Batch_Normalization 、Layer_Normalization 、Group_Normalization你分的清楚吗
作者简介:秃头小苏,致力于用最通俗的语言描述问题
往期回顾:目标检测系列——开山之作RCNN原理详解 目标检测系列——Fast R-CNN原理详解 目标检测系列——Faster R-CNN原理详解
近期目标:拥有10000粉丝
支持小苏:点赞、收藏⭐、留言
文章目录
-
- Batch_Normalization 、Layer_Normalization 、Group_Normalization你分的清楚吗
-
- 写在前面
- Batch_Normalization
- Layer_Normalization
- Group_Normalization
- 小结
Batch_Normalization 、Layer_Normalization 、Group_Normalization你分的清楚吗
写在前面
这节我将为大家带来Batch_Normalization 、Layer_Normalization 和 Group_Normalization的讲解,说讲解还是有点虚的啦,因为这节我并不准备讲。
“不准备讲!!!?那你写个嘚~~~”大佬们先别喷啊,这节我确实不会过多的讲解,写这篇的原因是因为我发现我对Batch_Normalization的理解稍有欠缺,于是就找了找资料,然后顺道看到了Layer_Normalization 和 Group_Normalization,于是自己就都学了一遍。这三篇作者都是太阳花的小绿豆 ,同时他在b站上的名字是霹雳吧啦Wz 。如果你看过我之前的文章,那么一定对这个名字比较熟悉,跟着这位UP主真的学到了很多,用两个字形容他,那就是宝藏。今天看他对这三个归一化的讲解也是有种豁然开朗的感觉,所以这里我会贴上他关于这些内容的讲解,大家可以根据需要查漏补缺,连接如下:
- Batch_Normalization
- Layer_Normalization
- Group_Normalization
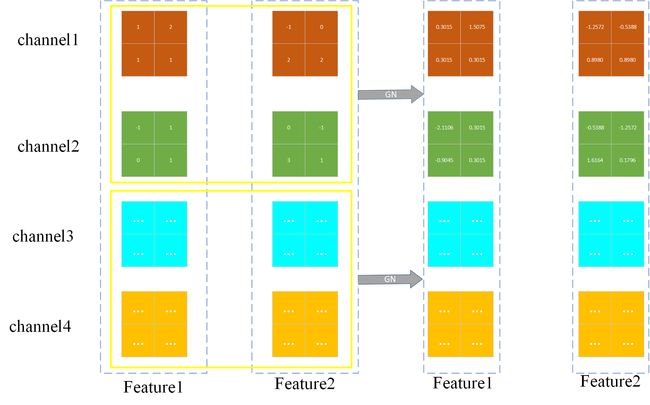
那你可能又要问了,“那你写这篇文章的意思何在,就是为了像我们推荐一下这个宝藏UP主嘛”。我的回答是:“是也不是”,我确实非常喜欢这位UP,也推荐大家去看看他的视频和文章,相信你会有所收获,因为这是我们共同的目标呀!!!一起加油叭,少年!!!✊✊✊我写这篇文章是因为我在UP主讲解的基础上又画了一些图,也希望可以帮到大家更好的理解。那就让我们一起来看看叭【注:我会放一些代码和图片,就不做讲解了,相信大家阅读了上面三篇基本都会了,下文代码是UP主文章中的,图为自己所画】
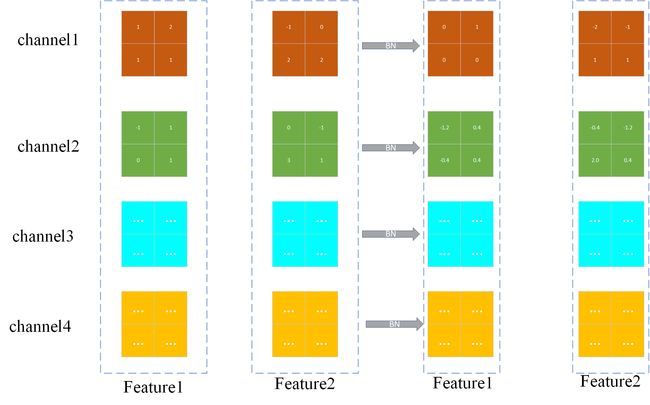
Batch_Normalization
## batch normalization
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
def bn_process(feature, mean, var):
feature_shape = feature.shape
for i in range(feature_shape[1]):
# [batch, channel, height, width]
feature_t = feature[:, i, :, :]
mean_t = feature_t.mean()
# 总体标准差
std_t1 = feature_t.std()
# 样本标准差
std_t2 = feature_t.std(ddof=1)
# bn process
# 这里记得加上eps和pytorch保持一致
feature[:, i, :, :] = (feature[:, i, :, :] - mean_t) / np.sqrt(std_t1 ** 2 + 1e-5)
# update calculating mean and var
mean[i] = mean[i] * 0.9 + mean_t * 0.1
var[i] = var[i] * 0.9 + (std_t2 ** 2) * 0.1
print(feature)
# 随机生成一个batch为2,channel为4,height=width=2的特征向量
# [batch, channel, height, width]
feature1 = torch.randn(2, 4, 2, 2)
# 初始化统计均值和方差
calculate_mean = [0.0, 0.0]
calculate_var = [1.0, 1.0]
# print(feature1.numpy())
# 注意要使用copy()深拷贝
bn_process(feature1.numpy().copy(), calculate_mean, calculate_var)
