数据库 使用(MySQL5.7)
文章目录
- 第一章 SQL语句
-
- 1. DDL 数据定义语言
- 2. DML 数据管理语言
-
- insert
- 蠕虫复制
- update
- delete
- 3. DQL 数据查询语言
-
- select
- and、or、between and
- in、not in
- %、_ 通配符
- 聚合函数
- group by 分组
- having
- order by 排序
- limit 分页
- all
- any
- 4. DCL 数据控制语言
- 第二章 数据库约束
-
- 1. 主键约束
- 2. 主键自增
- 3. 唯一约束
- 4. 非空约束
- 5. 默认值
- 6. 外键约束
- 第三章 数据库备份
-
- 1. 命令行方式
- 2. 图形界面 DataGrip方式
- 第四章 多表查询
-
- 1. 连接查询
- 2. 子查询
- 3. 多表查询规律总结
- 第五章 事务
-
- 1. 事务的四大特性 ACID
-
- 1.1 原子性
- 1.2 一致性
- 1.3 隔离性
- 1.4 持久性
- 2. 操作事务
-
- 2.1 SQL实现
- 2.2 Java实现
- 2.3 回滚原理(中间文件)
- 3. 事务并发问题
- 4. 事务的隔离级别
- 第六章 存储过程
- 第七章 索引
-
- 1. 先插入大批数据
- 2. 添加索引
- 3 索引的优缺点
-
- 3.1 优势
- 3.2 劣势
- 第七章 参考资料
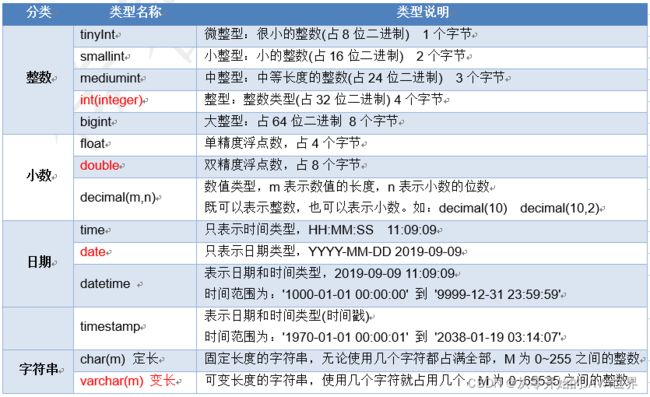
第一章 SQL语句
1. DDL 数据定义语言
- 创建、修改、删除 、查看数据库/表
# 创建、删除、修改、查看数据库
#1.创建数据库
create database xin;
create database if not exists xin; # 没有则创建数据库
create database if not exists xin charset = 'utf8'; #设置字符集utf8
create database if not exists xin character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;#设置字符集utf8 并核对
#2.查看
show databases; #查看所有数据库
show create database xin; #查看某个数据库定义时的信息
#3.修改数据库
alter database xin default character set utf8;#修改字符集
#4.删除数据库
drop database xin;
#5.切换数据库
use xin;
#6.查看正在使用的数据库
select database();
#创建、删除、修改、查看表
#1. 创建表
create table student
(
id int,
name varchar(8),
age int(3),
score double(5, 2)
);
create table student2 like student;#快速创建一个表结构相同的表
#2. 删除表
drop table student2;
drop table if exists student2;
#3. 查看表
desc student; #查看表结构
show create table student; #查看创建表时的sql
show tables; #查看某个库中所有的表
#4. 修改表结构
alter table student add gender char(1); # 添加一个字符
alter table student modify id int(8); # 修改某个字段的类型
alter table student change name username varchar(8);# 修改某个字段的名字、类型
alter table student character set utf8; #修改表的字符集
alter table student rename name; # == rename table student to t_student; #重命名表名
2. DML 数据管理语言
insert
insert into student(id, name, age ) value (1,'张三','18');
insert into student(id, name, age, score) value (2,'李四','18',145.50);
insert into student(id, name, age, score) values (3,'王五','18',99.50),(4,'赵六','25',80);
insert into student value (5,'李七','30',101.11);
蠕虫复制
- 两个表的结构一致
- 将一个表的部分数据复制到另一个表中
create table man_stuent like student;
insert into man_stuent select * from student where gender = '男';
update
update student set id = 2 where score is null;
update student set age =26,score=97.1 where id = 2;
delete
#3. delete 数据
delete from student where id = 2;
delete from student where age = 18 and score > 100;
delete from student where age between 17 and 20;
delete from student; #全删,逐条删除
truncate table student; #全删,drop表,新建一个结构一样的新表
3. DQL 数据查询语言
select
