(Fabric 学习三)Fabric2.2 多机部署 使用fabcar链码
注:参考博客:
Hyperledger Fabric多机及explorer搭建_routiao的博客-CSDN博客
一、准备条件
硬件环境:Ubuntu虚拟机两台,一共两台主机:主机1的IP:192.168.235.147;主机2的IP: 192.168.235.146
部署方案:1个orderer、2个组织、每个组织1个普通节点,通过静态IP的方式实现Hyperledger Fabric多机部署;orderer和org1放在192.168.235.147;org2放在192.168.235.146
192.168.235.147 orderer.example.com
192.168.235.147 peer0.org1.example.com
192.168.235.146 peer0.org2.example.com
二、创建实例演示的文件
我将文件放在fabric的fabric-samples文件夹中。
mkdir /home/xzd/go/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/scripts/fabric-samples/multipeer三、编写生成证书文件
生成证书文件的配置文件:crypto-config.yaml
当我们在./multipeer文件夹下面,我们可以选择touch一个crypto-config.yaml,但是其实官方可以给我们模板文件,将模板文件复制过来进行修改即可:
复制模板文件命令:
cryptogen showtemplate > crypto-config.yaml
如果这里出现了问题:cryptogen工具不存在啥的,就要配置一下外部的环境变量:
export PATH=${PWD}/../bin:$PATH进入文件中进行修改:
vim crypto-config.yaml编写配置文件
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "OrdererOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing orderer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OrdererOrgs:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Orderer
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: Orderer
Domain: example.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Specs" - See PeerOrgs below for complete description
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Specs:
- Hostname: orderer
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "PeerOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing peer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PeerOrgs:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Org1
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: Org1
Domain: org1.example.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "CA"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Uncomment this section to enable the explicit definition of the CA for this
# organization. This entry is a Spec. See "Specs" section below for details.
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# CA:
# Hostname: ca # implicitly ca.org1.example.com
# Country: US
# Province: California
# Locality: San Francisco
# OrganizationalUnit: Hyperledger Fabric
# StreetAddress: address for org # default nil
# PostalCode: postalCode for org # default nil
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Specs"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Uncomment this section to enable the explicit definition of hosts in your
# configuration. Most users will want to use Template, below
#
# Specs is an array of Spec entries. Each Spec entry consists of two fields:
# - Hostname: (Required) The desired hostname, sans the domain.
# - CommonName: (Optional) Specifies the template or explicit override for
# the CN. By default, this is the template:
#
# "{{.Hostname}}.{{.Domain}}"
#
# which obtains its values from the Spec.Hostname and
# Org.Domain, respectively.
# - SANS: (Optional) Specifies one or more Subject Alternative Names
# to be set in the resulting x509. Accepts template
# variables {{.Hostname}}, {{.Domain}}, {{.CommonName}}. IP
# addresses provided here will be properly recognized. Other
# values will be taken as DNS names.
# NOTE: Two implicit entries are created for you:
# - {{ .CommonName }}
# - {{ .Hostname }}
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Specs:
# - Hostname: foo # implicitly "foo.org1.example.com"
# CommonName: foo27.org5.example.com # overrides Hostname-based FQDN set above
# SANS:
# - "bar.{{.Domain}}"
# - "altfoo.{{.Domain}}"
# - "{{.Hostname}}.org6.net"
# - 172.16.10.31
# - Hostname: bar
# - Hostname: baz
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Template"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Allows for the definition of 1 or more hosts that are created sequentially
