人工智能-深度学习-手写数字识别
1.准备数据
手写数字识别的特征集是一组数值为0-9,大小为 28 * 28 矩阵的图片, 标签为与之对应的数字:
数据下载链接: 手写数字识别数据集
2.将数据格式化为 npz 文件
"""
将图片和标签整理为 npz 文件
"""
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
import json
# 读取图片
# 存到 npz 文件中的为 28 *28 的矩阵列表
train_file_path = "nums/train_x/"
train_x = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(train_file_path):
for f in files:
img = np.array(Image.open(os.path.join(root, f)))
train_x.append(img)
test_file_path = "nums/test_x/"
test_x = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(test_file_path):
for f in files:
img = np.array(Image.open(os.path.join(root, f)))
test_x.append(img)
train_object = open('nums/train_y.json', 'r')
train_y = json.load(train_object)
test_object = open('nums/test_y.json', 'r')
test_y = json.load(test_object)
np.savez('nums.npz', train_x=np.array(train_x), test_x=np.array(test_x),
train_y=np.array(train_y), test_y=np.array(test_y))
我们顺便记录下, 如何把npz里的数据还原成图片和json文件
"""
从 nums.npz 中读取各个图片和各自的标签
"""
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import json
# 加载数据
image_data = np.load("data/mnist.npz")
# 分别获取训练集和数据集
x_train = image_data["x_train"]
y_train = image_data["y_train"]
x_test = image_data["x_test"]
y_test = image_data["y_test"]
# 分别把训练集和测试集恢复为png 图片
for i in range(len(x_train)):
im = Image.fromarray(x_train[i])
im.save("nums/train_x/%05d.png" % (i + 1))
for i in range(len(x_test)):
im = Image.fromarray(x_test[i])
im.save("nums/test_x/%05d.png" % (i + 1))
# 分别把训练集和测试集的标签写入到json文件中
train_num_writer = open("nums/train_y.json", 'w')
train_num_writer.write(json.dumps(y_train.tolist(), ensure_ascii=False))
train_num_writer.close()
test_num_writer = open("nums/test_y.json", 'w')
test_num_writer.write(json.dumps(y_test.tolist(), ensure_ascii=False))
test_num_writer.close()
3.训练
采用交叉熵作为损失函数, 28* 28 的784个像素值作为特征向量, 这种训练方式很暴力, 后期如果有其他更精巧的训练方式再来补充, 大家可以先把这种训练当成深度学习中的hello world
"""
手写数字识别(以交叉熵为激活函数的深度学习)
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as fc
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as grid_spec
plt.switch_backend("TkAgg")
# 一. 准备训练集和测试集数据
# 从npz文件中加载数据
image_data = np.load("nums.npz")
# 获取训练集数据, 并将每张图片的 28 * 28 的矩阵转变为 1 * 784 的矩阵, 转为浮点数
# 除以 255 是为了
# 即我们把 784 个像素点的值处理后当做 784 个特征, 测试集特征同样如此
train_x = image_data["train_x"].reshape([-1, 784]).astype(np.float32) / 255
# 获取标签, 每个标签为图片对应的数字
train_y = image_data["train_y"].astype(np.float32)
# 获取测试集数据
test_x = image_data["test_x"].reshape([-1, 784]).astype(np.float32) / 255
