集合框架的使用
目录
为什么使用集合?
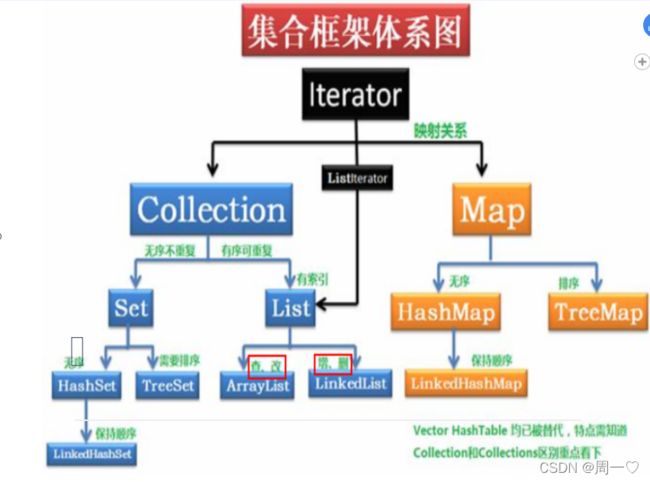
集合架构有哪些?
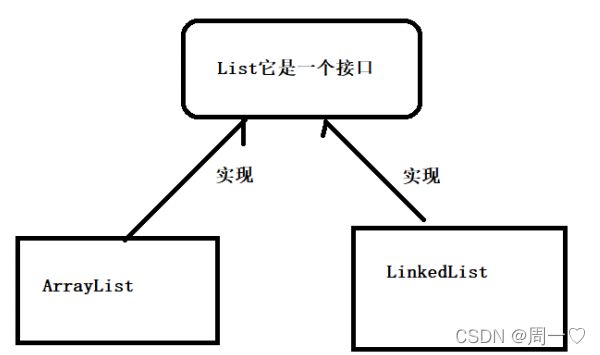
List集合
ArrayList集合
LinkedList集合
HashSet
TreeSet
在创建 TreeSet 时 为其指定排序得规则
Map 属于 key---value 键值对元素
HashMap
1.1为什么使用集合
思考: 数组有缺陷?--定容【一定数组定义好,他们得长度就无法改变.】如果需要改变数组得长度,变得很复杂。
1. 我们是否可以定义一个长度改变的容器。 --- 当然可以。
2. 手撕可变长度的容器。
1.2 集合的架构
1.3 List集合
1.3.0 ArrayList 创建集合对象
List list = new ArrayList();//创建一个集合对象如果没有指定集合容器的长度默认为10
List list1= new ArrayList(15);//长度为15的集合容器1.3.1 ArrayList 添加的操作(可以添加提任意类型)
list.add("java01");
list.add("java02");
list.add("java03");
list.add("java04");
list.add(new Date());
list.add(true);
System.out.println(list);1.3.2 ArrayList 删除的操作
System.out.println("==========删除下标为3的元素=========");
list.remove(3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("==========删除所有元素=============");
list.clear();
System.out.println(list); 1.3.3 ArrayList 修改的操作
list.set(1,"hello");
System.out.println(list); 1.3.4 ArrayList 查询操作
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("java01");
list.add("java02");
list.add("java03");
list.add("java02");
//查询的方法
Object o = list.get(1);//根据下标获取元素
System.out.println(o);
int size = list.size();//获取集合中元素的个数。
System.out.println(size);
boolean f = list.contains("java05");//判断元素是否在集合中,在显示true不在显示false
System.out.println(f);
int index = list.indexOf("java05");//查询元素在 集合中第一次出现的位置 System.out.println(index);
//遍历集合中的元素 for循环
for(int i=0;i1.3.5 ArrayList底层源码
从构造方法来入手。new ArrayList(22) 底层声明了一个Object类型的数组 名字elementData
Object[] elementData
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) { //大于0
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) { //等于初始化为一个空数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else { //抛出一个异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
==========add("java01")======E理解为Object类型================
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 扩容
elementData[size++] = e; //把元素赋值给数组的相应位置
return true;
}
==========indexOf("java02") 判断元素在集合中第一次的位置=============
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i])) //和数组中的每个元素内容进行比对
return i; //返回元素在集合中位置
}
return -1;
}
===========size() 请求数组的长度======================
public int size() {
return size;
}
============contain("java05")判断元素是否在集合中==============
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
===============get(1) 获取指定位置的元素========
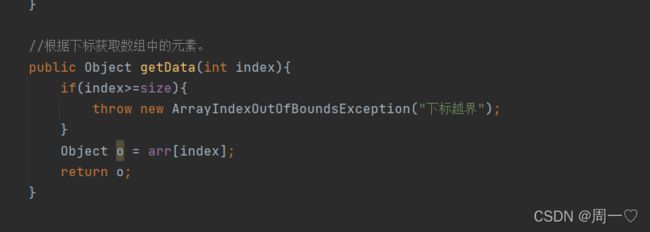
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); //判断指定的位置是否合法
return elementData(index);
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
============toString() 为什么不打印对象的引用地址
[java01, java02, java03, java02]因为重写了Object里面的toString方法。
public String toString() {
Iterator it = iterator();
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
通过对ArrayList方法的底层代码分析:底层就是对数组的操作。
ArrayList的底层就是基于数组实现的。 1.4 LinkedList
它是一个链表结构。
1.4.1 LinkedList 添加
//添加
linkedList.add("java01"); //追加尾部
linkedList.addFirst("java02"); //添加到头部
linkedList.addLast("java03");//追加到尾部
linkedList.addFirst("java04"); //追加到头部
linkedList.addLast("java05");//追加到尾部
System.out.println(linkedList);1.4.2 LinkedList 删除操作
//删除操作
linkedList.removeFirst();//移除头部元素
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.remove(2);//移除指定位置的元素
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.removeLast();//移除尾部的元素
System.out.println(linkedList);1.4.3 LinkedList 修改操作
//修改操作
linkedList.set(1,"java11");//将下标为1修改为java11
System.out.println(linkedList);1.4.4 LinkedList 查询操作
//查询操作
int size = linkedList.size();//求长度
boolean empty = linkedList.isEmpty();//是否为空
boolean b = linkedList.contains("java01");//判断元素是否在集合中
Object o = linkedList.get(1);//根据下标获取指定位置的元素
Object first = linkedList.getFirst();//获取第一个元素
System.out.println(first);
Object last = linkedList.getLast();
System.out.println(last); 1.4.5LinkedList 的底层源码。
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
该类的构造方法内是空的,没有任何的代码。 但是该类中有三个属性。
transient int size = 0; //索引
transient Node first; //第一个元素对象
transient Node last; //表示最后一个元素对象。
================ add的源码=====E:理解为
