ArcGIS Runtime SDK for iOS开发系列教程(7)——GeometryService与GeometryEngine使用
在我们使用其他WebAPIs开发应用时,常常会用到GeometryService进行空间位置判断、距离面积量测、缓冲区分析等几何操作。在ArcGIS for Server10.1中提供的GemetryService主要包括以下操作:
 那么,在ArcGIS for iOS中通过使用GeometryServiceTask可以很方便地使用ArcGIS的GeometryService,它所包括的操作主要有(下图左侧):
那么,在ArcGIS for iOS中通过使用GeometryServiceTask可以很方便地使用ArcGIS的GeometryService,它所包括的操作主要有(下图左侧):
同时,在ArcGIS for iOS中还封装了本地进行几何操作的类——GeometryEngine,极大的提高了几何操作的效率。他所提供的操作主要如上图的右侧。下面我们将通过最简单的缓冲区操作来向大家展示在ArcGIS for iOS中GeometryService和GeometryEngine的使用方法。
首先,我们构建一个支持ArcGIS的SDK的工程,在.h文件中添加GeometryServiceTask和相关协议GeometryServiceTaskDelegate,当然包括要素图层的添加,如下图:
有了上一讲中Tasks使用流程的实践,相信大家对使用协议的委托模式已经相当熟悉。接下来,我们需要对GeometryServicesTask进行初始化和实现GeometryServiceTaskDelegate的相关方法,首先在AGSMapViewTouchDelegate的地图点击实现方法方法中初始化GeometryServicesTask和相关参数
-(void)mapView:(AGSMapView *)mapView didClickAtPoint:(CGPoint)screen mapPoint:(AGSPoint *)mappoint graphics:(NSDictionary *)graphics
{
NSMutableArray *geometryArray=[NSMutableArray array];
[geometryArray addObject:mappoint];
AGSPictureMarkerSymbol *pt=[AGSPictureMarkerSymbol pictureMarkerSymbolWithImageNamed:@"ArcGIS.bundle/GPSDisplay.png"];
AGSGraphic *pushpin=[[AGSGraphic alloc]initWithGeometry:mappoint symbol:pt attributes:nil infoTemplateDelegate:nil];
[_graphicsLayer addGraphic:pushpin];
[pushpin release];
[_graphicsLayer dataChanged];
[_mapView centerAtPoint:mappoint animated:YES];
//GeometryService
self.gst=[[[AGSGeometryServiceTask alloc]initWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:kGeometryBufferService]]autorelease];
AGSSpatialReference *sr=[[[AGSSpatialReference alloc]initWithWKID:102100 WKT:nil]autorelease];
self.gst.delegate=self;
AGSBufferParameters *bufferParams=[[AGSBufferParameters alloc]init];
bufferParams.unit=kesriSRUnit_Meter;
bufferParams.bufferSpatialReference=sr;
bufferParams.distances = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
[NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:10000],
[NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:30000],
[NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:50000],
nil];
bufferParams.geometries = geometryArray;
bufferParams.outSpatialReference = sr;
bufferParams.unionResults = FALSE;
[self.gst bufferWithParameters:bufferParams];
[bufferParams release];
}
然后,添加GeometryService执行buffer操作的响应操作,成功返回处理:
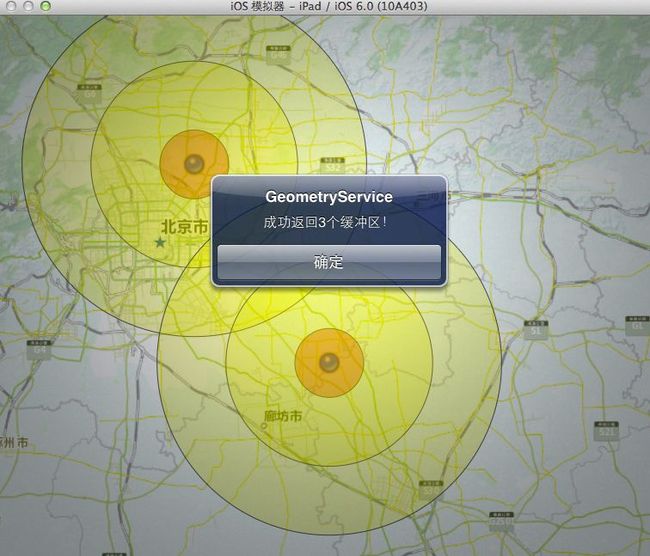
-(void)geometryServiceTask:(AGSGeometryServiceTask *)geometryServiceTask operation:(NSOperation *)op didReturnBufferedGeometries:(NSArray *)bufferedGeometries { UIAlertView *av = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"GeometryService" message:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"成功返回%d个缓冲区!", [bufferedGeometries count]] delegate:self cancelButtonTitle:@"确定" otherButtonTitles:nil]; [av show]; [av release]; // Create a SFS for the inner buffer zone AGSSimpleFillSymbol *innerSymbol = [AGSSimpleFillSymbol simpleFillSymbol]; innerSymbol.color = [[UIColor redColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.40]; innerSymbol.outline.color = [UIColor darkGrayColor]; // Create a SFS for the outer buffer zone AGSSimpleFillSymbol *outerSymbol = [AGSSimpleFillSymbol simpleFillSymbol]; outerSymbol.color = [[UIColor yellowColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.25]; outerSymbol.outline.color = [UIColor darkGrayColor]; // counter