八数码难题(8 puzzle)深度优先和深度优先算法
1 搜索策略
搜索策略是指在搜索过程中如何选择扩展节点的次序问题。一般来说,搜索策略就是采用试探的方法。它有两种类型:一类是回溯搜索,另一类是图搜索策略。
2 盲目的图搜索策略
图搜索策略又可分为两种:一种称为盲目的图搜索策略,或称无信息图搜索策略;而另一种称为启发式搜索策略,又称为有信息的图搜索策略。最常用的两种无信息图搜索策略是宽度优先搜索和深度优先搜索。
2.1 宽度优先搜索
它是从根节点(起始节点)开始,按层进行搜索,也就是按层来扩展节点。所谓按层扩展,就是前一层的节点扩展完毕后才进行下一层节点的扩展,直到得到目标节点为止。
这种搜索方式的优点是,只要存在有任何解答的话,它能保证最终找到由起始节点到目标节点的最短路径的解,但它的缺点是往往搜索过程很长。
2.2 深度优先搜索
它是从根节点开始,首先扩展最新产生的节点,即沿着搜索树的深度发展下去,一直到没有后继结点处时再返回,换一条路径走下去。就是在搜索树的每一层始终先只扩展一个子节点,不断地向纵深前进直到不能再前进(到达叶子节点或受到深度限制)时,才从当前节点返回到上一级节点,沿另一方向又继续前进。这种方法的搜索树是从树根开始一枝一枝逐渐形成的。
由于一个有解的问题树可能含有无穷分枝,深度优先搜索如果误入无穷分枝(即深度无限),则不可能找到目标节点。为了避免这种情况的出现,在实施这一方法时,定出一个深度界限,在搜索达到这一深度界限而且尚未找到目标时,即返回重找,所以,深度优先搜索策略是不完备的。另外,应用此策略得到的解不一定是最佳解(最短路径)。
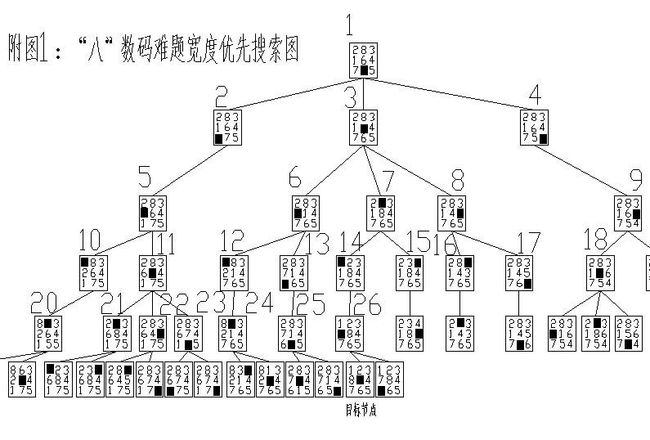
3 “八”数码难题的宽度优先搜索与深度优先搜索
3.1“八”数码难题的宽度优先搜索
步骤如下:
1、判断初始节点是否为目标节点,若初始节点是目标节点则搜索过程结束;若不是则转到第2步;
2、由初始节点向第1层扩展,得到3个节点:2、3、4;得到一个节点即判断该节点是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若2、3、4节点均不是目标节点则转到第3步;
3、从第1层的第1个节点向第2层扩展,得到节点5;从第1层的第2个节点向第2层扩展,得到3个节点:6、7、8;从第1层的第3个节点向第2层扩展得到节点9;得到一个节点即判断该节点是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若6、7、8、9节点均不是目标节点则转到第4步;
4、按照上述方法对下一层的节点进行扩展,搜索目标节点;直至搜索到目标节点为止。
5、搜索过程见附图1所示。
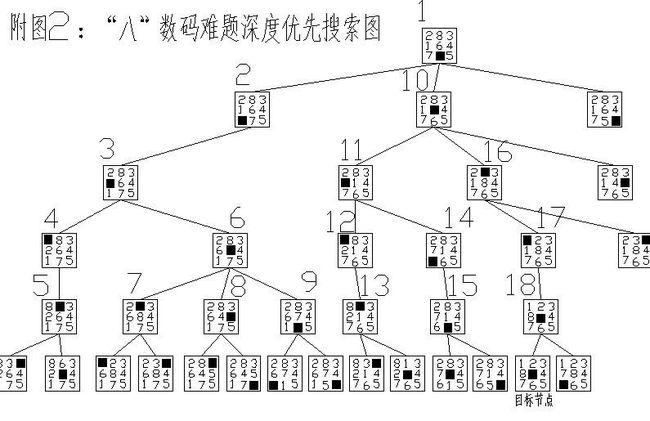
3.2 “八”数码难题的深度优先搜索
步骤如下:
1、设置深度界限,假设为5;
2、判断初始节点是否为目标节点,若初始节点是目标节点则搜索过程结束;若不是则转到第2步;
3、由初始节点向第1层扩展,得到节点2,判断节点2是否为目标节点;若是则搜索过程结束;若不是,则将节点2向第2层扩展,得到节点3;
4、判断节点3是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若不是则将节点3向第3层扩展,得到节点4;
5、判断节点4是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若不是则将节点4向第4层扩展,得到节点5;
6、判断节点5是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若不是则结束此轮搜索,返回到第2层,将节点3向第3层扩展得到节点6;
7、判断节点6是否为目标节点,若是则搜索过程结束;若不是则将节点6向第4层扩展,得到节点7;
8、判断节点7是否为目标节点,若是则结束搜索过程;若不是则将节点6向第4层扩展得到节点8;
9、依次类推,知道得到目标节点为止。
10、搜索过程见附图2所示。
3.3 搜索效率比较
不同搜索策略搜索效率的衡量指标:
1、外显率(P):反映搜索工程中,从初始节点向目标节点进行搜索的区域的宽度
P=L/T;P∈(0,1]
L:从初始节点到达目标的路径长度;
T:整个过程中生成的节点总数(不包括初始节点);
2、有效分支分数(B):表示每个有效节点平均生成的子节点数目
T=B+B2+…+BL,B≥1
当B=1时,T=1,此时搜索效率最高
3.3.1 采用宽度优先搜索时的搜索效率
L=5,T=26,则P=L/T=5/26=0.192,B=1.613;
3.3.1 采用宽度优先搜索时的搜索效率
L=5,T=18,则P=L/T=5/18=0.278,B=1.464;
由以上计算可以看出,深度优先搜索的效率明显高于宽度优先搜索。
3.4上述两种搜索策略的比较
在宽度优先搜索过程中,扩展到第26个节点时找到了目标节点;而在深度优先搜索过程中,扩展到第18个节点时得到了目标节点。
在宽度优先搜索过程中,需要遍历目标节点所在层之前每层的所有节点,即需要遍历所有的分支。而深度优先搜索过程中,则不需要遍历这么多的节点。所以,在“八”数码难题的求解过程中,深度优先搜索的效率明显比宽度优先搜索的效率要高。
一般情况下,深度优先适合深度大的树,不适合广度大的树,广度优先则正好相反。所谓深度大的树就是指起始节点到目标节点的中间节点多的树(可以理解成问题有很多中间解,这些解都可以认为是部分正确的,但要得到完全正确的结果——目标节点,就必须先依次求出这些中间解)。所谓广度大的树就是指起始节点到目标节点的可能节点很多的树(可以理解成问题有很多可能解,这些解要么正确,要么错误。要得到完全正确的结果——目标节点,就必须依次判断这些可能解是否正确)。
多数情况下,深度优先搜索的效率要高于宽度优先搜索。但某些时候,对于这两种搜索策略的优劣(或效率)还需要针对不同的问题进行具体分析比较。
深度优先C#代码:
public class DFS
{
static public bool DFSOn = false; //initial flag. if set initializes the array variables.
static public bool solving = false; //solving flag set whilst the algorithm is running.
static private bool trackBack = false; //trackBack flag set if the puzzle get stuck to track back moves
private static Stack stackDFS = new Stack(); //FIFO structure required for DFS
