image/1.jpg'
# 验证码类型,# 例:1004表示4位字母数字,不同类型收费不同。请准确填写,否则影响识别率。在此查询所有类型 http://www.yundama.com/price.html
codetype = 5000
# 超时时间,秒
timeout = 60
# 检查
yundama = YDMHttp(username, password, appid, appkey)
if (username == 'username'):
print('请设置好相关参数再测试')
else:
# 开始识别,图片路径,验证码类型ID,超时时间(秒),识别结果
return yundama.decode(file_path, codetype, timeout);
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 用户名
username = ''
# 密码
password = ''
# 软件ID,开发者分成必要参数。登录开发者后台【我的软件】获得!
appid =
# 软件密钥,开发者分成必要参数。登录开发者后台【我的软件】获得!
appkey = ''
# 图片文件
filename = 'image/captcha.jpg'
# 验证码类型,# 例:1004表示4位字母数字,不同类型收费不同。请准确填写,否则影响识别率。在此查询所有类型 http://www.yundama.com/price.html
codetype = 5000
# 超时时间,秒
timeout = 60
# 检查
if (username == 'username'):
print ('请设置好相关参数再测试')
else:
# 初始化
yundama = YDMHttp(username, password, appid, appkey)
# 登陆云打码
uid = yundama.login();
print('uid: %s' % uid)
# 登陆云打码
uid = yundama.login();
print ('uid: %s' % uid)
# 查询余额
balance = yundama.balance();
print ('balance: %s' % balance)
# 开始识别,图片路径,验证码类型ID,超时时间(秒),识别结果
text = yundama.decode(filename, codetype, timeout);
8. cookie的禁用。& 设置下载速度
http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/topics/autothrottle.html
setting.py:
# Disable cookies (enabled by default)
COOKIES_ENABLED = False设置下载速度:
# The initial download delay
#AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5给不同的spider设置自己的setting值
custom_settings = {
"COOKIES_ENABLED": True
}六、scrapy进阶开发
1. Selenium动态页面抓取
Selenium (浏览器自动化测试框架)
Selenium是一个用于Web应用程序测试的工具。Selenium测试直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样。支持的浏览器包括IE(7, 8, 9, 10, 11),Mozilla Firefox,Safari,Google Chrome,Opera等。这个工具的主要功能包括:测试与浏览器的兼容性——测试你的应用程序看是否能够很好得工作在不同浏览器和操作系统之上。测试系统功能——创建回归测试检验软件功能和用户需求。支持自动录制动作和自动生成 .Net、Java、Perl等不同语言的测试脚本
![]()
安装pip install selenium
文档地址:
http://selenium-python.readthedocs.io/api.html
安装webdriver.exe
天猫价格获取
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.selector import Selector
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe")
#天猫价格获取
browser.get("https://detail.tmall.com/item.htm?spm=a230r.1.14.3.yYBVG6&id=538286972599&cm_id=140105335569ed55e27b&abbucket=15&sku_properties=10004:709990523;5919063:6536025")
t_selector = Selector(text=browser.page_source)
print (t_selector.css(".tm-price::text").extract())
# print (browser.page_source)
browser.quit()知乎模拟登录
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.selector import Selector
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe")
#知乎模拟登陆
browser.get("https://www.zhihu.com/#signin")
browser.find_element_by_css_selector(".view-signin input[name='account']").send_keys("phone")
browser.find_element_by_css_selector(".view-signin input[name='password']").send_keys("password")
browser.find_element_by_css_selector(".view-signin button.sign-button").click()微博模拟登录
微博开放平台api
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.selector import Selector
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe")
