经典九道链表OJ题(附详细图解及代码)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一.反转链表(难度:简单)力扣.206
- 二.链表中倒数第k个结点(难度:简单)牛客
- 三.合并两个有序链表(难度:简单) 力扣.21
- 四.移除链表元素(难度:简单) 力扣.203
- 五.链表分割(难度:较难)牛客CM11
- 六.链表的回文结构(难度:较难)牛客OR36
- 七.相交链表(难度:简单)力扣.160
- 八.环形链表(难度:中等)力扣.142
- 九.复制带随机指针的链表(难度:中等)力扣.138
- 总结
前言
众所周知,链表是数据结构里面较为重要的。在我们学完链表的时候当然要练练题试试身手,顺便巩固一下知识。话不多说,直接上题~
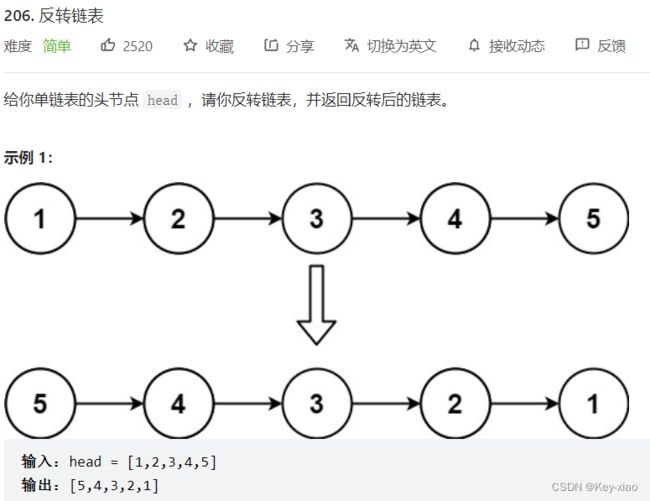
一.反转链表(难度:简单)力扣.206
思路:结点头插(运用双指针),例如在结点1处依次头插2 3 4 5
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//用next标记
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
二.链表中倒数第k个结点(难度:简单)牛客
思路:用快慢指针,快的先向前走k步,然后快慢同时走,保证两个指针间隔k
这里需要注意的是一些极端情况,例如链表只有5个结点,要输出倒数第6或者更大的结点,这样就直接返回NULL了。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*
* C语言声明定义全局变量请加上static,防止重复定义
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{// write code here
struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
while(k--)
{
if(fast)
fast = fast->next;
else//考虑假如链表5个数要求倒数第6个结点情况
return NULL;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
三.合并两个有序链表(难度:简单) 力扣.21
思路:新建一个空链表,拿链表1的头开始依次和链表2比大小尾插到新链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
else if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;//防止两个链表为空
struct ListNode *head=NULL; //创空链表
struct ListNode *tail=NULL;
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));//哨兵位
tail->next = NULL;
while(list1 && list2)
{//依次比大小进行头插
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next=list1;
tail = tail->next;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next=list2;
tail = tail->next;
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
if(list1)//剩下list1直接把剩下的list1一起插入
tail->next = list1;
else
tail->next = list2;
struct ListNode* list = head->next;
free(head);
return list;
}
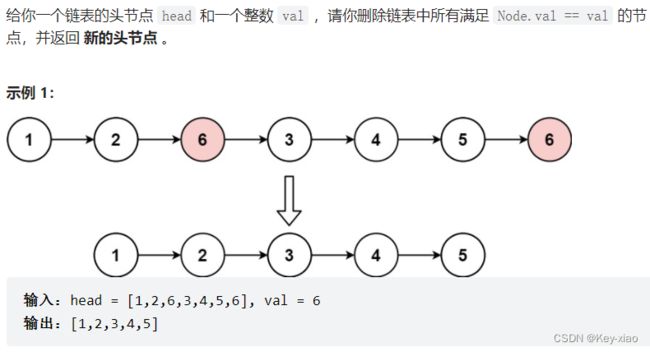
四.移除链表元素(难度:简单) 力扣.203
思路:从头节点开始进行元素删除,每删除一个元素,需要重新链接节点
注意:这里要考虑空链表的情况。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{//双指针
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)//相等的跳过
{
if(cur==head)//如果开头就相等
{//头删
head = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prev->next;
}
}
else//不相等直接往后走
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
好了下面要开始上点难度了,铁汁们 坚持就是胜利!!!