# from a template. By default, this looks like "peer%d" from 0 to Count-1.
# You may override the number of nodes (Count), the starting index (Start)
# or the template used to construct the name (Hostname).
#
# Note: Template and Specs are not mutually exclusive. You may define both
# sections and the aggregate nodes will be created for you. Take care with
# name collisions
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Template:
Count: 1
# Start: 5
# Hostname: {{.Prefix}}{{.Index}} # default
# SANS:
# - "{{.Hostname}}.alt.{{.Domain}}"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Users"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Count: The number of user accounts _in addition_ to Admin
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Users:
Count: 1
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Org2: See "Org1" for full specification
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: Org2
Domain: org2.example.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
Template:
Count: 1
Users:
Count: 1通过配置文件生成证书文件
cryptogen generate --config=crypto-config.yaml
生成文件可以复制到另外一个虚拟机的同等位置中,也可以通过scp命令将证书文件复制到其他虚拟机中。
四、编写生成通道文件
生成通道文件的配置文件:configtx.yaml
当我们在./multipeer文件夹下面,新建configtx.yaml,可以参考官方示例的该文件:
编写配置文件
# Copyright IBM Corp. All Rights Reserved.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
#
---
################################################################################
#
# Section: Organizations
#
# - This section defines the different organizational identities which will
# be referenced later in the configuration.
#
################################################################################
Organizations:
# SampleOrg defines an MSP using the sampleconfig. It should never be used
# in production but may be used as a template for other definitions
- &OrdererOrg
# DefaultOrg defines the organization which is used in the sampleconfig
# of the fabric.git development environment
Name: OrdererOrg
# ID to load the MSP definition as
ID: OrdererMSP
# MSPDir is the filesystem path which contains the MSP configuration
MSPDir: ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/msp
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For organization policies, their canonical path is usually
# /Channel///
Policies:
Readers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.member')"
Writers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.member')"
Admins:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.admin')"
OrdererEndpoints:
- orderer.example.com:7050
- &Org1
# DefaultOrg defines the organization which is used in the sampleconfig
# of the fabric.git development environment
Name: Org1MSP
# ID to load the MSP definition as
ID: Org1MSP
MSPDir: ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/msp
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For organization policies, their canonical path is usually
# /Channel///
Policies:
Readers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin', 'Org1MSP.peer', 'Org1MSP.client')"
Writers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin', 'Org1MSP.client')"
Admins:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin')"
Endorsement:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.peer')"
AnchorPeers:
- Host: peer0.org1.example.com
Port: 7051
- &Org2
# DefaultOrg defines the organization which is used in the sampleconfig
# of the fabric.git development environment
Name: Org2MSP
# ID to load the MSP definition as
ID: Org2MSP
MSPDir: ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/msp
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For organization policies, their canonical path is usually
# /Channel///
Policies:
Readers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org2MSP.admin', 'Org2MSP.peer', 'Org2MSP.client')"
Writers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org2MSP.admin', 'Org2MSP.client')"
Admins:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org2MSP.admin')"
Endorsement:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org2MSP.peer')"
AnchorPeers:
- Host: peer0.org2.example.com
Port: 9051
################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Capabilities
#
# - This section defines the capabilities of fabric network. This is a new
# concept as of v1.1.0 and should not be utilized in mixed networks with
# v1.0.x peers and orderers. Capabilities define features which must be
# present in a fabric binary for that binary to safely participate in the
# fabric network. For instance, if a new MSP type is added, newer binaries
# might recognize and validate the signatures from this type, while older
# binaries without this support would be unable to validate those
# transactions. This could lead to different versions of the fabric binaries
# having different world states. Instead, defining a capability for a channel
# informs those binaries without this capability that they must cease
# processing transactions until they have been upgraded. For v1.0.x if any
# capabilities are defined (including a map with all capabilities turned off)
# then the v1.0.x peer will deliberately crash.
#
################################################################################
Capabilities:
# Channel capabilities apply to both the orderers and the peers and must be
# supported by both.
# Set the value of the capability to true to require it.
Channel: &ChannelCapabilities
# V2_0 capability ensures that orderers and peers behave according
# to v2.0 channel capabilities. Orderers and peers from
# prior releases would behave in an incompatible way, and are therefore
# not able to participate in channels at v2.0 capability.
# Prior to enabling V2.0 channel capabilities, ensure that all
# orderers and peers on a channel are at v2.0.0 or later.
V2_0: true
# Orderer capabilities apply only to the orderers, and may be safely
# used with prior release peers.
# Set the value of the capability to true to require it.
Orderer: &OrdererCapabilities
# V2_0 orderer capability ensures that orderers behave according
# to v2.0 orderer capabilities. Orderers from
# prior releases would behave in an incompatible way, and are therefore
# not able to participate in channels at v2.0 orderer capability.
# Prior to enabling V2.0 orderer capabilities, ensure that all
# orderers on channel are at v2.0.0 or later.
V2_0: true
# Application capabilities apply only to the peer network, and may be safely
# used with prior release orderers.
# Set the value of the capability to true to require it.
Application: &ApplicationCapabilities
# V2_0 application capability ensures that peers behave according
# to v2.0 application capabilities. Peers from
# prior releases would behave in an incompatible way, and are therefore
# not able to participate in channels at v2.0 application capability.
# Prior to enabling V2.0 application capabilities, ensure that all
# peers on channel are at v2.0.0 or later.
V2_0: true
################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Application
#
# - This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for application related parameters
#
################################################################################
Application: &ApplicationDefaults
# Organizations is the list of orgs which are defined as participants on
# the application side of the network
Organizations:
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Application policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/Application/
Policies:
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins"
LifecycleEndorsement:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Endorsement"
Endorsement:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Endorsement"
Capabilities:
<<: *ApplicationCapabilities
################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Orderer
#
# - This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for orderer related parameters
#
################################################################################
Orderer: &OrdererDefaults
# Orderer Type: The orderer implementation to start
OrdererType: etcdraft
# Addresses used to be the list of orderer addresses that clients and peers
# could connect to. However, this does not allow clients to associate orderer
# addresses and orderer organizations which can be useful for things such
# as TLS validation. The preferred way to specify orderer addresses is now
# to include the OrdererEndpoints item in your org definition
Addresses:
- orderer.example.com:7050
EtcdRaft:
Consenters:
- Host: orderer.example.com
Port: 7050
ClientTLSCert: ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/tls/server.crt
ServerTLSCert: ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/tls/server.crt
# Batch Timeout: The amount of time to wait before creating a batch
BatchTimeout: 2s
# Batch Size: Controls the number of messages batched into a block
BatchSize:
# Max Message Count: The maximum number of messages to permit in a batch
MaxMessageCount: 10
# Absolute Max Bytes: The absolute maximum number of bytes allowed for
# the serialized messages in a batch.
AbsoluteMaxBytes: 99 MB
# Preferred Max Bytes: The preferred maximum number of bytes allowed for
# the serialized messages in a batch. A message larger than the preferred
# max bytes will result in a batch larger than preferred max bytes.
PreferredMaxBytes: 512 KB
# Organizations is the list of orgs which are defined as participants on
# the orderer side of the network
Organizations:
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Orderer policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/Orderer/
Policies:
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins"
