Camera1 源码解析系列(五)—— Camera1 takePicture() 流程解析
前言
前面几篇文章已经把 Camera 控制流的部分梳理得比较清楚了。在 Camera 流程中,还有一个重要的部分,即数据流。
Camera API 1 中,数据流主要是通过函数回调的方式,依照从下往上的方向,逐层 return 到 Applications 中。
本篇将数据流与 Camera 的控制流结合起来,从 takePicture() 方法切入,追踪一个比较完整的 Camera 流程。
1 Open 流程
Camera Open 的流程,在之前的一篇文章中已经比较详细地描述了。在这里,再关注一下这个流程中 Libraries 和 HAL 层的部分。
1.1 CameraService.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp connect():- 注意这里真正实现逻辑是在
connectHelper()函数中。
- 注意这里真正实现逻辑是在
connectHelper():- 这个函数实现比较长,截取其中的一段。
- 首先,如果客户端实例已经存在于
MediaRecorder,则直接将其取出返回。 - 若不存在,则先获取
deviceVersion,然后再调用makeClient()函数创建一个客户端。
template<class CALLBACK, class CLIENT>
Status CameraService::connectHelper(const sp<CALLBACK>& cameraCb, const String8& cameraId,
int api1CameraId, int halVersion, const String16& clientPackageName, int clientUid,
int clientPid, apiLevel effectiveApiLevel, bool legacyMode, bool shimUpdateOnly,
/*out*/sp<CLIENT>& device) {
binder::Status ret = binder::Status::ok();
...
sp<BasicClient> tmp = nullptr;
if(!(ret = makeClient(this, cameraCb, clientPackageName,
cameraId, api1CameraId, facing,
clientPid, clientUid, getpid(), legacyMode,
halVersion, deviceVersion, effectiveApiLevel,
/*out*/&tmp)).isOk()) {
return ret;
}
client = static_cast<CLIENT*>(tmp.get());
...
return ret;
}
makeClient():- 主要是根据
API版本以及HAL版本来选择生成具体的Client实例。 - 如果是
HAL1+Camera1,则创建的是CameraClient,如果是HAL3+Camera1,则创建的是Camera2Client。
- 主要是根据
Status CameraService::makeClient(const sp<CameraService>& cameraService,
const sp<IInterface>& cameraCb, const String16& packageName, const String8& cameraId,
int api1CameraId, int facing, int clientPid, uid_t clientUid, int servicePid,
bool legacyMode, int halVersion, int deviceVersion, apiLevel effectiveApiLevel,
/*out*/sp<BasicClient>* client) {
if (halVersion < 0 || halVersion == deviceVersion) {
// Default path: HAL version is unspecified by caller, create CameraClient
// based on device version reported by the HAL.
switch(deviceVersion) {
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0:
if (effectiveApiLevel == API_1) { // Camera1 API route
sp<ICameraClient> tmp = static_cast<ICameraClient*>(cameraCb.get());
*client = new CameraClient(cameraService, tmp, packageName,
api1CameraId, facing, clientPid, clientUid,
getpid(), legacyMode);
} else { // Camera2 API route
ALOGW("Camera using old HAL version: %d", deviceVersion);
return STATUS_ERROR_FMT(ERROR_DEPRECATED_HAL,
"Camera device \"%s\" HAL version %d does not support camera2 API",
cameraId.string(), deviceVersion);
}
break;
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_0:
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_1:
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_2:
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_3:
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_4:
if (effectiveApiLevel == API_1) { // Camera1 API route
sp<ICameraClient> tmp = static_cast<ICameraClient*>(cameraCb.get());
*client = new Camera2Client(cameraService, tmp, packageName,
cameraId, api1CameraId,
facing, clientPid, clientUid,
servicePid, legacyMode);
} else { // Camera2 API route
sp<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks> tmp =
static_cast<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks*>(cameraCb.get());
*client = new CameraDeviceClient(cameraService, tmp, packageName, cameraId,
facing, clientPid, clientUid, servicePid);
}
break;
default:
// Should not be reachable
ALOGE("Unknown camera device HAL version: %d", deviceVersion);
return STATUS_ERROR_FMT(ERROR_INVALID_OPERATION,
"Camera device \"%s\" has unknown HAL version %d",
cameraId.string(), deviceVersion);
}
} else {
// A particular HAL version is requested by caller. Create CameraClient
// based on the requested HAL version.
if (deviceVersion > CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0 &&
halVersion == CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0) {
// Only support higher HAL version device opened as HAL1.0 device.
sp<ICameraClient> tmp = static_cast<ICameraClient*>(cameraCb.get());
*client = new CameraClient(cameraService, tmp, packageName,
api1CameraId, facing, clientPid, clientUid,
servicePid, legacyMode);
} else {
// Other combinations (e.g. HAL3.x open as HAL2.x) are not supported yet.
ALOGE("Invalid camera HAL version %x: HAL %x device can only be"
" opened as HAL %x device", halVersion, deviceVersion,
CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0);
return STATUS_ERROR_FMT(ERROR_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT,
"Camera device \"%s\" (HAL version %d) cannot be opened as HAL version %d",
cameraId.string(), deviceVersion, halVersion);
}
}
return Status::ok();
}
1.2 CameraHardwareInterface.h
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device1/CameraHardwareInterface.h setCallback():- 设置
notify回调,这用来通知数据已经更新。 - 设置
data回调以及dataTimestamp回调,对应的是函数指针mDataCb与mDataCvTimestamp。 - 注意到,设置
mDevice->ops对应回调函数时,传入的不是之前设置的函数指针,而是__data_cb这样的函数。在该文件中,实现了__data_cb,将回调函数做了一层封装。
- 设置
/** Set the notification and data callbacks */
void setCallbacks(notify_callback notify_cb,
data_callback data_cb,
data_callback_timestamp data_cb_timestamp,
void* user)
{
mNotifyCb = notify_cb;
mDataCb = data_cb;
mDataCbTimestamp = data_cb_timestamp;
mCbUser = user;
ALOGV("%s(%s)", __FUNCTION__, mName.string());
if (mDevice->ops->set_callbacks) {
mDevice->ops->set_callbacks(mDevice,
__notify_cb,
__data_cb,
__data_cb_timestamp,
__get_memory,
this);
}
}
__data_cb():- 对原
callback函数简单封装,附加了一个防止数组越界判断。
- 对原
static void __data_cb(int32_t msg_type,
const camera_memory_t *data, unsigned int index,
camera_frame_metadata_t *metadata,
void *user)
{
ALOGV("%s", __FUNCTION__);
CameraHardwareInterface *__this =
static_cast<CameraHardwareInterface *>(user);
sp<CameraHeapMemory> mem(static_cast<CameraHeapMemory *>(data->handle));
if (index >= mem->mNumBufs) {
ALOGE("%s: invalid buffer index %d, max allowed is %d", __FUNCTION__,
index, mem->mNumBufs);
return;
}
__this->mDataCb(msg_type, mem->mBuffers[index], metadata, __this->mCbUser);
}
2 控制流
2.1 Framework
2.1.1 Camera.java
- 路径:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/Camera.java takePicture():- 设置快门回调。
- 设置各种类型的图片数据回调。
- 调用
JNI takePicture方法。 - 注意,传入的参数
msgType是根据相应CallBack是否存在而确定的,每种Callback应该对应一个二进制中的数位(如 1,10,100 中 1 的位置),于是这里采用|=操作给它赋值。
public final void takePicture(ShutterCallback shutter, PictureCallback raw,
PictureCallback postview, PictureCallback jpeg) {
mShutterCallback = shutter;
mRawImageCallback = raw;
mPostviewCallback = postview;
mJpegCallback = jpeg;
// If callback is not set, do not send me callbacks.
