深度学习之压缩模型大小且不掉点的方法---知识蒸馏
目录
原理
知识蒸馏代码演示(手写数字集)
1.导入相关包
2.准备训练集
3.搭建教师网络并训练
4.搭建学生网络并训练
5.对学生网络进行知识蒸馏训练
测试结果
总结
知识蒸馏的功能
原理
知识蒸馏的算法理论,就是将庞大的教师模型的重要的东西让学生模型来逼近和训练,让参数量少的学生模型能够和教师模型的效果差不多,或者比老师模型效果更好。
在说到知识蒸馏之前,首先说一下标签问题,在我们刚学习分类任务的时候,比如手写数字集,它的标签就是0,1-9,如下图,或者直接就是用独热编码的形式来作为标签。那么这样的做法到底好不好呢,对于这样的问题就有人说这样的标签容易让网络训练的过于绝对化,根据下面这个图显示,其实马也有一部分像驴,或者说驴也有一部分像马,如果将马的标签变成1,驴和汽车都是0,那么是不是就让驴和汽车的概率等同了,或者说驴和马的潜在关系直接被网络 忽略了。所以就又提出了soft targets。就是把标签要保持驴和马的潜在关系。
那么如何制作这样的标签来让学生网络学习到教师网络这种潜在的知识呢,就引出了蒸馏温度,如下图,当温度等于1的时候,就是一般的softmax,当温度稍微大一些的时候,那么原本被抑制成0的概率的类别就会拥有一些小概率,但是如果这个温度无限大的话,就会出现另一种问题,就是几个类别的概率没有了区分度,那么这个网络也就没有用了,所以对于温度T的选择也是非常重要的。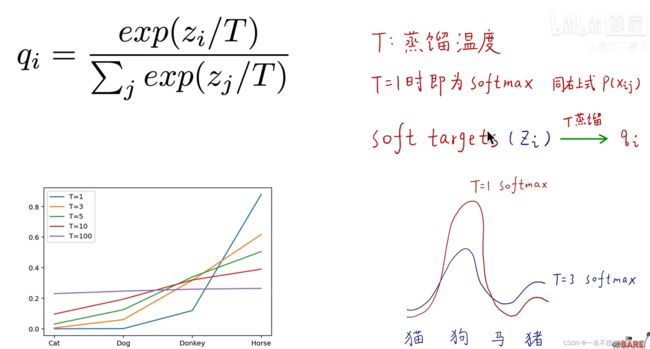
知识蒸馏算法,如下图,就是设计两个网络(学生和教师网络),将x输入两个网络中,其中教师网络是已经训练好了,有了训练权重,将教师网络的结果经过softlabel处理后,再和学生网络的结果经过softlabel处理后进行损失计算(采用的是KL散度损失),然后学生网络的结果再经过一般的sotmax处理后与一般的标签进行损失计算(交叉熵损失),最终两个损失结果在一个系数值的倍数下相乘再相加,最终得到总损失,进行训练。
知识蒸馏代码演示(手写数字集)
1.导入相关包
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
#from torchinfo import summary
#用于保存训练模型
def save_model(model,model_type,epoch):
model_out_path = "model/ckpt_%s_%d.pth" %(model_type,epoch)
torch.save(model, model_out_path)2.准备训练集
#设置随机种子
torch.manual_seed(0)
device=torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#使用cuda进行加速卷积运算
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark=True
#载入训练集
train_dataset=torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="dataset/",train=True,transform=transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)#如果不需要下载 download=False
test_dateset=torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="dataset/",train=False,transform=transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)#如果不需要下载 download=False
train_dataloder=DataLoader(train_dataset,batch_size=32,shuffle=True)
test_dataloder=DataLoader(test_dateset,batch_size=32,shuffle=True)3.搭建教师网络并训练
print("start training Teacher_model...")
