《高等运筹学》复习题手写解答 Advanced Operations Research: Final Exam:Review Exercises
文章目录
- Nonlinear Program 非线性规划
-
- KKT condition KKT条件
- Golden section method 黄金分割法
- Newton's method 牛顿法
- Gradient steepest descent/ ascent method 梯度下降/上升法
- Integer Programming 整数规划
-
- Branch and bound 分支定界法
- Gomory cutting plane algorithm 割平面法/ Column generation 列生成算法
- Dynamic programming 动态规划
-
- IP 有整数约束
- LP 无整数约束
- Linear programming 线性规划
-
- Central path 中心路径法(内点法)
- Karmarkar算法(内点法)
- Eliposoid method 椭球法(外点法)
- Transportation problem & unimodular matrix 运输问题与幺模矩阵
- Graph Theory 图论
-
- Maximum flow 最大流
- 附原题
Nonlinear Program 非线性规划
Problem 29.
Suppose p < 1 , p ≠ 0 p<1,p\neq 0 p<1,p=0 . Show that the function of
f ( x ) = ( ∑ i = 1 n x i p ) 1 / p f(x) ={( \sum_{i=1}^nx_i^p)}^{1/p} f(x)=(i=1∑nxip)1/p with d o m f = R + + n domf = R^n_{++} domf=R++n is concave.
Solution

Problem 18.
Let Ω Ω Ω be a subset of E n E^n En and let f ∈ C 2 f \in C^2 f∈C2 be a function on Ω Ω Ω. If x ∗ x^∗ x∗ is a relative minimum point of f f f over Ω Ω Ω, then for any d ∈ E n d\in E^n d∈En that is a feasible direction at x ∗ x^∗ x∗ we have
- ▽ f ( x ∗ ) d ≥ 0 \triangledown f(x^*)d\geq 0 ▽f(x∗)d≥0
- if ▽ f ( x ∗ ) d = 0 \triangledown f(x^*)d=0 ▽f(x∗)d=0, then d T ▽ 2 f ( x ∗ ) d ≥ 0 d^T\triangledown^2 f(x^*)d\geq 0 dT▽2f(x∗)d≥0
Solution
Problem 4.
Find the minimum number of c c c, such that any local optimal solution is a global optimal solution for the following nonlinear program of P 4 P4 P4.
P 4 ) max f ( x ) = − c ∗ x 1 2 + x 1 x 2 + 2 x 1 − 1 2 x 2 2 s . t . x 1 ≤ 2 P4) \max \ f(x) = −c∗x^2_1 + x_1x_2 + 2x_1 − \frac{1}{2}x_2^2 \\ s.t. \ \ x_1 ≤ 2 P4)max f(x)=−c∗x12+x1x2+2x1−21x22s.t. x1≤2
Solution

KKT condition KKT条件
Problem 3.
Show the KKT condition for the nonlinear program of P 3 P3 P3, and try to solve it with the KKT conditions.
P 3 ) max − 2 x 1 2 − 2 x 1 x 2 − x 2 2 + 10 x 1 + 10 x 2 s . t . x 1 2 + x 2 2 ≤ 5 3 x 1 + x 2 ≤ 6 P3) \ \max{ \ −2x^2_1 −2x_1x_2 −x^2_2 + 10x_1 + 10x_2} \\ s.t. \ \ \ x^2_1 + x^2_2 ≤ 5 \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ 3x_1 + x_2 ≤ 6 P3) max −2x12−2x1x2−x22+10x1+10x2s.t. x12+x22≤5 3x1+x2≤6
Solution

Golden section method 黄金分割法
Problem 16.
For the problem min f ( x ) \min{f(x)} minf(x) over x ∈ [ a , b ] x\in [a,b] x∈[a,b], we use golden section method to solve it. Please prove the convergence ratio is 0.618 0.618 0.618.
Newton’s method 牛顿法
Problem 17.
For one dimension nonlinear problem min f ( x ) \min f(x) minf(x) over x ∈ [ a , b ] x\in [a,b] x∈[a,b], we use Newton’s Method to solve it. Please prove the convergence ratio of Newton’s method is at least two.
Gradient steepest descent/ ascent method 梯度下降/上升法
*Problem 4.
max f ( x ) = − 1 2 x 1 2 + x 1 x 2 + 2 x 1 − 1 2 x 2 2 \max \ f(x) = −\frac{1}{2}x^2_1 + x_1x_2 + 2x_1 − \frac{1}{2}x_2^2 \\ max f(x)=−21x12+x1x2+2x1−21x22 Use the gradient steepest ascent method to find the optimal solution of above nonlinear program, with the start point x 0 = ( 0 , 4 ) T x_0 = (0,4)^T x0=(0,4)T.