to help us determine if the geometry returned is inner/outer NSUInteger i = 0; for (AGSGeometry* g in bufferedGeometries) { // initialize the graphic for geometry AGSGraphic *graphic = [[AGSGraphic alloc] initWithGeometry:g symbol:nil attributes:nil infoTemplateDelegate:nil]; // since we have 2 buffer distances, we know that 0-2 will be 100m buffer and 3-5 will be 300m buffer if (i < [bufferedGeometries count]/2) { graphic.symbol = innerSymbol; } else { graphic.symbol = outerSymbol; } // add graphic to the graphic layer [self.graphicsLayer addGraphic:graphic]; // release our alloc'd graphic [graphic release]; // increment counter so we know which index we are at i++; } // let the graphics layer know it has new graphics to draw [self.graphicsLayer dataChanged]; }
可以看出成功执行GeometryService的buffer操作后,返回结果是数组(NSArray *)bufferedGeometries,通过遍历将Geometry转化为要素来展示。另外,我们还需要添加出错的处理:
- (void)geometryServiceTask:(AGSGeometryServiceTask *)geometryServiceTask operation:(NSOperation*)op didFailBufferWithError:(NSError *)error {
UIAlertView *av = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"Error"
message:@"There was an error with the buffer task"
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"Ok"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[av show];
[av release];
}
这个与其他Tasks的提示类似,不做过多解释。这样,我们就完成了使用GeometryServiceTask来实现缓冲区分析的操作。
接下来,我们来看如何通过GeometryEngine来实现同样的操作:
-(void)mapView:(AGSMapView *)mapView didClickAtPoint:(CGPoint)screen mapPoint:(AGSPoint *)mappoint graphics:(NSDictionary *)graphics
{
NSMutableArray *geometryArray=[NSMutableArray array];
[geometryArray addObject:mappoint];
//[_graphicsLayer removeAllGraphics];
AGSPictureMarkerSymbol *pt=[AGSPictureMarkerSymbol pictureMarkerSymbolWithImageNamed:@"ArcGIS.bundle/GPSDisplay.png"];
AGSGraphic *pushpin=[[AGSGraphic alloc]initWithGeometry:mappoint symbol:pt attributes:nil infoTemplateDelegate:nil];
[_graphicsLayer addGraphic:pushpin];
[pushpin release];
[_graphicsLayer dataChanged];
[_mapView centerAtPoint:mappoint animated:YES];
//GeometryEngine
AGSGeometryEngine *geoEng=[AGSGeometryEngine defaultGeometryEngine];
// Create a SFS for the inner buffer zone
AGSSimpleFillSymbol *innerSymbol = [AGSSimpleFillSymbol simpleFillSymbol];
innerSymbol.color = [[UIColor redColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.40];
innerSymbol.outline.color = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
// Create a SFS for the outer buffer zone
AGSSimpleFillSymbol *outerSymbol = [AGSSimpleFillSymbol simpleFillSymbol];
outerSymbol.color = [[UIColor yellowColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.25];
outerSymbol.outline.color = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
for (int i=10; i>0;i--)
{
AGSPolygon *geBuffer=[geoEng bufferGeometries:geometryArray byDistance:i*1000];
AGSGraphic *gr = [[AGSGraphic alloc] initWithGeometry:geBuffer symbol:nil attributes:nil infoTemplateDelegate:nil];
if (i%2==1)
{
gr.symbol=outerSymbol;
}
else
{
gr.symbol=innerSymbol;
}
//[self.graphicsLayer addGraphic:gr];
}
[self.graphicsLayer dataChanged];
}
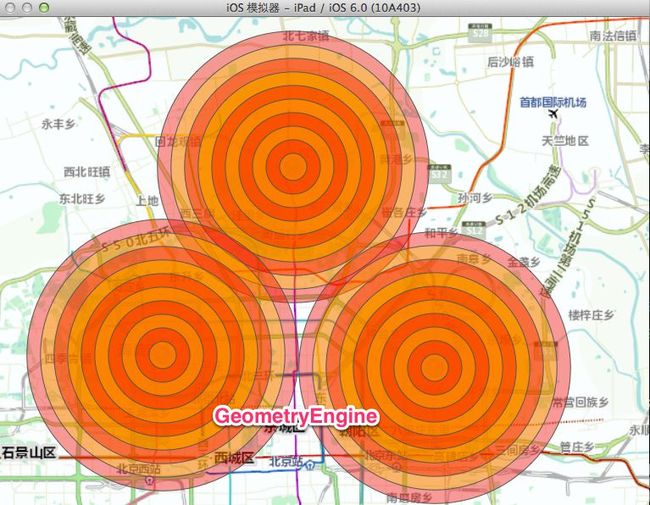
我们不难发现,使用GeometryEngine实现同样的buffer操作更加便捷,如果你实际操作的话,你还好发现它的效率要比GeomertyServiceTask高很多。
效果:
总结:本讲主要通过GeometryServiceTask和GeometryEngine的使用来向大家展示在ArcGIS for iOS中如何实现几何相关的操作,其他具体操作,如长度计算、面积量测等大家可以参考帮助文档。下一讲将向大家介绍Geoprocessor相关的操作,欢迎大家继续关注!