# BlockValidation specifies what signatures must be included in the block
# from the orderer for the peer to validate it.
BlockValidation:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
################################################################################
#
# CHANNEL
#
# This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for channel related parameters.
#
################################################################################
Channel: &ChannelDefaults
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Channel policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/
Policies:
# Who may invoke the 'Deliver' API
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
# Who may invoke the 'Broadcast' API
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
# By default, who may modify elements at this config level
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins"
# Capabilities describes the channel level capabilities, see the
# dedicated Capabilities section elsewhere in this file for a full
# description
Capabilities:
<<: *ChannelCapabilities
################################################################################
#
# Profile
#
# - Different configuration profiles may be encoded here to be specified
# as parameters to the configtxgen tool
#
################################################################################
Profiles:
TwoOrgsOrdererGenesis:
<<: *ChannelDefaults
Orderer:
<<: *OrdererDefaults
Organizations:
- *OrdererOrg
Capabilities:
<<: *OrdererCapabilities
Consortiums:
SampleConsortium:
Organizations:
- *Org1
- *Org2
TwoOrgsChannel:
Consortium: SampleConsortium
<<: *ChannelDefaults
Application:
<<: *ApplicationDefaults
Organizations:
- *Org1
- *Org2
Capabilities:
<<: *ApplicationCapabilities
生成创世块文件和通道文件
下面这四句话分别创建:genesis.block文件 channel.tx文件 以及两个锚节点Org1MSPanchors.tx 和Org2MSPanchors.tx,这些文件全部都保存在channel-artifacts文件夹中
configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsOrdererGenesis -channelID fabric-channel -outputBlock ./channel-artifacts/genesis.block
configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputCreateChannelTx ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx -channelID mychannel
configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputAnchorPeersUpdate ./channel-artifacts/Org1MSPanchors.tx -channelID mychannel -asOrg Org1MSP
configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputAnchorPeersUpdate ./channel-artifacts/Org2MSPanchors.tx -channelID mychannel -asOrg Org2MSP
将channel-artifacts文件夹复制到另外一虚拟机上,这样两台机子都有相同的创始块文件和通道文件了。
五、编写docker-compose文件
该文件是用来启动docker容器。
针对不同的节点,我们在./multipeer文件夹下面,需要编写三个不同的docker-compose配置文件
分别是orderer.yaml ,org1.yaml ,org2.yaml
其中orderer.yaml ,org1.yaml是放在192.168.235.147主机上
而org2.yaml是放在192.168.235.146主机上
编写orderer.yaml文件 在主机1上
注意:这里的extra_hosts中IP地址需要修改,一定要改成你的网络环境,其他地方可以不用动!!!!!!
version: '2'
services:
orderer.example.com:
container_name: orderer.example.com
image: hyperledger/fabric-orderer:latest
environment:
- FABRIC_LOGGING_SPEC=INFO
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LISTENPORT=7050
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISMETHOD=file
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISFILE=/var/hyperledger/orderer/orderer.genesis.block
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPID=OrdererMSP
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPDIR=/var/hyperledger/orderer/msp
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_ENABLED=true
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_PRIVATEKEY=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.key
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_CERTIFICATE=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.crt
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_ROOTCAS=[/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/ca.crt]
- ORDERER_KAFKA_TOPIC_REPLICATIONFACTOR=1
- ORDERER_KAFKA_VERBOSE=true
- ORDERER_GENERAL_CLUSTER_CLIENTCERTIFICATE=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.crt
- ORDERER_GENERAL_CLUSTER_CLIENTPRIVATEKEY=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.key
- ORDERER_GENERAL_CLUSTER_ROOTCAS=[/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/ca.crt]
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
command: orderer
volumes:
- ./channel-artifacts/genesis.block:/var/hyperledger/orderer/orderer.genesis.block
- ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp:/var/hyperledger/orderer/msp
- ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/tls/:/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls
ports:
- 7050:7050
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.235.146"
编写org1.yaml文件 在主机1上
这个也要修改IP地址!!!!
version: '2'
services:
couchdb0.org1.example.com:
container_name: couchdb0.org1.example.com
image: couchdb:3.1
environment:
- COUCHDB_USER=admin
- COUCHDB_PASSWORD=adminpw
ports:
- 5984:5984
peer0.org1.example.com:
container_name: peer0.org1.example.com
image: hyperledger/fabric-peer:latest
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer0.org1.example.com
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0:7051
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODEADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7052
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODELISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0:7052
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_BOOTSTRAP=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_EXTERNALENDPOINT=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- FABRIC_LOGGING_SPEC=INFO