Integer Programming 整数规划
Branch and bound 分支定界法
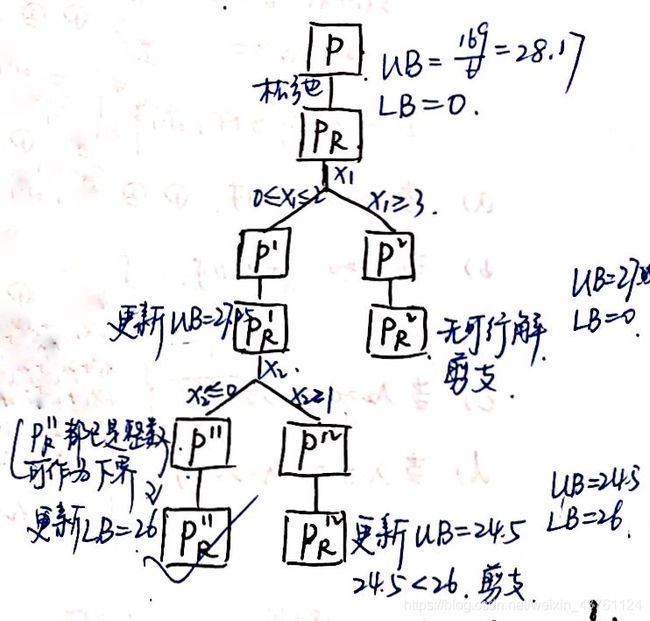
Problem 1.
Use branch and bound method to solve P 1 ) P1) P1).
Note that at each branching node, you can use graphic method to get the (local) upper bound for each node.
Draw the branch and bound tree, and point out the Node Program, GLB and LUB clearly.
P 1 ) max 13 x 1 + 5 x 2 s . t . 3 x 1 + 2 x 2 ≤ 6.5 − 2 x 1 + 3 x 2 ≤ 8 x 1 , x 2 ≥ 0 , i n t e g e r s P1) \max{\ \ \ 13x_1+5x_2}\\ s.t. \ \ 3x_1+2x_2\leq 6.5\\ -2x_1+3x_2\leq 8\\ x_1,x_2\geq0,integers P1)max 13x1+5x2s.t. 3x1+2x2≤6.5−2x1+3x2≤8x1,x2≥0,integers
Solution

branch and bound tree
Gomory cutting plane algorithm 割平面法/ Column generation 列生成算法
Problem 26.
min c T x s . t . Ax = b x ∈ i n t e g e r \min \textbf{\textit{c}}^T\textbf{\textit{x}}\\ s.t. \textbf{\textit{Ax}}=\textbf{\textit{b}}\\ \textbf{\textit{x}}\in integer mincTxs.t.Ax=bx∈integerFor above I P IP IP, suppose now we have a basic feasible solution corresponding to basis matrix B \textbf{\textit{B}} B and Non-basis N \textbf{\textit{N}} N, i.e., A = ( B , N ) \textbf{\textit{A}} = (\textbf{\textit{B}},\textbf{\textit{N}}) A=(B,N), and let a i j = ( B − 1 A j ) i a_{ij} = (\textbf{\textit{B}}^{−1}\textbf{\textit{A}}_j)_i aij=(B−1Aj)iand a i 0 = ( B − 1 b ) i a_{i0} = (\textbf{\textit{B}}^{−1}\textbf{\textit{b}})_i ai0=(B−1b)i. Prove:
x i + ∑ j ∈ N ⌊ a i j ⌋ x j ≤ ⌊ a i 0 ⌋ x_i+\sum_{j\in \textbf{\textit{N}}}\left \lfloor a_{ij} \right \rfloor x_{j}\leq \left \lfloor a_{i0} \right \rfloor xi+j∈N∑⌊aij⌋xj≤⌊ai0⌋
Solution

Problem 12.
Use the Gomory cutting plane algorithm to solve the following integer linear programming.
min x 1 − 2 x 2 s . t . − 4 x 1 + 6 x 2 ≤ 9 x 1 + x 2 ≤ 4 x 1 , x 2 ≥ 0 , i n t e g e r s \min \ \ x_1 −2x_2\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \\ s.t. \ \ −4x_1 + 6x_2 ≤ 9 \\ x_1 + x_2 ≤ 4 \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x_1,x_2 ≥ 0, integers min x1−2x2 s.t. −4x1+6x2≤9x1+x2≤4 x1,x2≥0,integers
Solution

Problem 28.
