【计算机视觉实战 2 】、特征匹配之Harris角点
特征匹配之Harris角点
- 前言
- 一、特征匹配的基本流程是什么?
-
- 1.流程
- 2.对特征点的要求
- 二、角点是什么?
-
- 1.角点
- 2.Harris角点检测
- 3.角点描述子
- 4.特征匹配
- 5.SIFT算子
- 总结
前言
图像匹配:
特征点匹配,是图像拼接、三维重建、相机标定等应用的关键步骤
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、特征匹配的基本流程是什么?
1.流程
1、根据特定准测,提取图像中的特征点
2、提取特征点周围的图像块,构造特征描述符
3、通过特征描述符对比,实现特征匹配
2.对特征点的要求
必须具有不变性,比如
几何不变性:位移、旋转、尺度
光度不变性:光照、曝光
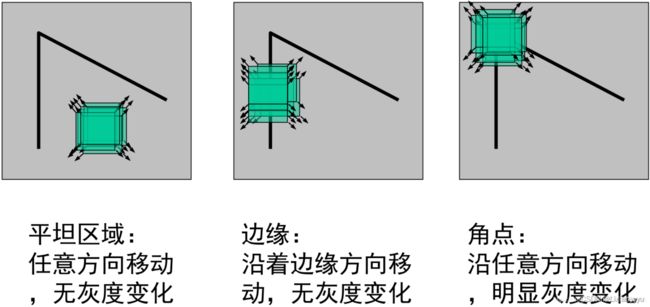
二、角点是什么?
1.角点
1、局部窗口沿各方向移动,均产生明显变化的点,
2、图像局部曲率突变的点
2.Harris角点检测
基本思想
从图像局部的小窗口观察图像特征,
角点:窗口向任何方向的移动都导致图像灰度的明显变化
数学表达
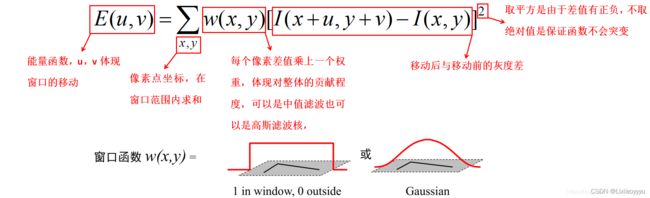
将 函数I(x+u,y+v)在(x,y)处泰勒展开,可得

