大话设计模式(五) 中介者模式 享元模式 解释器模式 访问者模式(完结附源码)
这篇写完,这本书就结束了。以后就只看这个文章了就不用再看那本书了o(^▽^)o
大话设计模式(一)简单工厂模式 策略模式 单一职责原则 开放-封闭原则 依赖倒置原则 装饰模式
大话设计模式(二)代理模式 工厂方法模式 原型模式 模板方法模式 迪米特法模式 外观模式
大话设计模式(三)建造者模式 观察者模式 抽象工厂模式 状态模式 适配器模式 备忘录模式
大话设计模式(四) 组合模式 迭代模式 单列模式 桥接模式 命令模式 职责链模式
大话设计模式(五) 中介者模式 享元模式 解释器模式 访问者模式(完结附源码)
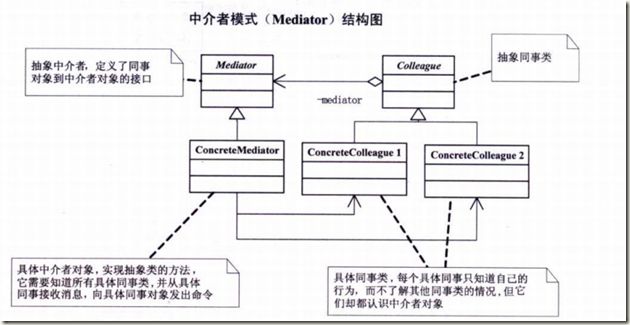
世界需要和平——中介者模式
中介者模式(Mediator),用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互,中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使得其耦合松散,二期额可以独立地改变他们之间的交互。
根据以上的结构图我们写出如下的代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Mediator { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ConcreteMediator m = new ConcreteMediator(); ConcreteColleague1 c1 = new ConcreteColleague1(m); ConcreteColleague2 c2 = new ConcreteColleague2(m); m.Colleague1 = c1; m.Colleague2 = c2; c1.Send("你吃过了么"); c2.Send("没有呢,你请客?"); Console.Read(); } } abstract class Mediator { public abstract void Send(string message, Colleague colleague); } //抽象同事类 abstract class Colleague { protected Mediator mediator; public Colleague(Mediator mediator) { this.mediator = mediator; } } class ConcreteMediator : Mediator { private ConcreteColleague1 colleague1; private ConcreteColleague2 colleague2; public ConcreteColleague1 Colleague1 { set { this.colleague1 = value; } } public ConcreteColleague2 Colleague2 { set { this.colleague2 = value; } } public override void Send(string message, Colleague colleague) { if (colleague == colleague1) { colleague2.Notify(message); } else { colleague1.Notify(message); } } } class ConcreteColleague1 : Colleague { public ConcreteColleague1(Mediator mediator) : base(mediator) { } public void Send(string message) { mediator.Send(message, this); } public void Notify(string message) { Console.WriteLine("同事1得到消息:" + message); } } class ConcreteColleague2 : Colleague { public ConcreteColleague2(Mediator mediator) : base(mediator) { } public void Send(string message) { mediator.Send(message, this); } public void Notify(string message) { Console.WriteLine("同事2得到消息:" + message); } } }
这里其实有点绕口,看的时候,不过我觉得设计模式都有那么点容易让人家迷糊的感觉,也许这就是这种模式的迷人之处。
中介者模式的优缺点:
中介者模式容易在系统中应用,也很容易在系统中无用。当系统出现了‘多对多’交互复杂的对象群时,不要急于使用中介模式,而要先反思你的系统在设计上是不是不合理。
优点:首先,Mediator的出现减少了各个Colleague的耦合,使得可以独立地改变和复用各个Colleague和Mediator,其次,由于把对象如何协作进行了抽象,将中介作为一个独立的概念并将其封装在一个对象中,这样关注的对象就从对象各自本身的行为转到他们之间的交互上来,也就是站在一个更宏观的角度去看待系统。
缺点:犹豫ConcreteMediator控制了集中化,于是就把交互复杂性变为了中介者的复杂性,这就使得中介会变得比任何一个ConcreteColleague都复杂
应用场景:中介者模式一般应用于一组对象以定义良好但是复杂的方式进行通信的场合,以及向定制一个分布在多个类中的行为,而又不想生成太多的子类的场合。
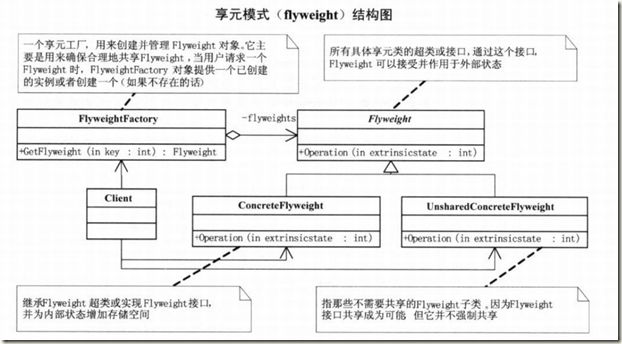
项目多也别傻做——享元模式
享元模式(Flyweight):运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
实现的代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Flyweight { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int extrinsicstate = 22; FlyweightFactory f = new FlyweightFactory(); Flyweight fx = f.GetFlyweight("X"); fx.Operation(--extrinsicstate); Flyweight fy = f.GetFlyweight("Y"); fx.Operation(--extrinsicstate); Flyweight fz = f.GetFlyweight("Z"); fx.Operation(--extrinsicstate); UnsharedConcreteFlyweight uf = new UnsharedConcreteFlyweight(); uf.Operation(--extrinsicstate); Console.Read(); } } abstract class Flyweight { public abstract void Operation(int extrinsicstate); } class ConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight { public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate) { Console.WriteLine("具体Flyweight:" + extrinsicstate); } } class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight { public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate) { Console.WriteLine("不共享的具体Flyweight:" + extrinsicstate); } } class FlyweightFactory { private Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable(); public FlyweightFactory() { flyweights.Add("X", new ConcreteFlyweight()); flyweights.Add("Y", new ConcreteFlyweight()); flyweights.Add("Z", new ConcreteFlyweight()); } public Flyweight GetFlyweight(string key) { return ((Flyweight)flyweights[key]); } } }
