Hive (十) --------- 企业级调优
目录
- 一、执行计划
- 二、Fetch 抓取
- 三、本地模式
- 四、表的优化
-
- 1. 小表大表 Join (MapJOIN)
- 2. 大表 Join 大表
- 3. Group By
- 4. Count(Distinct) 去重统计
- 5. 笛卡尔积
- 6. 行列过滤
- 五、合理设置 Map 及 Reduce 数
-
- 1. 复杂文件增加 Map 数
- 2. 小文件进行合并
- 3. 合理设置 Reduce 数
- 六、并行执行
- 七、严格模式
一、执行计划
基本语法
EXPLAIN [EXTENDED | DEPENDENCY | AUTHORIZATION] query
查看下面这条语句的执行计划
A、没有生成 MR 任务的
hive (default)> explain select * from emp;
Explain
STAGE DEPENDENCIES:
Stage-0 is a root stage
STAGE PLANS:
Stage: Stage-0
Fetch Operator
limit: -1
Processor Tree:
TableScan
alias: emp
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
Select Operator
expressions: empno (type: int), ename (type: string), job
(type: string), mgr (type: int), hiredate (type: string), sal (type:
double), comm (type: double), deptno (type: int)
outputColumnNames: _col0, _col1, _col2, _col3, _col4, _col5,_col6, _col7
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
ListSink
B、有生成 MR 任务的
hive (default)> explain select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by
deptno;
Explain
STAGE DEPENDENCIES:
Stage-1 is a root stage
Stage-0 depends on stages: Stage-1
STAGE PLANS:
Stage: Stage-1
Map Reduce
Map Operator Tree:
TableScan
alias: emp
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
Select Operator
expressions: sal (type: double), deptno (type: int)
outputColumnNames: sal, deptno
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
Group By Operator
aggregations: sum(sal), count(sal)
keys: deptno (type: int)
mode: hash
outputColumnNames: _col0, _col1, _col2
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats:
COMPLETE Column stats: NONE
Reduce Output Operator
key expressions: _col0 (type: int)
sort order: +
Map-reduce partition columns: _col0 (type: int)
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size:7020 Basic stats:COMPLETE Column stats: NONE
value expressions: _col1 (type: double), _col2 (type:bigint)
Execution mode: vectorized
Reduce Operator Tree:
Group By Operator
aggregations: sum(VALUE._col0), count(VALUE._col1)
keys: KEY._col0 (type: int)
mode: mergepartial
outputColumnNames: _col0, _col1, _col2
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
Select Operator
expressions: _col0 (type: int), (_col1 / _col2) (type: double)
outputColumnNames: _col0, _col1
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
File Output Operator
compressed: false
Statistics: Num rows: 1 Data size: 7020 Basic stats: COMPLETE
Column stats: NONE
table:
input format:org.apache.hadoop.mapred.SequenceFileInputFormat
output format:org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveSequenceFileOutputFormat
serde: org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe
Stage: Stage-0
Fetch Operator
limit: -1
Processor Tree:
ListSink
查看详细执行计划
hive (default)> explain extended select * from emp;
hive (default)> explain extended select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno
二、Fetch 抓取
Fetch 抓取是指,Hive 中对某些情况的查询可以不必使用 MapReduce 计算。例如:
SELECT * FROM employees; 在这种情况下,Hive 可以简单地读取 employee 对应的存储目录下的文件,然后输出查询结果到控制台。
在 hive-default.xml.template 文件中 hive.fetch.task.conversion 默认是 more,老版本 hive 默认是 minimal,该属性修改为 more 以后,在全局查找、字段查找、limit 查找等都不走 mapreduce。
<property>
<name>hive.fetch.task.conversionname>
<value>morevalue>
<description>
Expects one of [none, minimal, more].
Some select queries can be converted to single FETCH task minimizing
latency.
Currently the query should be single sourced not having any subquery
and should not have any aggregations or distincts (which incurs RS),
lateral views and joins.
