【数据结构与算法】顺序表
作者:旧梦拾遗186
专栏:数据结构成长日记
每日励志:
生活从来都不会辜负谁,觉得丧的时候就要让自己忙起来,世界没有变小,我们一定要让自己越来越可爱的活下去,不要消耗生命,而是享受生活。
前言:
今天小编带大家学习数据结构当中的顺序表
目录
一.线性表
二.顺序表
2.1概念及结构
2.2 接口实现
SeqList.h
SeqList.c
test.c
简化的顺序表代码 SeqList.c
一.线性表
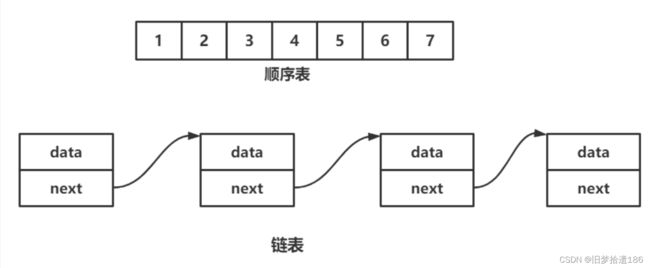
线性表 ( linear list ) 是 n 个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使 用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线 。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的, 线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
二.顺序表
2.1概念及结构
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
对于顺序表:我们可以分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表。
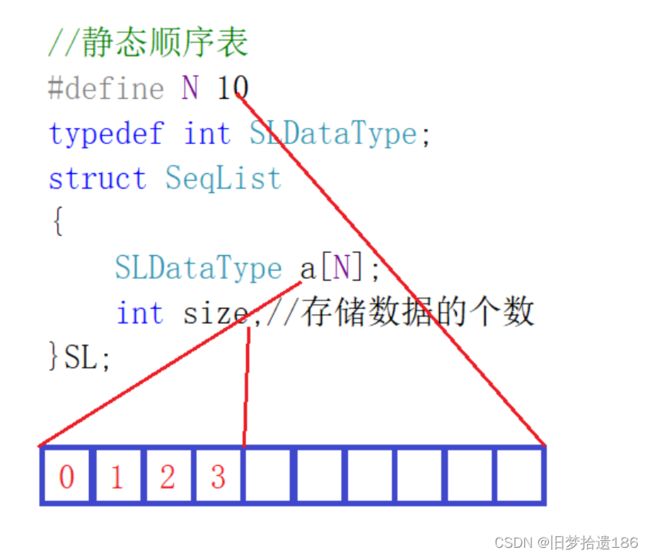
对于静态顺序表,我们该如何去定义呢?
我们可以看到,对于静态顺序表而言,里面的数组元素个数是固定的,不够灵活
对于动态顺序表:
//动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqLIst { SLDataType* a; int size;//存储数据的个数 int capacity;//存储空间的大小 }SL;
这里有一个问题
对于应该扩容多少究竟扩多少倍这个问题?
我们这里的代码实现默认的是扩容2倍(实际上空间满之后,不一定是扩容2倍):因为2倍比较合适,并不是必须一定是2倍,2倍2不会导致扩容过大或过小,如果扩容一次扩多了,将会存在空间浪费,扩少了,会导致频繁扩容,会导致效率损失。这并不是我们想要的
同时,还有另外一个问题,需要我们进行探讨一下:
在进行删除相关操作(如下面会说到的头删操作时)后面剩余的空间要不要进行缩容?
