单词接龙 II
说在前面
不知道大家对于算法的学习是一个怎样的心态呢?为了面试还是因为兴趣?不管是处于什么原因,算法学习需要持续保持,今天让我们一起来看看这一道题目————
单词接龙 II,主要使用到的知识点是广度优先搜索。
题目描述
按字典 wordList 完成从单词 beginWord 到单词 endWord 转化,一个表示此过程的 转换序列 是形式上像 beginWord -> s1 -> s2 -> … -> sk 这样的单词序列,并满足:
- 每对相邻的单词之间仅有单个字母不同。
- 转换过程中的每个单词 si(1 <= i <= k)必须是字典 wordList 中的单词。注意,beginWord 不必是字典 wordList 中的单词。
- sk == endWord
给你两个单词 beginWord 和 endWord ,以及一个字典 wordList 。请你找出并返回所有从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 ,如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回一个空列表。每个序列都应该以单词列表 [beginWord, s1, s2, …, sk] 的形式返回。
示例 1:
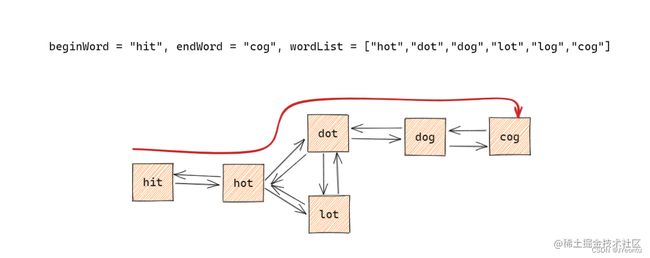
输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
输出:[["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]]
解释:存在 2 种最短的转换序列:
"hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog"
"hit" -> "hot" -> "lot" -> "log" -> "cog"
示例 2:
输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
输出:[]
解释:endWord "cog" 不在字典 wordList 中,所以不存在符合要求的转换序列。
提示:
1 <= beginWord.length <= 5
endWord.length == beginWord.length
1 <= wordList.length <= 500
wordList[i].length == beginWord.length
beginWord、endWord 和 wordList[i] 由小写英文字母组成
beginWord != endWord
wordList 中的所有单词 互不相同
思路分析
阅读完题目之后我们知道题目的要求是这样的:
- 给出起始单词和目标单词,要我们找出其实单词转化成目标单词的最少步数
- 每次转化可以从给出的字典中取一个与当前单词之间仅有单个字母不同的单词进行转换
主要就是这么两点,刚看到这里我马上动手来了一个dfs遍历,结果如下:
/**
* @param {string} beginWord
* @param {string} endWord
* @param {string[]} wordList
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var findLadders = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
let res = false;
let flag = new Array(wordList.length).fill(true);
let ans = [beginWord];
let ansList = [];
let minLen = Infinity;
const isDiff1 = function(w1,w2){
if(w1.length != w2.length || w1 == w2) return false;
let num = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < w1.length; i++){
if(w1[i] != w2[i]) num++;
if(num > 1) return false;
}
return true;
};
const dfs = function(nowWord){
if(nowWord === endWord){
res = true;
if(ans.length < minLen) {
minLen = ans.length;
ansList = [[...ans]];
}else if(ans.length == minLen){
ansList.push([...ans]);
}
return;
}
for(let i = 0; i < wordList.length && ans.length < minLen; i++){
if(flag[i] && isDiff1(nowWord,wordList[i])){
flag[i] = false;
ans.push(wordList[i]);
dfs(wordList[i]);
ans.pop();
flag[i] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(beginWord);
return ansList;
};
很明显,这道题目并不能使用dfs进行解题,所以我们应该转换一下思路,因为起始单词是固定的,所以我们可以求出所有单词的最短转换路径长度,如下图:
虽然中间还有很多条路径,但我们可以得到这么一条最短的道路,那么这条道路要怎么确定下来呢?很明显,这里我们需要先确定每一个单词由起始单词转换过来的最少步数
1、记录每个单词可以转换的下一个单词
将每一个单词可以转换的下一个单词存入对应的哈希表,便于后面进行转换时进行取值。
map[beginWord] = [];
for(let i = 0; i < wordList.length; i++){
map[wordList[i]] = [];
if(isDiff1(wordList[i],beginWord)){
map[beginWord].push(wordList[i]);
}
for(let j = 0; j < wordList.length; j++){
if(j == i) continue;
if(isDiff1(wordList[i],wordList[j])){
map[wordList[i]].push(wordList[j]);
}
}
}
2、计算转换的最少步数
从起始点出发,不断往后转换,比较从不同路径转换的步数大小,取最小步数。
const stepCalc = function(nowWord,step){
wordStep[nowWord] = step;
for(let key of map[nowWord]){
if(!wordStep[key] || wordStep[key] > step + 1){
stepCalc(key,step+1);
}
}
};
stepCalc(beginWord,0);
3、通过步数找出最短路径
由目标单词的步数往回推,找出其上一个转换单词。
const bfs = function(step,tarWord,ans){
if(step === 0){
if(isDiff1(beginWord,tarWord)){
ansList.push([beginWord,...ans]);
}
return;
}
if(!stepList[step]) return;
for(let key of stepList[step]){
if(isDiff1(key,tarWord)){
bfs(step-1,key,[key,...ans]);
}
}
};
bfs(wordStep[endWord] - 1,endWord,[endWord]);
完整代码
/**
* @param {string} beginWord
* @param {string} endWord
* @param {string[]} wordList
* @return {string[][]}
*/
const isDiff1 = function(w1,w2){
let num = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < w1.length; i++){
if(w1[i] != w2[i]) num++;
if(num > 1) return false;
}
return num == 1;
};
var findLadders = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
if(!wordList.includes(endWord)) return [];
const ansList = [];
const map = {};
const stepList = {};
const wordStep = {};
map[beginWord] = [];
for(let i = 0; i < wordList.length; i++){
map[wordList[i]] = [];
if(isDiff1(wordList[i],beginWord)){
map[beginWord].push(wordList[i]);
}
for(let j = 0; j < wordList.length; j++){
if(j == i) continue;
if(isDiff1(wordList[i],wordList[j])){
map[wordList[i]].push(wordList[j]);
}
}
}
const stepCalc = function(nowWord,step){
wordStep[nowWord] = step;
for(let key of map[nowWord]){
if(!wordStep[key] || wordStep[key] > step + 1){
stepCalc(key,step+1);
}
}
};
stepCalc(beginWord,0);
for(let key of wordList){
if(!stepList[wordStep[key]]) stepList[wordStep[key]] = [];
stepList[wordStep[key]].push(key);
}
const bfs = function(step,tarWord,ans){
if(step === 0){
if(isDiff1(beginWord,tarWord)){
ansList.push([beginWord,...ans]);
}
return;
}
if(!stepList[step]) return;
for(let key of stepList[step]){
if(isDiff1(key,tarWord)){
bfs(step-1,key,[key,...ans]);
}
}
};
bfs(wordStep[endWord] - 1,endWord,[endWord]);
return ansList;
};
说在后面
这里是JYeontu,喜欢算法,GDCPC打过卡;热爱羽毛球,大运会打过酱油。毕业一年,两年前端开发经验,目前担任H5前端开发,算法业余爱好者,有空会刷刷算法题,平时喜欢打打羽毛球 ,也喜欢写些东西,既为自己记录,也希望可以对大家有那么一丢丢的帮助,写的不好望多多谅解,写错的地方望指出,定会认真改进,在此谢谢大家的支持,我们下文再见。