UnityShader入门精要-基础纹理
纹理的基础知识
看了一部分unityshader入门精要的第七章纹理部分的开头,觉得理解起来相对前面的知识有难度,遂看了其他的教程(百人计划)来补充纹理的基础知识。
纹理的出现即一张贴图贴在模型表面,减轻建模的工作量,纹理即包含了一些信息。
纹理管线
模型空间位置--投影函数(展uv)--纹理映射--纹理坐标--通讯函数(平移缩放旋转等扩展)---新纹理坐标--纹理采样--纹理值
着色器中纹理通常以sampler形式存在,如二维纹理是sampler2D,在顶点着色器中完成uv计算会更有效率,纹理不只储存颜色信息,还存储如表面粗糙度等值。
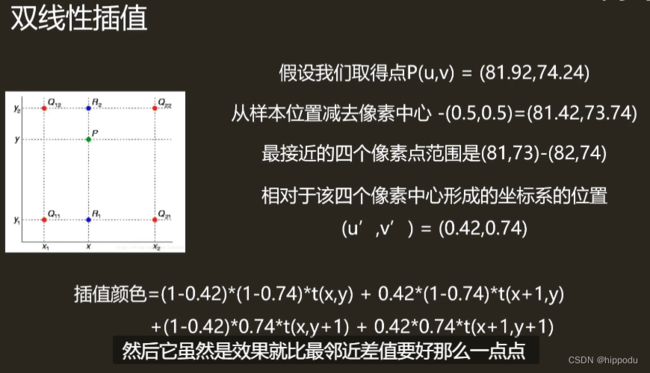
获取模型坐标转换为纹理坐标后,知道纹理大小为256x256,则将uv与256相乘,通过纹理采样的设置获得纹理颜色(如wrap mode、filter mode)
FilterMode纹理过滤:
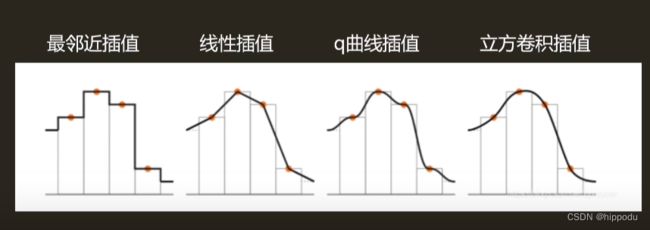
放大Magnification-- 最邻近 双线性插值 立方卷积
最邻近:每个像素读取最邻近纹素,多个像素读取同一纹素,效果不好。
双线性插值:采样四次计算量比最邻近大四倍,效果较好,克服了不连续的缺点,但提升有限。
立方卷积插值:除了相邻四个点,还考虑到变化率影响
光滑曲线插值:用一条曲线进行插值
纹理缩小--最邻近与双线性插值:
几个纹理覆盖一个像素,应该整合所有对某个像素有影响的纹理来决定像素颜色。颜色会丢失,浮点数运算带来闪烁。一般纹理来讲,每个像素最多有一个纹理来避免混点,为了达到这个目的,要么提高像素采样频率,要么降低纹理频率。
Mipmap降低纹理频率,预处理纹理,比原多1/3内存。原理见games101讲解
各向异性过滤Ripmap
积分图:以内存为代价,检索非正方形区域上的纹素值。
单张纹理
用一张纹理来代替物体的漫反射颜色
_MainTex_ST : 纹理名_ST的方式来声明某个纹理的属性,ST是缩放和平移的缩写, _MainTex_ST.xy存放的是缩放值, _MainTex_ST.zw存放偏移值。
函数tex2D用于对纹理采样,第一个参数是需要被采样的纹理,第二个参数是一个float2的纹理坐标,将返回计算得到的纹素值,将采样结果与颜色属性相乘作为材质的反射率albedo。
代码如下:
// Upgrade NOTE: replaced '_Object2World' with 'unity_ObjectToWorld'
// Upgrade NOTE: replaced 'mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP,*)' with 'UnityObjectToClipPos(*)'
Shader "Shaders/BasicTexture/SingleTexture" {
Properties {
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
_Specular ("Specular", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_Gloss ("Gloss", Range(8.0, 256)) = 20
}
SubShader {
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
fixed4 _Specular;
float _Gloss;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD0;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD1;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD2;
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
o.uv = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw;
// Or just call the built-in function
// o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos));
// Use the texture to sample the diffuse color
fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb * _Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz * albedo;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * max(0, dot(worldNormal, worldLightDir));
fixed3 viewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(i.worldPos));
fixed3 halfDir = normalize(worldLightDir + viewDir);
fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(max(0, dot(worldNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss);
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Specular"
}
纹理的属性
wrap mode属性:决定了纹理坐标超过 [0,1]范围后将会如何被平铺。Repeat为重复,Clamp会截取到0,1,其余部分不显示。要想要完成这样的效果需要对顶点纹理坐标进行变换
o.uv = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw;
// Or just call the built-in function
// o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);FilterMode属性:决定了当纹理由于变换而产生拉伸时将会采用哪种滤波模式,共有三种。
Point、Bilinear、Trilinear。得到图片的滤波效果以此提升,耗费的性能也依次增大
凹凸纹理
高度纹理
用一张高度图来实现凹凸映射,高度图中存储强度值用于表示模型表面局部的高度,好处是直观,缺点是计算更加复杂,实时计算中不能直接得到表面法线需要由像素的灰度值计算。使用时通常和法线映射一起使用。
法线纹理
法线纹理中存储的是表面的法线方向,由于法线方向的分量范围在[-1,1],像素的分量范围为[0,1],需要做映射,通常使用:
Pixel=(normal+1)/2
因此在shader中对法线纹理进行采样后,还需要unpack,进行一次反映射,得到原先法线方向。通常处理的法线实在顶点切线空间中的,切线空间的原点就是定点本身,z轴就是顶点的法线方向,x轴是顶点的切线方向,y轴是叉乘得到的 也称副切线。