0. none : disable hive.fetch.task.conversion
1. minimal : SELECT STAR, FILTER on partition columns, LIMIT only
2. more : SELECT, FILTER, LIMIT only (support TABLESAMPLE and
virtual columns)
description>
property>
三、本地模式
大多数的 Hadoop Job 是需要 Hadoop 提供的完整的可扩展性来处理大数据集的。不过,有时 Hive 的输入数据量是非常小的。在这种情况下,为查询触发执行任务消耗的时间可能会比实际 job 的执行时间要多的多。对于大多数这种情况,Hive 可以通过本地模式在单台机器上处理所有的任务。对于小数据集,执行时间可以明显被缩短。
用户可以通过设置 hive.exec.mode.local.auto 的值为 true,来让 Hive 在适当的时候自动启动这个优化。
set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true; //开启本地 mr
//设置 local mr 的最大输入数据量,当输入数据量小于这个值时采用 local mr 的方式,默认为 134217728,即 128M
set hive.exec.mode.local.auto.inputbytes.max=50000000;
//设置 local mr 的最大输入文件个数,当输入文件个数小于这个值时采用 local mr 的方式,默认为 4
set hive.exec.mode.local.auto.input.files.max=1
四、表的优化
1. 小表大表 Join (MapJOIN)
将 key 相对分散,并且数据量小的表放在 join 的左边,可以使用 map join 让小的维度表先进内存。在 map 端完成 join。
实际测试发现:新版的 hive 已经对小表 JOIN 大表和大表 JOIN 小表进行了优化。小表放在左边和右边已经没有区别。
案例实操
A、需求介绍
测试大表 JOIN 小表和小表 JOIN 大表的效率
B、开启 MapJoin 参数设置
设置自动选择 Mapjoin
set hive.auto.convert.join = true; 默认为 true
大表小表的阈值设置(默认 25M 以下认为是小表):
set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize = 25000000;
C、MapJoin 工作机制
D、建大表、小表和 JOIN 后表的语句
// 创建大表
create table bigtable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
// 创建小表
create table smalltable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
// 创建 join 后表的语句
create table jointable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimitedfields terminated by '\t';
E、分别向大表和小表中导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/bigtable' into table bigtable;
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/smalltable' into table smalltable;
F、小表 JOIN 大表语句
insert overwrite table jointable
select b.id, b.t, b.uid, b.keyword, b.url_rank, b.click_num, b.click_url
from smalltable s
join bigtable b
on b.id = s.id;
G、大表 JOIN 小表语句
insert overwrite table jointable
select b.id, b.t, b.uid, b.keyword, b.url_rank, b.click_num, b.click_url
from bigtable b
join smalltable s
on s.id = b.id;
2. 大表 Join 大表
空 KEY 过滤
有时 join 超时是因为某些 key 对应的数据太多,而相同 key 对应的数据都会发送到相同的 reducer 上,从而导致内存不够。此时我们应该仔细分析这些异常的 key,很多情况下,这些 key 对应的数据是异常数据,我们需要在 SQL 语句中进行过滤。例如 key 对应的字段为空,操作如下:
案例实操
A、配置历史服务器
配置 mapred-site.xml
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.addressname>
<value>hadoop102:10020value>
property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.webapp.addressname>
<value>hadoop102:19888value>
property>
启动历史服务器
sbin/mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start historyserver
查看 jobhistory
http://hadoop102:19888/jobhistory
B、创建原始数据空 id 表
// 创建空 id 表
create table nullidtable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
C、分别加载原始数据和空 id 数据到对应表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/nullid' into table nullidtable;
D、测试不过滤空 id