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2, eps=1e-5)
output = bn(feature1)
print(output)
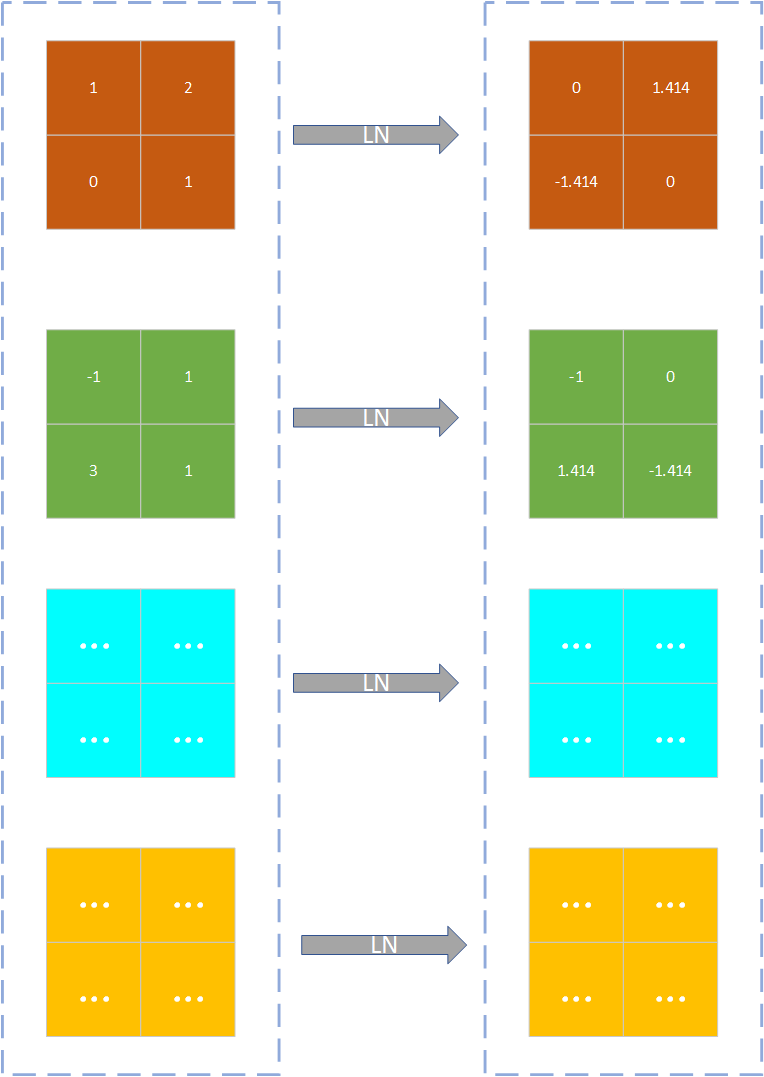
Layer_Normalization
##layer batchnormalization
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def layer_norm_process(feature: torch.Tensor, beta=0., gamma=1., eps=1e-5):
var_mean = torch.var_mean(feature, dim=[1, 2], unbiased=False)
# 均值
mean = var_mean[1]
# 方差
var = var_mean[0]
# layer norm process
feature = (feature - mean[..., None]) / torch.sqrt(var[..., None] + eps)
feature = feature * gamma + beta
return feature
def main():
t = torch.rand(4, 2, 3)
print(t)
# 仅在最后一个维度上做norm处理
norm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape=t.shape[-1], eps=1e-5)
# 官方layer norm处理
t1 = norm(t)
# 自己实现的layer norm处理
t2 = layer_norm_process(t, eps=1e-5)
print("t1:\n", t1)
print("t2:\n", t2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Group_Normalization
## group normalization
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def group_norm(x: torch.Tensor,
num_groups: int,
num_channels: int,
eps: float = 1e-5,
gamma: float = 1.0,
beta: float = 0.):
assert divmod(num_channels, num_groups)[1] == 0
channels_per_group = num_channels // num_groups
new_tensor = []
for t in x.split(channels_per_group, dim=1):
var_mean = torch.var_mean(t, dim=[1, 2, 3], unbiased=False)
var = var_mean[0]
mean = var_mean[1]
t = (t - mean[:, None, None, None]) / torch.sqrt(var[:, None, None, None] + eps)
t = t * gamma + beta
new_tensor.append(t)
new_tensor = torch.cat(new_tensor, dim=1)
return new_tensor
def main():
num_groups = 2
num_channels = 4
eps = 1e-5
img = torch.rand(2, num_channels, 2, 2)
print(img)
gn = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=num_channels, eps=eps)
r1 = gn(img)
print(r1)
r2 = group_norm(img, num_groups, num_channels, eps)
print(r2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
小结
那么这篇文章就到这里了,希望上文的一些图片可以帮助大家理解。这篇文章写还是有些草率,估计大家也不一定会很仔细的看了,但是我本来打算就是作为自己的一个速查手册,不记得的时候回来看看,所以就这样叭!!!对于文中一些不理解的点也欢迎评论区讨论交流。
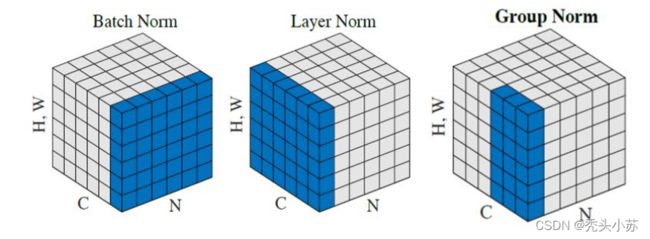
2022.08.02更新
最近刚好看到一张关于这三种Normalization区别的图例,觉得还不错,遂放在下面供大家参考:
如若文章对你有所帮助,那就
咻咻咻咻~~duang~~点个赞呗