I P ) min c T x s . t . A x = b x ≥ 0 a n d ∈ i n t e g e r s IP)\min{c^Tx} \\ s.t.\ \ Ax = b \\ x ≥ 0 \ and \in integers IP)mincTxs.t. Ax=bx≥0 and∈integersFor above I P IP IP, denote A = [ a 1 , a 2 , ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ , a n ] A = [a_1,a_2,··· ,a_n] A=[a1,a2,⋅⋅⋅,an] by columns. Let k < n k
I P R ) min c T x s . t . A x = b x ≥ 0 IPR)\min{c^Tx} \\ s.t.\ \ Ax = b \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ x ≥ 0 IPR)mincTxs.t. Ax=b x≥0 I P R k ) min c T x s . t . A k x = b x ≥ 0 IPR_k)\min{c^Tx} \\ s.t.\ \ A_kx = b \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ x ≥ 0 IPRk)mincTxs.t. Akx=b x≥0Suppose x k ∗ x_k^* xk∗, and x ∗ x^∗ x∗ is the optimal solution for subproblem I P R k ) IPR_k) IPRk) and I P R ) IPR) IPR) respectively, and objectives of O B J I P R k OBJ_{IPR_k} OBJIPRk, O B J I P R OBJ_{IPR} OBJIPR correspondingly. Let S = { a 1 , a 2 , ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ , a n } S = \{a_1,a_2,··· ,a_n\} S={a1,a2,⋅⋅⋅,an}, B B B is the basis related to x k ∗ x^∗_k xk∗ for I P R k IPR_k IPRk.
P P ) min c a − c B B − 1 a s . t . a ∈ S PP)\min c_a −c_BB^{−1}a\\ s.t.\ \ a \in S PP)minca−cBB−1as.t. a∈SPlease prove: If O B J P P ≥ 0 OBJ_{PP} ≥ 0 OBJPP≥0, then O B J I P R k = O B J I P R OBJ_{IPR_k} = OBJ_{IPR} OBJIPRk=OBJIPR
Dynamic programming 动态规划
IP 有整数约束
Problem 8.
Use dynamic programming method to solve the following integer programming.
max 2 x 1 + 3 x 2 + x 3 + 2 x 4 s . t . 5 x 1 + 7 x 2 + 6 x 3 + 5 x 4 ≤ 14 x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 ≥ 0 , i n t e g e r s \max {\ \ 2x_1 + 3x_2 + x_3 + 2x_4}\\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ s.t. \ \ \ 5x_1 + 7x_2 + 6x_3 + 5x_4 ≤ 14\\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4 ≥ 0, integers max 2x1+3x2+x3+2x4 s.t. 5x1+7x2+6x3+5x4≤14 x1,x2,x3,x4≥0,integersNote that you need to point out recursive formula clearly, and write down calculation steps clearly.
LP 无整数约束
*Problem 8.
Use dynamic programming method to solve the following linear programming.
max 2 x 1 + 3 x 2 + x 3 + 2 x 4 s . t . 5 x 1 + 7 x 2 + 6 x 3 + 5 x 4 ≤ 14 x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 ≥ 0 , \max {\ \ 2x_1 + 3x_2 + x_3 + 2x_4}\\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ s.t. \ \ \ 5x_1 + 7x_2 + 6x_3 + 5x_4 ≤ 14\\ \ \ \ \ x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4 ≥ 0, max 2x1+3x2+x3+2x4 s.t. 5x1+7x2+6x3+5x4≤14 x1,x2,x3,x4≥0,Note that you need to point out recursive formula clearly, and write down calculation steps clearly.
Linear programming 线性规划
Central path 中心路径法(内点法)
Problem 25.
Let ( x ( μ ) , y ( μ ) , s ( μ ) ) (x(\mu),y(\mu),s(\mu)) (x(μ),y(μ),s(μ)) be the central path of
x ◦ s = μ e A x = b A T y + s = c x ≥ 0 , s ≥ 0 x◦s = \mu e\\ Ax = b\\ A^Ty + s = c\\ x ≥ 0,s ≥ 0 x◦s=μeAx=bATy+s=cx≥0,s≥0 Then prove:
(a) The central path point ( x ( μ ) , y ( μ ) , s ( μ ) ) (x(\mu),y(\mu),s(\mu)) (x(μ),y(μ),s(μ)) is bounded for 0 < μ ≤ μ 0 0 < \mu ≤ \mu_0 0<μ≤μ0 and any given 0 < μ < ∞ 0 < \mu < ∞ 0<μ<∞.