切线空间来存储法线的优点:自由度高,切线空间下的法线纹理记录的是相对法线信息,即使应用到完全不同的的网格上也能得到合理的结果。可进行UV动画,凹凸移动,如火山熔岩效果。可重用,如一个砖块用一个纹理就可以用到所有的六个面上。可压缩,z方向总是正方向,可以仅存储XY方向,推导得到z方向。
实践:切线空间下计算
说明:基本思路为在顶点着色器中将视角方向和光照方向从模型空间变换到切线空间中,在片元着色器中通过纹理采样得到切线空间下的法线,再进行光照计算。
_BumpMap法线纹理,“bump”为其默认值;分别得到纹理与法线纹理的属性(ST);
TANGENT语义来描述顶点的切线方向,类型为float4而非float3,需要第四个分量来决定副切线的方向性;
模型空间到切线空间的变换矩阵rotation,为模型空间下切线方向、副切线方向、法线方向按行排列来得到。计算副切线时需要将tangent.w与叉乘的结果相乘来得到所需的方向,也可使用Unity提供的TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION直接计算得到rotation。
如果在纹理设置的部分没有设置normal map模式,就需要手动进行unpack。
// Upgrade NOTE: replaced 'mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP,*)' with 'UnityObjectToClipPos(*)'
Shader "Shaders/BasicTexture/NormalMapTangentSpace" {
Properties {
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap ("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
_BumpScale ("Bump Scale", Float) = 1.0
_Specular ("Specular", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_Gloss ("Gloss", Range(8.0, 256)) = 20
}
SubShader {
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
float4 _BumpMap_ST;
float _BumpScale;
fixed4 _Specular;
float _Gloss;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float3 lightDir: TEXCOORD1;
float3 viewDir : TEXCOORD2;
};
// Unity doesn't support the 'inverse' function in native shader
// so we write one by our own
// Note: this function is just a demonstration, not too confident on the math or the speed
// Reference: http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/218333/shader-inversefloat4x4-function.html
float4x4 inverse(float4x4 input) {
#define minor(a,b,c) determinant(float3x3(input.a, input.b, input.c))
float4x4 cofactors = float4x4(
minor(_22_23_24, _32_33_34, _42_43_44),
-minor(_21_23_24, _31_33_34, _41_43_44),
minor(_21_22_24, _31_32_34, _41_42_44),
-minor(_21_22_23, _31_32_33, _41_42_43),
-minor(_12_13_14, _32_33_34, _42_43_44),
minor(_11_13_14, _31_33_34, _41_43_44),
-minor(_11_12_14, _31_32_34, _41_42_44),
minor(_11_12_13, _31_32_33, _41_42_43),
minor(_12_13_14, _22_23_24, _42_43_44),
-minor(_11_13_14, _21_23_24, _41_43_44),
minor(_11_12_14, _21_22_24, _41_42_44),
-minor(_11_12_13, _21_22_23, _41_42_43),
-minor(_12_13_14, _22_23_24, _32_33_34),
minor(_11_13_14, _21_23_24, _31_33_34),
-minor(_11_12_14, _21_22_24, _31_32_34),
minor(_11_12_13, _21_22_23, _31_32_33)
);
#undef minor
return transpose(cofactors) / determinant(input);
}
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv.xy = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw;
o.uv.zw = v.texcoord.xy * _BumpMap_ST.xy + _BumpMap_ST.zw;
///
/// Note that the code below can handle both uniform and non-uniform scales
///
// Construct a matrix that transforms a point/vector from tangent space to world space
fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz);
fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w;
/*
float4x4 tangentToWorld = float4x4(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x, 0.0,
worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y, 0.0,
worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
// The matrix that transforms from world space to tangent space is inverse of tangentToWorld
float3x3 worldToTangent = inverse(tangentToWorld);
*/
//wToT = the inverse of tToW = the transpose of tToW as long as tToW is an orthogonal matrix.
