SpringMVC核心源码解析——从前端请求到后端响应,全过程源码讲解
了解SpringMVC
如果你是从事JavaWeb工作的研发工程师,那么对于SpringMVC肯定不会陌生。SpringMVC框架在MVC的基础上进行了封装,很大程度上解放了后端工程师,使得前后端解耦。
使用SpringMVC
本文的目的是解析SpringMVC中的核心源码,为了方便之后的源码讲解,先来了解SpringMVC的基本使用。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-coreartifactId>
<version>8.5.41version>
dependency>
dependencies>
web.xml(必须配置DispatcherServlet,并告诉它对应的配置文件位置,以及需要拦截的请求):
DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Applicationdisplay-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
springmvc-servlet.xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="controller"/>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
beans>
Controller类:
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "/WEB-INF/page/index.html";
}
}
index.html:
<html>
<head>
<title>SpringMVCtitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>indexh1>
body>
html>
到此,再配置tomcat服务器,将SpringMVC项目部署到tomcat中然后启动,访问对应的/index路径即可跳转访问到index.html页面。
SpringMVC的核心——DispatcherServlet
其实SpringMVC的底层并没有什么很高大上的实现,从配置文件中其实就可以看出,SpringMVC框架底层依赖的还是Servlet。因此如果想全面了解SpringMVC,需要有Servlet的源码基础。若有兴趣,在阅读本文之前可以先了解下我的另外一篇博客:Servlet源码解析。
有了Servlet的源码基础后,先来了解下SpringMVC的实现原理。其实SpringMVC的实现原理基于一个非常核心的Servlet——DispatchServlet。
首先了解下DispatchServlet的继承体系,如图:
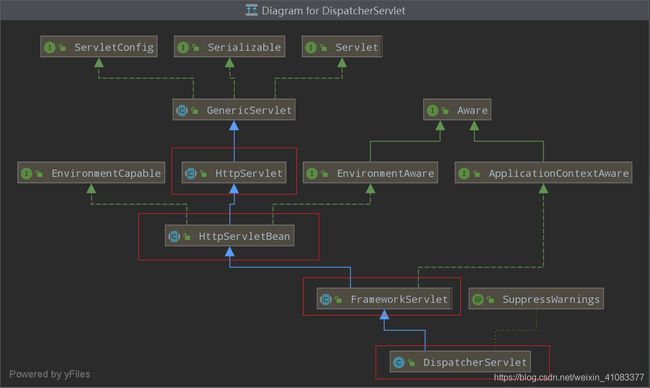
由上图可知,DispatchServlet最终间接继承了HttpServlet这个父类,说明DispatchServlet主要也是处理http请求的一个Servlet,具体细节在后面的源码再细说。
为了能够更好的理清之后的源码讲解的思路,先来熟悉下DispatchServlet的工作流程,如图:
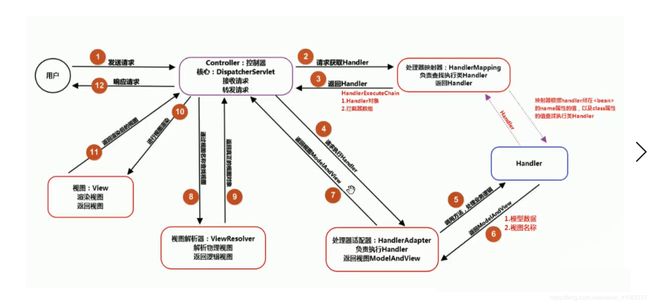
我们可以从图中看到,所有的流程都是围绕着DispatchServlet来展开。因此可以将DispatchServlet看作是请求的转发器,首先接收前端的request请求,然后根据请求路径通过HandlerMapping请求处理映射器找到对应的Handler请求处理器,再根据Handler通过HandlerAdapter请求处理适配器找到对应的适配器,并执行Handler。
最后将执行结果返回,并将其用ViewResolve视图解析器进行解析,如果解析成功,则响应视图。(在前后端主流工作模式中,通常是响应JSON数据)
SpringMVC源码讲解
了解完SpringMVC的整体执行流程后,开始对其中的流程细节进行源码讲解。
首先是核心DispatchServlet,再执行流程之前,DispatchServlet必须存在并完成初始化才能真正开始它的工作。
因此,首先需要知道DispatchServlet是如何创建并初始化:
在这里说下有关Servlet的相关流程:当一个request请求来到后端,那么就需要一个对应的Servlet来处理。这个Servlet就由相关的容器去创建并分配,而这个容器会在服务器启动时候根据配置文件的配置信息进行初始化。
因此得知,Servlet的初始化依赖于容器,而这个容器类的命名是StandarWrapper,每次请求到达后端都会首先调用allocate方法,分配对应的Servlet:
(以下的源码讲解以上面SpringMVC的使用例子为例进行讲解)
public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException {
if (unloading) {
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName()));
}
boolean newInstance = false; // 标识对应的Servlet是否已创建,默认是未创建
if (!singleThreadModel) { // 不是单例模式,则每次请求都返回同一个Servlet实例
if (instance == null || !instanceInitialized) { // Servlet实例为空,或者未初始化
synchronized (this) {
if (instance == null) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Allocating non-STM instance");
}
instance = loadServlet(); // 加载Servlet
newInstance = true; // 标示Servlet实例为已创建
if (!singleThreadModel) {
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
}
if (!instanceInitialized) { // Servlet实例未初始化
initServlet(instance); // 对Servlet实例进行初始化
}
}
}
if (singleThreadModel) {
if (newInstance) {
synchronized (instancePool) {
instancePool.push(instance);
nInstances++;
}
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(" Returning non-STM instance");
}
if (!newInstance) {
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
return instance; // 返回已创建并初始化完成的Servlet实例
}
}
... // 排除多余的干扰代码
}
loadServlet创建Servlet实例:
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null))
return instance;
PrintStream out = System.out;
if (swallowOutput) {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
}
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (servletClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager(); // 获取实例创建管理器
try {
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass); // 根据Servlet全限定类名(在服务器启动读取配置信息的时候赋值)创建Servlet实例
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notServlet", servletClass), e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
unavailable(null);
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e);
}
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e);
}
...