private static Stack stackMoves = new Stack(); //Stack stores everymove made. used for tracking back
private static ArrayList xVisitedList = new ArrayList(); //list to store all the states that have been expanded
private static ArrayList yVisitedList = new ArrayList();
public static Double[][] xTempPuzzle = new Double[3][]; //actual x & y 2-d arrays strore the pos of squares
public static Double[][] yTempPuzzle = new Double[3][];
//gets the number of moves made towards the goal state.
static public int getNumberOfMovesMade()
{
return stackMoves.Count;
}
//initialzes the 2-d arrays xTempPuzzle and yTempPuzzle and sets them to the current value of the
//Puzzle displayed on the screen.
static public void initializeArray()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
xTempPuzzle[i] = new Double[3];
yTempPuzzle[i] = new Double[3];
}
xTempPuzzle[0][0] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[0][0];
xTempPuzzle[0][1] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[0][1];
xTempPuzzle[0][2] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[0][2];
xTempPuzzle[1][0] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[1][0];
xTempPuzzle[1][1] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[1][1];
xTempPuzzle[1][2] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[1][2];
xTempPuzzle[2][0] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[2][0];
xTempPuzzle[2][1] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[2][1];
xTempPuzzle[2][2] = PuzzleData.xPuzzle[2][2];
yTempPuzzle[0][0] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[0][0];
yTempPuzzle[0][1] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[0][1];
yTempPuzzle[0][2] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[0][2];
yTempPuzzle[1][0] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[1][0];
yTempPuzzle[1][1] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[1][1];
yTempPuzzle[1][2] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[1][2];
yTempPuzzle[2][0] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[2][0];
yTempPuzzle[2][1] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[2][1];
yTempPuzzle[2][2] = PuzzleData.yPuzzle[2][2];
}
//resets all the variables. called when the reset button is clicked or the algorithm has finished
static public void resetAll()
{
xVisitedList.Clear();
yVisitedList.Clear();
stackDFS.Clear();
stackMoves.Clear();
DFSOn = true;
solving = false;
}
//the entry point method of this class. Get's called everytime a next move using DFS is required.
static public bool solvePuzzle()
{
if (DFSOn) { initializeArray(); DFSOn = false; }
if (PuzzleData.isFinalState(DFS.xTempPuzzle, DFS.yTempPuzzle)) { return true; }
addNextMove();
movePuzzle();
return false;
}
//Each square of the shuffle can have 3 values each for x and y position. Those values
//are 0, 100 & 200. This function checks if a left, up, down or right move is possible.