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_USELEADERELECTION=true
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_ORGLEADER=false
- CORE_PEER_PROFILE_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/ca.crt
- CORE_CHAINCODE_EXECUTETIMEOUT=300s
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_STATEDATABASE=CouchDB
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_COUCHDBADDRESS=couchdb0.org1.example.com:5984
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_USERNAME=admin
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_PASSWORD=adminpw
depends_on:
- couchdb0.org1.example.com
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
command: peer node start
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/msp:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/msp
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls
ports:
- 7051:7051
- 7052:7052
- 7053:7053
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.235.146"
cli:
container_name: cli
image: hyperledger/fabric-tools:latest
tty: true
stdin_open: true
environment:
- GOPATH=/opt/gopath
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- FABRIC_LOGGING_SPEC=INFO
- CORE_PEER_ID=cli
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt
- CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
command: /bin/bash
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./chaincode/go/:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go
- ./crypto-config:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/
- ./channel-artifacts:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/channel-artifacts
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.235.146"
编写org1.yaml文件 在主机2上
version: '2'
services:
couchdb0.org2.example.com:
container_name: couchdb0.org2.example.com
image: couchdb:3.1
environment:
- COUCHDB_USER=admin
- COUCHDB_PASSWORD=adminpw
ports:
- 5984:5984
peer0.org2.example.com:
container_name: peer0.org2.example.com
image: hyperledger/fabric-peer:latest
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer0.org2.example.com
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0:7051
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODEADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7052
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODELISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0:7052
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_BOOTSTRAP=peer0.org2.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_EXTERNALENDPOINT=peer0.org2.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org2MSP
- FABRIC_LOGGING_SPEC=INFO
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_USELEADERELECTION=true
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_ORGLEADER=false
- CORE_PEER_PROFILE_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/ca.crt
- CORE_CHAINCODE_EXECUTETIMEOUT=300s
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_STATEDATABASE=CouchDB
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_COUCHDBADDRESS=couchdb0.org2.example.com:5984
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_USERNAME=admin
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_COUCHDBCONFIG_PASSWORD=adminpw
depends_on:
- couchdb0.org2.example.com
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
command: peer node start
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/msp:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/msp
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls
ports:
- 7051:7051
- 7052:7052
- 7053:7053
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.235.146"
cli:
container_name: cli
image: hyperledger/fabric-tools:latest
tty: true
stdin_open: true
environment:
- GOPATH=/opt/gopath
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- FABRIC_LOGGING_SPEC=INFO
- CORE_PEER_ID=cli
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org2MSP
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
- CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
command: /bin/bash
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./chaincode/go/:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go
- ./crypto-config:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/
- ./channel-artifacts:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/channel-artifacts
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.235.147"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.235.146"所有的docker-compose配置文件都已经编写完毕!
六、启动服务
当我们在./multipeer文件夹下面需要打开容器:
在主机1中后台打开docker容器命令:
docker-compose -f orderer.yaml up -d
docker-compose -f org1.yaml up -d在主机2中后台打开docker容器命令:
docker-compose -f org2.yaml up -d打开后看效果
主机一:
主机二:
注:这里给一个将容器全部删除的办法,如果容器混乱 可以删除重来!!
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)七、进行通道操作
创建通道
在org1主机1上开始进行创建通道操作。
首先进入容器cli:
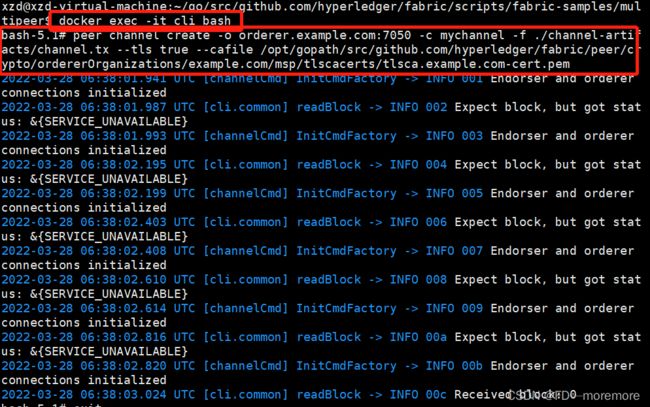
docker exec -it cli bash
创建一个通道,通道名字位mychannel
peer channel create -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem
效果:
说明通道创建成功,而通道文件mychannel.block的位置是在/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer中
我们需要将他拿出来,放到另外一个主机(也就是主机2)的容器的这个位置中。
首先现将这个mychannel.block文件从容器中拿出来放到宿主机(也就是主机1)上
我们先exit离开cli,然后在宿主机上打命令:(主机1)
docker cp cli:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/mychannel.block ./
然后我们就可以在本地找到这个mychannel.block文件(主机1)
将它复制到主机2中
然后在主机2中复制到容器cli中去(主机2中操作):
docker cp mychannel.block cli:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/
完成后主机2的容器cli中也有了相同的mychannel.block文件
加入通道
刚才只是创建了通道,但是并没有将节点加入到通道中,于是接下来开始加入通道操作。
使用命令将两个不同组织的peer0加入到同道中(org1主机1和org2主机2都进行操作)
docker exec -it cli bash
peer channel join -b mychannel.block
可以看见确实该peer节点已经加入到mychannel通道中了!