对M进行特征值分析,并定义R为角点响应函数

3.角点描述子
Harris角点检测紧急能够检测出图像中的兴趣点,没有给出通过比较图像间的兴趣点来寻找匹配角点的方法。
需要在每个点加入描述子信息,

harr角点检测
代码如下(示例):
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
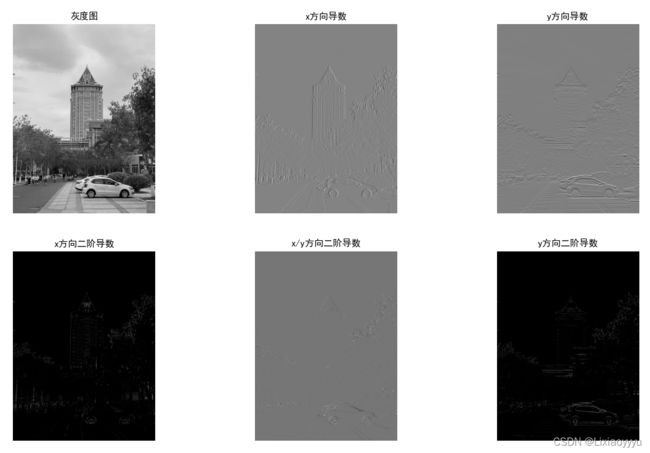
def compute_harris_response(img, sigma=3):
# 计算导数
imx = zeros(img.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(img, (sigma, sigma), (0, 1), imx)
imy = zeros(img.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(img, (sigma, sigma), (1, 0), imy)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 可视化原图
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.title('灰度图')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(img, plt.cm.gray)
# 可视化x方向导数图像
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.title('x方向导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx, plt.cm.gray)
# 可视化y方向导数图像
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.title('y方向导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.title('x方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx * imx, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.title('x/y方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx * imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.title('y方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imy * imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.show()
# 计算Harris矩阵的分量
Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx * imx, sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx * imy, sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy * imy, sigma)
# 计算特征值和迹
# 矩阵特征值的积等于行列式的值
Wdet = Wxx * Wyy - Wxy ** 2
# 主对角线上元素的和称为矩阵的迹,也是特征值的和
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / Wtr
# 从一幅Harris响应图像中返回角点。min_dist为分割角点和图像边界的最少像素数目
def get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=10, threshold=0.1):
# 寻找高于阈值的候选角点
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
# print(corner_threshold)
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
plt.imshow(harrisim_t, plt.cm.gray)
# 得到候选点的坐标(取出是角点的坐标)
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
# print(coords.shape)
# 以及它们的Harris响应值
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0], c[1]] for c in coords]
# 对候选点按照Harris响应值进行排序
index = argsort(candidate_values)
# 将可行点的位置保存到数组中
allowed_location = zeros(harrisim.shape)
# 相当于把外面一圈有响应值的点先舍去(匹配主体在中心)
allowed_location[min_dist:-min_dist, min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# 按照min_distance原则,选择最佳的Harris角点
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_location[coords[i, 0], coords[i, 1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_location[(coords[i, 0] - min_dist):(coords[i, 0] + min_dist),
(coords[i, 1] - min_dist):(coords[i, 1] + min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
# 绘制图像中检测到的角点
def plot_harris_point(image, filtered_coords):
figure()
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
show()
if "__main__" == __name__:
# 打开灰度图convert('L')
img = array(Image.open("IMG_9687.JPG").convert('L'))
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img)
filtered_coords = get_harris_points(harrisim, 6)
plot_harris_point(img, filtered_coords)
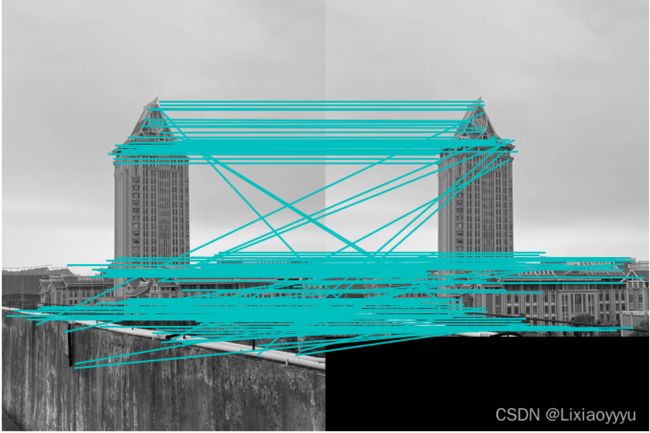
4.特征匹配
分析,对同一幅图片进行特征匹配,效果还是很好的,连接线主要是平行的
但是当从不同角度对尚大楼进行拍摄,就会有很多错误匹配。
图片尺寸均改为500*500

# 获得角点的特征描述(划分以角点为中心的5*5区域)
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid=5):
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid:coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid:coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
# 归一化互相关获得得分
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
n = len(desc1[0])
d = -ones((len(desc1), len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n - 1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i, j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:, 0]
return matchscores
# 进行两边对称版本的匹配
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2, threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1, threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 >= 0)[0]
# 筛去不匹配的点
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] != n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(img1, img2):
rows1 = img1.shape[0]
rows2 = img2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
img1 = concatenate((img1, zeros((rows2 - rows1, img1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
img2 = concatenate((img2, zeros((rows1 - rows2, img2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatenate((img1, img2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(img1, img2, locs1, locs2, matchscores, show_below=False):
img3 = appendimages(img1, img2)
if show_below:
img3 = vstack((img3, img3))
imshow(img3)
cols1 = img1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([locs1[i][1], locs2[m][1] + cols1], [locs1[i][0], locs2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
if "__main__" == __name__:
# 打开灰度图convert('L')
image = Image.open("IMG_9685.JPG").convert('L')
base_width = 500
w_percent = base_width / float(image.size[0])
h_size = int(float(image.size[1]) * float(w_percent))
image1 = image.resize((base_width, h_size), Image.ANTIALIAS)
image1.show()
image2 = Image.open("IMG_96731.JPG").convert('L')
w_percent = base_width / float(image2.size[0])
h_size = int(float(image2.size[1]) * float(w_percent))
image2 = image2.resize((base_width, h_size), Image.ANTIALIAS)
image2.show()
img1 = array(image1)
img2 = array(image2)
wid = 5
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d1 = get_descriptors(img1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d2 = get_descriptors(img2, filtered_coords2, wid)
print("starting matching")
matches = match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(img1, img2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
5.SIFT算子
1999年David G.lowe教授总结了基于特征不变技术的检测方法,在图像尺度空间基础上没吐出来对图像缩放、旋转保持不变性的图像局部特征描述算子—SIFT(尺度不变特征变化),该算法在2004年完善
可以解决的问题
1、目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
2、图像放射/投影变化(十点viewpoit)
3、弱光照影响
4、部分目标遮挡
5、杂物场景
6、噪声