(b) For 0 < μ ′ < μ 0 < {\mu}'< \mu 0<μ′<μ,
c T x ( μ ′ ) ≤ c T x ( μ ) a n d b T y ( μ ′ ) ≥ b T y ( µ ) c^Tx( {\mu}') ≤ c^Tx(\mu)\ \ and\ \ b^Ty( {\mu}') ≥ b^Ty(µ) cTx(μ′)≤cTx(μ) and bTy(μ′)≥bTy(µ)Furthermore, if x ( μ ′ ) ≠ x ( μ ) x( {\mu}')\neq x(\mu) x(μ′)=x(μ) and y ( μ ′ ) ≠ y ( μ ) y( {\mu}')\neq y(\mu) y(μ′)=y(μ).
c T x ( μ ′ ) < c T x ( μ ) a n d b T y ( μ ′ ) > b T y ( µ ) c^Tx( {\mu}') < c^Tx(\mu)\ \ and\ \ b^Ty( {\mu}') > b^Ty(µ) cTx(μ′)<cTx(μ) and bTy(μ′)>bTy(µ)
Solution


Problem 11.
Compute the central path for the following linear programming.
min x 1 s . t . x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 2 \min{\ x_1} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \\ s.t. \ \ x_1 + x_2 + x_3 = 2 min x1 s.t. x1+x2+x3=2
Solution

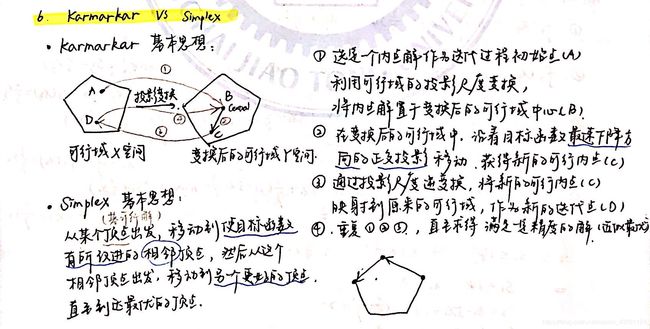
Karmarkar算法(内点法)
Problem 6.
What are the differences between Karmarkar method and Simplex method for linear programming? Please show the logics of them clearly. Possibly you can use figures to show what your idea.
Eliposoid method 椭球法(外点法)
Problem 7.
Use ellipsoid method solve:
max 0 s . t . x 1 + 5 x 2 ≤ 7 x 1 + 2 x 2 ≥ 6 x 1 , x 2 ≥ 0. \max \ \ 0 \\ s.t. \ \ x_1 + 5x_2 ≤ 7 \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x_1 + 2x_2 ≥ 6 \\ \ \ \ \ x_1,x_2 ≥ 0 . max 0s.t. x1+5x2≤7 x1+2x2≥6 x1,x2≥0.The initial Ellipsoid is taken to be E ( 0 , 100 × I 2 × 2 ) E(0,100×I_{2×2}) E(0,100×I2×2).
You only need to give THREE STEPS
Transportation problem & unimodular matrix 运输问题与幺模矩阵
Problem 20.
For transportation problem stated as follows.
There are m origins that contain various amounts of a commodity that must be shipped to n n n destinations to meet demand requirements. Specially, origin i i i contains an amount a i a_i ai, and destination j j j has a requirement of amount b i b_i bi. It is assumed that the system is balanced in the sense that total supply equals total demand. There is unit cost c i j c_{ij} cij associated with the shipping of the commodity from origin i i i to destination j j j. The problem is to find the shipping pattern between origins and destinations that satisfies all the requirements and minimized the total shipping cost.
(1) build an mixed integer linear programming model for above problem.
(2) If the row and column sums of a transportation problem are integers, then the basic variables in any basic solution are integers. 如果运输问题的行和列的和是整数,证明所有基可行解的基变量为整数。
Problem 21.
A matrix A \textbf{\textit{A}} A is said to be totally unimodular if the determinant of every square submatrix formed from it has value 0 , + 1 0,+1 0,+1 or − 1 −1 −1. (完全幺模矩阵的各阶子式均为0,1或-1)
(1) Show that the matrix A \textbf{\textit{A}} A defining the equality constraints of a transportation prolblem is totally unimodular. 证明运输问题的系数矩阵是完全幺模的。
(2) In the system of equations Ax = b \textbf{\textit{Ax}}=\textbf{\textit{b}} Ax=b, assume that A \textbf{\textit{A}} A is totally unimodular and that all elements of A \textbf{\textit{A}} A and b \textbf{\textit{b}} b are integers. Show that all basic solutions have integer components.