运行结果:
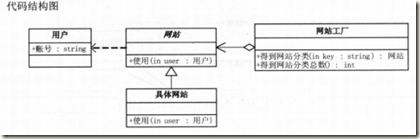
下面来实现小菜的网站共享代码:
namespace Flyweight_Web { abstract class WebSite { public abstract void Use(); } //具体网站类 class ConcreteWebSite : WebSite { private string name = ""; public ConcreteWebSite(string name) { this.name = name; } public override void Use() { Console.WriteLine("网站分类:" + name); } } //网站工厂类 class WebSiteFactory { private Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable(); //获得网站信息 public WebSite GetWebSiteCategory(string key) { if (!flyweights.ContainsKey(key)) { flyweights.Add(key, new ConcreteWebSite(key)); } return ((WebSite)flyweights[key]); } public int GetWebSiteCount() { return flyweights.Count; } } //客户端代码 public class Run { public static void GO() { WebSiteFactory f = new WebSiteFactory(); WebSite fx = f.GetWebSiteCategory("产品展示"); fx.Use(); WebSite fy = f.GetWebSiteCategory("产品展示"); fy.Use(); WebSite fz = f.GetWebSiteCategory("产品展示"); fz.Use(); WebSite fq = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fq.Use(); WebSite fw = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fw.Use(); WebSite fe = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fe.Use(); Console.WriteLine("网站分类总数为{0}", f.GetWebSiteCount()); Console.Read(); } } }
运行结果如下:
内部状态与外部状态
在享元对象内部并且不会随环境改变吧而改变的共享部分,可以称为是享元对象的内部状态,而随环境改变而改变的、不可以共享的状态就是外部状态。事实上,享元模式可以避免大量非常相似类的开销,在程序设计中,有时需要生成大量细粒度的类实力来表示数据。如果能发现这些实例出了几个参数外基本上都是相同的。有时就能够受大幅度地减少需要实例化的类的数量。如果能把这些参数移到类实力的外面,在方法调用时将他们传递进来,就可以通过共享大幅度地减少单个实例的数目。
根据以上的定义我们可以给网站来个升级:
小菜的web第二版:
namespace Flyweight_Web_Second { public class User { private string name; public User(string name) { this.name = name; } public string Name { get { return name; } } } //网站抽象类 abstract class WebSite { public abstract void Use(User user); } class ConcreteWebSite : WebSite { private string name = ""; public ConcreteWebSite(string name) { this.name = name; } public override void Use(User user) { Console.WriteLine("网站分类:" + name + "用户:" + user.Name); } } //网站工厂 class WebSiteFactory { private Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable(); //获得网站 public WebSite GetWebSiteCategory(string key) { if (!flyweights.ContainsKey(key)) { flyweights.Add(key, new ConcreteWebSite(key)); } return ((WebSite)flyweights[key]); } public int GetWebSiteCount() { return flyweights.Count; } } //客户端 public class Run { public static void GO() { WebSiteFactory f = new WebSiteFactory(); WebSite fx = f.GetWebSiteCategory("产品展示"); fx.Use(new User("小菜1")); WebSite fx2 = f.GetWebSiteCategory("产品展示"); fx2.Use(new User("小菜2")); WebSite fx3 = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fx3.Use(new User("小菜3")); WebSite fx4 = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fx4.Use(new User("小菜4")); WebSite fx5 = f.GetWebSiteCategory("博客"); fx5.Use(new User("小菜5")); Console.WriteLine("得到网站分类总数为{0}", f.GetWebSiteCount()); } } }
享元模式应用:如果一个应用程序使用了大量的对象,而大量的这些对象造成了很大的存储开销时就应该考虑使用;还有就是对象的大多数状态可以外部状态,如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象,此时可以考虑使用享元模式。
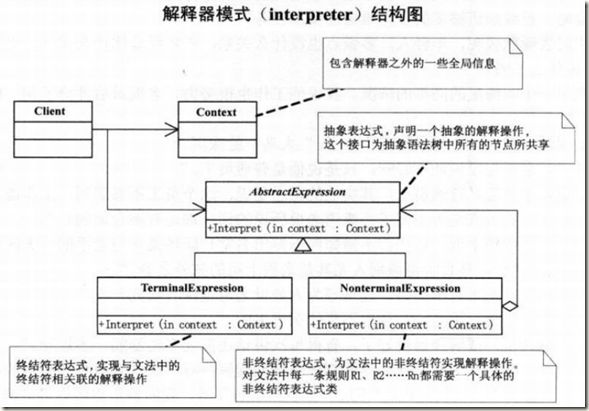
其实你不懂老板的心——解释器模式
解释器模式(interpreter),给定一个语言,定义他的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