int msgType = 0;
if (mShutterCallback != null) {
msgType |= CAMERA_MSG_SHUTTER;
}
if (mRawImageCallback != null) {
msgType |= CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE;
}
if (mPostviewCallback != null) {
msgType |= CAMERA_MSG_POSTVIEW_FRAME;
}
if (mJpegCallback != null) {
msgType |= CAMERA_MSG_COMPRESSED_IMAGE;
}
native_takePicture(msgType);
mFaceDetectionRunning = false;
}
2.2 Android Runtime
2.2.1 android_hardware_Camera.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_Camera.cpptakePicture():- 获取已经打开的
camera实例,调用其takePicture()接口。 - 注意,在这个函数中,对于
RAW_IMAGE有一些附加操作:- 如果设置了
RAW的callback,则要检查上下文中,是否能找到对应Buffer。 - 若无法找到
Buffer,则将CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE的信息去掉,换成CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY。 - 替换后,就只会获得
notification的消息,而没有对应的图像数据。
- 如果设置了
static void android_hardware_Camera_takePicture(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jint msgType)
{
ALOGV("takePicture");
JNICameraContext* context;
sp<Camera> camera = get_native_camera(env, thiz, &context);
if (camera == 0) return;
/*
* When CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE is requested, if the raw image callback
* buffer is available, CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE is enabled to get the
* notification _and_ the data; otherwise, CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY
* is enabled to receive the callback notification but no data.
*
* Note that CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY is not exposed to the
* Java application.
*/
if (msgType & CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE) {
ALOGV("Enable raw image callback buffer");
if (!context->isRawImageCallbackBufferAvailable()) {
ALOGV("Enable raw image notification, since no callback buffer exists");
msgType &= ~CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE;
msgType |= CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY;
}
}
if (camera->takePicture(msgType) != NO_ERROR) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "takePicture failed");
return;
}
}
2.3 C/C++ Libraries
2.3.1 Camera.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/camera/Camera.cpp takePicture():- 获取一个
ICamera,调用其takePicture接口。
- 获取一个
// take a picture
status_t Camera::takePicture(int msgType)
{
ALOGV("takePicture: 0x%x", msgType);
sp <::android::hardware::ICamera> c = mCamera;
if (c == 0) return NO_INIT;
return c->takePicture(msgType);
}
2.3.2 ICamera.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/camera/ICamera.cpp takePicture():- 利用
Binder机制发送相应指令到服务端。 - 如果是
HAL1+Camera1,实际调用到的是CameraClient::takePicture()函数。 - 如果是
HAL3+Camera1,实际调用到的是Camera2Client::takePicture()函数。
- 利用
// take a picture - returns an IMemory (ref-counted mmap)
status_t takePicture(int msgType)
{
ALOGV("takePicture: 0x%x", msgType);
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(ICamera::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeInt32(msgType);
remote()->transact(TAKE_PICTURE, data, &reply);
status_t ret = reply.readInt32();
return ret;
}
2.3.3 CameraClient.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/CameraClient.cpp takePicture():- 注意,
CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE指令与CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY指令不能同时有效,需要进行对应的检查。 - 对传入的指令过滤,只留下与
takePicture()操作相关的。 - 调用
CameraHardwareInterface中的takePicture()接口。
- 注意,
// take a picture - image is returned in callback
status_t CameraClient::takePicture(int msgType) {
LOG1("takePicture (pid %d): 0x%x", getCallingPid(), msgType);
Mutex::Autolock lock(mLock);
status_t result = checkPidAndHardware();
if (result != NO_ERROR) return result;
if ((msgType & CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE) &&
(msgType & CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY)) {
ALOGE("CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE and CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY"
" cannot be both enabled");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
// We only accept picture related message types
// and ignore other types of messages for takePicture().
int picMsgType = msgType
& (CAMERA_MSG_SHUTTER |
CAMERA_MSG_POSTVIEW_FRAME |
CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE |
CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY |
CAMERA_MSG_COMPRESSED_IMAGE);
enableMsgType(picMsgType);
return mHardware->takePicture();
}
2.3.4 Camera2Client.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/Camera2Client.cpp takePicture():- 调用了
mCaptureSequencer->startCapture()。
- 调用了
status_t Camera2Client::takePicture(int msgType) {
ATRACE_CALL();
Mutex::Autolock icl(mBinderSerializationLock);
status_t res;
if ( (res = checkPid(__FUNCTION__) ) != OK) return res;
{
SharedParameters::Lock l(mParameters);
switch (l.mParameters.state) {
case Parameters::DISCONNECTED:
case Parameters::STOPPED:
case Parameters::WAITING_FOR_PREVIEW_WINDOW:
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Cannot take picture without preview enabled",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
case Parameters::PREVIEW:
// Good to go for takePicture
res = commandStopFaceDetectionL(l.mParameters);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Unable to stop face detection for still capture",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId);
return res;
}
l.mParameters.state = Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE;
break;
case Parameters::RECORD:
// Good to go for video snapshot
l.mParameters.state = Parameters::VIDEO_SNAPSHOT;
break;
case Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE:
case Parameters::VIDEO_SNAPSHOT:
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Already taking a picture",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
ALOGV("%s: Camera %d: Starting picture capture", __FUNCTION__, mCameraId);
res = updateProcessorStream(mJpegProcessor, l.mParameters);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Can't set up still image stream: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId, strerror(-res), res);
return res;
}
}
// Need HAL to have correct settings before (possibly) triggering precapture
syncWithDevice();
res = mCaptureSequencer->startCapture(msgType);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Unable to start capture: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId, strerror(-res), res);
}
return res;
}
2.3.4.1 CaptureSequencer.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/client2/CaptureSequencer.cpp startCapture():- 这里
mStartCaptureSignal.signal()会激活mStartCaptureSignal条件。
- 这里
status_t CaptureSequencer::startCapture(int msgType) {
ALOGV("%s", __FUNCTION__);
ATRACE_CALL();
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
if (mBusy) {
ALOGE("%s: Already busy capturing!", __FUNCTION__);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
if (!mStartCapture) {
mMsgType = msgType;
mStartCapture = true;
mStartCaptureSignal.signal();
}
return OK;
}
CaptureSequencer 模块是 take picture 操作的重点,在 Camera2Client 中进行了创建,首先来看 CaptureSequencer 线程的 threadLoop 函数:
bool CaptureSequencer::threadLoop() {
sp<Camera2Client> client = mClient.promote();
if (client == 0) return false;
CaptureState currentState;
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mStateMutex);
currentState = mCaptureState;
}
currentState = (this->*kStateManagers[currentState])(client);
Mutex::Autolock l(mStateMutex);
if (currentState != mCaptureState) {
if (mCaptureState != IDLE) {
ATRACE_ASYNC_END(kStateNames[mCaptureState], mStateTransitionCount);
}
mCaptureState = currentState;//保留新的状态
mStateTransitionCount++;
if (mCaptureState != IDLE) {
ATRACE_ASYNC_BEGIN(kStateNames[mCaptureState], mStateTransitionCount);
}
ALOGV("Camera %d: New capture state %s",
client->getCameraId(), kStateNames[mCaptureState]);
mStateChanged.signal();
}
if (mCaptureState == ERROR) {
ALOGE("Camera %d: Stopping capture sequencer due to error",
client->getCameraId());
return false;
}
return true;
}
CaptureSequencer 是一个以不同的 state 状态机来循环工作的模块, currentState = (this->*kStateManagers[currentState])(client) 函数是执行对应状态机下的执行函数,其中的 state 值如下:
const CaptureSequencer::StateManager
CaptureSequencer::kStateManagers[CaptureSequencer::NUM_CAPTURE_STATES-1] = {
&CaptureSequencer::manageIdle,
&CaptureSequencer::manageStart,
&CaptureSequencer::manageZslStart,
&CaptureSequencer::manageZslWaiting,
&CaptureSequencer::manageZslReprocessing,
&CaptureSequencer::manageStandardStart,
&CaptureSequencer::manageStandardPrecaptureWait,
&CaptureSequencer::manageStandardCapture,
&CaptureSequencer::manageStandardCaptureWait,
&CaptureSequencer::manageBurstCaptureStart,
&CaptureSequencer::manageBurstCaptureWait,
&CaptureSequencer::manageDone,
};
我们以一个 standard capture 的操作模式,来分析一次 take picture 的过程。初始化的 mCaptureState(IDLE),进入的函数入口为 manageIdle:
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageIdle(
sp<Camera2Client> &/*client*/) {
status_t res;
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
while (!mStartCapture) {
res = mStartCaptureSignal.waitRelative(mInputMutex,
kWaitDuration);
if (res == TIMED_OUT) break;
}
if (mStartCapture) {
mStartCapture = false;
mBusy = true;
return START;
}
return IDLE;
}
函数主要在轮询 mStartCapture 的值,这个值是由上面提到的 mStartCaptureSignal.signal() 来启动的,Threadloop 线程被唤醒后,执行返回一个新的状态机 mCaptureState = START,然后触发下面的状态机处理方法:
manageStart():
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageStart(
sp<Camera2Client> &client) {
ALOGV("%s", __FUNCTION__);
status_t res;
ATRACE_CALL();
SharedParameters::Lock l(client->getParameters());
CaptureState nextState = DONE;
//下面这个方法就是用来创建拍照的metadata的接口。
res = updateCaptureRequest(l.mParameters, client);
//连拍模式状态机
if(l.mParameters.lightFx != Parameters::LIGHTFX_NONE &&
l.mParameters.state == Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE) {
nextState = BURST_CAPTURE_START;
}
else if (l.mParameters.zslMode &&
l.mParameters.state == Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE &&
l.mParameters.flashMode != Parameters::FLASH_MODE_ON) {//ZSL拍照模式,注意ZSL是不开闪光灯的。
nextState = ZSL_START;
} else { //正常模式-静态拍照
nextState = STANDARD_START;
}
mShutterNotified = false;
return nextState;
}
下面我们先分析 STANDARD_START (正常模式-静态拍照)的状态机情况。
manageStandardStart():
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageStandardStart(
sp<Camera2Client> &client) {
ATRACE_CALL();
bool isAeConverged = false;
// Get the onFrameAvailable callback when the requestID == mCaptureId
// We don't want to get partial results for normal capture, as we need
// Get ANDROID_SENSOR_TIMESTAMP from the capture result, but partial
// result doesn't have to have this metadata available.
// TODO: Update to use the HALv3 shutter notification for remove the
// need for this listener and make it faster. see bug 12530628.
client->registerFrameListener(mCaptureId, mCaptureId + 1,
this,
/*sendPartials*/false);
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
isAeConverged = (mAEState == ANDROID_CONTROL_AE_STATE_CONVERGED);
}
{
SharedParameters::Lock l(client->getParameters());
// Skip AE precapture when it is already converged and not in force flash mode.