test_y = image_data["test_y"].astype(np.float32)
# 二. 构建数学模型
# 将整个数学模型和参数进行封装
# 继承 nn.Module
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 定义线性模型, 并设特征为 5 个, 输出为 10 个(因为数字为 0-9 共十个数字 )
self.linear = nn.Linear(784, 128)
# 采用ReLU作为激活函数
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# 第二层神经网络
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 将x输入到第一层神经网络中
x = self.linear(x)
# 调用激活函数
x = self.relu(x)
# 传入第二层神经网络
x = self.linear2(x)
return x
# 三. 开始训练
# 设置学习率为 0.1
eta = 0.1
# 调用封装好的模型
model = Model()
# 开始进行训练
model.train()
# 损失函数采用 交叉熵作为损失函数
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 构建优化器, 采用 随机梯度下降法(Stochastic Gradient Descent)
# 调用 model.parameters() 传入参数和学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), eta)
# 进行迭代
for step in range(10000):
# 每次随机产生 32 个下标索引, 获取 32 个数据进行随机梯度下降
idx = np.random.randint(0, len(train_x), [32])
xin = train_x[idx]
din = train_y[idx]
# 将 numpy 类型的数据转为 Tensor 类型,
# 将标签的浮点类型转整数(loss函数需要标签为long类型)
xin, din = torch.from_numpy(xin), torch.from_numpy(din).long()
# 代入模型进行计算
y = model(xin)
# 计算损失函数, 然后从损失函数开始进行反向传播
# 损失函数, 这个是计算图的最终节点
loss = loss_fn(y, din)
# 反向传播, 计算梯度, 这个张量的所有梯度将会自动积累到.grad属性
loss.backward()
# 进行迭代
optimizer.step()
# 将优化器已计算的梯度置0, 否则会累加
optimizer.zero_grad()
if step % 50 == 49:
y_estimate = model(torch.from_numpy(test_x))
# 找出最大的数的索引, 索引是多少, 就是估计得值是多少
D_estimate = torch.argmax(y_estimate.detach(), 1).numpy()
print("第 %d 次迭代, 准确率: %.2f %%" % (step,np.mean(D_estimate == test_y) * 100))
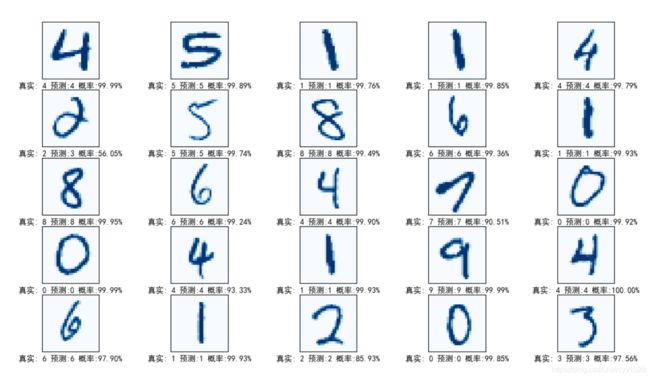
# 四. 绘制训练结果
# 建立编号为1, 大小为 14 * 8 的画图窗口 figure
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(14, 8))
# 指定放置子图的网格的几何形状, 为 5 行 5 列
gs = grid_spec.GridSpec(5, 5)
# 对测试集进行预测, 获得的 y 为 10000 * 10 的结果矩阵,
y = model(torch.from_numpy(test_x))
# 找出最大的数的索引, 索引是多少, 就是估计得值是多少
D = torch.argmax(y.detach(), 1).numpy()
# 将张量的每个元素缩放到(0,1)区间且和为1, 这个可以作为置信度
P = fc.softmax(y.detach(), 1)
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
# 0-10000 随机选取一个矩阵
index = np.random.randint(5000)
# 将该矩阵从 1 * 784 转为28 * 28
X = test_x[index].reshape(28, 28)
# 在第 i 行第 j 个位置的图像绘制 图像
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[i, j])
# 绘制该矩阵, 以蓝色显示
ax.matshow(X, cmap=plt.get_cmap("Blues"))
# 获取该数据的预测值(即标签矩阵中的最大值得索引)
idx = D[index]
# 获取预测结果矩阵中指定的预测标签矩阵中的数字, 即置信度
prob = P[index, idx]
# 书写 label, 在 x 轴方向上
ax.set_xlabel("真实: %d 预测:%d 概率:%.2f%%" % (test_y[index], idx, prob * 100))
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
# 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.show()