更新锚节点
org1
peer channel update -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/Org1MSPanchors.tx --tls --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem
org2
peer channel update -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/Org2MSPanchors.tx --tls --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem
八、安装并调用智能合约
我们随便找一个链码,在这里我使用的链码是fabric-samples/chaincode/fabcar/go中的链码
将他们复制到…/hyperledger/fabric/scripts/fabric-samples/multipeer/chaincode/go/fabcar文件夹
之后我们进入cli容器下进行进行配置:
docker exec -it cli bash
cd /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go/fabcar使用以下命令设置go语言依赖包
go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
go mod vendor
打包链码
配置好go语言依赖包后,我们可以开始打包链码
peer lifecycle chaincode package fabcar.tar.gz --path github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go/fabcar/ --label fabcar_1但是会出现问题:
报错:
Error: error getting chaincode bytes: ‘go list’ failed with: cannot find module providing package github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go: import lookup disabled by -mod=readonly
解决办法:
go env -w GO111MODULE=auto再打包一次,可以发现成功了!!
然后再通过之前将mychannel.block放到另外一台机子的方式一样,将fabcar.tar.gz文件放到主机2的容器中去。
先把打包好的链码从容器中拿出来
docker cp cli:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-cluster/chaincode/go/fabcar.tar.gz ./然后放到另外一台主机的multipeer/chaincode/go下
安装链码
使用以下命令分别在两个组织的虚拟机上安装链码(Org1和Org2的虚拟机中都要进行以下操作)
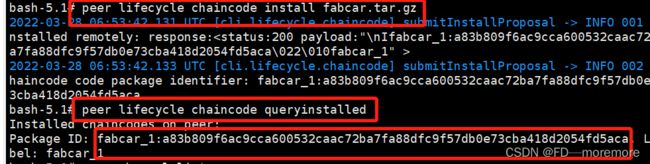
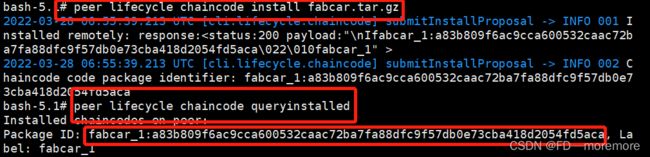
peer lifecycle chaincode install fabcar.tar.gz
使用以下命令分别在两个组织的虚拟机上安装链码(Org1和Org2的虚拟机中都要进行以下操作)。
peer lifecycle chaincode queryinstalled
批准链码
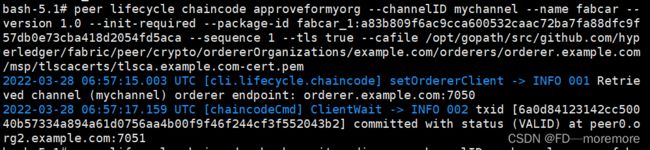
使用以下命令批准链码(Org1和Org2的虚拟机中都要进行以下操作,其中链码的ID要根据上面查询的结果替换到下面的命令中)。
peer lifecycle chaincode approveformyorg --channelID mychannel --name fabcar --version 1.0 --init-required --package-id fabcar_1:a83b809f6ac9cca600532caac72ba7fa88dfc9f57db0e73cba418d2054fd5aca --sequence 1 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem使用以下命令查看链码是否就绪(Org1和Org2的虚拟机中都要进行以下操作)
peer lifecycle chaincode checkcommitreadiness --channelID mychannel --name fabcar --version 1.0 --init-required --sequence 1 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem --output json提交链码
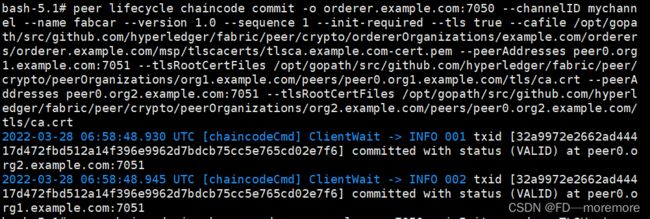