五.链表分割(难度:较难)牛客CM11
思路:创建两个空链表,一个放小于x的一个放大于x的,然后将两个链表链接起来
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
if(pHead == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* lessHead, *lessTail,*greaterHead, *greaterTail;
//创建两个空链表
lessHead = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* cur = pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val < x)
{
lessTail->next = cur;
lessTail = lessTail->next;
}
else
{
greaterTail->next = cur;
greaterTail = greaterTail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//链接两个链表
lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;
greaterTail->next = NULL;
pHead = lessHead->next;
free(lessHead);
free(greaterHead);
return pHead;
}
};
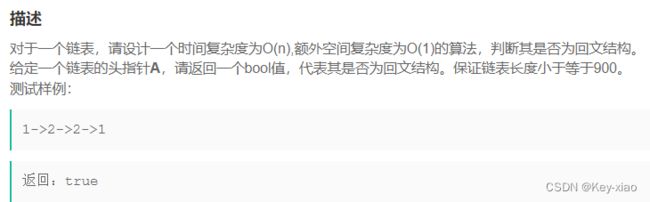
六.链表的回文结构(难度:较难)牛客OR36
思路:找到中间结点对后半部分进行逆置,然后一一对比后半部分和前半部分是不是每个结点都相等
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
if(A==NULL || A->next==NULL)
return true;
ListNode* slow, *fast, *prev, *cur, *next;//next标记
slow = fast = A;
//找中间点
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
prev = NULL;
cur = slow;
//逆置
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
while(A && prev)
{
if(A->val != prev->val)
return false;
A = A->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
return true;
}
};
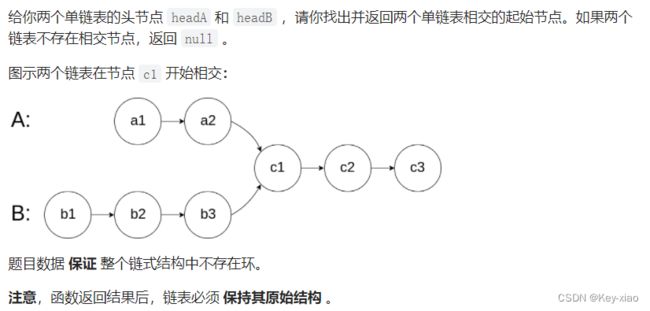
七.相交链表(难度:简单)力扣.160
思路:计算出两个链表的长度,长的先走相差的长度,然后两个链表同时走,直到遇到相同的节点,没有返回空
此处思路讲出来大家自己画下图锻炼一下自己。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode *curA = headA;
struct ListNode *curB = headB;
int lenA = 0,lenB =0;
while(curA)//计算两个链表长度
{
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while(curB)
{
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
int gap = abs(lenA-lenB);//求绝对值
struct ListNode *longlist = headA, *shortlist = headB;
if(lenAnext;
}
while(longlist && shortlist)//任意一个为空就结束
{
if(longlist == shortlist)
{
return longlist;
}
else
{
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
八.环形链表(难度:中等)力扣.142
思路:
如果链表存在环,则fast和slow会在环内相遇,定义相遇点到入口点的距离为X,定义环的长度为C,定义头到入口的距离为L,fast在slow进入环之后一圈内追上slow,则会得知:slow所走的步数为:L + X ,fast所走的步数为:L + X + N * C 并且fast所走的步数为slow的两倍
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *fast = head;
struct ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
//走到相遇点
if(fast == slow)
{// 求环的入口点
struct ListNode *meet = slow;
struct ListNode *start = head;
while(meet != start)
{
meet = meet->next;
start = start->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
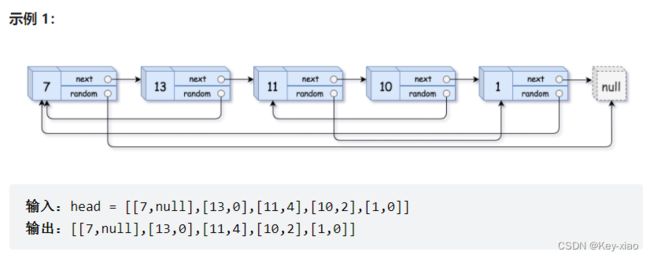
九.复制带随机指针的链表(难度:中等)力扣.138
思路:此题可以分三步进行:
1.拷贝链表的每一个节点,拷贝的节点先链接到被拷贝节点的后面
2.复制随机指针的链接:拷贝节点的随机指针指向被拷贝节点随机指针的下一个位置
3.拆解链表,把拷贝的链表从原链表中拆解出来
图解: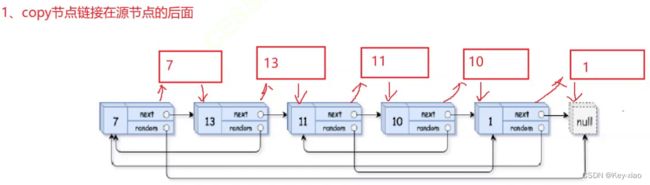

大家看的时候一定要跟着图中的线走
第三步图过于复杂大家也不方便看这里就不放了(其实是笔者想偷懒)
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
// 1.拷贝链表,并插入到原节点的后面
Node* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
Node* copy = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 插入
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代往下走
cur = next;
}
// 2.置拷贝节点的random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
if(cur->random != NULL)
copy->random = cur->random->next;
else
copy->random = NULL;
cur = copy->next;
}
// 3.解拷贝节点,链接拷贝节点
Node* copyHead = NULL, *copyTail = NULL;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
Node* next = copy->next;
// copy解下来尾插
if(copyTail == NULL)
{
copyHead = copyTail = copy;
}
else
{
copyTail->next = copy;
copyTail = copy;
}
cur->next = next;
cur = next;
}
return copyHead;
}
};
总结
好了,链表OJ就跟大家讨论到这里,大家刚学完链表会做几题呢
笔者刚学完的时候能独立做出来的一半都不到
最后大家一起加油哦~