如果一种特定类型的问题发生的频率足够高,那么可能就值得奖该问题的各个实例表述为一个简单语言中的句子。这样就可以构造一个解释器,该解释器通过解释这些句子来解决该问题。(正则表达式就是一种应用)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace interpret { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Context context = new Context(); IList<AbstractExpression> list = new List<AbstractExpression>(); list.Add(new TerminalExpression()); list.Add(new NonterminalExpression()); list.Add(new TerminalExpression()); list.Add(new TerminalExpression()); foreach (AbstractExpression exp in list) { exp.Interpret(context); } Console.Read(); } } abstract class AbstractExpression { public abstract void Interpret(Context context); } class TerminalExpression : AbstractExpression { public override void Interpret(Context context) { Console.WriteLine("终端解释器"); } } class NonterminalExpression : AbstractExpression { public override void Interpret(Context context) { Console.WriteLine("非终端解释器"); } } class Context { private string input; public string Input { get { return input; } set { input = value; } } private string output; public string Output { get { return output; } set { output = value; } } } }
代码是看懂了,其实我还有对这个概念有点迷糊。还要去别的文章看看这解释器模式到底是个什么概念
当有一个语言需要解释器执行,并且你可将该语言中的句子表示为一个抽象语法树时,可使用解释器。
优点:容易地改变和扩展文法,因为该模式使用类用来表示文法规则,你可使用继承来改变或扩展该文法,也比较容易实现文法,因为定义抽象语法树中各个节点的类的实现大体类似,这些类都易于直接编写。
不足:解释器模式为文法中的每一条规则至少定义了一个类,因此包含许多规则的文法可能难以管理和维护,建议当文法非常复杂时,使用其他技术如语法分析程序或编译器生成器来处理
男人和女人——访问者模式
先来两个关于男人与与人之间区别的代码:
OO模式
//OO实现 namespace Visitor { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IList<Person> persons = new List<Person>(); Person man1 = new Man(); man1.Action = "成功"; persons.Add(man1); Person woman1 = new Woman(); woman1.Action = "成功"; persons.Add(woman1); Person man2 = new Man(); man2.Action = "失败"; persons.Add(man2); Person woman2 = new Woman(); woman2.Action = "失败"; persons.Add(woman2); Person man3 = new Man(); man3.Action = "恋爱"; persons.Add(man3); Person woman3 = new Woman(); woman3.Action = "恋爱"; persons.Add(woman3); foreach (Person person in persons) { person.GetConclusion(); } Console.Read(); } } abstract class Person { protected string action; public string Action { get { return action; } set { action = value; } } //得到反应和结论 public abstract void GetConclusion(); } class Man : Person { public override void GetConclusion() { if (action == "成功") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,背后多半有一个伟大的女人。", this.GetType().Name, action); } else if (action == "失败") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,闷头喝酒,谁也不用劝。", this.GetType().Name, action); } else if (action == "恋爱") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,凡是不懂也要装懂。", this.GetType().Name, action); } } } class Woman : Person { public override void GetConclusion() { if (action == "成功") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,背后大多有一个不成功的男人。", this.GetType().Name, action); } else if (action == "失败") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,眼泪泪汪汪,谁也劝不了。", this.GetType().Name, action); } else if (action == "恋爱") { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,遇事懂也装不懂。", this.GetType().Name, action); } } } }
来个访问者模式:
//用了访问模式实现。 namespace Visiter_Demo { abstract class Action { //得到男人结论 public abstract void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA); public abstract void GetWomanConclusion(Woman concreteElementB); } abstract class Person { public abstract void Accecpt(Action visitor); } class Success : Action { public override void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA) { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,背后多半有一个伟大的女人。", this.GetType().Name, action); } public override void GetWomanConclusion(Man concreteElementB) { Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}时,背后大多有一个不成功的男人。", this.GetType().Name, action); } } //略 class Fialing : Action { public