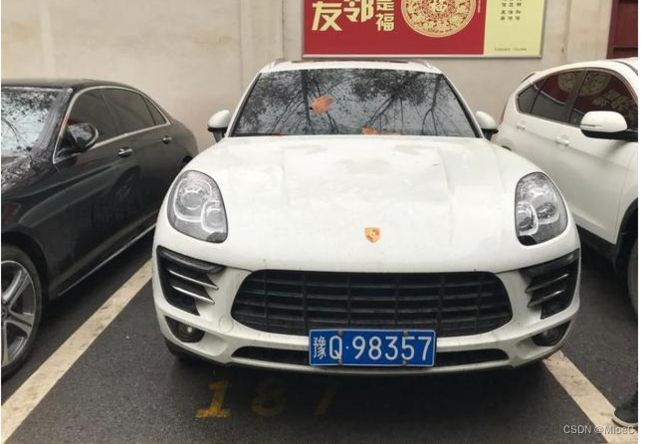
运用opencv 进行 车牌的识别(1)
文章目录
- 简介:
- 项目准备
- 项目阶段
- 车牌的处理和提取
-
- 原理:
- 实现:
- 筛选图像
- 分隔字符
- 函数入口定义
- 效果展示
- 完整代码
简介:
**无人停车场可以说是目前人工智能应用最普通的一个,核心的技术在于车牌的识别,那么作为人工智能的狂热者,自然不能错过这么好的项目。赶紧开始吧! **
项目准备
- python 环境
- opencv环境
- numpy环境
项目阶段
- 提取车牌部分
- 进行车牌的字符分隔
- 进行车牌的字符识别
- 进行车牌的倾斜调整等特殊情况优化
- 项目的落地和部署
车牌的处理和提取
原理:
- 对车牌进行去噪,运用opencv的形态学操作等方法分割成多个部分
- 根据车牌的比例,进行轮廓的筛选,识别出车牌部分
实现:
- 读取图片, 灰度处理
img = cv.imread(path)
img_gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- 进行高斯处理,运用sobel算子计算轮廓
img_gs = cv.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (5, 5), 0, 0, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
#sobel
sobel_x = cv.Sobel(img_gs, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0)
# sobel_y = cv.Sobel(img_gs, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1)
absX = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobel_x)
# absY = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobel_y)
# img = cv.addWeighted(sobel_x, 0.5, sobel_y, 0.5, 0)
image = absX
- 二值化处理,自适应
ret, image = cv.threshold(image, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
- 进行一次闭合操作, 连接一些小白点
kernelX = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (17, 5))
image = cv.morphologyEx(image, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernelX, iterations=3)
- 进行腐蚀膨胀操作, 去除一些噪点,扩大轮廓区域
#去除小白点
kernelX = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (20, 1))
kernelY = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (1, 19))
image = cv.erode(image, kernelX)
image = cv.erode(image, kernelY)
image = cv.dilate(image, kernelX)
image = cv.dilate(image, kernelY)
- 中值滤波,为了降低噪点
# 中值滤波
image = cv.medianBlur(image, 15)
- 进行轮廓检测
# 轮廓检测
contours, hierarchy = cv.findContours(image, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
筛选图像
- 一般车牌比例为长:宽 = 1:3~1:6, 根据这个原理
def filter_photo(img, contours):
# img_copy = img.copy()
for cont in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv.boundingRect(cont)
# cv.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
area = cv.contourArea(cont)
w_rate_h = float(w/h)
if(w_rate_h >= 3 and w_rate_h <= 6):
lpimage = img[y: y+h, x: x+w]
break
return lpimage, x, y, w, h
分隔字符
- 字符的分割比较简单,将图片进行二值化,提取白色的数字即可
# 字符分割
def split_img(img1):
img = cv.cvtColor(img1, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, before_threshold = cv.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
img = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (3, 3), 0)
ret, threshold = cv.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
# 变胖
kernel = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
edge1 = cv.morphologyEx(threshold, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# 中值去噪
edge2 = cv.medianBlur(edge1, 3)
# 提取轮廓
contours, hierarchy = cv.findContours(edge2, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
words = []
# 这里需要对选区进行处理,过滤高和宽的比在0.5~2.3内的数字
for i, cont in enumerate(contours):
word = []
x, y, w, h = cv.boundingRect(cont)
ratew_h = h/w
# cv.rectangle(img1, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
if ratew_h > 0.5 and ratew_h < 2.3:
word.append((x, y, w, h))
words.append(word)
words = sorted(words, key=lambda s: s[0], reverse=False)
# cv.drawContours(img1, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 截图处理
for i, area in enumerate(words):
(x, y, w, h) = area[0]
num_img = before_threshold[y: y+ h, x: x+ w]
# num_img = cv.cvtColor(num_img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# ret, num_img = cv.threshold(num_img, 177, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
cv.imwrite('./split/i%s.png'%i, num_img)
函数入口定义
def main():
path = './car1.png'
img, contours = hander_img(path)
area, x, y, w, h = filter_photo(img, contours)