initServlet(servlet); // 初始化Servlet实例对象
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1;
} finally {
if (swallowOutput) {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
if (getServletContext() != null) {
getServletContext().log(log);
} else {
out.println(log);
}
}
}
}
return servlet; // 返回加载完成的Servlet实例(其实就是DispatchServlet实例对象)
}
initServlet初始化Servlet实例:
private synchronized void initServlet(Servlet servlet) throws ServletException {
if (instanceInitialized && !singleThreadModel) return;
// 调用Servlet初始化方法
try {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
boolean success = false;
try {
Object[] args = new Object[] { facade };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("init", servlet, classType, args);
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
SecurityUtil.remove(servlet);
}
}
} else {
servlet.init(facade); // 实际上就是调用了Servlet实例的init方法进行初始化
}
instanceInitialized = true; // 标识Servlet实例已初始化
} catch (UnavailableException f) {
unavailable(f);
throw f;
} catch (ServletException f) {
throw f;
} catch (Throwable f) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(f);
getServletContext().log("StandardWrapper.Throwable", f );
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.initException", getName()), f);
}
}
通过调试进入DispatchServlet实例的init方法后,发现调用的是HttpServletBean中的init方法:
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 首先为Servlet实例初始化相应的配置参数
// 回想下web.xml中配置的参数(告诉Servlet实例配置文件的所在位置):
// contextConfigLocation
// classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml
//
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { // 参数不为空,初始化配置参数
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
initServletBean(); // 最后初始化Servlet实例
}
通过调试进入initServletBean方法,发现调用的是FrameworkServlet的initServletBean方法(主要是创建HandlerMapping映射处理器、HandlerAdapter处理适配器,以及初始化DispatchServlet):
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); // 创建并初始化HandlerMapping映射处理器,以及HandlerAdapter处理适配器
initFrameworkServlet(); // 初始化DispatchServlet实例
} catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
// 日志相关
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
可以看到initFrameworkServlet方法是空实现。原来DispatchServlet的初始化默认就到此结束了,这部分是留给继承它的的子类去实现扩展。
protected void initFrameworkServlet() throws ServletException {
}
1. 当DispatchServlet初始化完成后,下一步就是获取Handler请求处理器处理请求:
因为DispatchServlet处理的是http请求,因此在获取Handler请求处理器之前还需要经过HttpServlet的处理:
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
// 转换为http类型的请求和响应
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
service(request, response); // 处理请求
}
调用了FrameworkServlet的service方法:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod()); // 获取请求访问类型(GET/POST等等)
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) { // PATCH类型请求,或者为空
processRequest(request, response);
} else {
super.service(request, response); // 正常来说,GET和POST类型的请求是最多的
}
}
再调用HttpServlet的service请求,根据请求类型分别执行对应的方法:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
doGet(req, resp); // 处理GET请求
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { // 处理HEAD请求
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { // 处理HEAD请求
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { // 处理POST请求
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { // 处理DELETE请求
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { // 处理OPTIONS请求
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { // 处理TRACE请求
doTrace(req,resp);
} else { // 不符合请求类型
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
对于HttpServlet的各种doXXX方法都是提供给子类去实现的。而在此处的子类是FrameworkServlet,再以GET请求为例子继续讲解:
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response); // 重点关注这个方法
} catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
最终还是调用回了DispatchServlet的doService方法:
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// 备份request请求中的属性
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// 为请求设置相应框架特有的属性
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response); // 重点关注该方法
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); // 根据request请求获取对应的映射处理器(它已经被封装成处理器链,并包含真正的处理器)
if (mappedHandler == null) { // 没有可以处理该请求的映射处理器
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); // 响应报错
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 根据真正的处理器获取处理适配器
String method = request.getMethod(); // 获取请求访问的类型
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 重点关注,真正调用处理方法,并返回结果
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
} catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
} catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
遍历所有的HandlerMapping请求处理映射器,并根据请求获取Handler:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); // 获取Handler
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); // 获取请求处理器
if (handler == null) { // 获取的处理器为空,说明我们自定义的控制器无法处理该请求
handler = getDefaultHandler(); // 获取默认处理器
}
if (handler == null) { // 默认处理器也为空,说明当前无法处理该请求,直接返回空
return null;
}
if (handler instanceof String) { // 处理器为字符串类型,则说明是这个处理器是全限定类型,需要根据它进行实例化
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); // 根据当前请求和处理器封装成处理器执行链