hive (default)> insert overwrite table jointable select n.* from nullidtable n left join bigtable o on n.id = o.id;
E、测试过滤空 id
hive (default)> insert overwrite table
jointable select n.* from (select * from nullidtable where id is not null) n
left join bigtable o on n.id = o.id;
空 key 转换
有时虽然某个 key 为空对应的数据很多,但是相应的数据不是异常数据,必须要包含在 join 的结果中,此时我们可以表 a 中 key 为空的字段赋一个随机的值,使得数据随机均匀地分不到不同的 reducer 上。
例如:
案例实操:
不随机分布空 null 值:
A、设置 5 个 reduce 个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 5;
B、JOIN 两张表
insert overwrite table jointable
select n.* from nullidtable n left join bigtable b on n.id = b.id;
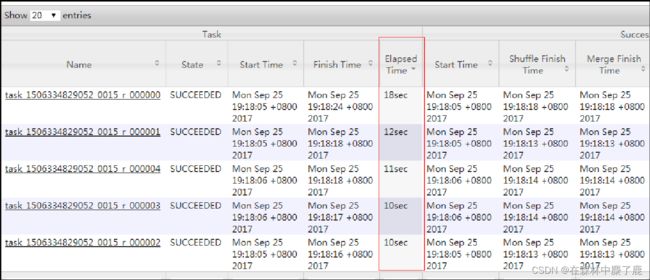
结果:如下图所示,可以看出来,出现了数据倾斜,某些 reducer 的资源消耗远大于其他 reducer。
A、设置 5 个 reduce 个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 5;
B、JOIN 两张表
insert overwrite table jointable
select n.* from nullidtable n full join bigtable o on
nvl(n.id,rand()) = o.id;
结果:如下图所示,可以看出来,消除了数据倾斜,负载均衡 reducer 的资源消耗。
SMB(Sort Merge Bucket join)
A、创建第二张大表
create table bigtable2(
id bigint,
t bigint,
uid string,
keyword string,
url_rank int,
click_num int,
click_url string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/bigtable' into table bigtable2;
B、测试大表直接 JOIN
insert overwrite table jointable
select b.id, b.t, b.uid, b.keyword, b.url_rank, b.click_num, b.click_url
from bigtable s
join bigtable2 b
on b.id = s.id;
C、创建分通表 1,桶的个数不要超过可用 CPU 的核数
create table bigtable_buck1(
id bigint,
t bigint,
uid string,
keyword string,
url_rank int,
click_num int,
click_url string
)
clustered by(id)
sorted by(id)
into 6 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/bigtable' into table bigtable_buck1;
D、创建分通表 2,桶的个数不要超过可用 CPU 的核数
create table bigtable_buck2(
id bigint,
t bigint,
uid string,
keyword string,
url_rank int,
click_num int,
click_url string
)
clustered by(id)
sorted by(id)
into 6 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/bigtable' into table
bigtable_buck2;
E、设置参数
set hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin = true;
set hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin.sortedmerge = true;
set hive.input.format=org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.BucketizedHiveInputFormat;
F、测试
insert overwrite table jointable
select b.id, b.t, b.uid, b.keyword, b.url_rank, b.click_num, b.click_url
from bigtable_buck1 s
join bigtable_buck2 b
on b.id = s.id;
3. Group By
默认情况下,Map 阶段同一 Key 数据分发给一个 reduce,当一个 key 数据过大时就倾斜了

并不是所有的聚合操作都需要在 Reduce 端完成,很多聚合操作都可以先在 Map 端进行部分聚合,最后在 Reduce 端得出最终结果。
开启 Map 端聚合参数设置
A、是否在 Map 端进行聚合,默认为 True
set hive.map.aggr = true
B、在 Map 端进行聚合操作的条目数目
set hive.groupby.mapaggr.checkinterval = 100000
C、有数据倾斜的时候进行负载均衡 (默认是 false)
set hive.groupby.skewindata = true
当选项设定为 true,生成的查询计划会有两个 MR Job。第一个 MR Job 中,Map 的输出结果会随机分布到 Reduce 中,每个 Reduce 做部分聚合操作,并输出结果,这样处理的结果是相同的 Group By Key 有可能被分发到不同的 Reduce 中,从而达到负载均衡的目的;第二个 MR Job 再根据预处理的数据结果按照 Group By Key 分布到 Reduce 中(这个过程可以保证相同的 Group By Key 被分布到同一个 Reduce 中),最后完成最终的聚合操作。
