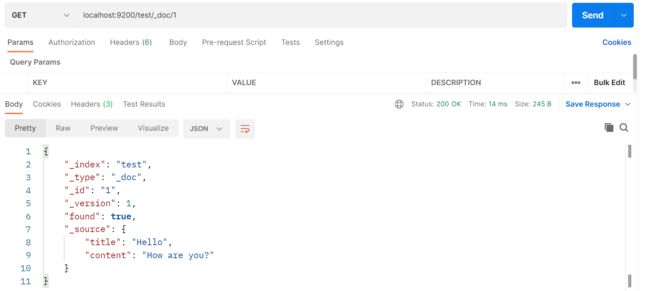
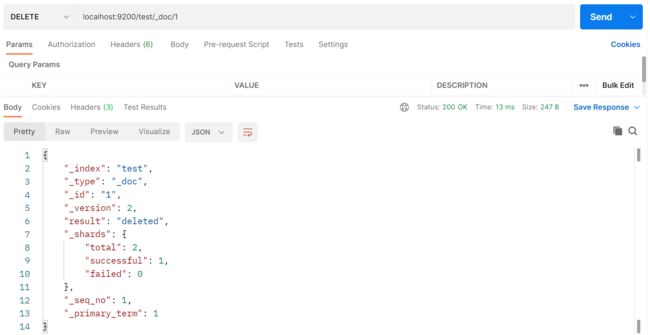
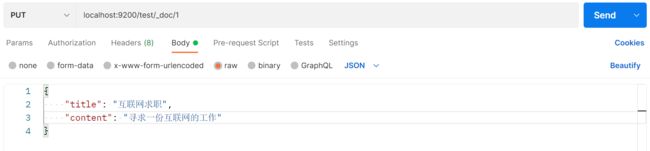
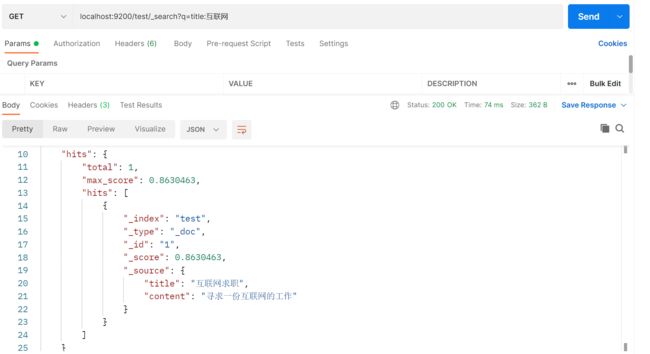
【Java项目】社区论坛项目
项目现已经发布在 Gitee 平台,欢迎 Star 收藏!
项目地址:https://gitee.com/realBeBetter/community
一、项目介绍
仿照牛客网的社区论坛,包括页面以及后端开发、数据库搭建。
使用技术
整体框架:Spring Boot 2.4.10、Spring 5.3.9 、jdk 11.0
版本控制:Git 2.33.1
数据库:MySQL 8.0.23 、Redis 3.2.100
模板引擎:Thymeleaf
应用服务器:Apache Tomcat 9.0.52
消息队列:Kafka 2.12-2.8.1
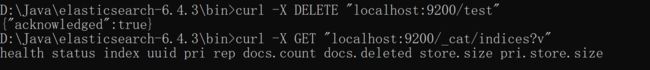
分布式搜索:Elasticsearch 6.4.3
二、环境搭建
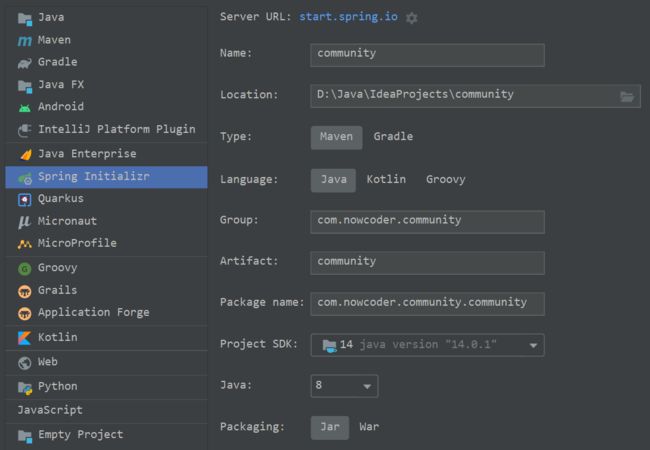
构建项目
使用Spring Initializr工具初始化项目,名称的处理相关如下:
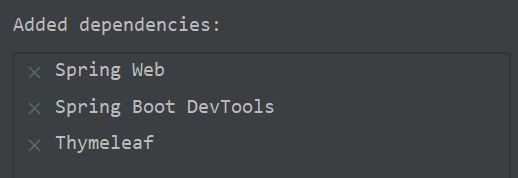
需要事先导入的依赖有:
之后需要在依赖中手动导入 AOP 依赖,AspectJ依赖包。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.9.6version>
dependency>
在yml配置文件中设置端口以及访问的路径:
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /community
三、框架入门
Spring框架
Inversion of Control:控制反转,是一种面向对象编程的设计思想。
Dependency Injection:依赖注入,是 IoC 思想的实现方式。
IoC Container:IoC容器,是实现依赖注入的关键,本质上是一个工厂。
实现自动装配
Spring Boot的启动类在启动的时候,会自动地创建 IoC 容器,并且扫描某些包下的某些Bean,实现自动装配。扫描的包,包括使用了 @Component 注解以及它的衍生注解(@Service、@Controller、@Repository)的类。
获取容器对象
想要获取到 IoC 容器对象,通常需要实现特定的接口:implements ApplicationContextAware。实现接口之后,再重写特定的方法,用一个成员变量保存形参中的容器对象即可。
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
// 实现ApplicationContextAware接口,用于获取IoC容器
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// 将容器暂存到成员变量中,让成员变量获得容器,方便其他测试方法使用
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
通过容器获取Bean
在使用 @Repository 注解标识一个dao类的时候,如果该接口有多个实现类,通过容器.getBean的方式获取的Bean是根据类型来获取的,这个时候容器就不知道该返回哪一个Bean了。使用 @Primary 注解可以默认标识容器返回哪一个实现类。或者直接通过Bean的名称来获取,Bean的名称根据BeanNameGenerator的默认生成规则为首字母小写后的结果,也可以在@Repository注解中自定义Bean的名称。
使用Spring管理Bean
在Bean的内部,可以管理构造方法以及销毁之前的方法。构造之后可以通过 @PostConstruct 注解标识初始化之后需要运行的方法,销毁之前可以通过 @PreDestroy 来标识销毁之前需要运行的方法。构造方法运行之后,这个Bean就完成了实例化,销毁之后代表这个 Bean 生命周期结束,整个过程中,Bean 是以单例的形式存在的。在 Spring 容器中,Bean 实例默认是单例的,整个过程中只会被实例化和初始化一次,也只会被销毁一次。如果想要指定创建的 Bean 为多例的,只需要在标识了 @Component 注解的类上使用 @Scope 注解标识为 prototype 即可。
配置第三方的类为Bean
一般这样的情况是单独创建一个文件夹,然后创建一个单独的Config类,使用 @Configuration 注解标识该类,之后使用 @Bean 注解将构造方法返回的构造完毕的对象装配到 IoC 容器中。
@Configuration
public class ConfigDemo {
/**
* 标识一个第三方的类为 Bean,一般使用的是 @Bean 注解来完成
* @return
*/
@Bean
public SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
}
这样配置之后,是可以直接通过applicationContext.getBean方法获取到Bean对象的。
@Test
public void testSimpleDateFormat() {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = applicationContext.getBean(SimpleDateFormat.class);
System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()));
}
遇到的问题:
错误点一:使用Junit的时候,提示junit-vintage错误,经排查发现是test注解导包错误,导致无法使用test。正确的导包应该使用
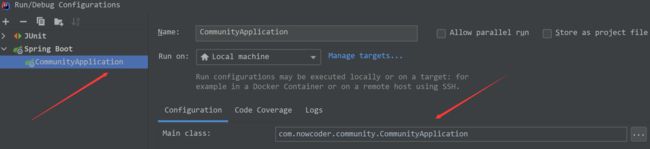
import org.junit.Test;下的包。错误点二:Spring Boot启动的时候报找不到类XXX。这个是因为环境配置的问题,在Spring Boot初始化创建项目的时候,更改了目录会导致配置的类层级关系发生改变无法找到。解决方式:删除不必要的启动配置类,最后使用正确的启动类路径。
Spring 的主要作用以及配置过程:
- 导入Spring需要的依赖包
- 在需要注入到 IoC 容器中的类或者对象上标注相应的注解,将 Bean 注入到容器中交由 IoC 容器管理,降低组件之间的耦合度
Spring MVC框架
Spring MVC 框架主要用来处理web请求,web开发基于HTTP协议(超文本传输协议)实现。
HTTP,Hyper Text Transfer Protocol,超文本传输协议,是一个在应用层用于传输HTML等内容的协议。它规定了浏览器和服务器之间如何进行通信,以及通信时的数据格式。
HTTP协议文档:HTTP | MDN (mozilla.org)
使用 MVC 获取 HTTP 请求参数
在使用 MVC 框架的时候,我们通常使用 HttpServletRequest 对象和 HttpServletResponse 对象,可以通过这两个类来封装请求和应答对象。
/**
* 获取Http请求的参数,并打印
* @param request
* @param response
*/
@RequestMapping("/http")
public void http(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println(request.getMethod());
System.out.println(request.getServletPath());
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = headerNames.nextElement();
String value = request.getHeader(name);
System.out.println(name + " : " + value);
}
// 获取请求的参数
System.out.println(request.getParameter("Code"));
// 设置返回的数据类型
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
// 这样的写法,最终会自动关闭 () 里面的读写流,可以简化开发,避免手动close流
try (PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter()) {
writer.write("牛客网
"); // 写标题
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
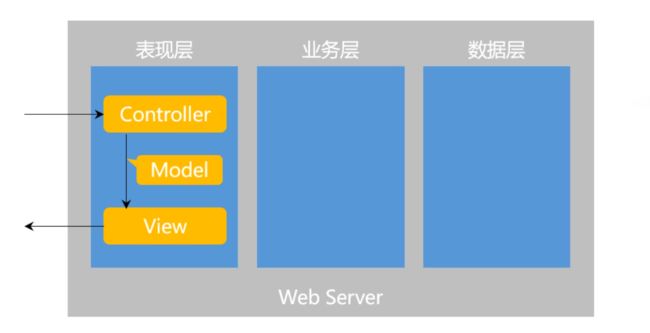
三层架构
三层架构包括表现层、业务层、数据访问层。
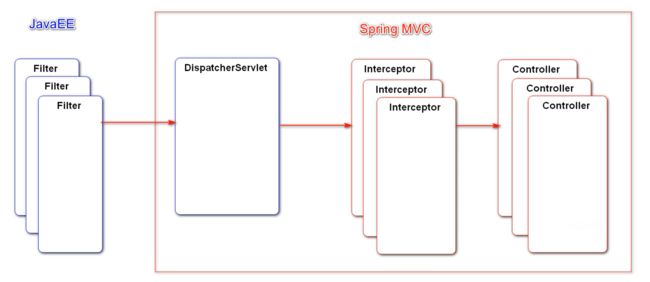
MVC主要负责的是表现层的工作,MVC一共包括Model模型层、View视图层、Controller控制层。在三层架构中负责表现层的工作,MVC的核心组件是前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 。前端控制器在整个前端的业务中主要是为了解决以下步骤中的一些问题:
参考文档:Web on Servlet Stack (spring.io)
模板引擎
在开发中,如果想要给浏览器返回一个动态的网页,要使用模板引擎来完成这件事。模板引擎的作用主要是生成动态的HTML文件。最常见常用的就是ThymeLeaf模板引擎,优点在于倡导自然模板,即使用HTML文件为模板。它常用的语法包括:标准表达式、判断与循环(主要是循环判断集合元素)、模板的布局(主要包括如何复用网页中相同的部分的页面)。
参考文档:Thymeleaf、Thymeleaf入门到吃灰 - 鞋破露脚尖儿 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
处理GET请求
在处理用户的GET请求的时候,一般传参有两种方式。一种是使用参数名=参数值,另外一种是直接拼接在请求的URL中。两种方式分别适合于不同的场景。
第一种请求的方式,使用 Key = Value 的形式进行传参,多个参数之间使用 & 符号进行分隔。
// ①GET 请求的处理 /students?current=1&limit=20 当前是第一页,一共显示20条数据