org1或org2 提交一次即可
peer lifecycle chaincode commit -o orderer.example.com:7050 --channelID mychannel --name fabcar --version 1.0 --sequence 1 --init-required --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem --peerAddresses peer0.org1.example.com:7051 --tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt --peerAddresses peer0.org2.example.com:7051 --tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
初始化链码
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.example.com:7050 --isInit --ordererTLSHostnameOverride orderer.example.com --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem -C mychannel -n fabcar --peerAddresses peer0.org1.example.com:7051 --tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt --peerAddresses peer0.org2.example.com:7051 --tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt -c '{"function":"initLedger","Args":[]}'调用查询方法
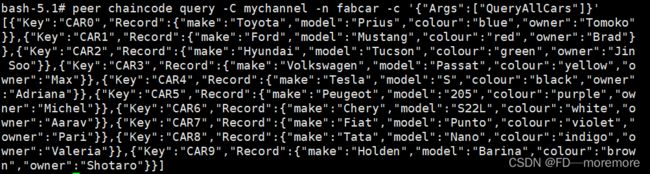
若搭建成功,初始化在org1完成 那么就可以org2中查询到结果。
peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n fabcar -c '{"Args":["QueryAllCars"]}'
自此,我们的多机部署实验完成!
调用链码
新增一个资产
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.example.com:7050 \
--tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem \
-C mychannel -n fabcar --peerAddresses peer0.org1.example.com:7051 \
--tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt \
--peerAddresses peer0.org2.example.com:7051 \
--tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt \
-c '{"Args":["CreateCar","24","kobe","bryant","black","lakers"]}'查询单个资产
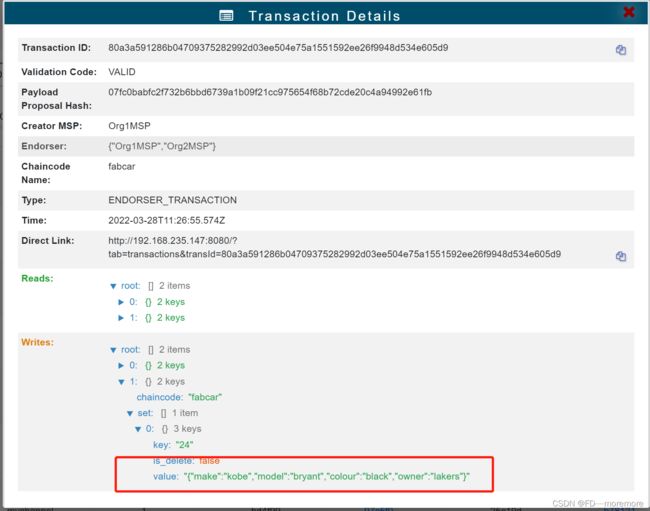
查询刚才添加到区块中的信息
peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n fabcar -c '{"Args":["QueryCar","24"]}'当然我们也可以配置可视化页面(这个参考我文章参考的文章的可视化页面配置)
可以看到确实有区块被记录下来
修改资产的拥有者
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.example.com:7050 \
--tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem \
-C mychannel -n fabcar --peerAddresses peer0.org1.example.com:7051 \
--tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt \
--peerAddresses peer0.org2.example.com:7051 \
--tlsRootCertFiles /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt \
-c '{"Args":["ChangeCarOwner","23","Cavaliers"]}'此时会重新写入一个区块
看了一下没有链码中没有删除资产的方法,之后编写链码再补上这个删除操作!