# * 全查,效率慢
-- 1.性能损失 * 需要有mysql程序解析
-- 2.性能损失 * 代表所有字段 不管需要还是不需要都会查询
select * from student;
# 所有字段全查,推荐
select id, name, age , score from student;
# 查询,显示时给与别名
select id ID, name 姓名, age 年龄, score 分数 from student;
# 查询 去除重复数据,一般都是查单列时使用
select distinct age from student;
select distinct name,age from student; #两个字段都一样才算重复
# 字段可以参与运算
select age + 1 from student;#所有人年龄加一
# case when ... then when ...then else... end
select ename,
sal,
case
when sal >= 3000 then '三级'
when sal > 2000 then '2级'
else '1级'
end
from emp;
and、or、between and
select * from t_student where age>35 and gender='男';
select * from t_student where age>35 or gender='男';
select * from t_student where english between 75 and 90;
select id ,ifnull(salary,'没有工资') from t_student;
in、not in
# id 在(1,2,3)之中的, 等价于 id = 1 or id = 2 or id =3
select * from student where id in (1, 2, 3);
# id 不在(1,2,3)之中的, 等价于 id != 1 and id != 2 and id =3
select * from student where id not in (1, 2, 3);
%、_ 通配符
# %多个占位符
select * from student where name like '%三';
# _单个占位符
select * from student where name like '_三';
聚合函数
-- 聚合函数 select 聚合函数名(列表) from xx表 ....
-- count 数数
-- max 最大值
-- min 最小值
-- sum 求和
-- avg 求平均值
-- 查询所有学生的总数
-- select count(*) from xx表
-- 查询个数 鼓励 select count(*) mysql底层专门做了优化
select count(*) from t_student;
group by 分组
select gender,round(avg(score),2) from student group by gender;
select gender,max(age),avg(score) from student group by gender;
select age,name from student group by age having age = 18;
having
- having 可以单独跟select
- 如果有group by 则一定要在group by后面
select * from student having age > 18;
select * from student group by age having age >20;
order by 排序
# order by 字段 asc . 升序
# order by 字段 desc . 降序
# order by 字段1,字段2 . 在字段1升序排的基础上按字段2降序排
select * from student order by age ;
select * from student order by age desc ;
select * from student order by age desc,score desc;
limit 分页
select * from student limit 0,10; 起始索引,查询条目数
计算公式:起始索引=(当前页码-1)* 每页条数
all
select empno from emp
where sal >= all(select sal from emp); sal 大于等于 all()最大值
any
select empno from emp
where sal >= any(select sal from emp); sal >= any()最小值
- oracle 用rownumber
- sql server 用top
MySQL中ALL 和 ANY的用法
4. DCL 数据控制语言
# 创建新用户 CREATE USER '用户名'@'主机名' IDENTIFIED BY '密码';
create user 'zhx'@'localhost' identified by '123456';#
create user 'zhx'@'%' identified by '123456'; # 任意远程主机登陆,可以使用通配符%
# 授权 GRANT 权限1, 权限2... ON 数据库名.表名 TO '用户名'@'主机名';
# grant xx权限(create、drop、alter、insert、update、delete、select...) on 库.表 to 哪个用户
grant select,delete on *.* to 'zhx'@'localhost'; # 给zhx用户授予对所有库所有表的全部权限。
# 移除权限
revoke delete on *.* from 'zhx'@'localhost';
# 删除用户
drop user 'zhx'@'localhost';