@RequestMapping(path = "/students", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getStudents(
@RequestParam(name = "current", required = false, defaultValue = "1") int current,
@RequestParam(name = "limit", required = false, defaultValue = "1") int limit) {
System.out.println(current);
System.out.println(limit);
return "some students";
}
第二种方式,直接将请求参数写在URL中,并不明文记录参数的key值,直接使用参数的Value值。参数和参数之间使用 / 进行分隔。
// ②查询单个学生,id为123,不使用参数的时候,直接编排到url中时:/student/123
@RequestMapping(path = "/student/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
System.out.println(id);
return " a student";
}
处理POST请求
- 因为 GET 请求是直接将参数或者 Value 暴露在URL中,这样会导致数据安全性,另外 GET 请求的URL长度也是有限制的,所以GET请求并不可能满足开发中的所有需求。POST请求相比于GET请求则没有上面的问题,POST请求在进行的时候,使用的是请求体,避免了URL直接暴露请求参数的问题。
在POST请求中,一般用来处理表单数据发送。准备的表单如下:
注意其中的action值,这个路径就是表单提交之后返回的路径。比如现在action之后的路径是/community/Hello/student,那么表单提交之后返回的路径就是localhost:8080/community/Hello/student,我们在controller中间需要针对表单数据做出的处理,就要创建一个方法,映射到 /community/Hello/student 路径下。
<form method="post" action="/community/Hello/student">
<p>
姓名:<input type="text" name="name">
p>
<p>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age">
p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="保存">
p>
form>
编写的controller部分,我们使用的是POST的请求方式。表单的数据,我们只需要在方法的参数传入和表单 name 属性值一致的参数,就可以获取表单输入的值。
/**
* 请求的参数填写的应该和html表单中的名字一致
* @param name
* @param age
* @return
*/
// POST 请求参数的处理
@RequestMapping(path = "/student", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String saveStudent(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("name : " + name);
System.out.println("age : " + age);
return "success";
}
运行结果:
![]()
以上的过程,就代表了MVC对于POST请求处理的一个过程。
响应HTML数据
请求响应之后,我们需要给浏览器返回一个页面,这个时候我们需要创建一个html页面用于返回请求的响应结果。通常在controller中处理请求,我们使用的是ModelAndView,返回的ModelAndView对象。
// 响应HTML请求,直接使用ModelAndView完成
@RequestMapping(path = "/teacher", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView getTeacher() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 添加的数据是一个键值对的形式,返回就是直接返回一个对象
modelAndView.addObject("name", "张三");
modelAndView.addObject("age", 30);
// 设置一个视图,规定返回的是哪一个html页面。html页面通常放在templates目录下
// 下面的路径名,则表示返回的页面是 templates 目录下的 demo 目录下的 view.html
modelAndView.setViewName("/demo/view");
return modelAndView;
}
在开发页面的时候,我们要想把model添加的Object对象值渲染到页面中,需要使用模板引擎,现在用的比较多的是ThymeLeaf模板引擎。在声明中加上ThymeLeaf的声明,使用ThymeLeaf提供的语法,之后就可以将文本渲染到页面中。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Teachertitle>
head>
<body>
<p th:text="${name}">p>
<p th:text="${age}">p>
body>
html>
根据两者相结合,请求 http://localhost:8080/community/Hello/teacher 应该返回的是 name 和 age 的数据。
此外,还有另外一种响应的方式。这个方式直接返回一个页面,不使用 ModelAndView,而是在参数列表中使用 Model 对象,将 Model 对象传入,向 Model 中添加数据,最后返回的 String 就是一个网页的页面文件。
这种方式只是使用的 Model 对象,相比于上一种方式,只是使用的对象不同,添加参数的方法不同。其余的没有区别。
// 响应HTML请求,使用简化的方式,直接返回String
@RequestMapping(path = "/school", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getSchool(Model model) {
// 这里直接使用 Model 对象添加数据,完成数据的添加
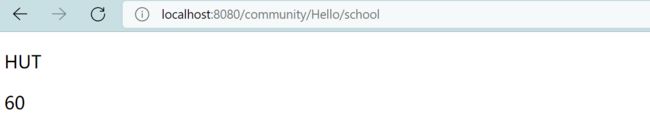
model.addAttribute(" name : ", "HUT");
model.addAttribute("age: ", "60");
return "/demo/view";
}
编译之后,请求路径 http://localhost:8080/community/Hello/school ,运行的结果:
响应 JSON 请求数据
利用 JSON 字符串,可以将Java对象很方便地转换为其他语言的对象,一般方便转换为JS对象。
// 响应 JSON 数据,处理异步请求
// Java 对象 -> JSON 字符串 -> JS 对象,JSON 只是起到一个中间值的作用,方便将 Java 对象转换为其他语言对象
@RequestMapping(path = "/emp", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody // 不加这个注解,会认为返回一个html页面
public Map<String, Object> getEmp() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 20);
map.put("salary", 8000.00);
return map;
}
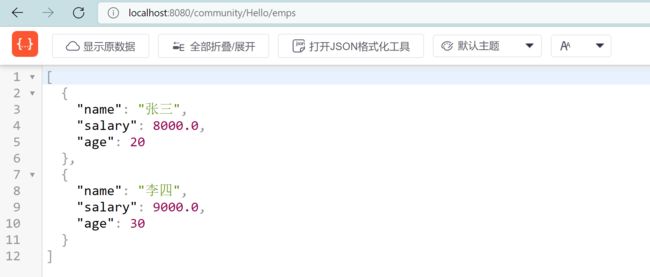
编译之后,请求 http://localhost:8080/community/Hello/emp 之后,可以得到 JSON 字符串的结果:
这样就成功返回了一个 JSON 格式的字符串。但是这个字符串中,仅有一个对象。要返回多个对象,返回值应该设置为一个 List 集合,这样就可以返回多个对象。
// 响应 JSON 数据,处理异步请求
// Java 对象 -> JSON 字符串 -> JS 对象,JSON 只是起到一个中间值的作用,方便将 Java 对象转换为其他语言对象
@RequestMapping(path = "/emps", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody // 不加这个注解,会认为返回一个html页面
public List<Map<String, Object>> getEmps() {
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 20);
map.put("salary", 8000.00);
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "李四");
map.put("age", 30);
map.put("salary", 9000.00);
list.add(map);
return list;
}
运行结果:
浏览器向服务器传参有两种方式,一是在通过get请求,在路径后加问号携带参数,如/xxx?id=1。另一种是通过post请求,在request请求体中携带表单中的参数,这种参数在路径上是看不到的。这两种方式所传的参数,在服务端都可以通过request.getParameter(参数名)这样的方式来获取。而@RequestParam注解,就相当于是request.getParameter(),是从request对象中获取参数的。有时,我们也愿意利用请求路径本身来传参,即将参数拼到路径里,如/xxx/1,这里的1就是参数,那么在解析路径的时候,也是能获取到这个参数的。而@PathVarible就是解析路径,从中获得对应级次的参数。
ModelAndView对象需要主动进行实例化,而Model对象只需要写在参数列表中,MVC框架会自动实例化Model对象。Model对象你可以放任何数据,但是它的作用正如它的名字,主要是用于放模型数据的。ModelAndView对象既可以存放模型数据,也可以存储模板路径。
Spring MVC主要是用来处理请求:
- 创建Controller类,在 Controller 类上标注 @Controller 注解,将类注入到 IoC 容器。
- 在类名上标注 @RequestMapping 注解,表示请求访问的上级 URL 路径