#搭建教师网络并训练
class Teacher_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=1,num_class=10):
super(Teacher_model, self).__init__()
self.fc1=nn.Linear(784,1200)
self.fc2=nn.Linear(1200,1200)
self.fc3=nn.Linear(1200,10)
self.relu=nn.ReLU()
self.dropout=nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self,x):
x=x.view(-1,784)
x=self.fc1(x)
x=self.dropout(x)
x=self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
#训练教师网络
model=Teacher_model()
model=model.to(device)
#损失函数和优化器
loss_function=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optim=torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
epoches=6
for epoch in range(epoches):
model.train()
for image,label in train_dataloder:
image,label=image.to(device),label.to(device)
optim.zero_grad()
out=model(image)
loss=loss_function(out,label)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
model.eval()
num_correct=0
num_samples=0
with torch.no_grad():
for image,label in test_dataloder:
image=image.to(device)
label=label.to(device)
out=model(image)
pre=out.max(1).indices
num_correct+=(pre==label).sum()
num_samples+=pre.size(0)
acc=(num_correct/num_samples).item()
state = {
'net': model.state_dict(),
'test_acc': acc,
'epoch': epoch,
}
save_model(state,"Teacher",epoch)
model.train()
print("teacher: epoches:{},accurate={}".format(epoch,acc))4.搭建学生网络并训练
print("start training Student_model...")
#构建学生模型
class Student_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=1,num_class=10):
super(Student_model, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 20)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(20, 20)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(20, 10)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
#self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784)
x = self.fc1(x)
#x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
#x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
#训练学生网络
model=Student_model()
model=model.to(device)
#损失函数和优化器
loss_function=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optim=torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
epoches=6
for epoch in range(epoches):
model.train()
for image,label in train_dataloder:
image,label=image.to(device),label.to(device)
optim.zero_grad()
out=model(image)
loss=loss_function(out,label)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
model.eval()
num_correct=0
num_samples=0
with torch.no_grad():
for image,label in test_dataloder:
image=image.to(device)
label=label.to(device)
out=model(image)
pre=out.max(1).indices
num_correct+=(pre==label).sum()
num_samples+=pre.size(0)
acc=(num_correct/num_samples).item()
state = {
'net': model.state_dict(),
'test_acc': acc,
'epoch': epoch,
}
save_model(state,"Student",epoch)
model.train()
print("student: epoches:{},accurate={}".format(epoch,acc))5.对学生网络进行知识蒸馏训练
print("start training Student_model knowledge transfer...")
#开始进行知识蒸馏算法
teacher_model.eval()
model=Student_model()
model=model.to(device)
#蒸馏温度
T=7
hard_loss=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
alpha=0.3
soft_loss=nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean")
optim=torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
epoches=5
for epoch in range(epoches):
model.train()
for image,label in train_dataloder:
image,label=image.to(device),label.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_output=teacher_model(image)
optim.zero_grad()
out=model(image)
loss=hard_loss(out,label)
ditillation_loss=soft_loss(F.softmax(out/T,dim=1),F.softmax(teacher_output/T,dim=1))
loss=loss*alpha+ditillation_loss*(1-alpha)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
model.eval()
num_correct=0
num_samples=0
with torch.no_grad():
for image,label in test_dataloder:
image=image.to(device)
label=label.to(device)
out=model(image)
pre=out.max(1).indices
num_correct+=(pre==label).sum()
num_samples+=pre.size(0)
acc=(num_correct/num_samples).item()
state = {
'net': model.state_dict(),
'test_acc': acc,
'epoch': epoch,
}
save_model(state,"Student_after",epoch)
model.train()
print("student_after: epoches:{},accurate={}".format(epoch,acc))测试结果
教师网络模型大小9359KB,学生网络大小67KB,知识蒸馏只训练了5个epoch作为示例准确度比较低,继续训练效果会越来越好
总结
知识蒸馏的功能
1、提升模型精度
用户如果对目前的网络模型A的精度不是很满意,那么可以先训练一个更高精度的teacher模型B(通常参数量更多,时延更大),然后用这个训练好的teacher模型B对student模型A进行知识蒸馏,得到一个更高精度的模型。
2、降低模型时延,压缩网络参数
用户如果对目前的网络模型A的时延不满意,可以先找到一个时延更低,参数量更小的模型B,通常来讲,这种模型精度也会比较低,然后通过训练一个更高精度的teacher模型C来对这个参数量小的模型B进行知识蒸馏,使得该模型B的精度接近最原始的模型A,从而达到降低时延的目的。
3、图片标签之间的域迁移
用户使用狗和猫的数据集训练了一个teacher模型A,使用香蕉和苹果训练了一个teacher模型B,那么就可以用这两个模型同时蒸馏出一个可以识别狗,猫,香蕉以及苹果的模型,将两个不同与的数据集进行集成和迁移。
4、降低标注量
该功能可以通过半监督的蒸馏方式来实现,用户利用训练好的teacher网络模型来对未标注的数据集进行蒸馏,达到降低标注量的目的。