对于删除顺序表没有缩容的概念,虽然可以缩容,都是我们不会去缩容,缩容要付出极大的代价。对于realloc我们知道扩容有2种情况(取决于后面的空间够不够):一种是原地扩容,返回原来的地址,另一种是异地扩容,返回的不是同一个地址。
如果我们扩容扩的比原来还小呢?会不会进行缩容?可能会原地缩容或者异地缩容
对于删除数据后面剩余的空间有点多,我们确实可以用realloc进行缩容,但是付出的代价有点多:可能会在新空间开一个空间,将其里面的数据进行拷贝,将旧空间释放掉。这就是要付出的代价,这是性能的代价。
有没有想过,缩容之后,如果又要插入数据,这时候我们又得扩容,扩容又得申请新的空间,在释放旧空间,在插入数据。这不就是在反复横跳。况且现在计算机的空间也没那么少
我们可以认为缩容是一种以时间换空间的方案。不缩容是在以空间换时间,而不缩容后面插入数据我们可能都不需要进行扩容,这就是不缩容的优势。虽然缩容是可以的,但是没有系统会去做。
2.2 接口实现
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致 N 定大了,空 间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间 大小,所以下面我们实现 动态顺序表 。
我们将会实现的功能是:
初始化顺序表、销毁顺序表、尾插数据、头插数据、尾删数据、头删数据、查找数据、在某个位置插入数据、在某个位置删除数据、修改数据。以及中间实现过程中会涉及到的打印数据、扩容操作等。
很显然,在实现某个位置插入数据的功能的时候,我们就能用在某个位置插入函数取代尾插和头插操作
在实现某个位置删除数据的功能,我们就能用这个函数取代尾删和头删操作
面对这么多的操作,我们采用模块化设计,分为3个板块,同时,我们应该在边实现功能函数的过程中边进行调试操作,不要让自己的代码出现过多的错误。我们可以在主函数的部分通过设计void TestSeqList()里面存放一些功能函数来看看自己的代码是否能够达到预期的效果,这点能够大大提高我们代码的准确性。
SeqList.h
#pragma once //#ifndef __SEQLIST_H__ //#define __SEQLIST_H__ //#endif #include#include #include 静态顺序表 //#define N 10 //typedef int SLDataType; //struct SeqList //{ // SLDataType a[N]; // int size; //}; //动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqLIst { SLDataType* a; int size; //存储数据的个数 int capacity;//存储空间的大小 }SL; //初始化 void SLInit(SL* psl); //销毁 void SLDestory(SL* psl); //打印 void SLPrint(const SL* psl); //尾插头插 尾删头删 //尾插 void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x); //头插 void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x); //尾删 void SLPopBack(SL* psl); //头删 void SLPopFront(SL* psl); //查找 int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDataType x); //插入 void SLInsert(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x); //删除 void SLErase(SL* psl, size_t pos); //修改 void SLModify(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
这一部分就是对SeqList.h里面声明的函数进行实现的部分,是最为重要的部分,对于这一部分的函数,千万不要把SeList.h里面的函数全部实现完再去测试,那样子会大大提高工作量,出现错误很不好找,最好的办法就是写完一个函数去测试一个函数,调试看看有没有bug。这点至关重要。
#include "SeqList.h" void SLPrint(const SL* psl) { assert(psl); for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++) { printf("%d ", psl->a[i]); } //注意换行 printf("\n"); } void SLInit(SL* psl) { assert(psl); psl->a = NULL; psl->capacity = psl->size = 0; } void SLDestory(SL* psl) { assert(psl); if (psl->a) { free(psl->a); psl->a = NULL; psl->capacity = psl->size = 0; } } //扩容,后面会用到扩容这个操作,我们干脆将其封装成一个函数即可 void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl) { assert(psl); //检查容量 if (psl->size == psl->capacity) { //如果是0那就容量初始化为4,否则就增加2倍 int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2; //注意是sizeof(SLDataType)*newCapacity SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity); //注意realloc会出现的情况 if (NULL == tmp) { perror("realloc fail"); return; //exit(-1); } psl->a = tmp; psl->capacity = newCapacity; } } //尾插 void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); psl->a[psl->size] = x; psl->size++; //SLInsert(psl, psl->size, x);//直接调用SLInsetrt函数也可以实现尾插 } //头插 void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); int end = psl->size-1; while (end>=0) { psl->a[end+1] = psl->a[end]; --end; } psl->a[0] = x; psl->size++; //SLInsert(psl, 0, x);//直接调用SLInsert也可以实现头插 } //尾删 void SLPopBack(SL* psl) { assert(psl); //温柔的检查——元素的合理性 /*if (psl->size == 0) { return; }*/ //暴力的检查,直接报错——元素的合理性 assert(psl->size > 0); psl->size--; //SLErase(psl, psl->size - 1);//直接调用SLErase也可以实现尾删 } //头删 void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size > 0); int begin = 0; while (begin < psl->size - 1) { psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1]; ++begin; } psl->size--; //SLErase(psl, 0);//直接调用SLErase也可以实现头删 } //查找 int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++) { if (psl->a[i] == x) { return i; } } return -1; } //插入 void SLInsert(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); assert(pos <=psl->size); SLCheckCapacity(psl); int end = psl->size - 1; //强转为int,这点很重要,因为pos为size_t类型,不强转会发生算术转化,永远跳不出循环 while (end >=(int)pos) { psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end]; --end; } psl->a[pos] = x; psl->size++; } //删除 void SLErase(SL* psl, size_t pos) { assert(psl); assert(pos < psl ->size); size_t begin = pos; while (begin < psl->size - 1) { psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1]; ++begin; } psl->size--; } //修改 void SLModify(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); assert(pos < psl->size); psl->a[pos] = x; }
test.c
温馨提示:一定要通过调用每个TestSeqList()函数确认里面涉及到的功能函数没有bug我们在去进行菜单的实现,同时,一旦里面的函数多了,我们极有可能忘记这个是测试什么功能函数的,所以我的建议是:写好注释,方便自己的理解复习,同时也让别人能够看得懂。不要本末倒置了。导致出现问题而不知道错在哪里,这样子得不偿失。
(对于菜单,博主这里并没有全部完善,但是整个框架已经搭起来了,而且可以正确运行起来。如果有需要,直接进行补充即可,可以参考之前博主类似的菜单内容。)
//测试尾插、打印、头插 void TestSeqList1() { SL s; SLInit(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 1); SLPushBack(&s, 2); SLPushBack(&s, 3); SLPushBack(&s, 4); SLPushBack(&s, 5); SLPushBack(&s, 6); SLPrint(&s); SLPushFront(&s, 10); SLPushFront(&s, 20); SLPushFront(&s, 30); SLPrint(&s); SLDestory(&s); } //测试尾删 void TestSeqList2() { SL s; SLInit(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 1); SLPushBack(&s, 2); SLPushBack(&s, 3); SLPushBack(&s, 4); SLPrint(&s); SLPopBack(&s); SLPopBack(&s); SLPrint(&s); SLPopBack(&s); SLPopBack(&s); SLPrint(&s); SLPopBack(&s); SLPrint(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 10); SLPushBack(&s, 20); SLPushBack(&s, 30); SLPushBack(&s, 40); SLPrint(&s); SLDestory(&s); } //测试头删 void TestSeqList3() { SL s; SLInit(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 1); SLPushBack(&s, 2); SLPushBack(&s, 3); SLPushBack(&s, 4); SLPrint(&s); SLPopFront(&s); SLPopFront(&s); SLPrint(&s); SLDestory(&s); } //测试插入 void TestSeqList4() { SL s; SLInit(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 1); SLPushBack(&s, 2); SLPushBack(&s, 3); SLPushBack(&s, 4); SLPrint(&s); SLInsert(&s, 2, 30); SLPrint(&s); SLInsert(&s, 0, 30); SLPrint(&s); /*int x = 0; scanf("%d", &x); int pos = SLFind(&s, x); if (pos != -1) { SLInsert(&s, pos, x * 100); }*/ SLPrint(&s); } //测试删除 void TestSeqList5() { SL s; SLInit(&s); SLPushBack(&s, 1); SLPushBack(&s, 2); SLPushBack(&s, 3); SLPushBack(&s, 4); SLPushBack(&s, 5); SLPrint(&s); SLErase(&s, 0); SLPrint(&s); int x = 0; scanf("%d", &x); int pos = SLFind(&s, x); if (pos != -1) { SLErase(&s, pos); } SLPrint(&s); } void menu() { printf("**********************\n"); printf("1.尾插数据 2.头插数据\n"); printf("3.尾删数据 4.头删数据\n"); printf("5.查找数据 6.插入数据\n"); printf("7.删除数据 8.修改数据\n"); printf("9.打印数据 -1.退出\n"); printf("**********************\n"); } int main() { SL s; SLInit(&s); int option = 0; int x = 0; do { menu(); printf("请输入你的操作:>"); scanf("%d", &option); switch (option) { case 1: printf("请连续输入要插入的数据,-1为结束\n"); scanf("%d", &x); while (x != -1) { SLPushBack(&s, x); scanf("%d", &x); } break; case 2: //后面内容自己进行补充说明 break; case 3: break; case 4: break; case 5: break; case 6: break; case 7: break; case 8: break; case 9: SLPrint(&s); default: return; } } while (option); SLDestory(&s); return 0; }