if (l.mParameters.flashMode != Parameters::FLASH_MODE_ON && isAeConverged) {
return STANDARD_CAPTURE;
}
mTriggerId = l.mParameters.precaptureTriggerCounter++;
}
client->getCameraDevice()->triggerPrecaptureMetering(mTriggerId);
mAeInPrecapture = false;
mTimeoutCount = kMaxTimeoutsForPrecaptureStart;
return STANDARD_PRECAPTURE_WAIT;
}
- 上面的方法做了这几件事:
- 注册拍照图片可用监听对象
- 判断当前 AE(自动曝光)状态是否收敛,如果收敛了,拍照状态机为
STANDARD_CAPTURE。如果 AE 已经收敛那么拍照状态机就是STANDARD_PRECAPTURE_WAIT,就会下发 AE 收敛消息,等待HALAE 收敛完成。
manageStandardCapture():- 这里
client->getCameraDevice()->capture()会在Camera3Device中根据metadata中的数据,创建请求,并将请求发送给HAL,后面的流程会在下一节HAL中分析。
- 这里
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageStandardCapture(
sp<Camera2Client> &client) {
status_t res;
ATRACE_CALL();
SharedParameters::Lock l(client->getParameters());
Vector<int32_t> outputStreams;
uint8_t captureIntent = static_cast<uint8_t>(ANDROID_CONTROL_CAPTURE_INTENT_STILL_CAPTURE);
/**
* Set up output streams in the request
* - preview
* - capture/jpeg
* - callback (if preview callbacks enabled)
* - recording (if recording enabled)
*/
//下面默认会将preview和capture流id保存到临时数组outputStreams中。
outputStreams.push(client->getPreviewStreamId());
outputStreams.push(client->getCaptureStreamId());
if (l.mParameters.previewCallbackFlags &
CAMERA_FRAME_CALLBACK_FLAG_ENABLE_MASK) {
outputStreams.push(client->getCallbackStreamId());
}
//这里如果是video_snapshot模式,则会修改捕获意图为ANDROID_CONTROL_CAPTURE_INTENT_VIDEO_SNAPSHOT
if (l.mParameters.state == Parameters::VIDEO_SNAPSHOT) {
outputStreams.push(client->getRecordingStreamId());
captureIntent = static_cast<uint8_t>(ANDROID_CONTROL_CAPTURE_INTENT_VIDEO_SNAPSHOT);
}
//将各种需要的流ID,保存到metadata中,为了在Camera3Device中查找到对应流对象。
res = mCaptureRequest.update(ANDROID_REQUEST_OUTPUT_STREAMS,
outputStreams);
if (res == OK) {//保存到请求ID
res = mCaptureRequest.update(ANDROID_REQUEST_ID,
&mCaptureId, 1);
}
if (res == OK) {//保存捕获意图到metadata中。
res = mCaptureRequest.update(ANDROID_CONTROL_CAPTURE_INTENT,
&captureIntent, 1);
}
if (res == OK) {
res = mCaptureRequest.sort();
}
if (res != OK) {//如果出问题,拍照结束。一般不会走到这里。
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Unable to set up still capture request: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId(), strerror(-res), res);
return DONE;
}
// Create a capture copy since CameraDeviceBase#capture takes ownership
CameraMetadata captureCopy = mCaptureRequest;
//此处省略一些metadata检查代码,不影响分析。
/**
* Clear the streaming request for still-capture pictures
* (as opposed to i.e. video snapshots)
*/
if (l.mParameters.state == Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE) {
// API definition of takePicture() - stop preview before taking pic
res = client->stopStream();//如果是静态拍照,注意是非ZSL模式,则会停止preview预览流。
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Unable to stop preview for still capture: "
"%s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId(), strerror(-res), res);
return DONE;
}
}
// TODO: Capture should be atomic with setStreamingRequest here
res = client->getCameraDevice()->capture(captureCopy);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Unable to submit still image capture request: "
"%s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId(), strerror(-res), res);
return DONE;
}
mTimeoutCount = kMaxTimeoutsForCaptureEnd;
return STANDARD_CAPTURE_WAIT;
}
manageStandardCaptureWait():
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageStandardCaptureWait(
sp<Camera2Client> &client) {
status_t res;
ATRACE_CALL();
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
// Wait for new metadata result (mNewFrame)
// 这里mNewFrameReceived在拍照帧没准备好之前为false,一旦拍照帧准备好了,FrameProcessor会回调之前注册的onResultAvailable()方法,在该方法中将mNewFrameReceived设置为true,并激活mNewFrameSignal条件,下面的等待操作就会继续往下走了。
while (!mNewFrameReceived) {
//这里会等待100ms
res = mNewFrameSignal.waitRelative(mInputMutex, kWaitDuration);
if (res == TIMED_OUT) {
mTimeoutCount--;
break;
}
}
// Approximation of the shutter being closed
// - TODO: use the hal3 exposure callback in Camera3Device instead
//下面是通知shutter事件,即播放拍照音,并将CAMERA_MSG_SHUTTER,CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE_NOTIFY回传给上层。
if (mNewFrameReceived && !mShutterNotified) {
SharedParameters::Lock l(client->getParameters());
/* warning: this also locks a SharedCameraCallbacks */
shutterNotifyLocked(l.mParameters, client, mMsgType);
mShutterNotified = true;//已经通知shutter事件了。
}
// Wait until jpeg was captured by JpegProcessor
//mNewCaptureSignal该条件是在jpeg 图片数据enqueue到bufferqueue时激活的。这里做一下小结
//这里会用到两个contiion对象mNewFrameSignal和mNewCaptureSignal,其中当hal回传jpeg帧时,会先
//return buffer即先激活mNewCaptureSignal,才会激活mNewFrameSignal。所以到了下面条件,直接
//为真。
while (mNewFrameReceived && !mNewCaptureReceived) {
res = mNewCaptureSignal.waitRelative(mInputMutex, kWaitDuration);
if (res == TIMED_OUT) {
mTimeoutCount--;
break;
}
}
if (mTimeoutCount <= 0) {
ALOGW("Timed out waiting for capture to complete");
return DONE;
}
//如果mNewFrameReceived && mNewCaptureReceived为真,说明真的收到jepg帧了。
if (mNewFrameReceived && mNewCaptureReceived) {
//这里主要做了2件事情
//1.检查捕获ID是否一样,否则就直接报错。
//2.检查事件戳是否正确,这个一般是不会错的。
client->removeFrameListener(mCaptureId, mCaptureId + 1, this);
mNewFrameReceived = false;
mNewCaptureReceived = false;
return DONE;//返回状态机DONE.
}
//如果还没准备好,则会继续等待下去,一般发生在等待100ms超时。
return STANDARD_CAPTURE_WAIT;
}
manageDone():
CaptureSequencer::CaptureState CaptureSequencer::manageDone(sp<Camera2Client> &client) {
status_t res = OK;
ATRACE_CALL();
mCaptureId++;
if (mCaptureId >= Camera2Client::kCaptureRequestIdEnd) {
mCaptureId = Camera2Client::kCaptureRequestIdStart;
}
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
mBusy = false;
}
int takePictureCounter = 0;
{
SharedParameters::Lock l(client->getParameters());
switch (l.mParameters.state) {
case Parameters::DISCONNECTED:
ALOGW("%s: Camera %d: Discarding image data during shutdown ",
__FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId());
res = INVALID_OPERATION;
break;
case Parameters::STILL_CAPTURE:
res = client->getCameraDevice()->waitUntilDrained();
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Can't idle after still capture: "
"%s (%d)", __FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId(),
strerror(-res), res);
}
l.mParameters.state = Parameters::STOPPED;
break;
case Parameters::VIDEO_SNAPSHOT:
l.mParameters.state = Parameters::RECORD;
break;
default:
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: Still image produced unexpectedly "
"in state %s!",
__FUNCTION__, client->getCameraId(),
Parameters::getStateName(l.mParameters.state));
res = INVALID_OPERATION;
}
takePictureCounter = l.mParameters.takePictureCounter;
}
sp<ZslProcessorInterface> processor = mZslProcessor.promote();
if (processor != 0) {
ALOGV("%s: Memory optimization, clearing ZSL queue",
__FUNCTION__);
processor->clearZslQueue();
}
/**
* Fire the jpegCallback in Camera#takePicture(..., jpegCallback)
*/
if (mCaptureBuffer != 0 && res == OK) {
ATRACE_ASYNC_END(Camera2Client::kTakepictureLabel, takePictureCounter);
Camera2Client::SharedCameraCallbacks::Lock
l(client->mSharedCameraCallbacks);
ALOGV("%s: Sending still image to client", __FUNCTION__);
if (l.mRemoteCallback != 0) {//将图片数据回传到上层,上层会去做一下拷贝。
l.mRemoteCallback->dataCallback(CAMERA_MSG_COMPRESSED_IMAGE,
mCaptureBuffer, NULL);
} else {
ALOGV("%s: No client!", __FUNCTION__);
}
}
mCaptureBuffer.clear();
return IDLE;
}
拍照完成,状态机返回到 IDLE。
2.4 HAL
这里我们也分两种情况的流程来分析,分别是 CameraClient 和 Camera2Client 调用下来的。
2.4.1 HAL1 的流程
2.4.1.1 CameraHardwareInterface.h
● 路径:frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device1/CameraHardwareInterface.h
takePicture():- 通过
mDevice中设置的函数指针,调用HAL层中具体平台对应的takePicture操作的实现逻辑。 - 控制流程到了
HAL层后,再向Linux Drivers发送控制指令,从而使具体的Camera设备执行指令,并获取数据。
- 通过
/**
* Take a picture.
