嵌入式C++(十三)
文章目录
- 一 类型转换
-
- 1.1 static_cast强制类型转换
- 1.2 reinterpret_cast
- 1.3 const_cast
- 1.4 dynamic_cast
- 二 算法
-
- 2.1 遍历算法
- 2.2 查找算法
- 2.3 排序算法
- 2.4 拷贝替换
- 三 设计模式
-
- 3.1 设计原则
- 3.2 单例模式-懒汉式
- 3.3 单例模式-饿汉式
- 3.4 工厂模式
- 3.5 抽象工厂模式
一 类型转换
c 方式强制类型转换存在的问题
1. 过于粗暴
任意类型之间都能转换,编译器很难判断其正确性
2. 难于定位
在源码中无法快速定位所有使用强制类型转换的语句
1.1 static_cast强制类型转换
1.用于基本类型间的转换,但是不能用于基本类型指针之间的转换
2.用于有继承关系类对象之间的转换和类指针之间的转换。
3.static_cast是在编译期间转换的,无法在运行时检测类型,所以类型之间转换可能存在风险。
#include
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
};
class Child :public Parent
{
};
int main(void)
{
int a = 1;
char ch = 'x';
a = static_cast(ch); //用于普通类型之间的转换
//int *p = static_cast(&ch);
Parent p;
Child c;
//p = c;
p = static_cast(c); //用于有继承关系的类对象之间的转换
//c = static_cast(p);
Parent *p1 = static_cast(&c); //类对象指针之间的转换
}
1.2 reinterpret_cast
#include
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int c = 200;
int b = 100;
char *p = reinterpret_cast(&c); //用于普通指针之间的转换(不安全)
cout << *(p + 1) << endl;
//cout << *(&b + 1) << endl;
int *q = reinterpret_cast(100); //用于数字和指针之间的转换(很容易出现野指针)
*q = 1;
return 0;
}
1.3 const_cast
#include
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
const int a = 1; //常量
int *p = const_cast(&a);
*p = 100;
cout << a << endl;
cout << *p << endl;
const int &m = 1;
int &n = const_cast(m);
n = 100;
cout << m << endl;
cout << n << endl;
const int x = 1;
int &y = const_cast(x);
y = 100;
cout << x << endl;
cout << y << endl;
int z = 200;
const int *p1= &z;
int *q = const_cast(p1);
*q = 300;
cout << *q << endl;
cout << *p1 << endl;
return 0;
}
1.4 dynamic_cast
#include
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
public:
virtual void f()
{
}
};
class Child :public Parent
{
public:
void f()
{
}
};
int main(void)
{
Child *c = new Child;
delete c;
//c = static_cast(new Parent); //派生类指针指向基类对象(错误)
c = dynamic_cast(new Parent); //运行时候会进行类型检查,不能转换,会返回NULL,比static_cast安全
if (NULL == c)
{
cout << "转换失败" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "转换成功" << endl;
delete c;
}
return 0;
}
二 算法
更易型算法
非更易型算法
排序算法
#include
# //数学运算的模板函数
# //提供了一些模板类,用来声明函数对象
2.1 遍历算法
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
};
void show(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
int array[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector v(array,array + 5);
//for_each
//for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), show); //回调函数
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print()); //函数对象的形式遍历
//transform遍历过程中可以修改数据
string s("hello world");
transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),::toupper);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 查找算法
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool GreaterTwo(int x)
{
return x > 2;
}
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
};
class GreaterThree
{
public:
bool operator()(int x)
{
return x > 3;
}
};
void show(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
int array[7] = { 6,2,4,5,2,5 };
vector v(array, array + 6);
auto it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "不存在重复且相邻的元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 4); //查找有序的序列,二分查找法 // [1,3) 3 [4,7)
if (ret)
{
cout << "元素存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "元素不存在" << endl;
}
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 2);
cout << num << endl;
num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterTwo); //一元谓词 回调函数
cout << num << endl;
it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "元素不存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterThree());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "元素不存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.3 排序算法
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool GreaterTwo(int x)
{
return x > 2;
}
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
};
class GreaterThree
{
public:
bool operator()(int x)
{
return x > 3;
}
};
void show(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
vector v1;
vector v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.emplace_back(rand() % 10);
v2.emplace_back(rand() % 10);
}
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), less());
stable_sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), less());
for (auto &v : v1)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto &v : v2)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector v3;
v3.resize(20);
merge(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(),v2.end(),v3.begin());
for (auto &v : v3)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
random_shuffle(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto &v : v1)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
reverse(v3.begin(), v3.end());
for (auto &v : v3)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
string s("hello world");