# 修改管理员密码
# 要在未登陆MySQL的情况下操作。新密码不需要加上引号
# mysqladmin -u root -p password 新密码
# 修改普通用户密码
set password for '用户名'@'主机名' = password('新密码');
select * from user;
第二章 数据库约束
- 数据库约束的作用:
对表中的数据进行进一步的限制,保证数据的正确性、有效性和完整性。 - 约束种类:
PRIMARY KEY: 主键约束 (B+ 二分查找树 ,查询快)UNIQUE: 唯一约束NOT NULL: 非空约束DEFAULT: 默认值 了解FOREIGN KEY: 外键约束
1. 主键约束
- 用来唯一标识一条记录。
PRIMARY KEY- 主键必须包含唯一的值
- 主键列不能包含NULL值
# 1. 在创建表的时候给字段添加主键
字段名 字段类型 PRIMARY KEY
# 2. 在已有表中添加主键(了解)
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD PRIMARY KEY(字段名);
2. 主键自增
- 主键如果让我们自己添加很有可能重复,我们通常希望在每次插入新记录时,数据库自动生成主键字段的值
字段名 字段类型 PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT
AUTO_INCREMENT 表示自动增长(字段类型必须是整数类型)
# DELETE和TRUNCATE的区别
- DELETE 删除表中的数据,但不重置AUTO_INCREMENT的值。
- TRUNCATE 摧毁表,重建表,AUTO_INCREMENT重置为1
# insert 失败 主键也会加一
3. 唯一约束
- 在这张表中这个字段的值不能重复
字段名 字段类型 UNIQUE
4. 非空约束
- 这个字段必须设置值,不能是NULL
字段名 字段类型 NOT NULL
5. 默认值
- 往表中添加数据时,如果不指定这个字段的数据,就使用默认值
字段名 字段类型 DEFAULT 默认值
6. 外键约束
- 两个表之间的关系
说明:如果两张表是多对多的关系,需要创建第三张表,并在第三张表中增加两列,引入其他两张表的主键作为自己的外键。
foreign key( 当前表中的列名 ) references 被引用表名(被引用表的列名);
foreign key( coder_id ) references coder(id);
constraint [外键约束名称] foreign key(当前表中的列名) references 被引用表名(被引用表的列名)
举例:constraint coder_project_id foreign key(coder_id) references coder(id);
关键字解释:
constraint: 添加约束,可以不写
foreign key(当前表中的列名): 将某个字段作为外键
references 被引用表名(被引用表的列名) : 外键引用主表的主键
外键的级联
在修改和删除主表的主键时,同时更新或删除从表的外键值,称为级联操作
ON UPDATE CASCADE – 级联更新,主键发生更新时,外键也会更新
ON DELETE CASCADE – 级联删除,主键发生删除时,外键也会删除
-- 添加外键约束,并且添加级联更新和级联删除
constraint c_id_fk foreign key(coder_id) references coder(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE,
);
级联更新:ON UPDATE CASCADE 主键修改后,外键也会跟着修改
级联删除:ON DELETE CASCADE 主键删除后,外键对应的数据也会删除
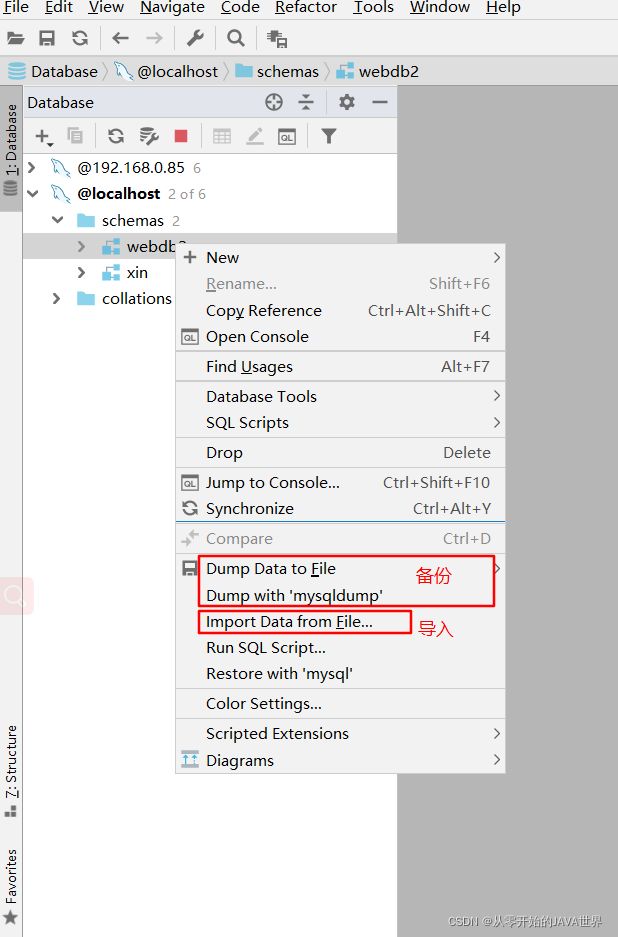
第三章 数据库备份
1. 命令行方式
#备份数据,将数据的表、数据,转成sql保存
mysqldump --no-defaults -u root -p 要备份的数据库名 > 硬盘SQL文件绝对路径
mysqldump --no-defaults -u root -p webdb2 > d:\aa.sql
#恢复数据,其实就是执行sql语句
恢复数据库语法:mysql -u 用户名 -p 导入库名 < 硬盘SQL文件绝对路径
mysql -u root -p webdb2 < d:\aa.sql
2. 图形界面 DataGrip方式
第四章 多表查询
- 笛卡尔积: 一个表三条数据,另一个表两条数据,联表查询出3*2=6条数据
1. 连接查询
# 内连接
# 隐式内连接
select * from student a,teacher b where a.id = b.id;
# 显式内连接
select * from student a inner join teacher b on a.id = b.id;
select * from student a join teacher b on a.id = b.id;
# 外连接
# 左外连接 左边的是主表
select * from student a left join teacher b on a.id = b.id;
select * from student a left outer join teacher b on a.id = b.id;
# 右外连接 右边的是主表
select * from student a right outer join teacher b on a.id = b.id;
2. 子查询
- 子查询内部的select的结果相当于一个临时表,在临时表的结果上查询。
# select 嵌套
select * from student where age >(select avg(age) from student);
3. 多表查询规律总结