*/
status_t takePicture()
{
ALOGV("%s(%s)", __FUNCTION__, mName.string());
if (mDevice->ops->take_picture)
return mDevice->ops->take_picture(mDevice);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
2.4.2 HAL3 的流程
2.4.2.1 Camera3Device.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp capture():mRequestThread->queueRequest()将新的请求放入到队列中。RequestThread是与HAL交互的核心类。
status_t Camera3Device::capture(CameraMetadata &request) {
ATRACE_CALL();
Mutex::Autolock l(mLock);
// TODO: take ownership of the request
switch (mStatus) {
case STATUS_ERROR:
CLOGE("Device has encountered a serious error");
return INVALID_OPERATION;
case STATUS_UNINITIALIZED:
CLOGE("Device not initialized");
return INVALID_OPERATION;
case STATUS_IDLE:
case STATUS_ACTIVE:
// OK
break;
default:
SET_ERR_L("Unexpected status: %d", mStatus);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
sp<CaptureRequest> newRequest = setUpRequestLocked(request);
if (newRequest == NULL) {
CLOGE("Can't create capture request");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
return mRequestThread->queueRequest(newRequest);
}
RequestThread 实例是在 Camera3Device::initializeCommonLocked 中创建并 run 起来的,这是 openCamera 的流程。线程 run 起来后就是循环调用 threadLoop 了,用来处理 request 队列。
threadLoop():mHal3Device->ops->process_capture_request()发送request 到HAL。- 函数太长,只截取关键部分。
bool Camera3Device::RequestThread::threadLoop() {
status_t res;
...
// Create request to HAL
camera3_capture_request_t request = camera3_capture_request_t();
...
// Submit request and block until ready for next one
res = mHal3Device->ops->process_capture_request(mHal3Device, &request);
if (res != OK) {
SET_ERR("RequestThread: Unable to submit capture request %d to HAL"
" device: %s (%d)", request.frame_number, strerror(-res), res);
cleanUpFailedRequest(request, nextRequest, outputBuffers);
return false;
}
...
// Return input buffer back to framework
if (request.input_buffer != NULL) {
Camera3Stream *stream =
Camera3Stream::cast(request.input_buffer->stream);
res = stream->returnInputBuffer(*(request.input_buffer));
// Note: stream may be deallocated at this point, if this buffer was the
// last reference to it.
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: RequestThread: Can't return input buffer for frame %d to"
" its stream:%s (%d)", __FUNCTION__,
request.frame_number, strerror(-res), res);
// TODO: Report error upstream
}
}
return true;
}
3 数据流
由于数据流是通过 callback 函数实现的,所以探究其流程我们从底层向上层进行分析。同样,我们也分两种情况。
3.1 HAL1 的流程
3.1.1 HAL
3.1.1.1 CameraHardwareInterface.h
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device1/CameraHardwareInterface.h - 这里我们只选择
dataCallback相关流程进行分析。 __data_cb():- 该回调函数是在同文件中实现的
setCallbacks()函数中设置的。 Camera设备获得数据后,就会往上传输,在HAL层中会调用到这个回调函数。- 通过函数指针
mDataCb调用从上一层传入的回调,从而将数据上传。 - 这个
mDataCb指针对应的,是CameraClient类中实现的dataCallback()。
- 该回调函数是在同文件中实现的
static void __data_cb(int32_t msg_type,
const camera_memory_t *data, unsigned int index,
camera_frame_metadata_t *metadata,
void *user)
{
ALOGV("%s", __FUNCTION__);
CameraHardwareInterface *__this =
static_cast<CameraHardwareInterface *>(user);
sp<CameraHeapMemory> mem(static_cast<CameraHeapMemory *>(data->handle));
if (index >= mem->mNumBufs) {
ALOGE("%s: invalid buffer index %d, max allowed is %d", __FUNCTION__,
index, mem->mNumBufs);
return;
}
__this->mDataCb(msg_type, mem->mBuffers[index], metadata, __this->mCbUser);
}
3.1.2 C/C++ Libraries
3.1.2.1 CameraClient.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/CameraClient.cpp dataCallback():- 这个回调在该文件实现的
initialize()函数中设置到CameraHardwareInterface中。 - 启动这个回调后,就从
Cookie中获取已连接的客户端。 - 根据
msgType,启动对应的handle操作。 - 选择其中一个分支的
handle函数来看。
- 这个回调在该文件实现的
void CameraClient::dataCallback(int32_t msgType,
const sp<IMemory>& dataPtr, camera_frame_metadata_t *metadata, void* user) {
LOG2("dataCallback(%d)", msgType);
sp<CameraClient> client = static_cast<CameraClient*>(getClientFromCookie(user).get());
if (client.get() == nullptr) return;
if (!client->lockIfMessageWanted(msgType)) return;
if (dataPtr == 0 && metadata == NULL) {
ALOGE("Null data returned in data callback");
client->handleGenericNotify(CAMERA_MSG_ERROR, UNKNOWN_ERROR, 0);
return;
}
switch (msgType & ~CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA) {
case CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_FRAME:
client->handlePreviewData(msgType, dataPtr, metadata);
break;
case CAMERA_MSG_POSTVIEW_FRAME:
client->handlePostview(dataPtr);
break;
case CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE:
client->handleRawPicture(dataPtr);
break;
case CAMERA_MSG_COMPRESSED_IMAGE:
client->handleCompressedPicture(dataPtr);
break;
default:
client->handleGenericData(msgType, dataPtr, metadata);
break;
}
}
handleRawPicture():- 在
open流程中,connect()函数调用时,mRemoteCallback已经设置为一个客户端实例,其对应的是ICameraClient的强指针。 - 通过这个实例,这里基于
Binder机制来启动客户端的dataCallback。 - 客户端的
dataCallback是实现在Camera类中。
- 在
// picture callback - raw image ready
void CameraClient::handleRawPicture(const sp<IMemory>& mem) {
disableMsgType(CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE);
ssize_t offset;
size_t size;
sp<IMemoryHeap> heap = mem->getMemory(&offset, &size);
sp<hardware::ICameraClient> c = mRemoteCallback;
mLock.unlock();
if (c != 0) {
c->dataCallback(CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE, mem, NULL);
}
}
3.1.2.2 Camera.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/camera/Camera.cpp dataCallback():- 调用
CameraListener的postData接口,将数据继续向上传输。 postData接口的实现是在android_hardware_Camera.cpp中。
- 调用