split_img(area)
# cv.imwrite('./pai.png', area)
# cv.imshow('img2', area)
# cv.waitKey(0)
# cv.destroyAllWindows()
main()
效果展示
完整代码
- 车牌提取
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def hander_img(path):
img = cv.imread(path)
img_gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_gs = cv.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (5, 5), 0, 0, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
#sobel
sobel_x = cv.Sobel(img_gs, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0)
# sobel_y = cv.Sobel(img_gs, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1)
absX = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobel_x)
# absY = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobel_y)
# img = cv.addWeighted(sobel_x, 0.5, sobel_y, 0.5, 0)
image = absX
ret, image = cv.threshold(image, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
kernelX = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (17, 5))
image = cv.morphologyEx(image, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernelX, iterations=3)
#去除小白点
kernelX = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (20, 1))
kernelY = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (1, 19))
image = cv.erode(image, kernelX)
image = cv.erode(image, kernelY)
image = cv.dilate(image, kernelX)
image = cv.dilate(image, kernelY)
# 中值滤波
image = cv.medianBlur(image, 15)
# 轮廓检测
contours, hierarchy = cv.findContours(image, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# cv.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0),3)
# cv.imshow('img', image)
# cv.imshow('img2', image)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
return img, contours
- 车牌定位
def filter_photo(img, contours):
# img_copy = img.copy()
for cont in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv.boundingRect(cont)
# cv.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
area = cv.contourArea(cont)
w_rate_h = float(w/h)
if(w_rate_h >= 3 and w_rate_h <= 6):
lpimage = img[y: y+h, x: x+w]
break
return lpimage, x, y, w, h
cv.imshow("photo", img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
- 分割字符
# 字符分割
def split_img(img1):
img = cv.cvtColor(img1, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, before_threshold = cv.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
img = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (3, 3), 0)
ret, threshold = cv.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_OTSU)
# 变胖
kernel = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
edge1 = cv.morphologyEx(threshold, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# 中值去噪
edge2 = cv.medianBlur(edge1, 3)
# 提取轮廓
contours, hierarchy = cv.findContours(edge2, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
words = []
for i, cont in enumerate(contours):
word = []
x, y, w, h = cv.boundingRect(cont)
ratew_h = h/w
# cv.rectangle(img1, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
if ratew_h > 0.5 and ratew_h < 2.3:
word.append((x, y, w, h))
words.append(word)
words = sorted(words, key=lambda s: s[0], reverse=False)
# cv.drawContours(img1, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 截图处理
for i, area in enumerate(words):
(x, y, w, h) = area[0]
num_img = before_threshold[y: y+ h, x: x+ w]
# num_img = cv.cvtColor(num_img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# ret, num_img = cv.threshold(num_img, 177, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
cv.imwrite('./split/i%s.png'%i, num_img)
- main
def main():
path = './car2.png'
img, contours = hander_img(path)
area, x, y, w, h = filter_photo(img, contours)
split_img(area)
# cv.imwrite('./pai.png', area)
cv.imshow('img2', area)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
main()