- 不管我们查询几张表,表连接查询会产出笛卡尔积,我们需要消除笛卡尔积,拿到正确的数据。我们需要找到表与表之间通过哪个字段关联起来的(通常是
外键=主键) - 消除笛卡尔积规律:2张表需要1个条件,3张表需要2个条件,4张表需要3个条件。(条件数量=表的数量-1),每张表都要参与进来
- 多表连接查询步骤:
3.1. 确定要查询哪些表
3.2. 确定表连接条件
3.3. 确定查询字段
第五章 事务
- 在关系数据库中,一个事务可以是一条SQL语句,一组SQL语句或整个程序。
1. 事务的四大特性 ACID
1.1 原子性
- 原子性是指事务**包装的一组sql(一组业务逻辑)是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
1.2 一致性
- 通俗得讲就是事物的结果与预期相符
- 事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。
1.3 隔离性
- 多个用户并发的访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不能被其他用户的事务干扰,多个并发的事务之间要相互隔离。
- 一个事务的成功或者失败对于其他的事务是没有影响。2个事务应该相互独立。
1.4 持久性
- 指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库的改变将是永久性的,哪怕数据库发生异常,重启之后数据亦然存在。
2. 操作事务
| 事务的操作 | MySQL操作事务的语句 |
|---|---|
| 手动开启事务 | start transaction |
| 手动提交事务 | commit |
| 手动回滚事务 | rollback |
| 设置回滚点 | savepoint 名字 |
| 回到回滚点 | rollback to 名字 |
| 查询事务的自动提交情况 | show variables like ‘%commit%’; |
| 设置事务的手动提交方式 | set autocommit = 0 – 关闭自动提交 |
2.1 SQL实现
# commit
start transaction #开启事务
update emp set salary = salary + 500 where id = 1001 and ename = '迪丽热巴';
update emp set salary = salary - 500 where id = 1002 and ename = '杨幂';
...
commit;# 多条sql都执行成功,commit
# rollback
start transaction #开启事务
update emp set salary = salary + 500 where id = 1001 and ename = '迪丽热巴';
update emp set salary = salary - 500 where id = 1002 and ename = '杨幂';
...
rollback;# 有一条sql执行失败就必须rollback回滚,撤销已经成功执行的sql语句,回到开启事务之前的状态.
# 注意:只要提交事务,那么数据就会长久保存了,就不能回滚事务了。即提交或者回滚事务都是代表结束当前事务的操作。
# 使用回滚点
start transaction;
update emp set salary = salary + 1000 where id = 1002;
update emp set salary = salary - 1000 where id = 1003;
savepoint a;
update emp set salary = salary + 2000 where id = 1004;
update emp set salary = salary - 2000 where id = 1005;
rollback to a; //回滚到a
commit ;
2.2 Java实现
package transaction_demo;
import mysql_use.DruidUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//工具类获取连接
Connection connection = DruidUtil.getConnection();
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
addMoney(connection, 500, 1002); //给1002转入500
subMoney(connection, 500, 1003); // 1003转出500
connection.commit(); //都成功则提交
} catch (Exception e) {
connection.rollback();//异常则回滚,保证原子性,一致性
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
connection.close();
}
}
public static void addMoney(Connection connection, Object... args) throws SQLException {
connection = DruidUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "update emp set salary = salary + ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
}
public static void subMoney(Connection connection, Object... args) throws SQLException {