// callback from camera service when frame or image is ready
void Camera::dataCallback(int32_t msgType, const sp<IMemory>& dataPtr,
camera_frame_metadata_t *metadata)
{
sp<CameraListener> listener;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
listener = mListener;
}
if (listener != NULL) {
listener->postData(msgType, dataPtr, metadata);
}
}
3.1.3 Android Runtime
3.1.3.1 android_hardware_Camera.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_Camera.cpp postData():- 是
JNICameraContext类的成员函数,该类继承了CameraListener。 - 首先获取虚拟机指针。
- 然后过滤掉
CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA信息。 - 进入分支处理。
- 对于数据传输路径,关键是在于
copyAndPost()函数。
- 是
void JNICameraContext::postData(int32_t msgType, const sp<IMemory>& dataPtr,
camera_frame_metadata_t *metadata)
{
// VM pointer will be NULL if object is released
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
JNIEnv *env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
if (mCameraJObjectWeak == NULL) {
ALOGW("callback on dead camera object");
return;
}
int32_t dataMsgType = msgType & ~CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA;
// return data based on callback type
switch (dataMsgType) {
case CAMERA_MSG_VIDEO_FRAME:
// should never happen
break;
// For backward-compatibility purpose, if there is no callback
// buffer for raw image, the callback returns null.
case CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE:
ALOGV("rawCallback");
if (mRawImageCallbackBuffers.isEmpty()) {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(mCameraJClass, fields.post_event,
mCameraJObjectWeak, dataMsgType, 0, 0, NULL);
} else {
copyAndPost(env, dataPtr, dataMsgType);
}
break;
// There is no data.
case 0:
break;
default:
ALOGV("dataCallback(%d, %p)", dataMsgType, dataPtr.get());
copyAndPost(env, dataPtr, dataMsgType);
break;
}
// post frame metadata to Java
if (metadata && (msgType & CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA)) {
postMetadata(env, CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA, metadata);
}
}
copyAndPost():- 首先确认
Memory中数据是否存在。 - 申请
Java字节数组(jbyteArray, jbyte*),并将Memory数据赋予到其中。 - 重点是这个函数:
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(mCameraJClass, fields.post_event, mCameraJObjectWeak, msgType, 0, 0, obj);- 它的功能是将图像传给
Java端。 - 通过字段
post_event,在c++中调用Java的方法,并传入对应的参数。 - 最终调用到
Java端的postEventFromNative()方法。
- 首先确认
void JNICameraContext::copyAndPost(JNIEnv* env, const sp<IMemory>& dataPtr, int msgType)
{
jbyteArray obj = NULL;
// allocate Java byte array and copy data
if (dataPtr != NULL) {
ssize_t offset;
size_t size;
sp<IMemoryHeap> heap = dataPtr->getMemory(&offset, &size);
ALOGV("copyAndPost: off=%zd, size=%zu", offset, size);
uint8_t *heapBase = (uint8_t*)heap->base();
if (heapBase != NULL) {
const jbyte* data = reinterpret_cast<const jbyte*>(heapBase + offset);
if (msgType == CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE) {
obj = getCallbackBuffer(env, &mRawImageCallbackBuffers, size);
} else if (msgType == CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_FRAME && mManualBufferMode) {
obj = getCallbackBuffer(env, &mCallbackBuffers, size);
if (mCallbackBuffers.isEmpty()) {
ALOGV("Out of buffers, clearing callback!");
mCamera->setPreviewCallbackFlags(CAMERA_FRAME_CALLBACK_FLAG_NOOP);
mManualCameraCallbackSet = false;
if (obj == NULL) {
return;
}
}
} else {
ALOGV("Allocating callback buffer");
obj = env->NewByteArray(size);
}
if (obj == NULL) {
ALOGE("Couldn't allocate byte array for JPEG data");
env->ExceptionClear();
} else {
env->SetByteArrayRegion(obj, 0, size, data);
}
} else {
ALOGE("image heap is NULL");
}
}
// post image data to Java
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(mCameraJClass, fields.post_event,
mCameraJObjectWeak, msgType, 0, 0, obj);
if (obj) {
env->DeleteLocalRef(obj);
}
}
3.1.4 Framework
3.1.4.1 Camera.java
- 路径:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/Camera.java - 以下两个方法都是
EventHandler的成员,这个类继承了Handler类。 postEventFromNative():- 首先确定
Camera是否已经实例化。 - 确认后,通过
Camera的成员mEventHandler的obtainMessage方法将从Native环境中获得的数据封装成Message类的一个实例,然后调用sendMessage()方法将数据传出。
- 首先确定
private static void postEventFromNative(Object camera_ref,
int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj)
{
Camera c = (Camera)((WeakReference)camera_ref).get();
if (c == null)
return;
if (c.mEventHandler != null) {
Message m = c.mEventHandler.obtainMessage(what, arg1, arg2, obj);
c.mEventHandler.sendMessage(m);
}
}
handleMessage():sendMessage()方法传出的数据会通过这个方法作出处理,从而发送到对应的回调类中。- 注意到几个不同的回调类(
mRawImageCallback、mJpegCallback等)中都有onPictureTaken()方法,通过调用这个方法,底层传输到此的数据最终发送到最上层的Android应用中,上层应用通过解析Message就可以得到拍到的图像,从而得以进行后续的操作。
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch(msg.what) {
case CAMERA_MSG_SHUTTER:
if (mShutterCallback != null) {
mShutterCallback.onShutter();
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_RAW_IMAGE:
if (mRawImageCallback != null) {
mRawImageCallback.onPictureTaken((byte[])msg.obj, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_COMPRESSED_IMAGE:
if (mJpegCallback != null) {
mJpegCallback.onPictureTaken((byte[])msg.obj, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_FRAME:
PreviewCallback pCb = mPreviewCallback;
if (pCb != null) {
if (mOneShot) {
// Clear the callback variable before the callback
// in case the app calls setPreviewCallback from
// the callback function
mPreviewCallback = null;
} else if (!mWithBuffer) {
// We're faking the camera preview mode to prevent
// the app from being flooded with preview frames.