- 在方法上标注 @RequestMapping 注解,表示请求访问的下级 URL 路径。如果标注了 @ResponseBody 注解,表示该方法返回的对象会被写入到 Response 的 Body 数据区;如果不标注,则会认为返回的是一个 html 页面。
- Spring MVC 可以支持的返回方式:ModelAndView, Model, ModelMap, Map,View, String, void
- Spring MVC 主要用来响应 GET 请求或者 POST 请求,HTML 请求 以及 JSON 请求。
Mybatis框架
Mybatis框架的核心组件:
- SqISessionFactory:用于创建SqlSession的工厂类。
- SqlSession:MyBatis的核心组件, 用于向数据库执行SQL。
- 主配置文件:XML配置文件,可以对MyBatis的底层行为做出详细的配置。
- Mapper接口:就是DAO接口,在MyBatis中习惯性的称之为Mapper。
- Mapper映射器:用于编写SQL,并将SQL和实体类映射的组件,采用XML、注解均可实现。
核心用户表 User 表,包含了 Id、username、password、salt(加盐值)、email、type(0代表普通用户、1代表管理员、2代表版主)、status(用户状态,0代表没有激活,1代表已经激活)、activation_code(激活码)、header_url(用户头像图片的访问路径)、create_time(用户注册的时间)。
SALT值属于随机值。用户注册时,系统用来和用户密码进行组合而生成的随机数值,称作salt值,通称为加盐值。通常用户在注册的时候,将用户密码通过MD5加密之后存放在数据库中,经过MD5加密之后并不一定能够保证安全,所以会在加密之后加上随机产生的Salt值,使得到的密文更具有安全性,不易被查询到原有密码,即便有密文查询到的值,也添加了Salt值。
参考文档:salt值_百度百科 (baidu.com)
使用Mybatis查询流程
①引入Mybatis依赖以及Spring整合Mybatis、MySQL连接的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.4version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.23version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
②构建实体对应类:Entity.User类,并添加对应的所有Get和Set方法、toString()方法
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
private String email;
private int type;
private int status;
private int activationCode;
private String headerUrl;
private Date createTime;
}
③创建相应的dao层的接口,编写需要使用的查询方法,等待使用xml文件将接口中的方法变为可用状态。接口使用@Mapper注解标注,可以让Mybatis识别该接口是一个dao接口。除了使用@Mapper注解,还可以使用@Repository注解来标注该接口,实现的效果是一致的。
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
User selectById(int id);
User selectByName(String username);
User selectByEmail(String email);
int insertUser(User user);
int updateStatus(int id, int status);
int updateHeader(int id, String headerUrl);
int updatePassword(int id, String password);
}
④在resources文件夹下,新建mapper文件夹,添加对应的Mapper文件:UserMapper.xml
在文件头部添加映射文件头,根据相应的方法,编写相应的标签,包含不同的sql语句。
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.nowcoder.community.dao.UserMapper">
<sql id="selectFields">
id, username, password, salt, email, type, status, activation_code, header_url, create_time
sql>
<sql id="insertFields">
username, password, salt, email, type, status, activation_code, header_url, create_time
sql>
<select id="selectById" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where id = #{id}
select>
<select id="selectByName" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where username = #{username}
select>
<select id="selectByEmail" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where email = #{email}
select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User" keyProperty="id">
insert into user(<include refid="insertFields">include>)
values(#{username}, #{password}, #{salt}, #{email}, #{type}, #{status}, #{activationCode}, #{headerUrl}, #{createTime})
insert>
<update id="updateStatus">
update user set status = #{status} where id = #{id}
update>
<update id="updateHeader">
update user set header_url = #{headerUrl} where id = #{id}
update>
<update id="updatePassword">
update user set password = #{password} where id = #{id}
update>
mapper>
其中的
⑤编写完Mapper.xml文件中的sql语句之后,我们就可以通过接口的实例化对象来调用相关的方法。方法执行的时候,会自动将sql语句映射到对应的方法上,完成对应的数据操作。
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testSelectUser() {
User user = userMapper.selectById(101);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(userMapper.selectByName("liubei"));
System.out.println(userMapper.selectByEmail("[email protected]"));
}
编写完毕之后,调用相关的方法,会返回相关的语句执行结果。最后查询数据库也可以直接获得语句运行之后的状态。
总结Mybatis编写的顺序:
- 先编写好数据库中数据表对应的实体类放到 Entity 包中,编写好对应的 Get 和 Set 以及 toString 方法
- 在 dao 层编写 Mapper 接口,标注
@Mapper或者@Repository注解,接口内部编写需要的一些方法声明 - 在 resources 目录下的 mapper 目录中新建一个 mapper.xml 文件,在文件中添加 mapper 映射,设置 namespace 为 dao 下对应的 Mapper 接口,然后编写相关方法对应的 sql 语句
- 编写语句取值的时候,使用 #{parameterName} 获取方法声明中的参数,以 preparedStatement 的形式添加进 sql 语句中,完成对数据库的相关操作。
Git版本控制
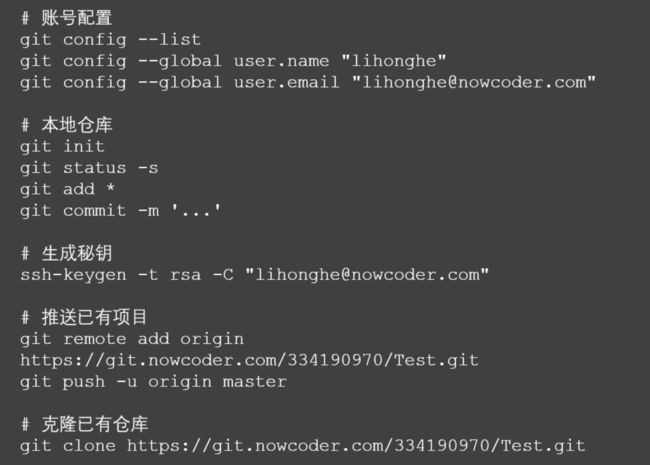
利用 Git 将代码推送到代码托管平台,对代码进行版本控制以及代码备份。
git 操作之后,使用 git init 初始化 git 仓库。 git add ... 命令添加文件,使用通配符匹配文件名。git commit -m '...' 将文件提交到仓库中。
使用 git remote add origin[name] address 命令创建远程仓库,之后使用 git push -u origin[name] master[branch] 将本地仓库推送到远程仓库中。
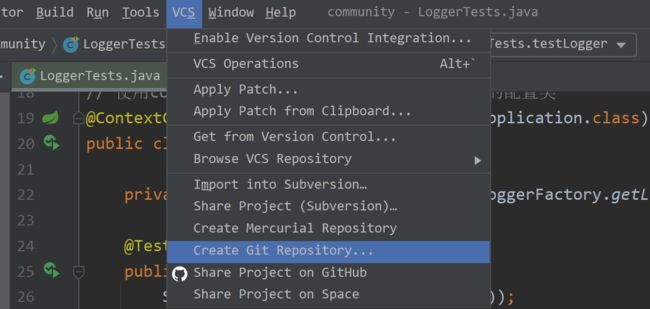
在IDEA中使用 Git 的配置:
① 选择项目中的 VCS 选项,创建 Git 仓库:
②创建 Git 仓库之后,菜单栏就会将 VCS 更改为 Git ,之后选择 Git 中的选项 Commit :
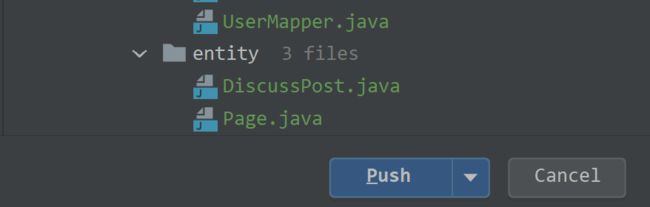
③选中需要提交的代码文件,一般包括: Java 代码文件、配置文件;选择完毕文件之后直接点击 Commit 即可。
④上面的步骤完成之后就相当于提交到了本地仓库,之后我们使用 push 功能将本地仓库的代码推送到远程仓库。
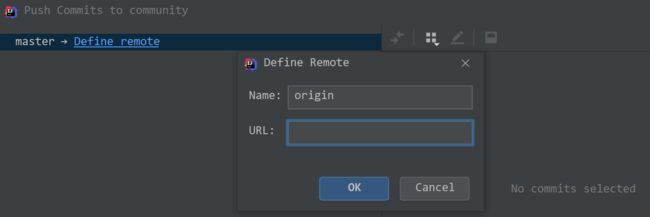
在此之前,我们要先创建一个远程的仓库。选择的是 Gitee 的仓库,然后得到仓库的地址:
https://gitee.com/realBeBetter/community.git
⑤定义远程仓库,第一次提交,没有选择远程的仓库,所以需要定义远程仓库:
URL 填写之前的仓库地址即可,Name 选择默认的 origin 即可。
⑥ 推送选中的代码文件:
⑦ 选择推送之后,如果初次使用会提示登录账号密码,填写完毕之后等待提交就可以了。
四、开发首页
开发社区首页
社区首页设置为一次性显示 10 个帖子,需要通过数据库的查询以及结果的处理完成。
实现思路:查询出十个帖子,并且根据帖子查询出发表用户,将帖子和用户存储进一个Map,之后遍历Map,填充到前端页面中。
讨论帖处理