connection = DruidUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "update emp set salary = salary - ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
}
}
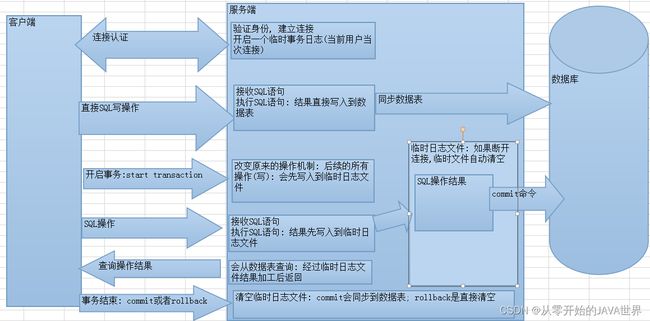
2.3 回滚原理(中间文件)
- 一个用户登录成功以后,服务器会创建一个临时日志文件。日志文件用来保存用户事务状态。
- 如果没有使用事务,则所有的操作直接写到
- 数据库中,不会使用日志文件。
- 如果开启事务,将所有的写操作写到日志文件中。
- 如果这时用户提交了事务,则将日志文件中所有的操作写到数据库中。
- 如果用户回滚事务,则日志文件会被清空,不会影响到数据库的操作。
3. 事务并发问题
| 并发访问的问题 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 脏读 | 一个事务读取到了另一个事务中尚未提交的数据。最严重,杜绝发生。 |
| 不可重复读 | 一个事务中两次读取的数据内容不一致,这是事务update时引发的问题 |
| 幻读(虚读) | 一个事务内读取到了别的事务插入或者删除的数据,导致前后读取记录行数不同。这是insert或delete时引发的问题 |
4. 事务的隔离级别
- 为了解决事务并发问题。
上面的级别最低,下面的级别最高。“是”表示会出现这种问题,“否”表示不会出现这种问题。
| 级别 | 名字 | 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | 数据库默认隔离级别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 读未提交 | read uncommitted | 是 | 是 | 是 | |
| 2 | 读已提交 | read committed | 否 | 是 | 是 | Oracle和SQL Server |
| 3 | 可重复读 | repeatable read | 否 | 否 | 是 | MySQL |
| 4 | 串行化 | serializable | 否 | 否 | 否 |
2、安全和性能对比
安全性:serializable > repeatable read > read committed > read uncommitted
性能 : serializable < repeatable read < read committed < read uncommitted
3、注意:其实三个问题,开发中最严重的问题就是脏读,这个问题一定要避免,而关于不可重复读和虚读其实只是感官上的错误,并不是逻辑上的错误。就是数据的时效性,所以这种问题并不属于很严重的错误。如果对于数据的时效性要求不是很高的情况下,我们是可以接受不可重复读和虚读的情况发生的。
第六章 存储过程
MySQL 存储过程
第七章 索引
1. 先插入大批数据
# 准备数据,使用存储过程插入10000000条数据
create database itcast01;
use itcast01;
-- 1. 准备表
CREATE TABLE user(
id INT,
username VARCHAR(32),
password VARCHAR(32),
sex VARCHAR(6),
email VARCHAR(50)
);
-- 2. 创建存储过程,实现批量插入记录
DELIMITER $$ -- 声明存储过程的结束符号为$$
-- 可以将下面的存储过程理解为java中的一个方法
CREATE PROCEDURE auto_insert()
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1;
START TRANSACTION; -- 开启事务
WHILE(i<=10000000)DO
INSERT INTO user VALUES(i,CONCAT('jack',i),MD5(i),'male',CONCAT('jack',i,'@itcast.cn'));
SET i=i+1;
END WHILE;
COMMIT; -- 提交
END$$ -- 声明结束
DELIMITER ; -- 重新声明分号为结束符号
-- 3. 查看存储过程
SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE auto_insert;
-- 4. 调用存储过程,插入千万条数据
CALL auto_insert();
2. 添加索引
-- 创建普通索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段);
-- 创建唯一索引
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(字段);
-- 创建普通组合索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段1,字段2,..);
-- 创建唯一组合索引
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(字段1,字段2,..);
# 显示索引
show index from 表名;
# 删除索引
drop index 索引名 on 表名;
# 修改表时删除
alter table 表名 drop index 索引名;
3 索引的优缺点
3.1 优势
- 根据索引字段查询,能大幅提高查询速度(数据量越大越明显)
- 索引底层就是B+ 树(二分查找树),先通过索引字段二分查找,找到某个叶子结点(存储着该条数据的主键值),再通过查找主键的B+树 找到具体的叶子结点拿到数据。
- 索引走了两次二分查找树,索引B+一次,主键B+一次。
3.2 劣势
- 增删改操作时需要同步更新索引。
- 索引需要占用一定的物理空间
第七章 参考资料
MySQL |菜鸟教程
B站黑马程序员
MySQL中ALL 和 ANY的用法
如何理解事务一致性?
百度百科