使用SpringMVC集成SpringSession的问题
最近在使用SpringSession时遇到一个问题,错误日志如下:
Exception sending context initialized event to listener instance of class org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!先说下项目的配置情况:
SpringSession完全按照官方文档配置如下,
@EnableRedisHttpSession
public class Config {
@Bean
public JedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory(@RedisServerPort int port) {
JedisConnectionFactory connection = new JedisConnectionFactory();
connection.setPort(port);
return connection;
}
}public class Initializer
extends AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer {
public Initializer() {
super(Config.class);
}
}web.xml也是标准的配置方法:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:config/spring/rpc-service.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:config/spring/spring-mvc-main.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>要想知道这个错误产生的原因,先要弄清楚Spring的容器(ApplicationContext)的继承原理及SpringMVC如何使用这一机制的。
Spring容器的继承关系
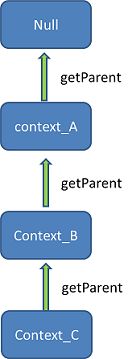
如上图那样,容器之间可以像对象的继承关系一样,子容器通过setParent方法来设置自己的父容器。在调用容器的getBean查找实例时,依次从当前容器往父容器查找,直到找到满足的对象即返回,如果一直没有找到则返回Null.
SpringMVC中的容器即它们的关系
在使用SpringMVC时,必需要配置org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet这样的一个servlet。在初始化此实例时,会生成一个WebApplicationContext容器,生成容器后会检查当前ServletContext环境下是否已经存在"rootContext",如果存在,则通过setParent方法设置为父容器。源代码在这里(org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext):
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}那这个rootContext从哪里来的呢?答案是org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener,它是一个标准的javax.servlet.ServletContextListener实现,在容器启动的时候创建一个全局唯一的rootContext,代码在:org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}总结下结果:servlet容器通过ContextLoaderListener创建一个root容器,并设置为SpringMVC的父容器。 到止应该明白了文章最开始的报错信息的来源了,就是在这个方法里报错。出错的原因有且只有一个:就是给servlet容器注册了两个ContextLoaderListener。一个是在web.xml配置文件里配置的,那另一个在哪里注册的呢?接着分析。
SpringSession的加载机制
集成SpringSession是很简单的,只要实现一个"AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer "的子类即可,然后在子类的构造器中传一个标注了EnableRedisHttpSession的注解类,此注解继承了Configuration,所以在类Initializer进行初始化时,会调用“org.springframework.session.web.context.AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer#onStartup”方法,代码如下:
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
beforeSessionRepositoryFilter(servletContext);
if(configurationClasses != null) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootAppContext.register(configurationClasses);
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext));
}
insertSessionRepositoryFilter(servletContext);
afterSessionRepositoryFilter(servletContext);
}现在我们找到了另外一个往servlet容器中注册ContextLoaderListener的地方了,也就是在这个地方抛错了。找到了问题的根源,解决问题就很简单了。
解决问题
其实只要保证ContextLoaderListener只注册一次就不会有这个问题了,所以有两个选择做法:要么别在web.xml里配置ContextLoaderListener,要么在Initializer类的构造方法中,不要调用父类的有参数构造器,而是调用空参构造器。为了遵守SpringMVC官方的开发规范,最好还是要配置下ContextLoaderListener,把非web层而的对象单独配置,比如service层对象。而web层的东西配置在dispatcher容器中。但是这样即使这样做了,会报别外一个错误,说"org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"找不到。所以要在spring的配置文件中加入如下配置:
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="hostName" value="xxxx"/>
<property name="port" value="xxxx"/>
<property name="password" value="xxx"/>
</bean>如果你加入这个配置,也还是报相同错误的话,那么就要检查下这个配置是放在哪个spring的配置文件下,如果放在ContextLoaderListener的配置文件下就不会报错,而放在DispatcherServlet的配置下就会报错。原因还是从代码(org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy#findWebApplicationContext)里看:
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// the user has injected a context at construction time -> use it
if (this.webApplicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
if (!((ConfigurableApplicationContext)this.webApplicationContext).isActive()) {
// the context has not yet been refreshed -> do so before returning it
((ConfigurableApplicationContext)this.webApplicationContext).refresh();
}
}
return this.webApplicationContext;
}
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName != null) {
return WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
}
else {
return WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
}
}这个方法的最后几行可以看出,SpringSession所需要的所有基础对象,比如Redis连接对象,Redis模板对象,都是从WebApplicationContext从获取。而WebApplicationContext根据getContextAttribute()的值不同先获取的方式也不同。如果getContextAttribute()返回为Null,则取的容器是rootContext,即ContextLoaderListener生成的容器。反之,获取的是DispatcherServlet容器。知道了原因,解决方式就清晰了。重写Initializer的getDispatcherWebApplicationContextSuffix方法。Initializer最终的代码如下:
@EnableRedisHttpSession
public class Initializer extends AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer
{
@Override
protected String getDispatcherWebApplicationContextSuffix()
{
return "mvc"; # 这里返回的字符串就是你配置DispatcherServlet的名称
而本文前面提到的Config类可以删除不用了。