OpenCv 入门 -- 答题卡的数字识别
OpenCv 入门
OpenCv 入门 -- 答题卡的数字识别 @ Fu Xianjun. All Rights Reserved.文章目录
- OpenCv 入门
- 前言
- 一、导入库
- 二、透视变换、寻找轮廓
- 三、输出结果
- 四、结果展示
- 总结
前言
OpenCV是一个跨平台计算机视觉库,用C++语言编写,用于图像处理、分析。本文将讲解如何使用OpenCv对答题卡的数字识别。一、导入库
日常导包:
import cv2
import numpy as np
预处理:
def cv_show(name,img):
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
ANSWER_KEY = {0:1,1:4,2:0,3:3,4:1}
img = cv2.imread("test_01.png")
contours_Img = img.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#灰度图
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)#高斯(平滑处理)
edge = cv2.Canny(blur,75,200)#边缘检测
#轮廓检测
cnts,h = cv2.findContours(edge,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)#外边缘
cv2.drawContours(img,cnts,-1,(0,255,0),2)#绘制轮廓
cv_show("img",img)
二、透视变换、寻找轮廓
def cv_show(name,img):
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def order_points(pts):
rect = np.zeros((4,2),dtype="float32")
s = pts.sum(axis=1)
rect[0]=pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2]=pts[np.argmax(s)]
d = np.diff(pts,axis=1)
rect[1]=pts[np.argmin(d)]
rect[3]=pts[np.argmax(d)]
return rect
def four_point_transform(image,pts):
rect = order_points(pts)
(tl,tr,br,bl)=rect
widthA = np.sqrt((br[0]-bl[0])**2+(br[1]-bl[1])**2)
widthB = np.sqrt((tr[0]-tl[0])**2+(tr[1]-tl[1])**2)
maxWidth = max(int(widthA),int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt((tr[0]-br[0])**2+(tr[1]-br[1])**2)
heightB = np.sqrt((tl[0]-bl[0])**2+(tl[1]-bl[1])**2)
maxHeight = max(int(heightA),int(heightB))
print(rect)
dst = np.array([[0,0],[maxWidth-1,0],[maxWidth-1,maxHeight-1],[0,maxHeight-1]],dtype="float32")
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect,dst)
warp = cv2.warpPerspective(image,M(maxWidth,maxHeight))
return warp
def sort_contours(cnts, method="left-to-right"):
reverse = False
i = 0
if method == "right-to-left" or method == "bottom-to-top":
reverse = True
if method == "top-to-bottom" or method == "bottom-to-top":
i = 1
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts]
(cnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(cnts, boundingBoxes), key=lambda b: b[1][i], reverse=reverse))
return cnts, boundingBoxes
三、输出结果
ANSWER_KEY = {0:1,1:4,2:0,3:3,4:1}
image = cv2.imread("test_05.png")
contour_Img = image.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
edge = cv2.Canny(blur,75,200)
cnt = cv2.findContours(edge, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
cv2.drawContours(contour_Img, cnt, -1,(0,255,0),2)
dotCnt = None
if len(cnt)>0:
cnt = sorted(cnt, key = cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)
for c in cnt:
peri = cv2.arcLength(c,True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02*peri,True)
if len(approx)==4:
dotCnt=approx
warp = four_point_transform(gray, dotCnt.reshape(4,2))
thresh = cv2.threshold(warp,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV|cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
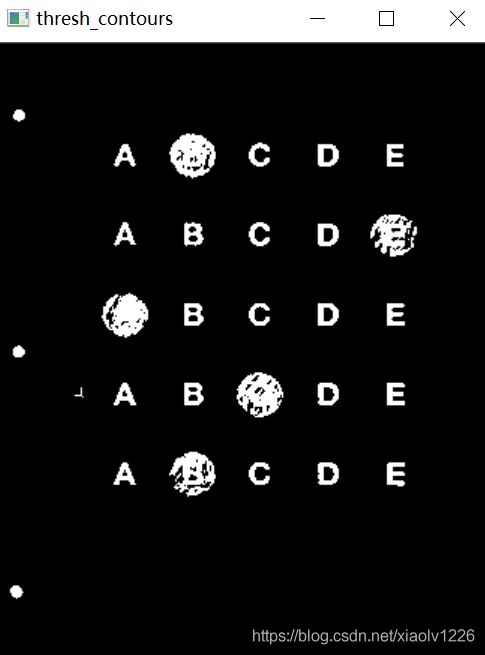
thresh_contours = thresh.copy()
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh_contours,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
cv2.drawContours(thresh_contours, cnts, -1,(0,255,255),2)
questionCnts = []
#遍历
for c in cnts:
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar = w/float(h)
if w>=20 and h >=20 and ar>0.9 and ar<1.1:
questionCnts.append(c)
questionCnts = sort_contours(questionCnts, method="top-to-bottom")[0]
final = cv2.cvtColor(warp,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
correct=0
for (q,i) in enumerate(np.arange(0,len(questionCnts),5)):
cnts = sort_contours(questionCnts[i:i+5])[0]
bubbled = None
for (j,c)in enumerate(cnts):
mask = np.zeros(thresh.shape,dtype="uint8")
cv2.drawContours(mask, [c], -1,255,-1)
mask = cv2.bitwise_and(thresh,thresh,mask=mask)
total = cv2.countNonZero(mask)
if bubbled is None or total >bubbled[0]:
bubbled = (total,j)
color = (0,0,255)
k = ANSWER_KEY[q]
if k==bubbled[1]:
color = (0,255,0)
correct+=1
cv2.drawContours(final, cnts[k], -1,color,2)
score = (correct/5.0)*100
cv2.putText(final,"Total:{:.2f}".format(score),(10,30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.9,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.imshow("final",final)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
四、结果展示
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了如何使用OpenCv对答题卡进行数字识别,及OpenCv的基础应用。