python数据分析_Python数据分析、挖掘常用工具
源 / Python爱好者社区 作者 / 深度沉迷学习
Python语言: 简要概括一下Python语言在数据分析、挖掘场景中常用特性:- 列表(可以被修改),元组(不可以被修改)
- 字典(结构)
- 集合(同数学概念上的集合)
- 函数式编程(主要由lambda()、map()、reduce()、filter()构成)
Python数据分析常用库:
 Python数据挖掘相关扩展库
Python数据挖掘相关扩展库
NumPy
提供真正的数组,相比Python内置列表来说速度更快,NumPy也是Scipy、Matplotlib、Pandas等库的依赖库,内置函数处理数据速度是C语言级别的,因此使用中应尽量使用内置函数。 示例: NumPy基本操作import numpy as np # 一般以np为别名a = np.array([2, 0, 1, 5])print(a)print(a[:3])print(a.min())a.sort() # a被覆盖print(a)b = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])print(b*b)[2 0 1 5][2 0 1]0[0 1 2 5][[ 1 4 9] [16 25 36]]Scipy
NumPy和Scipy让Python有了MATLAB味道。 Scipy依赖于NumPy,NumPy提供了多维数组功能,但只是一般的数组并不是矩阵。 比如两个数组相乘时,只是对应元素相乘。 Scipy提供了真正的矩阵,以及大量基于矩阵运算的对象与函数。 Scipy包含功能有最优化、线性代数、积分、插值、拟合、特殊函数、快速傅里叶变换、信号处理、图像处理、常微分方程求解等常用计算。 示例: Scipy求解非线性方程组和数值积分# 求解方程组from scipy.optimize import fsolvedef f(x): x1 = x[0] x2 = x[1] return [2 * x1 - x2 ** 2 - 1, x1 ** 2 - x2 - 2]result = fsolve(f, [1, 1])print(result)# 积分from scipy import integratedef g(x): # 定义被积函数 return (1 - x ** 2) ** 0.5pi_2, err = integrate.quad(g, -1, 1) # 输出积分结果和误差print(pi_2 * 2, err)[ 1.91963957 1.68501606]3.141592653589797 1.0002356720661965e-09Matplotlib
Python中著名的绘图库,主要用于二维绘图,也可以进行简单的三维绘图。 示例: Matplotlib绘图基本操作import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npx = np.linspace(0, 10, 10000) # 自变量x,10000为点的个数y = np.sin(x) + 1 # 因变量yz = np.cos(x ** 2) + 1 # 因变量zplt.figure(figsize=(8, 4)) # 设置图像大小# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei' # 标签若有中文,则需设置字体# plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 保存图像时若负号显示不正常,则添加该句# 两条曲线plt.plot(x, y, label='$\sin (x+1)$', color='red', linewidth=2) # 设置标签,线条颜色,线条大小plt.plot(x, z, 'b--', label='$\cos x^2+1$')plt.xlim(0, 10) # x坐标范围plt.ylim(0, 2.5) # y坐标范围plt.xlabel("Time(s)") # x轴名称plt.ylabel("Volt") # y轴名称plt.title("Matplotlib Sample") # 图的标题plt.legend() # 显示图例plt.show() # 显示作图结果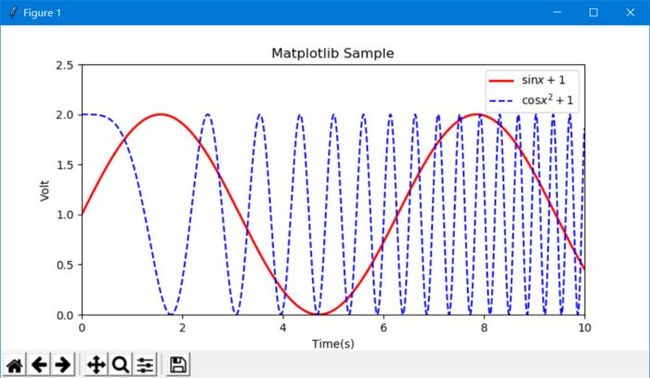
Pandas
Pandas是Python下非常强大的数据分析工具。 它建立在NumPy之上,功能很强大,支持类似SQL的增删改查,并具有丰富的数据处理函数,支持时间序列分析功能,支持灵活处理缺失数据等。 Pandas基本数据结构是Series和DataFrame。 Series就是序列,类似一维数组,DataFrame则相当于一张二维表格,类似二维数组,它每一列都是一个Series。 为定位Series中的元素,Pandas提供了Index对象,类似主键。 DataFrame本质上是Series的容器。 示例: Pandas简单操作import pandas as pds = pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])d = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18]], columns=['a', 'b', 'c'])d2 = pd.DataFrame(s)print(s)print(d.head()) # 预览前5行print(d.describe())# 读取文件(路径最好别带中文)df=pd.read_csv("G:\\data.csv", encoding="utf-8")print(df)a 1b 2c 3dtype: int64 a b c0 1 2 31 4 5 62 7 8 93 10 11 124 13 14 15 a b ccount 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000mean 8.500000 9.500000 10.500000std 5.612486 5.612486 5.612486min 1.000000 2.000000 3.00000025% 4.750000 5.750000 6.75000050% 8.500000 9.500000 10.50000075% 12.250000 13.250000 14.250000max 16.000000 17.000000 18.000000Empty DataFrameColumns: [1068, 12, 蔬果, 1201, 蔬菜, 120104, 花果, 20150430, 201504, DW-1201040010, 散称, 生鲜, 千克, 0.973, 5.43, 2.58, 否]Index: []Scikit-Learn