首先要针对首页的数据进行处理,首页一般要包含若干个用户发布的讨论帖。在数据库中为 discuss_post ,建表语句为:
CREATE TABLE `discuss_post` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`title` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`content` text,
`type` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '0-普通; 1-置顶;',
`status` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '0-正常; 1-精华; 2-拉黑;',
`create_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`comment_count` int DEFAULT NULL,
`score` double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `index_user_id` (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=281 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
comment_count 字段是用来标注帖子的评论数量的,这里做冗余处理(直接将帖子的评论数量存储在帖子的表中),避免频繁的关联查询造成效率低下。
score 字段用来存储帖子的分数,标注帖子的热度质量等评判因素,给帖子进行排名(暂时用不上)。
需要根据上述流程完成一次请求的处理。首页中的数据处理,首先解决用户以及帖子的相关信息处理。
前端处理
将前端页面的html文件添加上thymeleafa的模板引擎声明
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
将相对路径下的静态文件进行声明,声明的格式为:
th:href="@{../static/css/global.css}"
th:src="@{../static/js/global.js}"
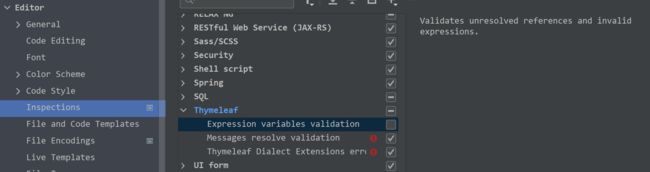
如果 ThymeLeaf 的表达式中发生报错,修改表达式检查即可。
后端处理
主要使用Controller,完成对数据的填充处理。将数据以Map的格式进行处理: List,填充到前端页面中的时候,使用ThymeLeaf模板引擎:
<li class="media pb-3 pt-3 mb-3 border-bottom" th:each="map:${discussPosts}">
<a href="site/profile.html">
<img th:src="${map.user.headerUrl}" class="mr-4 rounded-circle" alt="用户头像" style="width:50px;height:50px;">
a>
<div class="media-body">
<h6 class="mt-0 mb-3">
<a href="#" th:utext="${map.post.title}">备战春招,面试刷题跟他复习,一个月全搞定!a>
<span class="badge badge-secondary bg-primary" th:if="${map.post.type==1}">置顶span>
<span class="badge badge-secondary bg-danger" th:if="${map.post.status==1}">精华span>
h6>
<div class="text-muted font-size-12">
<u class="mr-3" th:utext="${map.user.username}">寒江雪u> 发布于 <b th:utext="${#dates.format(map.post.createTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">2019-04-15 15:32:18b>
<ul class="d-inline float-right">
<li class="d-inline ml-2">赞 11li>
<li class="d-inline ml-2">|li>
<li class="d-inline ml-2">回帖 7li>
ul>
div>
div>
li>
其中,th:each="map:${discussPosts}" 表示循环 Map 中的数据,复制出多个
- 标签进行显示。
th:src="${map.user.headerUrl}"表示map.get("user").getHeaderUrl(),其余的类似。
th:utext="${map.post.title}"使用 utext 代替 text 可以替换其中的转义字符,不会出现转义字符。
ThymeLeaf中,@后面是填写路径的,$后面是填写变量数据的,#{}是mapper中的写法 -
@Controller public class HomeController { @Autowired private DiscussPostService discussPostService; @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping(path = "/index", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getIndexPage(Model model) { // 获取主页,应该获取不同的用户的不同帖子 List<DiscussPost> list = discussPostService.findDiscussPosts(0, 0, 10); List<Map<String, Object>> discussPosts = new ArrayList<>(); if (list != null) { // 表示查询到讨论帖,应该直接帖子的内容封装成Map再进行展示,存储到 discussPosts 里面 for (DiscussPost discussPost : list) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("post", discussPost); User user = userService.findUserById(discussPost.getUserId()); map.put("user", user); discussPosts.add(map); } } model.addAttribute("discussPosts", discussPosts); return "index"; } }开发分页组件
分页显示所有帖子,在分页的时候,要判断页码数、上一页以及下一页的显示逻辑、首页末页的跳转等。
为了方便分页数据的显示,编写一个 Page 实体类,专门用来存储相关的页面信息。
public class Page { /** * 当前页面 */ private int current = 1; /** * 显示上限数量 */ private int limit = 10; /** * 数据总数,用于计算总页数 */ private int rows; /** * 查询路径,复用分页链接 */ private String path; public int getCurrent() { return current; } public void setCurrent(int current) { // 避免非法数据传进 if (current >= 1) { this.current = current; } } public int getLimit() { return limit; } public void setLimit(int limit) { // 设置合法的上限数据 if (limit >= 1 && limit <= 100) { this.limit = limit; } } public int getRows() { return rows; } public void setRows(int rows) { if (rows >= 0) { this.rows = rows; } } public String getPath() { return path; } public void setPath(String path) { this.path = path; } /** * 获取当前页的起始行 * * @return */ public int getOffset() { // current * limit - limit return (current - 1) * limit; } /** * 页面上要显示总页码,计算出总页数 * * @return */ public int getTotal() { // rows / limit ,需要进一处理 if (rows % limit == 0) { return rows / limit; } else { return rows / limit + 1; } } /** * 获取起始页码,页面中的五个页码标签中最开始 * * @return */ public int getFrom() { int from = current - 2; return from < 1 ? 1 : from; } /** * 获取结尾页码,页面下方页码标签的最末尾一个 * * @return */ public int getTo() { int to = current + 2; int total = getTotal(); return to > total ? total : to; } }分页显示中,规定最多显示五个页面数字。直接存储在 Page 类中,可以更加方便获取。
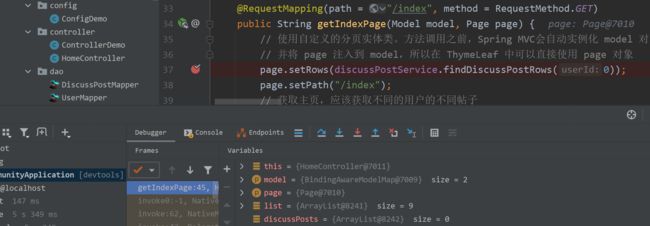