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
2.4 拷贝替换
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void show(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
vector v1(5, 1);
vector v2(5, 2);
v2.resize(6);
copy(v1.begin(),v1.end(),++(v2.begin()));
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), show);
cout << endl;
swap(v1, v2);
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), show);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
三 设计模式
创建型模式:
工厂模式,抽象工厂模式,单例模式,建造者模式等
结构型模式:
关注类和对象的组合,继承被用来组合接口和定义组合对象
适配器模式,桥接模式 组合模式,外观模式 等
行为型模式:
关注对象之间的通信
3.1 设计原则
1.开放封闭原则:所有新增的功能不是通过类的改动来实现,而是通过新增代码来实现。
2.依赖倒置原则:依赖与抽象,不依赖于具体的实现
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class BankWoker
{
public:
virtual void Worker() = 0;
};
class GetMoney :public BankWoker
{
public:
void Worker()
{
cout << "取款业务" << endl;
}
};
class SaveMoney :public BankWoker
{
public:
void Worker()
{
cout << "存款业务" << endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
BankWoker *b = new GetMoney;
b->Worker();
delete b;
b = new SaveMoney;
b->Worker();
return 0;
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class HardDisk
{
public:
virtual void work() = 0;
};
class CPU
{
public:
virtual void work() = 0;
};
class AHardDisk :public HardDisk
{
public:
void work()
{
cout << "hard disk work..." << endl;
}
};
class ACPU:public CPU
{
public:
virtual void work()
{
cout << "ACPU WORK..." << endl;
}
};
class Computer
{
private:
HardDisk *m_h;
CPU *m_c;
public:
Computer(HardDisk *h, CPU *c)
{
m_h = h;
m_c = c;
}
void work()
{
m_h->work();
m_c->work();
}
};
int main(void)
{
CPU *c = new ACPU;
HardDisk *h = new AHardDisk;
Computer com(h,c);
com.work();
return 0;
}
3.2 单例模式-懒汉式
保证一个类只能生成唯一的实例对象,也就是说,在整个程序中,只存在一个实例对象。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
private:
static Singleton *m_instance;
static int count;
Singleton()
{
}
public:
static Singleton *GetInstance()
{
if (NULL == m_instance)
{
cout<<"m_instance = NULL!"< 3.3 单例模式-饿汉式
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
private:
static Singleton *m_instance;
static int count;
Singleton()
{
}
public:
static Singleton *GetInstance()
{
/*if (NULL == m_instance)
{
cout<<"m_instance = NULL!"< 3.4 工厂模式
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Fruit
{
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
};
class Apple :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is apple" << endl;
}
};
class Banana :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is Banana" << endl;
}
};
class Pear :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is Pear" << endl;
}
};
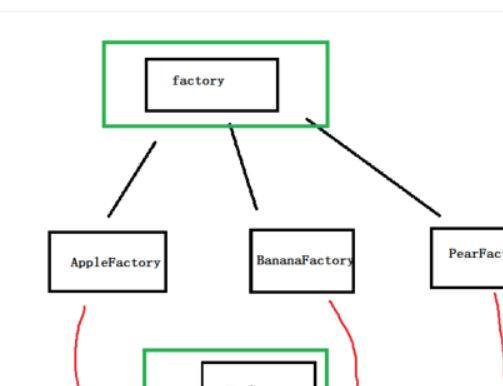
class Factory
{
public:
virtual Fruit *Create() = 0;
};
class AppleFactory :public Factory
{
public:
Fruit *Create()
{
return new Apple;
}
};
class BananaFactory :public Factory
{
public:
Fruit *Create()
{
return new Banana;
}
};
class PearFactory :public Factory
{
public:
Fruit *Create()
{
return new Pear;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Factory *f = new AppleFactory;
Fruit *fruit;
fruit = f->Create();
fruit->show();
delete f;
delete fruit;
f = new BananaFactory;
fruit = f->Create();
fruit->show();
return 0;
}
3.5 抽象工厂模式
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Fruit
{
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
};
class NorthApple :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is NorthApple" << endl;
}
};
class SouthApple :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is SouthApple" << endl;
}
};
class NorthBanana :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is NorthBanana" << endl;
}
};
class SouthBanana :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is SouthBanana" << endl;
}
};
class NorthPear :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is NorthPear" << endl;
}
};
class SouthPear :public Fruit
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "this is SouthPear" << endl;
}
};
class Factory
{
public:
virtual Fruit *CreateApple() = 0;
virtual Fruit *CreateBanana() = 0;
virtual Fruit *CreatePear() = 0;
};
class NorthFactory :public Factory
{
public:
virtual Fruit *CreateApple()
{
return new NorthApple;
}
virtual Fruit *CreateBanana()
{
return new NorthBanana;
}
virtual Fruit *CreatePear()
{
return new NorthPear;
}
};
class SouthFactory :public Factory
{
public:
virtual Fruit *CreateApple()
{
return new SouthApple;
}
virtual Fruit *CreateBanana()
{
return new SouthBanana;
}
virtual Fruit *CreatePear()
{
return new SouthPear;
}
};
void Create(Factory *f)
{
Fruit *fruit;
fruit = f->CreateApple();
fruit->show();
delete fruit;
fruit = f->CreateBanana();
fruit->show();
delete fruit;
}
int main(void)
{
Factory *f = new SouthFactory;
Create(f);
delete f;
f = new NorthFactory;
Create(f);
Fruit *f1 = new SouthApple;
f1->show();
return 0;
}
3.6 建造者模式