override void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void GetWomanConclusion(Man concreteElementB) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } //恋爱 略 class Amativeness : Action { public override void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void GetWomanConclusion(Man concreteElementB) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } class Man : Person { public override void Accecpt(Action visitor) { visitor.GetManConclusion(this); } } class Woman : Person { public override void Accecpt(Action visitor) { visitor.GetWomanConclusion(this); } } class ObjectStructure { private IList<Person> elements = new List<Person>(); public void Attach(Person element) { elements.Add(element); } //移除 public void Detach(Person element) { elements.Remove(element); } //查看信息 public void Display(Action visitor) { foreach (Person item in elements) { item.Accecpt(visitor); } } static void Main(string[] args) { ObjectStructure o = new ObjectStructure(); o.Attach(new Man()); o.Attach(new Woman()); Success s = new Success(); o.Display(s); } } }
这样,要是再来个结婚的我们只要添加如下一个类就好了:
class Marriage:Action { public override void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void GetWomanConclusion(Woman concreteElementB) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
访问者使用场景:访问者模式适用于数据结构相对稳定的系统,他把数据结构和作用于结构上的操作之间的耦合解脱开,使得操作集合可以相对自由地演化。
访问者模式目的:把处理数据结构分离出来,很多系统可以按照算法和数据结构分开,如果这样的系统有比较稳定的数据结构,又易于变化的算法的话,使用访问者模式就是比较合适的。因为访问者模式使得算法操作的增加变得容易。
访问者模式的优点:增加新操作很容易,因为增加新的操作就意味着增加一个新的访问者,访问者模式将有关的行为集中到一个访问者对象中。
访问者模式基本代码:
namespace Visiter { abstract class Visitor { public abstract void VisitConcreteElementA(ConcreteElementA concreteElementA); public abstract void VisitConcreteElementB(ConcreteElementB concreteElementB); } class ConcreteVisitor1 : Visitor { public override void VisitConcreteElementA(ConcreteElementA concreteElementA) { Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementA.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name); } public override void VisitConcreteElemtntB(ConcreteElementB concreteElementB) { Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementB.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name); } } class ConcreteVisitor2 : Visitor { public override void VisitConcreteElementA(ConcreteElementA concreteElementA) { Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementA.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name); } public override void VisitConcreteElemtntB(ConcreteElementB concreteElementB) { Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementB.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name); } } abstract class Element { public abstract void Accept(Visitor visitor); } class ConcreteElementA : Element { public override void Accept(Visitor visitor) { visitor.VisitConcreteElementA(this); } public void OperationA(); } class ConcreteElementB : Element { public override void Accept(Visitor visitor) { visitor.VisitConcreteElementB(this); } public void OperationB(); } class ObjectStructure { private IList<Element> elements = new List<Element>(); public void Attach(Element element) { elements.Add(element); } public void Detach(Element element) { elements.Remove(element); } public void Accept(Visitor visitor) { foreach (Element e in elements) { e.Accept(visitor); } } } //客户端代码: public class Run { public static void Go() { ObjectStructure o = new ObjectStructure(); o.Attach(new ConcreteElementA()); o.Attach(new ConcreteElementB()); ConcreteVisitor1 v1 = new ConcreteVisitor1(); ConcreteVisitor2 v2 = new ConcreteVisitor2(); o.Accept(v1); o.Accept(v2); Console.Read(); } } }