Scikit-Learn依赖NumPy、Scipy和Matplotlib,是Python中强大的机器学习库,提供了诸如数据预处理、分类、回归、聚类、预测和模型分析等功能。 示例: 创建线性回归模型from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionmodel= LinearRegression()print(model)- 所有模型都提供的接口:
model.fit(): 训练模型,监督模型是fit(X,y),无监督模型是fit(X)
- 监督模型提供的接口:
model.predict(X_new): 预测新样本 model.predict_proba(X_new): 预测概率,仅对某些模型有用(LR)
- 无监督模型提供的接口:
model.ransform(): 从数据中学到新的“基空间” model.fit_transform(): 从数据中学到的新的基,并将这个数据按照这组“基”进行转换Scikit-Learn本身自带了一些数据集,如花卉和手写图像数据集等,下面以花卉数据集举个栗子,训练集包含4个维度——萼片长度、宽度,花瓣长度和宽度,以及四个亚属分类结果。 示例:
from sklearn import datasets # 导入数据集from sklearn import svmiris = datasets.load_iris() # 加载数据集clf = svm.LinearSVC() # 建立线性SVM分类器clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target) # 用数据训练模型print(clf.predict([[5, 3, 1, 0.2], [5.0, 3.6, 1.3, 0.25]]))[0 0]Keras
Keras是基于Theano的深度学习库,它不仅可以搭建普通神经网络,还可以搭建各种深度学习模型,如自编码器、循环神经网络、递归神经网络、卷积神经网络等,运行速度也很快,简化了搭建各种神经网络模型的步骤,允许普通用户轻松搭建几百个输入节点的深层神经网络,定制度也很高。 示例: 简单的MLP(多层感知器)from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers.core import Dense, Dropout, Activationfrom keras.optimizers import SGDmodel = Sequential() # 模型初始化model.add(Dense(20, 64)) # 添加输入层(20节点)、第一隐藏层(64节点)的连接model.add(Activation('tanh')) # 第一隐藏层用tanh作为激活函数model.add(Dropout(0.5)) # 使用Dropout防止过拟合model.add(Dense(64, 64)) # 添加第一隐藏层(64节点)、第二隐藏层(64节点)的连接model.add(Activation('tanh')) # 第二隐藏层用tanh作为激活函数model.add(Dense(64, 1)) # 添加第二隐藏层(64节点)、输出层(1节点)的连接model.add(Activation('sigmod')) # 第二隐藏层用sigmod作为激活函数sgd=SGD(lr=0.1,decay=1e-6,momentum=0.9,nesterov=True) # 定义求解算法model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',optimizer=sgd) # 编译生成模型,损失函数为平均误差平方和model.fit(x_train,y_train,nb_epoch=20,batch_size=16) # 训练模型score = model.evaluate(X_test,y_test,batch_size=16) # 测试模型- Keras中文文档
- 如何计算两个文档的相似度(二)
Genism
Genism主要用来处理语言方面的任务,如文本相似度计算、LDA、Word2Vec等。 示例:import loggingfrom gensim import modelslogging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s : %(levelname)s : %(message)s', level=logging.INFO)sentences = [['first', 'sentence'], ['second', 'sentence']] # 将分好词的句子按列表形式输入model = models.Word2Vec(sentences, min_count=1) # 用以上句子训练词向量模型print(model['sentence']) # 输出单词sentence的词向量2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : collecting all words and their counts2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : PROGRESS: at sentence #0, processed 0 words, keeping 0 word types2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : collected 3 word types from a corpus of 4 raw words and 2 sentences2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : Loading a fresh vocabulary2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : min_count=1 retains 3 unique words (100% of original 3, drops 0)2017-10-24 19:02:40,785 : INFO : min_count=1 leaves 