简化的顺序表代码 SeqList.c
#include "SeqList.h" void SLPrint(const SL* psl) { assert(psl); for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; ++i) { printf("%d ", psl->a[i]); } printf("\n"); } void SLInit(SL* psl) { assert(psl); psl->a = NULL; psl->capacity = psl->size = 0; } void SLDestory(SL* psl) { assert(psl); /*if (psl->a) {*/ free(psl->a); psl->a = NULL; psl->capacity = psl->size = 0; //} } void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl) { // 检查容量 if (psl->size == psl->capacity) { int newCapcity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2; SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, newCapcity*sizeof(SLDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return; //exit(-1); } psl->a = tmp; psl->capacity = newCapcity; } } // https://cplusplus.com/reference/ void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { /*assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); psl->a[psl->size] = x; psl->size++;*/ SLInsert(psl, psl->size, x); } void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { //assert(psl); //SLCheckCapacity(psl); 挪动数据 //int end = psl->size - 1; //while (end >= 0) //{ // psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end]; // --end; //} //psl->a[0] = x; //psl->size++; SLInsert(psl, 0, x); } void SLPopBack(SL* psl) { //assert(psl); 温柔的检查 ///*if (psl->size == 0) //{ //return; //}*/ 暴力的检查 //assert(psl->size > 0); //psl->size--; SLErase(psl, psl->size - 1); } void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { //assert(psl); //assert(psl->size > 0); ///*int begin = 0; //while (begin < psl->size-1) //{ // psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1]; // ++begin; //}*/ //int begin = 1; //while (begin < psl->size) //{ // psl->a[begin-1] = psl->a[begin]; // ++begin; //} //--psl->size; SLErase(psl, 0); } int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; ++i) { if (psl->a[i] == x) { return i; } } return -1; } //void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x) void SLInsert(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); assert(pos <= psl->size); SLCheckCapacity(psl); // 挪动数据 /*int end = psl->size - 1; while (end >= (int)pos) { psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end]; --end; }*/ size_t end = psl->size; while (end > pos) { psl->a[end] = psl->a[end-1]; --end; } psl->a[pos] = x; ++psl->size; } // 顺序表删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* psl, size_t pos) { assert(psl); assert(pos < psl->size); size_t begin = pos; while (begin < psl->size - 1) { psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1]; ++begin; } psl->size--; } void SLModify(SL* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x) { assert(psl); assert(pos < psl->size); psl->a[pos] = x; }
结语:
每个人的成长都是能力和想要得到的东西,不断匹配的过程,当你的才华和欲望不匹配时,你就该静下心来学习了,如果小编的总结能对你有所帮助,希望小伙伴们三连加关注哦,你的支持是小编创作的最大动力。