#selenium 完成微博模拟登录
browser.get("http://weibo.com/")
import time
time.sleep(5)
browser.find_element_by_css_selector("#loginname").send_keys("[email protected]")
browser.find_element_by_css_selector(".info_list.password input[node-type='password'] ").send_keys("password")
browser.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="pl_login_form"]/div/div[3]/div[6]/a').click()模拟JavaScript鼠标下滑
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.selector import Selector
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe")
#开源中国博客
browser.get("https://www.oschina.net/blog")
import time
time.sleep(5)
for i in range(3):
browser.execute_script("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight); var lenOfPage=document.body.scrollHeight; return lenOfPage;")
time.sleep(3)页面不加载图片
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.selector import Selector
# 设置chromedriver不加载图片
chrome_opt = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
prefs = {"profile.managed_default_content_settings.images":2}
chrome_opt.add_experimental_option("prefs", prefs)
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe",chrome_options=chrome_opt)
browser.get("https://www.oschina.net/blog")phantomjs无界面的浏览器获取天猫价格
#phantomjs, 无界面的浏览器, 多进程情况下phantomjs性能会下降很严重
browser = webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path="C:/phantomjs-2.1.1-windows/bin/phantomjs.exe")
browser.get("https://detail.tmall.com/item.htm?spm=a230r.1.14.3.yYBVG6&id=538286972599&cm_id=140105335569ed55e27b&abbucket=15&sku_properties=10004:709990523;5919063:6536025")
t_selector = Selector(text=browser.page_source)
print (t_selector.css(".tm-price::text").extract())
print (browser.page_source)
# browser.quit()2.selenium集成进scrapy
如何集成
创建中间件。
from selenium import webdriver
from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse
class JSPageMiddleware(object):
#通过chrome请求动态网页
def process_request(self, request, spider):
if spider.name == "jobbole":
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe")
spider.browser.get(request.url)
import time
time.sleep(3)
print ("访问:{0}".format(request.url))
return HtmlResponse(url=spider.browser.current_url, body=spider.browser.page_source, encoding="utf-8", request=request)使用selenium集成到具体spider中
信号量:
dispatcher.connect 信号的映射,当spider结束该做什么
from scrapy.xlib.pydispatch import dispatcher
from scrapy import signals
#使用selenium
def __init__(self):
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="D:/Temp/chromedriver.exe")
super(JobboleSpider, self).__init__()
dispatcher.connect(self.spider_closed, signals.spider_closed)
def spider_closed(self, spider):
#当爬虫退出的时候关闭chrome
print ("spider closed")
self.browser.quit()- python下无界面浏览器
pip install pyvirtualdisplay
linux使用:
from pyvirtualdisplay import Display
display = Display(visible=0, size=(800, 600))
display.start()
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get()错误:cmd=[‘xvfb’,’help’]