float3x3 worldToTangent = float3x3(worldTangent, worldBinormal, worldNormal);
// Transform the light and view dir from world space to tangent space
o.lightDir = mul(worldToTangent, WorldSpaceLightDir(v.vertex));
o.viewDir = mul(worldToTangent, WorldSpaceViewDir(v.vertex));
///
/// Note that the code below can only handle uniform scales, not including non-uniform scales
///
// Compute the binormal
// float3 binormal = cross( normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz) ) * v.tangent.w;
// // Construct a matrix which transform vectors from object space to tangent space
// float3x3 rotation = float3x3(v.tangent.xyz, binormal, v.normal);
// Or just use the built-in macro
// TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION;
//
// // Transform the light direction from object space to tangent space
// o.lightDir = mul(rotation, normalize(ObjSpaceLightDir(v.vertex))).xyz;
// // Transform the view direction from object space to tangent space
// o.viewDir = mul(rotation, normalize(ObjSpaceViewDir(v.vertex))).xyz;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 tangentLightDir = normalize(i.lightDir);
fixed3 tangentViewDir = normalize(i.viewDir);
// Get the texel in the normal map
fixed4 packedNormal = tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw);
fixed3 tangentNormal;
// If the texture is not marked as "Normal map"
// tangentNormal.xy = (packedNormal.xy * 2 - 1) * _BumpScale;
// tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy)));
// Or mark the texture as "Normal map", and use the built-in funciton
tangentNormal = UnpackNormal(packedNormal);
tangentNormal.xy *= _BumpScale;
tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy)));
fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb * _Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz * albedo;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * max(0, dot(tangentNormal, tangentLightDir));
fixed3 halfDir = normalize(tangentLightDir + tangentViewDir);
fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(max(0, dot(tangentNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss);
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Specular"
}
实践:世界空间下计算
说明:在世界空间下计算光照模型,需要在顶点着色器中计算从切线空间到世界空间的变换矩阵,并把它传递到世界空间的变换矩阵,并把它传递到片元着色器。
代码与上面的区别在要计算世界空间下顶点切线、副切线、法线的矢量表示,并把它们按列拜访得到从切线空间到世界空间的变换矩阵,将每一行分别存储在float4中,w分量表示世界空间下顶点位置的xyz分量。
Unity中的法线纹理类型
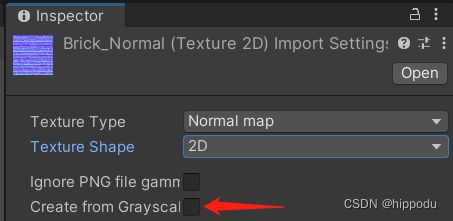
当把法线纹理的纹理类型标识成Normal map时,可以使用Unity的内置函数UnpackNormal得到正确的法线方向,复选框中有选项create from grayscale用于从高度图中生成法线纹理,如果使用高度图则需要勾选,这样就会根据高度图来生成一张切线空间下的法线纹理。勾选后
bumpiness用于控制凹凸成都,filtering用于决定计算凹凸程度的方式。
渐变纹理
纹理可以用于存储任何表面信息,常见的用法是使用渐变纹理控制漫反射光照的结果,实现不同风格。实现并无特殊之处,要注意需要把渐变纹理的wrapmode设为clamp模式,防止对纹理采样时由于浮点数精度造成的问题。
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 worldNormal=normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir=normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos));
fixed3 ambient=UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz;
fixed halfLambert=0.5*dot(worldNormal,worldLightDir)+0.5;
fixed3 diffuseColor=tex2D(_RampTex,fixed2(halfLambert,halfLambert)).rgb*_Color.rgb;
fixed3 diffuse=_LightColor0.rgb*diffuseColor;
fixed3 viewDir=normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(i.worldPos));
fixed3 halfDir=normalize(worldLightDir+viewDir);
fixed3 specular=_LightColor0.rgb*_Specular.rgb*pow(max(0,dot(worldNormal,halfDir)),_Gloss);
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);
}遮罩纹理
遮罩允许我们保护某些区域使其免于某些修改,如希望某些地方反光强一些某些区域弱一些,就可以使用一张遮罩纹理来控制光照,另一种常见应用是制作地形材质时候需要混合多张图片如表现草地 石子 裸露土地等纹理。
一般流程通过采样得到遮罩纹理的纹素,然后使用其中某些通道的值来与某种表面属性相乘,这样 该通道值为0时就可以保护表面不受该属性影响。
仅呈现处理遮罩计算的部分
fixed4 frag(v2f i) :SV_Target{
fixed3 tangentLightDir=normalize(i.lightDir);
fixed3 tangentViewDir=normalize(i.viewDir);
fixed3 tangentNormal =UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap,i.uv));
tangentNormal.xy*=_BumpScale;
tangentNormal.z=sqrt(1.0-saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy,tangentNormal.xy)));
fixed3 albedo=tex2D(_MainTex,i.uv).rgb*_Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient=UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz*albedo;
fixed3 diffuse=_LightColor0.rgb*albedo*max(0,dot(tangentNormal,tangentLightDir));
fixed3 halfDir=normalize(tangentLightDir+tangentViewDir);
fixed3 specularMask=tex2D(_SpecularMask,i.uv).r*_SpecularScale;
fixed3 specular=_LightColor0.rgb*_Specular.rgb*pow(max(0,dot(tangentNormal,halfDir)),_Gloss)*specularMask;
return fixed4(ambient+diffuse+specular,1.0);
}