hive (default)> select deptno from emp group by deptno;
Stage-Stage-1: Map: 1 Reduce: 5 Cumulative CPU: 23.68 sec HDFS Read:
19987 HDFS Write: 9 SUCCESS
Total MapReduce CPU Time Spent: 23 seconds 680 msec
OK
deptno
10
20
30
优化以后
hive (default)> set hive.groupby.skewindata = true;
hive (default)> select deptno from emp group by deptno;
Stage-Stage-1: Map: 1 Reduce: 5 Cumulative CPU: 28.53 sec HDFS Read:
18209 HDFS Write: 534 SUCCESS
Stage-Stage-2: Map: 1 Reduce: 5 Cumulative CPU: 38.32 sec HDFS Read:
15014 HDFS Write: 9 SUCCESS
Total MapReduce CPU Time Spent: 1 minutes 6 seconds 850 msec
OK
deptno
10
20
30
4. Count(Distinct) 去重统计
数据量小的时候无所谓,数据量大的情况下,由于 COUNT DISTINCT 操作需要用一个 Reduce Task 来完成,这一个 Reduce 需要处理的数据量太大,就会导致整个 Job 很难完成,一般 COUNT DISTINCT 使用先 GROUP BY 再 COUNT 的方式替换,但是需要注意 group by 造成的数据倾斜问题。
案例实操
A、创建一张大表
hive (default)> create table bigtable(id bigint, time bigint, uid string, keyword, string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
B、加载数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/bigtable' into table bigtable;
C、设置 5 个 reduce 个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 5;
D、执行去重 id 查询
hive (default)> select count(distinct id) from bigtable;
Stage-Stage-1: Map: 1 Reduce: 1 Cumulative CPU: 7.12 sec HDFS Read:
120741990 HDFS Write: 7 SUCCESS
Total MapReduce CPU Time Spent: 7 seconds 120 msec
OK
c0
100001
Time taken: 23.607 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
E、采用 group by 去重 id
hive (default)> select count(id) from (select id from bigtable group by id) a;
Stage-Stage-1: Map: 1 Reduce: 5 Cumulative CPU: 17.53 sec HDFS Read:
120752703 HDFS Write: 580 SUCCESS
Stage-Stage-2: Map: 1 Reduce: 1 Cumulative CPU: 4.29 sec2 HDFS Read:
9409 HDFS Write: 7 SUCCESS
Total MapReduce CPU Time Spent: 21 seconds 820 msec
OK
_c0
100001
Time taken: 50.795 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
虽然会多用一个 Job 来完成,但在数据量大的情况下,这个绝对是值得的。
5. 笛卡尔积
尽量避免笛卡尔积,join 的时候不加 on 条件,或者无效的 on 条件,Hive 只能使用 1 个 reducer 来完成笛卡尔积。
6. 行列过滤
列处理:在 SELECT 中,只拿需要的列,如果有分区,尽量使用分区过滤,少用 SELECT *。
行处理:在分区剪裁中,当使用外关联时,如果将副表的过滤条件写在 Where 后面,那么就会先全表关联,之后再过滤,比如:
案例实操:
A、测试先关联两张表,再用 where 条件过滤
hive (default)> select o.id from bigtable b join bigtable o on o.id = b.id where o.id <= 10;
Time taken: 34.406 seconds, Fetched: 100 row(s)
B、通过子查询后,再关联表
hive (default)> select b.id from bigtable b join (select id from bigtable where id <= 10) o on b.id = o.id;
Time taken: 30.058 seconds, Fetched: 100 row(s)
另外,分区与分桶也是优化表的方式之一,详情见上一篇文章
五、合理设置 Map 及 Reduce 数
通常情况下,作业会通过 input 的目录产生一个或者多个 map 任务。
主要的决定因素有:input 的文件总个数,input 的文件大小,集群设置的文件块大小。
是不是 map 数越多越好?
答案是否定的。如果一个任务有很多小文件(远远小于块大小 128m),则每个小文件也会被当做一个块,用一个 map 任务来完成,而一个 map 任务启动和初始化的时间远远大于逻辑处理的时间,就会造成很大的资源浪费。而且,同时可执行的 map 数是受限的。
是不是保证每个 map 处理接近 128m 的文件块,就高枕无忧了?