os error
sudo apt-get install xvfb
pip install xvfbwrapper
scrapy-splash:
支持分布式,稳定性不如chorme
https://github.com/scrapy-plugins/scrapy-splash
selenium grid
支持分布式
splinter
https://github.com/cobrateam/splinter
scrapy的暂停重启
scrapy crawl lagou -s JOBDIR=job_info/001
pycharm进程直接杀死 kiil -9
一次 ctrl+c可接受信号
Lib\site-packages\scrapy\dupefilters.py
先hash将url变成定长的字符串
然后使用集合set去重
telnet
远程登录
telnet localhost 6023 连接当前spiderest()命令查看spider当前状态
spider.settings["COOKIES_ENABLED"]
Lib\site-packages\scrapy\extensions\telnet.py
数据收集 & 状态收集
Scrapy提供了方便的收集数据的机制。数据以key/value方式存储,值大多是计数值。 该机制叫做数据收集器(Stats Collector),可以通过 Crawler API 的属性 stats 来使用。在下面的章节 常见数据收集器使用方法 将给出例子来说明。
无论数据收集(stats collection)开启或者关闭,数据收集器永远都是可用的。 因此您可以import进自己的模块并使用其API(增加值或者设置新的状态键(stat keys))。 该做法是为了简化数据收集的方法: 您不应该使用超过一行代码来收集您的spider,Scrpay扩展或任何您使用数据收集器代码里头的状态。
http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/topics/stats.html
状态收集,数据收集器
# 收集伯乐在线所有404的url以及404页面数
handle_httpstatus_list = [404]七、scrapy-redis 分布式爬虫
1. 分布式爬虫设计及redis介绍
多个爬虫如何进行调度,一个集中的状态管理器
优点:
- 利用多机器带宽
- 利用多ip加速爬取速度
两个问题:
- request队列的集中管理
- 去重集中管理
分布式。
2. redis命令
hexists course_dict mtianyan
hexists course_dict mtianyan2
Redis HEXISTS命令被用来检查哈希字段是否存在。
返回值
回复整数,1或0。
- 1, 如果哈希包含字段。
- 0 如果哈希不包含字段,或key不存在。
hdel course_dict mtianyan
Redis HDEL命令用于从存储在键散列删除指定的字段。如果没有这个哈希中存在指定的字段将被忽略。如果键不存在,它将被视为一个空的哈希与此命令将返回0。
返回值回复整数,从散列中删除的字段的数量,不包括指定的但不是现有字段。
hgetall course_dict
Redis Hgetall 命令用于返回哈希表中,所有的字段和值。
在返回值里,紧跟每个字段名(field name)之后是字段的值(value),所以返回值的长度是哈希表大小的两倍。
hset course_dict bobby “python scrapy”
Redis Hset 命令用于为哈希表中的字段赋值 。
如果哈希表不存在,一个新的哈希表被创建并进行 HSET 操作。
如果字段已经存在于哈希表中,旧值将被覆盖。
hkey course_dict
Redis Keys 命令用于查找所有符合给定模式 pattern 的 key 。。
hvals course_dict
Redis Hvals 命令返回哈希表所有字段的值。
lpush mtianyan “scary”
rpush mtianyan “scary”
存入key-value
lrange mtianyan 0 10
取出mtianyan的0到10
![]()
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| lpop/rpop | 左删除/右删除 |
| llen mtianyan | 长度 |
| lindex mtianyan 3 | 第几个元素 |
| sadd | 集合做减法 |
| siner | 交集 |
| spop | 随机删除 |
| srandmember | 随机选择多个元素 |
| smembers | 获取set所有元素 |
| srandmember | 随机选择多个元素 |
| zadd | 每个数有分数 |
| zcount key 0 100 | 0-100分数据量统计 |
3. scrapy-redis搭建分布式爬虫
需要的环境:
Python 2.7, 3.4 or 3.5
Redis >= 2.8
Scrapy >= 1.1
redis-py >= 2.10
pip install redis
setting.py设置
SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler"
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 300
}要继承redisspider
from scrapy_redis.spiders import RedisSpider
class MySpider(RedisSpider):
name = 'myspider'
def parse(self, response):
# do stuff
pass启动spider
scrapy runspider myspider.py
push urls to redis:放置初始url进入队列
redis-cli lpush myspider:start_urls http://google.com
搭建示例
1. 创建新的scrapy项目
2. 去github拷贝scrapy-redis源码
不同spider使用不同redis list
将队列从内存放入redis中
next_requests
所有的yield出去的request会被
ScrapyRedisTest\scrapy_redis\scheduler.py
的以及重写的enqueue_request接收
八、elasticsearch搭建搜索引擎