4 word corpus (100% of original 4, drops 0)2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : deleting the raw counts dictionary of 3 items2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : sample=0.001 downsamples 3 most-common words2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : downsampling leaves estimated 0 word corpus (5.7% of prior 4)2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : estimated required memory for 3 words and 100 dimensions: 3900 bytes2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : resetting layer weights2017-10-24 19:02:40,786 : INFO : training model with 3 workers on 3 vocabulary and 100 features, using sg=0 hs=0 sample=0.001 negative=5 window=52017-10-24 19:02:40,788 : INFO : worker thread finished; awaiting finish of 2 more threads2017-10-24 19:02:40,788 : INFO : worker thread finished; awaiting finish of 1 more threads2017-10-24 19:02:40,788 : INFO : worker thread finished; awaiting finish of 0 more threads2017-10-24 19:02:40,789 : INFO : training on 20 raw words (0 effective words) took 0.0s, 0 effective words/s2017-10-24 19:02:40,789 : WARNING : under 10 jobs per worker: consider setting a smaller `batch_words' for smoother alpha decay[ -1.54225400e-03 -2.45212857e-03 -2.20486755e-03 -3.64410551e-03 -2.28137174e-03 -1.70348200e-03 -1.05830852e-03 -4.37875278e-03 -4.97106137e-03 3.93485563e-04 -1.97932171e-03 -3.40653211e-03 1.54990738e-03 8.97102174e-04 2.94041773e-03 3.45200230e-03 -4.60584508e-03 3.81468004e-03 3.07120802e-03 2.85422982e-04 7.01598416e-04 2.69670971e-03 4.17246483e-03 -6.48593705e-04 1.11404411e-03 4.02203249e-03 -2.34672683e-03 2.35153269e-03 2.32632101e-05 3.76200466e-03 -3.95653257e-03 3.77303245e-03 8.48884694e-04 1.61545759e-03 2.53374409e-03 -4.25464474e-03 -2.06338940e-03 -6.84972096e-04 -6.92955102e-04 -2.27969326e-03 -2.13766913e-03 3.95324081e-03 3.52649018e-03 1.29243149e-03 4.29229392e-03 -4.34781052e-03 2.42843386e-03 3.12117115e-03 -2.99768522e-03 -1.17538485e-03 6.67148328e-04 -6.86432002e-04 -3.58940102e-03 2.40547652e-03 -4.18888079e-03 -3.12567432e-03 -2.51603196e-03 2.53451476e-03 3.65199335e-03 3.35336081e-03 -2.50071986e-04 4.15537134e-03 -3.89242987e-03 4.88173496e-03 -3.34603712e-03 3.18462006e-03 1.57053335e-04 3.51517834e-03 -1.20337342e-03 -1.81524854e-04 3.57784083e-05 -2.36600707e-03 -3.77405947e-03 -1.70441647e-03 -4.51521482e-03 -9.47134569e-04 4.53894213e-03 1.55767589e-03 8.57840874e-04 -1.12304837e-03 -3.95945460e-03 5.37869288e-04 -2.04461766e-03 5.24829782e-04 3.76719423e-03 -4.38512256e-03 4.81262803e-03 -4.20147832e-03 -3.87057988e-03 1.67581497e-03 1.51928759e-03 -1.31744961e-03 3.28474329e-03 -3.28777428e-03 -9.67226923e-04 4.62622894e-03 1.34165725e-03 3.60148447e-03 4.80416557e-03 -1.98963983e-03]- 如何计算两个文档的相似度(二)
-END-
转载声明:本文选自「Python爱好者社区」
重磅推出全新学习模式
用打卡学Python
每天30分钟
30天学会Python编程

世界正在奖励坚持学习的人!