// Set to oneshot mode again.
setHasPreviewCallback(true, false);
}
pCb.onPreviewFrame((byte[])msg.obj, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_POSTVIEW_FRAME:
if (mPostviewCallback != null) {
mPostviewCallback.onPictureTaken((byte[])msg.obj, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_FOCUS:
AutoFocusCallback cb = null;
synchronized (mAutoFocusCallbackLock) {
cb = mAutoFocusCallback;
}
if (cb != null) {
boolean success = msg.arg1 == 0 ? false : true;
cb.onAutoFocus(success, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_ZOOM:
if (mZoomListener != null) {
mZoomListener.onZoomChange(msg.arg1, msg.arg2 != 0, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA:
if (mFaceListener != null) {
mFaceListener.onFaceDetection((Face[])msg.obj, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_ERROR :
Log.e(TAG, "Error " + msg.arg1);
if (mErrorCallback != null) {
mErrorCallback.onError(msg.arg1, mCamera);
}
return;
case CAMERA_MSG_FOCUS_MOVE:
if (mAutoFocusMoveCallback != null) {
mAutoFocusMoveCallback.onAutoFocusMoving(msg.arg1 == 0 ? false : true, mCamera);
}
return;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Unknown message type " + msg.what);
return;
}
}
3.2 HAL3 的流程
HAL3 的流程中,与 TakePicture 紧密相关的主要有4个线程 CaptureSequencer,JpegProcessor,Camera3Device::RequestThread,FrameProcessorBase。在 Camera2client 对象初始化后,已经有3个线程已经 run 起来了,还有一个 RequestThread 线程是在 Camera3Device 初始化时创建的。下面我们就按照线程来分析。
3.2.1 FrameProcessor
3.2.1.1 Camera3Device.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp processCaptureResult():- 当
HALcallback回来数据时会触发mResultSignal.signal(),通知waitForNextFrame()方法条件发生变化。
- 当
void Camera3Device::processCaptureResult(const camera3_capture_result *result) {
ATRACE_CALL();
status_t res;
uint32_t frameNumber = result->frame_number;
if (result->result == NULL && result->num_output_buffers == 0) {
SET_ERR("No result data provided by HAL for frame %d",
frameNumber);
return;
}
...
// Return completed buffers to their streams with the timestamp
for (size_t i = 0; i < result->num_output_buffers; i++) {
Camera3Stream *stream =
Camera3Stream::cast(result->output_buffers[i].stream);
res = stream->returnBuffer(result->output_buffers[i], timestamp);
// Note: stream may be deallocated at this point, if this buffer was the
// last reference to it.
if (res != OK) {
SET_ERR("Can't return buffer %d for frame %d to its stream: "
" %s (%d)", i, frameNumber, strerror(-res), res);
}
}
// Finally, signal any waiters for new frames
if (result->result != NULL) {
mResultSignal.signal();
}
}
waitForNextFrame():- 当有数据返回时,此方法返回
OK,触发FrameProcessorBase::threadLoop()中的操作。
- 当有数据返回时,此方法返回
status_t Camera3Device::waitForNextFrame(nsecs_t timeout) {
status_t res;
Mutex::Autolock l(mOutputLock);
while (mResultQueue.empty()) {
res = mResultSignal.waitRelative(mOutputLock, timeout);
if (res == TIMED_OUT) {
return res;
} else if (res != OK) {
ALOGW("%s: Camera %d: No frame in %" PRId64 " ns: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, mId, timeout, strerror(-res), res);
return res;
}
}
return OK;
}
3.2.1.2 FrameProcessorBase.cpp
- 路径:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/FrameProcessorBase.cpp threadLoop():- 当
waitForNextFrame()返回OK时,会调用processNewFrames()。
- 当
bool FrameProcessorBase::threadLoop() {
status_t res;
sp<CameraDeviceBase> device;
{
device = mDevice.promote();
if (device == 0) return false;
}
res = device->waitForNextFrame(kWaitDuration);
if (res == OK) {
processNewFrames(device);
} else if (res != TIMED_OUT) {
ALOGE("FrameProcessorBase: Error waiting for new "
"frames: %s (%d)", strerror(-res), res);
}
return true;
}
processNewFrames():- 这里会调用
processSingleFrame()方法。
- 这里会调用
void FrameProcessorBase::processNewFrames(const sp<CameraDeviceBase> &device) {
status_t res;
ATRACE_CALL();
CaptureResult result;
//从Device对象中获取到result对象,即hal返回来的帧数据。
while ( (res = device->getNextResult(&result)) == OK) {
// TODO: instead of getting frame number from metadata, we should read
// this from result.mResultExtras when CameraDeviceBase interface is fixed.