//It does so by looking at the current x and y position of the blank square of the puzzle.
static private bool isValidMove(int direction)
{
if (direction == 0) //check if sliding left is possible
{
if (DFS.xTempPuzzle[2][2] >= 100) { return true; }
}
else if (direction == 1) //check if sliding up is possible
{
if (DFS.yTempPuzzle[2][2] >= 100) { return true; }
}
else if (direction == 2)//check if sliding right is possible
{
if (DFS.xTempPuzzle[2][2] < 200) { return true; }
}
else if (direction == 3) //check if sliding down is possible
{
if (DFS.yTempPuzzle[2][2] < 200) { return true; }
}
return false;
}
//Checks if the current state has been expanded before or not contrary to the name
//it doesn't check all the visited states but expanded states.
static private bool isVisitedState()
{
for (int cnt = xVisitedList.Count - 1; cnt > -1; cnt--)
{
int sameElementCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if ((((Double[][])xVisitedList[cnt])[i][j] == xTempPuzzle[i][j]) &&
((Double[][])yVisitedList[cnt])[i][j] == yTempPuzzle[i][j])
{
sameElementCnt++;
}
}
}
if (sameElementCnt == 9) { return true; }
}
return false;
}
//The method below checks for a valid move and then checks if the state has been visited
//if not the it adds that direction to the stackDFS variable.
static private void addNextMove()
{
bool moveAdded = false;
if (isValidMove(0))
{
PuzzleData.moveLeft(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
if (isVisitedState())
{
PuzzleData.moveRight(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else
{
PuzzleData.moveRight(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
stackDFS.Push(0);
moveAdded = true;
}
}
if (isValidMove(1))
{
PuzzleData.moveUp(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
if (isVisitedState())
{
PuzzleData.moveDown(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else
{
PuzzleData.moveDown(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
stackDFS.Push(1);
moveAdded = true;
}
}
if (isValidMove(2))
{
PuzzleData.moveRight(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
if (isVisitedState())
{
PuzzleData.moveLeft(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else
{
PuzzleData.moveLeft(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
stackDFS.Push(2);
moveAdded = true;
}
}
if (isValidMove(3))
{
PuzzleData.moveDown(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
if (isVisitedState())
{
PuzzleData.moveUp(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else
{
PuzzleData.moveUp(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
stackDFS.Push(3);
moveAdded = true;
}
}
//if no move could be found happens when the current state cannot get out because all the
//neighbouring states have already been expanded. It adds the opposite of the last move made
//which makes the puzzle go back one step.
if (!moveAdded)
{
int lastMove = (int)stackMoves.Pop();
if (lastMove == 0) { lastMove = 2; }
else if (lastMove == 1) { lastMove = 3; }
else if (lastMove == 2) { lastMove = 0; }
else if (lastMove == 3) { lastMove = 1; }
stackDFS.Push(lastMove);
trackBack = true; //trackBack flag is set for the movePuzzle method. see there for more explanation.
}
}
//Method that updates the puzzle with the direction popped of the DFS stack. Then adds the new puzzle state
//to the visited list.
static private void movePuzzle()
{
int direction = (int)stackDFS.Pop();
if (direction == 0) //Move Left
{
PuzzleData.moveLeft(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else if (direction == 1) //Move Up
{
PuzzleData.moveUp(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else if (direction == 2) //Move Right
{
PuzzleData.moveRight(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
else if (direction == 3) //Move Down
{
PuzzleData.moveDown(xTempPuzzle, yTempPuzzle);
}
//if the trackBack flag is set as there were no moves, it doesn't add the move to the movesList stack.
if (!trackBack) { addMove(direction); }
addVisitedList();
trackBack = false;
}
//adds the cuurent state the puzzle is in to the visitedList.
static private void addVisitedList()
{
Double[][] xTemp = new Double[3][];
xTemp[0] = new Double[3];
xTemp[1] = new Double[3];
xTemp[2] = new Double[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
xTemp[i][j] = xTempPuzzle[i][j];
}
}
xVisitedList.Add(xTemp);
Double[][] yTemp = new Double[3][];
yTemp[0] = new Double[3];
yTemp[1] = new Double[3];
yTemp[2] = new Double[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
yTemp[i][j] = yTempPuzzle[i][j];
}
}
yVisitedList.Add(yTemp);
}
//adds the previous move (while NOT trackingBack) to the visited list.
static private void addMove(int direction)
{
stackMoves.Push(direction);
}
}