Object==========================。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
//上一个节点 数据 下一个节点
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
ast = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
==================Node的源码 =======================================
private static class Node {
E item; //数据
Node next; //下一个节点
Node prev; //上一个节点
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
} 1.5HashSet
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果没有指定容器的大小 默认为16 负载因子为0.75
HashSet hashSet= new HashSet();
//添加操作
hashSet.add("java01");
hashSet.add("java02");
hashSet.add("java04");
hashSet.add("java03");
hashSet.add("java02");
HashSet set2=new HashSet();
set2.add("刘德华");
set2.add("张学友");
set2.add("黎明");
hashSet.addAll(set2); //把set2中的每个元素添加到hashset中
System.out.println(hashSet); //元素不能重复 而且无序
//删除
hashSet.remove("黎明");
// hashSet.clear();//清空容器集合
System.out.println(hashSet);
//查询操作
boolean empty = hashSet.isEmpty(); //判断是否为空
System.out.println(empty);
boolean b = hashSet.contains("刘德华");//判断元素是否在容器中
System.out.println(b);
//迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();//获取迭代器对象 有序:有下标
while (iterator.hasNext()){//判断是否指定能够移动
Object next = iterator.next();//指定移动并获取当前的元素
System.out.println(next);
}
// //遍历--- foreach
// for(Object o: hashSet){
// System.out.println(o);
// }
}1.6 TreeSet
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(); //TreeSet不允许重复元素
treeSet.add(new Student("张三",17));
treeSet.add(new Student("李四",16));
treeSet.add(new Student("王五",16));
treeSet.add(new Student("赵六",15));
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}
class Student implements Comparable{
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
//排序:---返回如果大于0 表示当前元素比o大 如果返回-1 当前添加的元素比o小 返回0表示相同元素。
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Student student= (Student) o;
System.out.println(this+"===================>"+o);
if(this.age>student.age){
return 1;
}
if(this.age 1.7 在创建 TreeSet 时 为其指定排序得规则
//1 我们之前 创建过TreeSet对象。
/*2 TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(); 但是在创建对象时 并没有为 其指定排序得规则,那么就要求该集合得元素有排序规则。 如果元素得类 已经创建完成,不能修改该类得源码,这时我们又想把该类得对象放入得 TreeSet容器中。 这时就需要你在创建TreeSet时指定排序得规则。*/
public class MyComparator implements Comparator {
//需要比对得两个对象
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Student s1= (Student) o1;
Student s2= (Student) o2;
if(s1.getAge()>s2.getAge()){
return 1;
}else if(s1.getAge() comparator
//为TreeSet容器指定了排序规则
TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(new MyComparator());
treeSet.add(new Student(18,"张三"));
treeSet.add(new Student(17,"李四"));
treeSet.add(new Student(19,"王五"));
treeSet.add(new Student(19,"赵六"));
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
} 1.8Map 属于键值对模式
map 中得每个元素属于键值对模式。 如果往 map 中添加元素时 需要添加 key和 value. 它也属于一个接口,该接口常见得实现类有 : HashMap.
1.8.1 如何创建 Map 对象
//默认初始化大小为16 负载因子为0.75
Map map=new HashMap();
//初始化大小
Map map2=new HashMap(16);
//初始化大小 负载因子
Map map3=new HashMap(16,0.78f); 1.8.2添加操作
//默认初始化大小为16 负载因子为0.75
Map map=new HashMap();
//添加操作 key: name value: 张三
map.put("name","张三"); //注意: 要求map得key必 须唯一
map.put("age",18);
map.put("name","王五"); //因为key不能重复,所以后 者会把前者覆盖
Map m1=new HashMap();
m1.put("k1","v1");
m1.put("k2","v2");
map.putAll(m1); //把m1中得每个元素 添加到map中
map.putIfAbsent("age",28) ;//如果指定得key存在, 则不放入map中,如果不存在则放入map中 System.out.println(map); 1.8.3 删除操作
//删除操作
map.remove("age2");//根据指定得key移除元素
System.out.println(map);
map.clear(); //清空map容器
System.out.println(map);1.8.4 修改操作
//修改操作
map.replace("name","刘德华");//替换元素
System.out.println(map);1.8.5 查询
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("k1","v1");
map.put("k4","v4");
map.put("k2","v2");
map.put("k3","v3");
//查询操作
boolean f = map.containsKey("k5");//判断map是否 存在指定得key
Object v = map.get("k5"); //根据指定的key获取对应 得value值
System.out.println(v); Set keys = map.keySet();//返回该map中所有得key
System.out.println(keys);
//遍历map.
for(Object k:keys){ Object value= map.get(k);
System.out.println(k+"================>"+value);
}
}