elasticsearch介绍:一个基于lucene的搜索服务器,分布式多用户的全文搜索引擎 java开发的 基于restful web接口
自己搭建的网站或者程序,添加搜索功能比较困难
所以我们希望搜索解决方案要高效
零配置并且免费
能够简单的通过json和http与搜索引擎交互
希望搜索服务很稳定
简单的将一台服务器扩展到多台服务器
内部功能:
分词 搜索结果打分 解析搜索要求
全文搜索引擎:solr sphinx
很多大公司都用elasticsearch 戴尔 Facebook 微软等等
-
elasticsearch对Lucene进行了封装,既能存储数据,又能分析数据,适合与做搜索引擎
关系数据搜索缺点:
无法对搜素结果进行打分排序
没有分布式,搜索麻烦,对程序员的要求比较高
无法解析搜索请求,对搜索的内容无法进行解析,如分词等
数据多了,效率低
需要分词,把关系,数据,重点分出来 -
nosql数据库:
文档数据库 json代码,在关系数据库中数据存储,需要存到多个表,内部有多对多等关系之类的,需要涉及到多个表才能将json里面的内容存下来,nosql直接将一个json的内容存起来,作为一个文档存档到数据库。
mongodb:
1. elasticsearch安装与配置
- java sdk安装
- elasticsearch安装官网下载 不使用官网的版本,提供原始的插件不多
- elasticsearc-rtf github搜索,中文发行版,已经安装了很多插件 https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-rtf
- 运行elasticsearch的方法,在bin文件目录下进入命令行,执行elasticsearch.bat
5.配置文件:elasticsearch-rtf\elasticsearch-rtf-master\config\elasticsearch.yml
![]()
2. elasticsearch两个重要插件:head和kibana的安装
head插件相当于Navicat,用于管理数据库,基于浏览器
https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head
Running with built in server
git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git
cd elasticsearch-head
npm install
npm run start
open http://localhost:9100/配置elasticsearch与heade互通
![]()
kibana.bat
![]()
2. elasticsearch基础概念
- 集群:一个或多个节点组织在一起
- 节点:一个集群中的一台服务器
- 分片:索引划分为多份的能力,允许水平分割,扩展容量,多个分片响应请求
- 副本:分片的一份或多分,一个节点失败,其他节点顶上
|index | 数据库|
|type | 表|
|document | 行|
|fields | 列|
集合搜索和保存:增加了五种方法:
OPTIONS & PUT & DELETE & TRACE & CONNECT
3. 倒排索引:
![]()
![]()
倒排索引待解决的问题:
![]()
![]()
![]()
4. elasticsearch命令
PUT lagou/job/1
1为idPUT lagou/job/
不指明id自动生成uuid。修改部分字段
POST lagou/job/1/_updateDELETE lagou/job/1
elasticserach批量操作:
查询index为testdb下的job1表的id为1和job2表的id为2的数据
GET _mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_index":"testdb",
"_type":"job1",
"_id":1
},
{
"_index":"testdb",
"_type":"job2",
"_id":2
}
]
}index已经指定了,所有在doc中就不用指定了
GET testdb/_mget{
"docs":[
{
"_type":"job1",
"_id":1
},
{
"_type":"job2",
"_id":2
}
]
}连type都一样,只是id不一样
GET testdb/job1/_megt
{
"docs":[
{
"_id":1
},
{
"_id":2
}
]
}或者继续简写
GET testdb/job1/_megt
{
"ids":[1,2]
}elasticsearch的bulk批量操作:可以合并多个操作,比如index,delete,update,create等等,包括从一个索引到另一个索引:
- action_and_meta_data\n
- option_source\n
- action_and_meta_data\n
- option_source\n
- ….
- action_and_meta_data\n
- option_source\n
每个操作都是由两行构成,除了delete除外,由元信息行和数据行组成
注意数据不能美化,即只能是两行的形式,而不能是经过解析的标准的json排列形式,否则会报错
POST _bulk
{"index":...}
{"field":...}elasticserach的mapping映射
elasticserach的mapping映射:创建索引时,可以预先定义字段的类型以及相关属性,每个字段定义一种类型,属性比mysql里面丰富,前面没有传入,因为elasticsearch会根据json源数据来猜测是什么基础类型。M挨批评就是我们自己定义的字段的数据类型,同时告诉elasticsearch如何索引数据以及是否可以被搜索。
作用:会让索引建立的更加细致和完善,对于大多数是不需要我们自己定义
相关属性的配置
- String类型: 两种text keyword。text会对内部的内容进行分析,索引,进行倒排索引等,为设置为keyword则会当成字符串,不会被分析,只能完全匹配才能找到String。 在es5已经被废弃了
- 日期类型:date 以及datetime等
- 数据类型:integer long double等等
- bool类型
- binary类型
- 复杂类型:object nested
- geo类型:geo-point地理位置
- 专业类型:ip competition
- object :json里面内置的还有下层{}的对象
- nested:数组形式的数据
elasticserach查询:
大概分为三类:
- 基本查询:
- 组合查询:
- 过滤:查询同时,通过filter条件在不影响打分的情况下筛选数据
match查询:
后面为关键词,关于python的都会提取出来,match查询会对内容进行分词,并且会自动对传入的关键词进行大小写转换,内置ik分词器会进行切分,如python网站,只要搜到存在的任何一部分,都会返回
GET lagou/job/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"title":"python"
}
}
}term查询
区别,对传入的值不会做任何处理,就像keyword,只能查包含整个传入的内容的,一部分也不行,只能完全匹配
terms查询
title里传入多个值,只要有一个匹配,就会返回结果
控制查询的返回数量
GET lagou/_serach
{
"query":{
"match":{
"title":"python"
}
},
"form":1,
"size":2
}通过这里就可以完成分页处理洛,从第一条开始查询两条
match_all 返回所有
GET lagou/_search
{
“query”:{
“match_all”:{}
}
}
match_phrase查询 短语查询
GET lagou/_search
{
"query":{
"match_phrase":{
"title":{
"query":"python系统",
"slop":6
}
}
}
}python系统,将其分词,分为词条,满足词条里面的所有词才会返回结果,slop参数说明两个词条之间的最小距离
multi_match查询
比如可以指定多个字段,比如查询title和desc这两个字段包含python的关键词文档
GET lagou/_search
{
"query":{
"multi_match":{
"query":"python",
"fileds":["title^3","desc"]
}
}
}query为要查询的关键词 fileds在哪些字段里查询关键词,只要其中某个字段中出现了都返回
^3的意思为设置权重,在title中找到的权值为在desc字段中找到的权值的三倍
指定返回字段
GET lagou/_search{
"stored_fields":["title","company_name"],
"query":{
"match":{
"title":"pyhton"
}
}
}通过sort把结果排序
GET lagou/_search
{
"query";{
"match_all":{}
},
"sort":[{
"comments":{
"order":"desc"
}
}]
}
sort是一个数组,里面是一个字典,key就是要sort的字段,asc desc是升序降序的意思
查询范围 range查询
GET lagou/_search
{
“query”;{
“range”:{
“comments”:{
“gte”:10,
“lte”:20,
“boost”:2.0
}
}
}
}
range是在query里面的,boost是权重,gte lte是大于等于 小于等于的意思
对时间的范围查询,则是以字符串的形式传入
wildcard模糊查询,可以使用通配符*
组合查询:bool查询
bool查询包括了must should must_not filter来完成
格式如下:
bool:{
"filter":[],
"must":[],
"should":[],
"must_not":[],
}
5. 把爬取的数据保存至elasticsearch
class ElasticsearchPipeline(object):
#将数据写入到es中
def process_item(self, item, spider):
#将item转换为es的数据
item.save_to_es()
return itemelasticsearch-dsl-py
High level Python client for Elasticsearch
pip install elasticsearch-dsl
items.py 中将数据保存至es
def save_to_es(self):
article = ArticleType()
article.title = self['title']
article.create_date = self["create_date"]
article.content = remove_tags(self["content"])
article.front_image_url = self["front_image_url"]
if "front_image_path" in self:
article.front_image_path = self["front_image_path"]
article.praise_nums = self["praise_nums"]
article.fav_nums = self["fav_nums"]
article.comment_nums = self["comment_nums"]
article.url = self["url"]
article.tags = self["tags"]
article.meta.id = self["url_object_id"]
article.suggest = gen_suggests(ArticleType._doc_type.index, ((article.title,10),(article.tags, 7)))
article.save()
redis_cli.incr("jobbole_count")
return6. elasticsearch结合django搭建搜索引擎
获取elasticsearch的查询接口
body={
"query":{
"multi_match":{
"query":key_words,
"fields":["tags", "title", "content"]
}
},
"from":(page-1)*10,
"size":10,
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": [''],
"post_tags": [''],
"fields": {
"title": {},
"content": {},
}
}
}使django与其交互。
--------------------- 本文来自 天涯明月笙 的CSDN 博客 ,全文地址请点击:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_23079443/article/details/73920584?utm_source=copy