@RequestMapping(path = "/index", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getIndexPage(Model model, Page page) { // 使用自定义的分页实体类。方法调用之前,Spring MVC会自动实例化 model 对象以及 page 对象 // 并将 page 注入到 model,所以在 ThymeLeaf 中可以直接使用 page 对象 page.setRows(discussPostService.findDiscussPostRows(0)); page.setPath("/index"); // 获取主页,应该获取不同的用户的不同帖子 List<DiscussPost> list = discussPostService.findDiscussPosts(0, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit()); List<Map<String, Object>> discussPosts = new ArrayList<>(); if (list != null) { // 表示查询到讨论帖,应该直接帖子的内容封装成Map再进行展示,存储到 discussPosts 里面 for (DiscussPost discussPost : list) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("post", discussPost); User user = userService.findUserById(discussPost.getUserId()); map.put("user", user); discussPosts.add(map); } } model.addAttribute("discussPosts", discussPosts); return "index"; }前端中,我们要将ThymeLeaf模板引擎中的数据进行修改。
<nav class="mt-5" th:if="${page.rows>0}"> <ul class="pagination justify-content-center"> <li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=1)}">首页a>li> <li th:class="|page-item ${page.current==1?'disabled':''}|"><a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.current -1})}">上一页a>li> <li th:class="|page-item ${page.current==i?'active':''}|" th:each="i:${#numbers.sequence(page.from, page.to)}"><a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${i})}" th:text="${i}">1a>li> <li th:class="|page-item ${page.current==page.total?'disabled':''}|"><a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.current +1})}">下一页a>li> <li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.total})}">末页a>li> ul> nav>根据业务逻辑,判断是否能够点击响应页面或者是显示相关页面。
项目调试技巧
响应状态码的含义:HTTP 响应代码 - HTTP | MDN (mozilla.org)
重定向是一个能够以非常低的耦合状态实现页面的跳转。服务端断点调试技巧:在程序中打断点,Debug 启动服务之后,查看值的状态,调查错误信息。
客户端断点调试技巧:在前端代码中打断点,之后使用浏览器的开发工具进行调试。
设置日志级别,并将日志输出到不同的终端:
Spring Boot内置的日志:Chapter 2: Architecture (qos.ch)
package org.slf4j; public interface Logger { // Printing methods: 级别从低到高排名 public void trace(String message); public void debug(String message); public void info(String message); public void warn(String message); public void error(String message); }设置不同的日志级别,使用相应的配置文件就可以指定将日志文件输出到指定文件夹。
public class LoggerTests { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerTests.class); @Test public void testLogger() { System.out.println(logger.getName()); // 日志输出打印 logger.debug("debug log"); logger.info("info log"); logger.warn("warn log"); logger.error("error log"); } }在配置文件中进行相关的配置即可:
logging: # 日志级别设置 level: com.nowcoder.community: debug # 文件路径。要设置文件指定名称只使用name即可 file: path: D:/Java/IdeaProjects/community/log name: D:/Java/IdeaProjects/community/log/community.log logback: rollingpolicy: max-file-size: 5MB file-name-pattern: D:/Java/IdeaProjects/community/log/error/log-error-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log max-history: 30五、开发登录模块
发送邮件
登录的时候,为了让用户选择邮件验证码登录,要实现发送邮件的功能。
实现步骤:
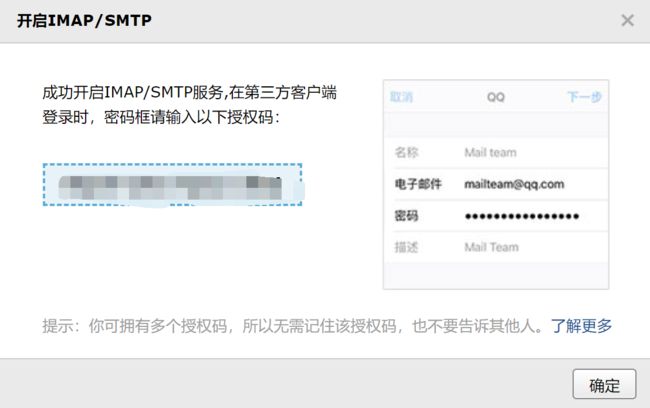
一、邮箱设置:发送邮件,启用 SMTP 邮箱客户端。
找到自己使用邮箱客户端提供的 SMTP 服务,打开服务即可。
打开服务之后,一般会有一个授权码,之后会使用到:
nkphtzkshprpdidj二、Spring Mail:导入 jar 包,设置邮箱参数,使用 JavaMailSender 发送邮件
添加 JavaMailSender 服务的 jar 包:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mailartifactId> dependency>邮箱参数配置:
# 邮箱相关参数配置 # 接收邮件服务器:imap.qq.com,使用SSL,端口号993 # 发送邮件服务器:smtp.qq.com,使用SSL,端口号465或587 mail: host: smtp.qq.com port: 465 username: ### password: ### 一般是填写授权码 protocol: smtps properties: mail: smtp: ssl: enable: true主要设置发送邮件的邮箱账号、密码、协议等信息。
使用 JavaMailSender 发送邮件:
@Component public class MailClient { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger("Mail Logger"); @Autowired private JavaMailSender mailSender; // 发送邮件的发送者用户名字 @Value("${spring.mail.username}") private String from; public void sendMail(String to, String subject, String content) { // 使用 MimeMessage 构建邮件主体 try { MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage(); MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage); helper.setFrom(from); helper.setTo(to); helper.setSubject(subject); // 加参数表示允许支持 html 文本 helper.setText(content, true); // 使用 send 方法发送邮件 mailSender.send(helper.getMimeMessage()); } catch (MessagingException e) { logger.error("邮件发送失败" + e.getMessage()); e.printStackTrace(); } } }配置完毕之后,直接使用测试类进行测试即可。
三、模板引擎:使用 ThymeLeaf 模板引擎发送 HTML 邮件
首先编写一个 HTML 文件,使用模板引擎:
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>邮件示例title> head> <body> <p>欢迎你,<span style="color: aqua" th:utext="${username}">span>p> body> html>之后在测试类中注入 Thymeleaf 提供的模板引擎对象,让模板引擎来负责格式化 HTML 文件。
// 使用模板引擎,主动获取 html 页面 @Autowired private TemplateEngine templateEngine;使用测试类,先利用模板引擎中的 context 对象设置变量值,之后使用模板引擎格式化 HTML 文件,再将格式化之后生成的字符串发送到目标邮箱,就完成了邮件的发送。
@Test public void testSendHtmlMail () { Context context = new Context(); context.setVariable("username", "Test 用户"); // 模板引擎调用网页,将其中的数据填充之后,生成一个 HTML 网页字符串对象,格式化网页 String process = templateEngine.process("/mail/demo", context); System.out.println(process); mailClient.sendMail("[email protected]", "HTML 测试", process); }启动的时候出现过错误:Consider defining a bean of type ‘org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender’ in your configuration.