camera_metadata_entry_t entry;
entry = result.mMetadata.find(ANDROID_REQUEST_FRAME_COUNT);
//此处省略一些错误检查代码,不影响分析代码。
if (!processSingleFrame(result, device)) {
break;
}
}
return;
}
processSingleFrame():- 这里会调用
processListeners()方法。
- 这里会调用
bool FrameProcessorBase::processSingleFrame(CaptureResult &result,
const sp<CameraDeviceBase> &device) {
ALOGV("%s: Camera %d: Process single frame (is empty? %d)",
__FUNCTION__, device->getId(), result.mMetadata.isEmpty());
return processListeners(result, device) == OK;
}
processListeners():- 这里会根据
HAL返回来的数据,查找到requestId,并根据requestId查找到当前帧的监听对象。找到后,就调用了onResultAvailable()方法。
- 这里会根据
status_t FrameProcessorBase::processListeners(const CaptureResult &result,
const sp<FrameProducer> &device) {
ATRACE_CALL();
camera_metadata_ro_entry_t entry;
bool isPartialResult =
result.mResultExtras.partialResultCount < mNumPartialResults;
entry = result.mMetadata.find(ANDROID_REQUEST_ID);
if (entry.count == 0) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %s: Error reading frame id", __FUNCTION__, device->getId().string());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
int32_t requestId = entry.data.i32[0];
List<sp<FilteredListener> > listeners;
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
List<RangeListener>::iterator item = mRangeListeners.begin();
// Don't deliver partial results to listeners that don't want them
while (item != mRangeListeners.end()) {
if (requestId >= item->minId && requestId < item->maxId &&
(!isPartialResult || item->sendPartials)) {
sp<FilteredListener> listener = item->listener.promote();
if (listener == 0) {
item = mRangeListeners.erase(item);
continue;
} else {
listeners.push_back(listener);
}
}
item++;
}
}
ALOGV("%s: Camera %s: Got %zu range listeners out of %zu", __FUNCTION__,
device->getId().string(), listeners.size(), mRangeListeners.size());
List<sp<FilteredListener> >::iterator item = listeners.begin();
for (; item != listeners.end(); item++) {
(*item)->onResultAvailable(result);
}
return OK;
}
3.2.1.3 CaptureSequencer.cpp
- 路径:
/frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/client2/CaptureSequencer.cpp onResultAvailable():
void CaptureSequencer::onResultAvailable(const CaptureResult &result) {
ATRACE_CALL();
ALOGV("%s: New result available.", __FUNCTION__);
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
mNewFrameId = result.mResultExtras.requestId;
mNewFrame = result.mMetadata;
if (!mNewFrameReceived) {
mNewFrameReceived = true;
mNewFrameSignal.signal();
}
}
3.2.2 JpegProcessor
3.2.2.1 JpegProcessor.cpp
- 路径:
/frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/client2/JpegCompressor.cpp onFrameAvailable():mCaptureAvailableSignal.signal()这里激活了mCaptureAvailableSignal条件。
void JpegProcessor::onFrameAvailable(const BufferItem& /*item*/) {
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
if (!mCaptureAvailable) {
mCaptureAvailable = true;
mCaptureAvailableSignal.signal();
}
}
threadLoop():- 处理线程一直在等待
mCaptureAvailableSignal条件可用,当满足时会调用processNewCapture()。
- 处理线程一直在等待
bool JpegProcessor::threadLoop() {
status_t res;
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
while (!mCaptureAvailable) {
//这里会等待mCaptureAvailableSignal条件100ms,
res = mCaptureAvailableSignal.waitRelative(mInputMutex,
kWaitDuration);
if (res == TIMED_OUT) return true;
}
mCaptureAvailable = false;
}
do {
res = processNewCapture();
} while (res == OK);
return true;
}
processNewCapture():sequencer->onCaptureAvailable()调用CaptureSequencer的onCaptureAvailable(),同时将buffer的时间戳以及buffer传进去。
status_t JpegProcessor::processNewCapture() {
ATRACE_CALL();
status_t res;
sp<Camera2Heap> captureHeap;
sp<MemoryBase> captureBuffer;
CpuConsumer::LockedBuffer imgBuffer;
//由于之前我们创建bufferQueue时,我们只允许有一个buffer,所以
//下面ACQUIRE buffer操作,获取到的肯定是jpeg图片buffer.
res = mCaptureConsumer->lockNextBuffer(&imgBuffer);//
//此处省略部分功能代码,不过不影响分析代码
//下面mCaptureHeap就是在更新jpeg流的时候创建的一个匿名共享内存,
// TODO: Optimize this to avoid memcopy
captureBuffer = new MemoryBase(mCaptureHeap, 0, jpegSize);
void* captureMemory = mCaptureHeap->getBase();
//下面将图片数据拷贝到匿名共享内存中
memcpy(captureMemory, imgBuffer.data, jpegSize);
//release buffer操作,将buffer归还给bufferQueue.
mCaptureConsumer->unlockBuffer(imgBuffer);
sp<CaptureSequencer> sequencer = mSequencer.promote();
if (sequencer != 0) {
sequencer->onCaptureAvailable(imgBuffer.timestamp, captureBuffer);
}
return OK;
}
3.2.2.2 CaptureSequencer.cpp
- 路径:
/frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api1/client2/CaptureSequencer.cpp onCaptureAvailable():- 获取当前帧事件戳。
- 保存当前帧
buffer。 - 设置
mNewCaptureReceived标志位为true。 - 激活
mNewCaptureSignal条件,拍照状态机一直会等待这个条件。
void CaptureSequencer::onCaptureAvailable(nsecs_t timestamp,
sp<MemoryBase> captureBuffer) {
ATRACE_CALL();
ALOGV("%s", __FUNCTION__);
Mutex::Autolock l(mInputMutex);
mCaptureTimestamp = timestamp;
mCaptureBuffer = captureBuffer;
if (!mNewCaptureReceived) {
mNewCaptureReceived = true;
mNewCaptureSignal.signal();
}
}
4 流程简图
4.1 HAL1 的流程
4.2 HAL3 的流程
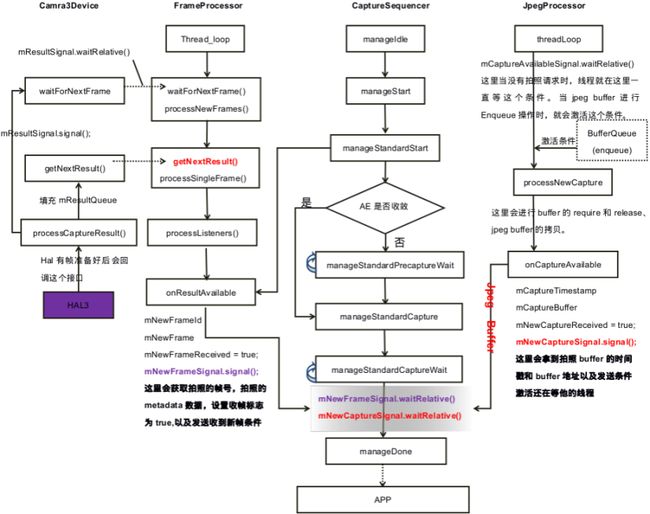
针对该图有下面几点注意的( 这里拍照状态机只针对是 STILL_TAKEPICTURE):
- 所有事件驱动源都是在
HAL3回帧动作激活的。当HAL3回帧后,会激活mResultSignal以及在onFrameAvailable激活mCaptureAvailableSignal条件。如果没有回帧,所以拍照线程都在阻塞等待状态。 STLL_TakePicture状态机在standardStart状态时,会注册一个帧监听对象给FrameProcessor线程,如图所示。- 在准备抓取拍照帧时,首先要判断 AE 是否收敛,如果没有收敛,要等待 AE 收敛才能进行图片捕获状态。
- 当进行图片捕获动作后,要阻塞等待拍照数据回传上来。如果等待超时会循环等待下去(100ms为一单位,等待3.5s应用就会报错)。
5 总结
在这篇文章中,我们从 Camera.takePicture() 方法着手,联系之前的 Open 流程,将整个 Camera 流程简单地梳理了一遍。不管是控制流还是数据流,都是要通过五大层次依次执行下一步的。控制流是将命令从顶层流向底层,而数据流则是将底层的数据流向顶层。如果要自定义一个对数据进行处理的 C++ 功能库,并将其加入相机中,我们可以通过对 HAL 层进行一些修改,将 RAW 图像流向我们的处理过程,再将处理后的 RAW 图像传回 HAL 层(需要在 HAL 层对 RAW 格式进行一些处理才能把图像上传),最后通过正常的回调流程把图像传到顶层应用中,就可以实现我们的自定义功能了。