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
} else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request); // 调用父类的方法获取请求处理器
} finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 获取请求访问路径(在本例中是:/index)
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); // 根据请求和访问路径,获取处理请求的控制器方法
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); // 控制器方法不为空,则说明可以处理该请求,则创建控制器实例
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
创建对应的控制器实例(通过这个方法其实可以说明,所谓的Handler请求处理器,就是我们自己定义的Controller控制器):
public HandlerMethod createWithResolvedBean() {
Object handler = this.bean;
if (this.bean instanceof String) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "Cannot resolve bean name without BeanFactory");
String beanName = (String) this.bean; // 其实bean属性是字符串类型,为对应控制器的全限定类名
handler = this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName); // 通过全限定类名创建控制器实例(在本例中是:创建TestController实例)
}
return new HandlerMethod(this, handler); // 返回请求处理方法对象,其中包含控制器实例
}
对于获取Handler处理器还有最后一步,将Handler处理器封装成 处理器执行链,往其中添加拦截器:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH); // 获取请求访问路径(在本例中是:/index)
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); // 添加拦截器
}
} else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); // 添加拦截器
}
}
return chain; // 返回处理器链
}
到此,能够处理当前请求的Handler请求处理器已创建完成。
2. Handler请求处理器已经创建完成,那么下一步就是获取HandlerAdapter处理适配器:
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) { // 遍历所有的请求处理器适配器
if (adapter.supports(handler)) { // 适配器匹配处理器
return adapter; // 匹配成功,则返回该适配器
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));
}
protected boolean supportsInternal(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
return true; // 始终返回true
}
3. 获取到了请求处理器,以及请求适配器,接下来就是利用适配器调用处理器中的真正处理方法:
通过这个方法可以知道调用处理方法的返回结果是ModeAndView类型:
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request); // 检查request请求是否合法
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { // 判断是否需要同步执行处理方法,默认是false
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else { // 默认不需要同步执行
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); // 调用反射机制执行处理方法(其中也包含了解析方法参数)
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
} else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav; // 返回执行结果
}
最后调用自定义的TestController控制器的对应方法index():
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "/WEB-INF/page/index.html";
}
4. 最后判断返回的结果,是否需要渲染视图:
处理控制器方法返回的结果:
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) { // 异常判断
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
} else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { // 判断结果是否包含需要渲染的视图(在本例中返回的结果是index页面的路径,因此需要条件为true)
render(mv, request, response); // 渲染并响应视图
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
} else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
渲染并响应视图:
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
Locale locale = (this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale); // 将请求的语言环境应用于响应
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName(); // 获取视图名(本例中是:/WEB-INF/page/index.html)
if (viewName != null) { // 视图名不为空
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); // 解析视图名,并返回视图对象
if (view == null) { // 视图对象为空,则说明视图不存在,抛出异常
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + "' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
} else { // 视图名为空,有可能返回的结果中已经包含了视图
view = mv.getView(); // 从结果获取视图对象
if (view == null) { // 视图为空,抛出异常
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); // 响应视图
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
解析视图名,并返回视图对象:
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { // 遍历所有的视图解析器
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); // 解析视图名
if (view != null) { // 解析出来的视图对象不为空,说明解析成功,则返回视图对象
return view;
}
}
}
return null;
}
解析视图名:
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
if (!isCache()) { // 判断是否启用了缓存
return createView(viewName, locale); // 未启用则新建视图
} else {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(viewName, locale);
View view = this.viewAccessCache.get(cacheKey); // 在缓存中获取视图
if (view == null) { // 首次从缓存中获取为空
synchronized (this.viewCreationCache) {
view = this.viewCreationCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
view = createView(viewName, locale); // 创建视图
if (view == null && this.cacheUnresolved) { // 创建视图为空,说明创建失败
view = UNRESOLVED_VIEW; // 将视图对象赋值为无法解析的视图
}
if (view != null && this.cacheFilter.filter(view, viewName, locale)) { // 视图不为空,再通过视图解析器链进行解析
// 解析成功,设置缓存
this.viewAccessCache.put(cacheKey, view);
this.viewCreationCache.put(cacheKey, view);
}
}
}
} else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatKey(cacheKey) + "served from cache");
}
}
return (view != UNRESOLVED_VIEW ? view : null); // 返回视图对象
}
}
最后响应视图:
public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("View " + formatViewName() +
", model " + (model != null ? model : Collections.emptyMap()) +
(this.staticAttributes.isEmpty() ? "" : ", static attributes " + this.staticAttributes));
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
到此,SpringMVC框架从请求到响应的核心流程源码解析到此结束。