答案也是不一定。比如有一个 127m 的文件,正常会用一个 map 去完成,但这个文件只有一个或者两个小字段,却有几千万的记录,如果 map 处理的逻辑比较复杂,用一个 map任务去做,肯定也比较耗时。
针对上面的问题 ,我们需要采取两种方式来解决:即减少 map 数和增加 map 数。
1. 复杂文件增加 Map 数
当 input 的文件都很大,任务逻辑复杂,map 执行非常慢的时候,可以考虑增加 Map 数,来使得每个 map 处理的数据量减少,从而提高任务的执行效率。增加 map 的方法为:
根据 computeSliteSize(Math.max(minSize,Math.min(maxSize,blocksize)))=blocksize=128M 公式,调整 maxSize 最大值。让 maxSize 最大值低于 blocksize 就可以增加 map 的个数。
案例实操:
A、执行查询
hive (default)> select count(*) from emp;
Hadoop job information for Stage-1: number of mappers: 1; number of
reducers: 1
B、设置最大切片值为 100 个字节
hive (default)> set mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize=100;
hive (default)> select count(*) from emp;
Hadoop job information for Stage-1: number of mappers: 6; number of
reducers: 1
2. 小文件进行合并
在 map 执行前合并小文件,减少 map 数:CombineHiveInputFormat 具有对小文件进行合并的功能(系统默认的格式)。HiveInputFormat 没有对小文件合并功能。
set hive.input.format = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.CombineHiveInputFormat;
在 Map-Reduce 的任务结束时合并小文件的设置:
在 map-only 任务结束时合并小文件,默认 true
SET hive.merge.mapfiles = true;
在 map-reduce 任务结束时合并小文件,默认 false
SET hive.merge.mapredfiles = true;
合并文件的大小,默认 256M
SET hive.merge.size.per.task = 268435456;
当输出文件的平均大小小于该值时,启动一个独立的 map-reduce 任务进行文件 merge
SET hive.merge.smallfiles.avgsize = 16777216;
3. 合理设置 Reduce 数
调整 reduce 个数方法一
A、每个 Reduce 处理的数据量默认是 256MB
hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer=25600000
B、每个任务最大的 reduce 数,默认为 1009
hive.exec.reducers.max=1009
C、计算 reducer 数的公式
N=min(参数 2,总输入数据量/参数 1)
调整 reduce 个数方法二
在 hadoop 的 mapred-default.xml 文件中修改,设置每个 job 的 Reduce 个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 15;
reduce 个数并不是越多越好
A、过多的启动和初始化 reduce 也会消耗时间和资源;
B、另外,有多少个 reduce,就会有多少个输出文件,如果生成了很多个小文件,那么如果这些小文件作为下一个任务的输入,则也会出现小文件过多的问题;在设置 reduce 个数的时候也需要考虑这两个原则:处理大数据量利用合适的 reduce 数;使单个 reduce 任务处理数据量大小要合适;
六、并行执行
Hive 会将一个查询转化成一个或者多个阶段。这样的阶段可以是 MapReduce 阶段、抽样阶段、合并阶段、limit 阶段。或者 Hive 执行过程中可能需要的其他阶段。默认情况下,Hive 一次只会执行一个阶段。不过,某个特定的 job 可能包含众多的阶段,而这些阶段可能并非完全互相依赖的,也就是说有些阶段是可以并行执行的,这样可能使得整个 job 的执行时间缩短。不过,如果有更多的阶段可以并行执行,那么 job 可能就越快完成。
通过设置参数 hive.exec.parallel 值为 true,就可以开启并发执行。不过,在共享集群中,需要注意下,如果 job 中并行阶段增多,那么集群利用率就会增加。
set hive.exec.parallel=true; //打开任务并行执行
set hive.exec.parallel.thread.number=16; //同一个 sql 允许最大并行度,默认为8。
当然,得是在系统资源比较空闲的时候才有优势,否则,没资源,并行也起不来。
七、严格模式
Hive 可以通过设置防止一些危险操作:
分区表不使用分区过滤
将 hive.strict.checks.no.partition.filter 设置为 true 时,对于分区表,除非 where 语句中含有分区字段过滤条件来限制范围,否则不允许执行。换句话说,就是用户不允许扫描所有分区。进行这个限制的原因是,通常分区表都拥有非常大的数据集,而且数据增加迅速。没有进行分区限制的查询可能会消耗令人不可接受的巨大资源来处理这个表。
使用 order by 没有 limit 过滤
将 hive.strict.checks.orderby.no.limit 设置为 true 时,对于使用了 order by 语句的查询,要求必须使用 limit 语句。因为 order by 为了执行排序过程会将所有的结果数据分发到同一个Reducer 中进行处理,强制要求用户增加这个 LIMIT 语句可以防止 Reducer 额外执行很长一段时间。
笛卡尔积
将 hive.strict.checks.cartesian.product 设置为 true 时,会限制笛卡尔积的查询。对关系型数据库非常了解的用户可能期望在 执行 JOIN 查询的时候不使用 ON 语句而是使用 where 语句,这样关系数据库的执行优化器就可以高效地将 WHERE 语句转化成那个 ON 语句。不幸的是,Hive 并不会执行这种优化,因此,如果表足够大,那么这个查询就会出现不可控的情况。
JVM 重用与压缩这两种优化方式,详见以前的文章。