与Problem20(2)的区别在于:此时 A \textbf{\textit{A}} A是任意矩阵,秩不再是 m + n − 1 m+n-1 m+n−1
Graph Theory 图论
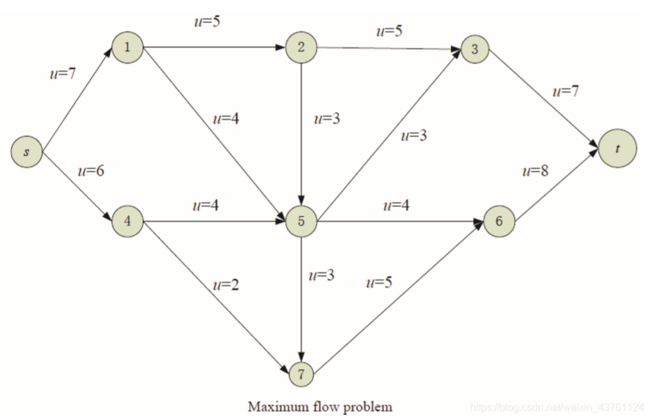
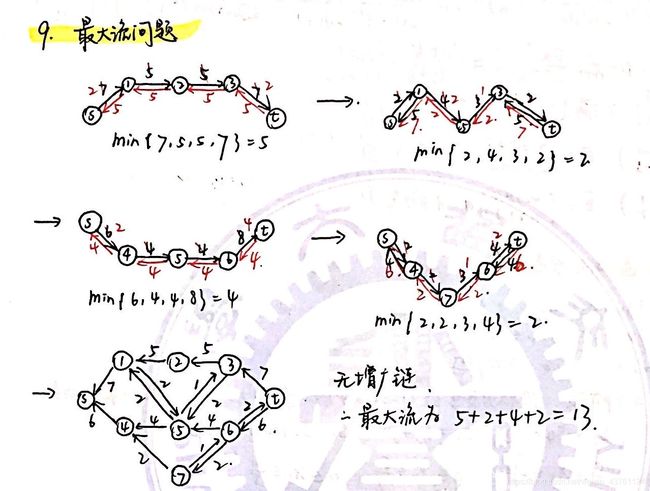
Maximum flow 最大流
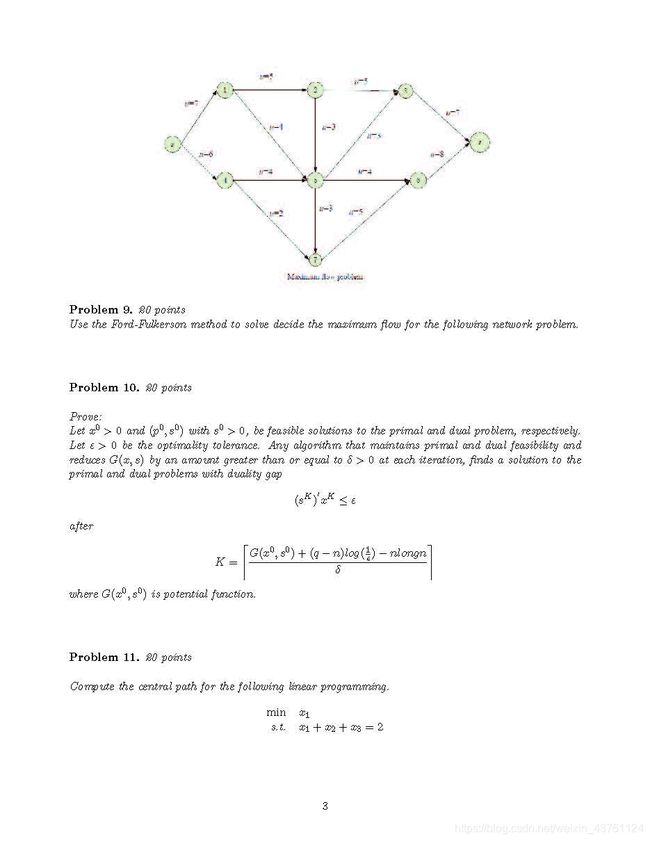
Problem 9.
Use the Ford-Fulkerson method to solve decide the maximum flow for the following network problem.