最后发现是 IDEA 的错误,无缘无故又找不到依赖包了。在 pom.xml 文件中删除邮件使用的依赖包,刷新一下,运行一遍,之后再重新添加依赖,刷新一遍,之后再次重新运行,解决问题。
注册功能
注册功能的实现中,首先要针对用户的注册过程,将用户自定义的用户名以及密码等数据写入到数据库中。注册过程分为多个步骤,注册功能实现的步骤:
一、点击注册链接,跳转到注册页面,获取注册页面
@Controller public class LoginController { @RequestMapping(path = "/register", method = RequestMethod.GET) // 获取注册页面 public String getRegisterPage() { return "/site/register"; } }之后修改前端页面中的相关数据部分:
<a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/index}">首页a> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/register}">注册a>二、通过表单提交数据
- 表单数据完整性验证(前端验证)
修改前端页面中的 Thymeleaf 页面部分,并且完成密码相关的填充。
<input type="email" th:class="|form-control ${emailMessage!=null?'is-invalid':''}|" th:value="${user!=null?user.email:''}" id="email" name="email" placeholder="请输入您的邮箱!" required> <div class="invalid-feedback" th:utext="${emailMessage}"> 该邮箱已注册! div>- 服务端验证账号、邮件是否存在
通过 UserService 中的 register 方法,通过传入的 userId 以及 email 来验证账号是否已经注册。
public Map<String, Object> register(User user) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); // 空值处理 if (user == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!"); } // 用户名为空 if (StringUtils.isBlank(user.getUsername())) { map.put("usernameMessage", "用户名不能为空!"); return map; } // 密码为空 if (StringUtils.isBlank(user.getPassword())) { map.put("passwordMessage", "密码不能为空!"); return map; } // 邮箱为空 if (StringUtils.isBlank(user.getEmail())) { map.put("emailMessage", "邮箱不能为空!"); return map; } // 验证账号的合法性 User selectUser = userMapper.selectByName(user.getUsername()); if (selectUser != null) { // 账号用户名存在,表示应该更换用户名 map.put("usernameMessage", "用户名已存在!"); return map; } // 验证邮箱的合法性 selectUser = userMapper.selectByEmail(user.getEmail()); if (selectUser != null) { // 邮箱已经被注册,表示应该更换邮箱注册,或者找回密码 map.put("emailMessage", "邮箱已被注册!"); } // 注册账号,要将数据写入到数据库中 // 一、设置 salt 值 user.setSalt(CommunityUtil.generatorUUID().substring(0, 5)); // 二、设置被加密的密码值 user.setPassword(CommunityUtil.md5(user.getPassword() + user.getSalt())); // 三、设置用户类型 user.setType(0); // 四、设置用户状态,默认为未激活 user.setStatus(0); // 五、设置用户的激活码 user.setActivationCode(CommunityUtil.generatorUUID()); // 六、设置默认头像路径 user.setHeaderUrl("http://images.nowcoder.com/head/" + new Random().nextInt(1000) + "t.png"); // 七、设置注册时间 user.setCreateTime(new Date()); // 八、保存用户 userMapper.insertUser(user); // 九、发送激活邮件 Context context = new Context(); context.setVariable("email", user.getEmail()); // 填充网页链接:http://locolhost:8080/community/activation/userId/activationCode String url = domain + contextPath + "/activation/" + user.getId() + "/" + user.getActivationCode(); context.setVariable("url", url); // 模板引擎调用网页,将其中的数据填充之后,生成一个 HTML 网页字符串对象,格式化网页 String process = templateEngine.process("/mail/activation", context); mailClient.sendMail(user.getEmail(), "激活账号链接", process); return map; }- 服务端发送激活邮件
设置特定的验证邮件,发送验证激活链接,点击链接之后将激活状态改变。
public int activation(int userId, String activationCode) { // 查询到用户,获取到激活码,判断激活码是否正确 User user = userMapper.selectById(userId); String selectCode = user.getActivationCode(); if (user.getStatus() == 1) { // 表示已经激活过,重复激活 return ACTIVATION_REPEAT; }else if (activationCode.equals(selectCode)) { // 激活码匹配,激活成功,修改激活状态 userMapper.updateStatus(userId, 1); return ACTIVATION_SUCCESS; } else { // 激活码不匹配,应该返回失败 return ACTIVATION_FAILED; } }三、激活账号服务
- 点击激活邮件中的链接,激活账号
// 填充网页链接:http://locolhost:8080/community/activation/userId/activationCode // 直接访问路径,使用 GET 方式即可 @RequestMapping(path = "/activation/{userId}/{activationCode}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String activation(Model model, @PathVariable("userId") int userId, @PathVariable("activationCode") String activationCode) { int activation = userService.activation(userId, activationCode); // 结果表示请求的链接是否完成了激活操作 if (activation == ACTIVATION_SUCCESS) { // 激活成功 model.addAttribute("message", "激活成功!您的账号已经可以正常使用了!"); model.addAttribute("target", "/login"); } else if (activation == ACTIVATION_FAILED) { // 激活失败 model.addAttribute("message", "激活失败!请检查您的激活链接是否正确!"); model.addAttribute("target", "/index"); } else if (activation == ACTIVATION_REPEAT) { // 重复激活 model.addAttribute("message", "无效操作!该账号已经进行了激活!"); model.addAttribute("target", "/index"); } return "/site/operate-result"; }会话管理
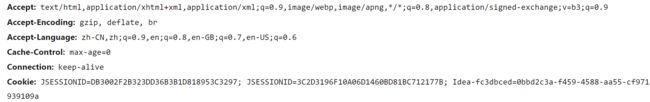
HTTP 是无状态的、有会话的。在同一连接中,两个执行成功的请求之间是没有任何关系的,这样用户就没有办法在同一网站中进行连续的交互。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 HTTP Cookies 来解决这个问题。
HTTP Cookie 是服务器发送到浏览器并保存在本地的一小块数据,它会在浏览器下一次向服务器发送请求的时候被携带发送到服务器。Cookie 通常会记录一些信息,包括请求的浏览器标识以及用户的登录状态等。通过对 Cookie 的支持,使得 HTTP 可以记录稳定的状态信息。
Cookie 的作用通常有三个:① 会话状态管理;② 个性化设置; ③ 跟踪用户行为分析。
Cookie
使用 Cookie 的步骤通常包括:创建 Cookie 对象、设置 Cookie 的生效范围、设置 Cookie 的生效时间、添加 Cookie 到返回对象中。
@RequestMapping(path = "/cookie/set", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String setCookie(HttpServletResponse response) { // 创建 Cookie 对象 Cookie cookie = new Cookie("Code", CommunityUtil.generatorUUID()); // 设置 Cookie 的生效范围,哪些路径下生效 cookie.setPath("/community"); // 设置 Cookie 的生效时间 cookie.setMaxAge(60 * 10); // 添加 Cookie response.addCookie(cookie); return "set Cookie"; }启动项目,输入目标 URL,可以在浏览器的客户端的开发工具看到 Cookie 的相关信息:
对于 Cookie 的使用,可以通过
@CookieValue来获取目标的 Cookie 对象:@RequestMapping(path = "/cookie/get", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getCookie(@CookieValue("Code") String code) { System.out.println(code); return "get Cookie"; }点击目标链接,可以看到浏览器的信息状态:
Session
对于会话的管理,除了 HTTP 协议提供的 Cookie 解决方案,还有 Java EE 提供的 Session 方案。Session 是用于在服务端记录客户端信息,相比于 Cookie,它存放的位置不一样。Cookie 保存在本地浏览器,Session 保存在服务器,安全性会更高,但同时也会增加服务器的内存消耗。
对于 Session 的设置,使用上和 Model 对象的使用类似,只需要在参数列表中添加
HttpSession对象,之后 MVC 框架将会自动将对象实例化,之后再向 session 对象中添加数据即可。@RequestMapping(path = "/session/set", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String setSession(HttpSession session) { session.setAttribute("id", 1); session.setAttribute("name", "Test"); return "set session"; }运行的时候访问特定的 URL 路径,查看网络,可以发现 SessionID 的一些信息:
使用的时候只需要通过 session 对象调用相对应的 get 方法即可。
@RequestMapping(path = "/session/get", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getSession(HttpSession session) { System.out.println(session.getAttribute("id")); System.out.println(session.getAttribute("name")); return "get session"; }运行的结果可以看到:
运行之后可以看到相同的
JSessionID字段值,控制台也相应输出 session 对应的 key-value 值。Session 在分布式服务中出现的问题
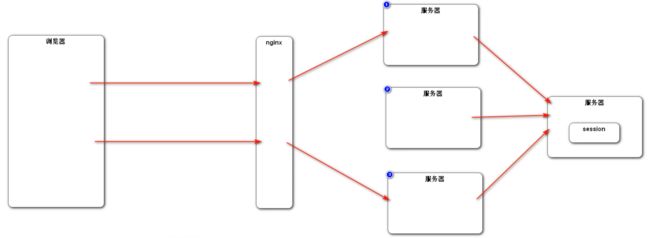
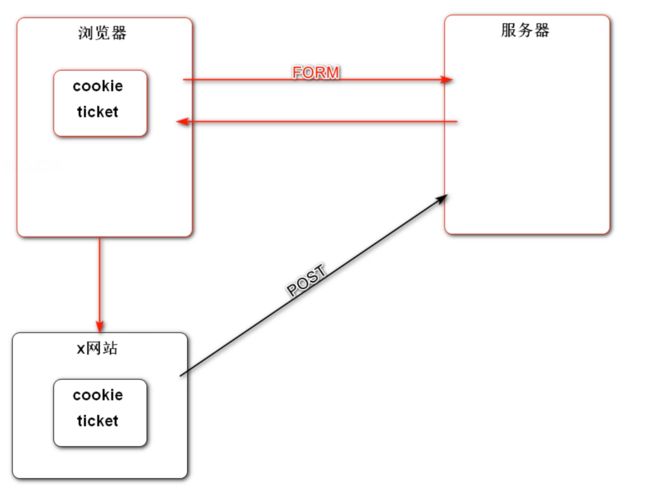
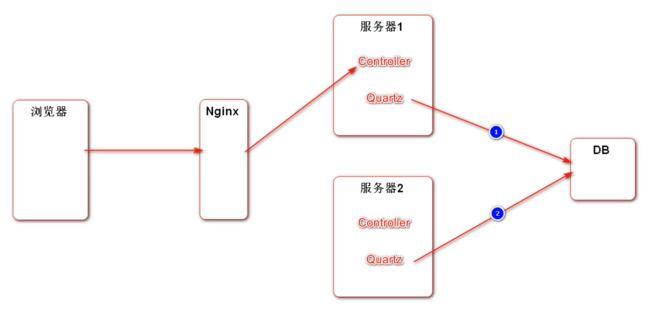
如果在分布式环境中使用 Session 来管理会话,那么由于多服务器的存在,使用 Nginx 等负载均衡组件可能造成下次请求的服务器与第一次请求的服务器不一致,导致无法访问到第一次的 Session ,造成无法管理 Session 。
解决方法一:粘性 Session 。指的是在负载均衡中,将第一次分配的服务器和客户端绑定。之后的连接中的步骤,所有的请求都由这台服务器管理。这样带来的问题:① 无法真正实现在某一时间点上的负载均衡,导致负载均衡的效果下降;② 如果在提供服务的时候该服务器发生故障,那么后续的服务将无法再提供,分布式作用下降。
解决方法二:同步 Session。在不同的服务器之间将 Session 进行同步。带来的弊端:① 对于所有的服务器,同步以及存储 Session 会带来额外的性能开销;② 同步 Session 会造成不同的服务器之间的耦合性加强。
解决方法三:共享 Session。额外部署一台服务器来存储 Session,当其他服务器要获取 Session 的时候,都向这台 Session 服务器获取 Session 数据。这样的弊端也很明显:① 整体的容错率下降,如果 Session 服务器出现问题,最终会导致所有服务不可用; ② 所有的 Session 都在一台服务器上,也会造成性能瓶颈,违背了分布式设计的初衷。
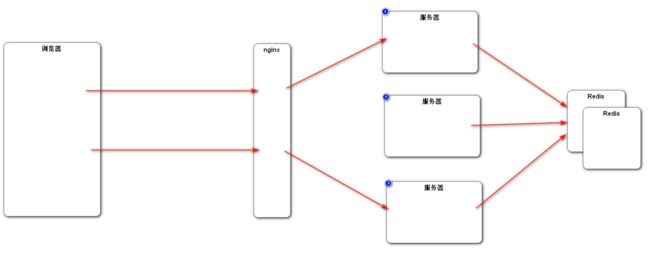
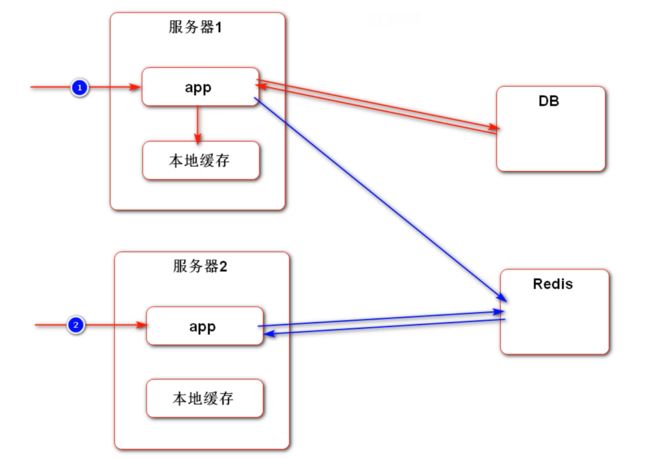
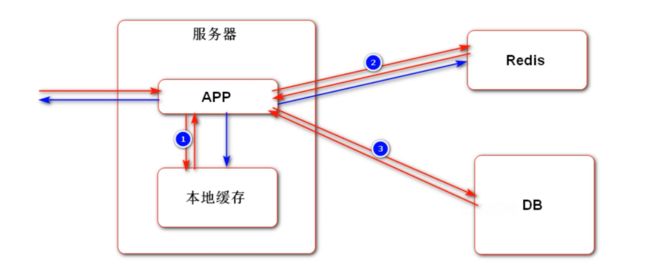
最终解决办法:尽量使用 Cookie 来存储会话数据;如果存在敏感数据不方便存储在 Cookie 中,可以存储在 Redis 等非关系型数据库中。这样做的好处有:① 不需要在服务器之间进行 Session 的同步,只需要在 Redis 集群中进行即可; ② 本身 Redis 的访问速度比较快,不会造成性能瓶颈;③ 方便进行 Session 的管理。
生成验证码
生成验证码我们可以选用 Kaptcha 工具包来完成。生成验证码一共分为三个步骤:
一、导入 Kaptcha 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pengglegroupId> <artifactId>kaptchaartifactId> <version>2.3.2version> dependency>二、配置 Kaptcha 类,编写 Kaptcha 配置类
@Configuration public class KaptchaConfig { @Bean public Producer getKaptchaConfig() /*kaptchaConfig()*/ { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.image.width", "100"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.image.height", "40"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.font.size", "32"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.font.color", "0,0,0"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.char.string", "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.char.length", "4"); properties.setProperty("kaptcha.noise.impl", "com.google.code.kaptcha.impl.NoNoise"); DefaultKaptcha kaptcha = new DefaultKaptcha(); Config config = new Config(properties); kaptcha.setConfig(config); return kaptcha; } }遇到的问题:依赖下载之后找不到对应的接口包,查看 Maven 依赖发现是红的,但是在 pom.xml 文件中并没有提示。刷新、删除依赖语句再添加均无效。
解决方法:在 maven 本地仓库中找到对应的文件夹删除依赖,之后重新下载依赖解决。遇到的问题:Consider renaming one of the beans or enabling overriding by setting… 考虑重新给 Bean 进行命名。最后发现是 public class KaptchaConfig 中的类名和 @Bean 配置的原有方法名 kaptchaConfig() 冲突了,导致配置类和 @Bean 生成的 Bean 的名字相同。
解决方法:修改方法名字即可。三、生成随机字符串,再由随机字符串生成验证码图片
@Autowired private Producer kaptchaProducer; // 登录的页面中,再自动访问该路径,返回生成的验证码图片 @RequestMapping(path = "/kaptcha", method = RequestMethod.GET) public void getKaptcha(HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) { // 生成验证码并返回 String text = kaptchaProducer.createText(); BufferedImage image = kaptchaProducer.createImage(text); // 将验证码存入 Session session.setAttribute("kaptcha", text); // 将图片输出给浏览器 response.setContentType("image/png"); try { ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream(); ImageIO.write(image, "png", outputStream); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("响应验证码失败:" + e.getMessage()); } }后端的处理逻辑是通过 Response 对象将验证码生成的图片写入到浏览器。前端的处理逻辑是通过将验证码图片的访问路径映射到 Controller 方法设定的路径上。
但是还需要将设置的刷新按钮点击事件绑定到获取新的图片方法上。为了适配浏览器获取静态图片的动作,需要在路径末尾拼接一些其他的干扰参数,避免浏览器认为是在重复请求相同的静态资源而停止请求。
<div class="col-sm-4"> <img th:src="@{/kaptcha}" id="kaptcha" style="width:100px;height:40px;" class="mr-2"/> <a href="javascript:refresh_kaptcha();" class="font-size-12 align-bottom">刷新验证码a> div><script> function refresh_kaptcha() { var path = CONTEXT_PATH + "/kaptcha?p=" + Math.random(); $("#kaptcha").attr("src", path); } script>参考文档:http://code.google.com/p/kaptcha/
kaptcha谷歌验证码工具 - 勤俭的搬运工 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)登录与退出
登录与退出功能属于网站的基础功能,整个过程需要对用户的会话状态进行管理,跟踪用户在使用过程中的整个活动。实现登录与推出功能包括三个步骤:
一、访问登录页面:
点击顶部区域内的链接,打开登录页面
二、登录:
验证账号、密码、验证码
成功时,生成登录凭证,发送给客户端。登录凭证在数据库中存储有对应的数据表,届时登录状态的维护依靠登录凭证来进行。
失败时,跳回登录页面,使用重定向而不是直接返回。
Service 服务层代码:
// 登录方法,要求返回一个 Map ,表示用户登录的状态 // 由于数据库存储的是加密的密码,所以在使用的时候要将传入的 password 进行加密之后和数据库中的密码进行比对 public Map<String, Object> login(String username, String password, long expiredSeconds) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); // 空值处理 if (StringUtils.isBlank(username)) { map.put("usernameMessage", "用户名不能为空!"); return map; } if (StringUtils.isBlank(password)) { map.put("passwordMessage", "密码不能为空!"); return map; } // 合法性验证,验证账号和密码是否合法 User user = userMapper.selectByName(username); // 验证账号是否存在 if (user == null) { map.put("usernameMessage", "该账号不存在!"); return map; } // 验证账号是否已经激活 if (user.getStatus() == 0) { map.put("usernameMessage", "该账号未激活,请先激活账号!"); } // 验证密码 password = CommunityUtil.md5(password + user.getSalt()); if (!user.getPassword().equals(password)) { // 验证不为空的情况下且两者不相等,表示查询到该用户密码不正确 map.put("passwordMessage", "密码不正确!"); return map; } // 符合登录条件,生成登录凭证 LoginTicket loginTicket = new LoginTicket(); loginTicket.setUserId(user.getId()); loginTicket.setStatus(0); loginTicket.setTicket(CommunityUtil.generatorUUID()); loginTicket.setExpired(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expiredSeconds * 1000)); loginTicketMapper.insertLoginTicket(loginTicket); map.put("ticket", loginTicket.getTicket()); return map; }Controller 控制层代码:
调用 UserService 层提供的登录方法,对登录进行验证,编写在 LoginController 类中:
// 登录方法,使用的 URL 路径可以和之前相同,只要方法不相同就不会发生冲突 @RequestMapping(path = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String login(String username, String password, String code, boolean rememberMe, HttpSession session, HttpServletResponse response, Model model) { // 检查验证码 String kaptcha = session.getAttribute("kaptcha").toString(); if (StringUtils.isBlank(kaptcha) || StringUtils.isBlank(code) || !kaptcha.equalsIgnoreCase(code)) { // 验证码错误 model.addAttribute("codeMessage", "验证码错误!"); return "/site/login"; } // 检查账号,密码 int expiredSeconds = rememberMe ? REMEMBER_EXPIRED_SECONDS : DEFAULT_EXPIRED_SECONDS; Map<String, Object> map = userService.login(username, password, expiredSeconds); if (map.containsKey("ticket")) { // 表示登录成功,需要让客户端携带登录凭证 // 这个 ticket 应该使用 Cookie 存放到客户端 Cookie cookie = new Cookie("ticket", map.get("ticket").toString()); cookie.setPath(contextPath); cookie.setMaxAge(expiredSeconds); response.addCookie(cookie); return "redirect:/index"; } else { // 登录失败,将提示信息展示到前台页面 // 如果不是相应的错误类型,那么获取到的数据也是空值,不会显示 model.addAttribute("usernameMessage", map.get("usernameMessage")); model.addAttribute("passwordMessage", map.get("passwordMessage")); return "/site/login"; } }三、退出:
将登录凭证修改为失效状态
Service 层,编写在 UserService 类中。
public void logout(String ticket) { // 1 表示无效 loginTicketMapper.updateStatus(ticket, 1); }跳转到网站首页,Controller 层负责:
@RequestMapping(path = "/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String logout(@CookieValue("ticket") String ticket) { userService.logout(ticket); return "redirect:/login"; }使用重定向,将会默认使用 Get 请求方式。
显示登录信息
拦截器示例:
① 自定义拦截器,实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口
编写步骤:创建一个类实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,使用 @Component 将这个类注入到 IoC 容器。
在该类中实现三个接口,分别为 preHandler 、postHandler 、 afterCompletion 。拦截的时间点分别为 Controller 运行之前(预处理回调方法)、在 Controller 运行之后(后处理回调方法)、在视图渲染之后(整个请求处理完毕回调方法)。// 发生在 Controller 访问之前 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { logger.debug("preHandle " + handler.toString()); return HandlerInterceptor.super.preHandle(request, response, handler); } // 发生在 Controller 访问之后,视图渲染完成之前 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { logger.debug("postHandle " + handler.toString()); HandlerInterceptor.super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView); } // 发生在 模板引擎加载之后 / 视图渲染完毕之后 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { logger.debug("afterCompletion " + handler.toString()); HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex); }preHandle方法的返回值是布尔类型,根据返回值决定是否拦截/放行。返回 false 表示请求结束,后续的 Interceptor 和 Controller 都不会再执行。postHandler方法在请求之后进行执行,这一个步骤中可以对 Controller 处理之后的 ModelAndView 对象进行处理。afterCompletion方法在视图渲染之后执行,这个时间点也就是请求结束之后。主要是进行资源清理的工作,比如异常处理资源释放会放在这一步。② 配置拦截器,指定拦截、放行的路径
编写步骤:在 config 包下创建一个配置类,实现
WebMvcConfigurer接口。再在该类上添加 @Configuration 注解标注为配置类。重写 addInterceptors 方法,根据拦截器的处理需求,向其中添加拦截器、放行请求路径(addInterceptor)以及拦截请求路径(addPathPatterns)。@Autowired private InterceptorDemo interceptorDemo; @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(interceptorDemo) .excludePathPatterns("/**/*.css", "/**/*.js", "/**/*.png", "/**/*.jpg", "/**/*.jpeg") .addPathPatterns("/register", "/login"); }至此,拦截器已经可以正常运行了。
拦截器应用:
在项目中,拦截器所应当实现的作用就是拦截未登录用户的一些越权请求,将请求转向注册/登录页面。
首先实现一个拦截器:
@Component public class LoginTicketInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Autowired private UserService userService; @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 处理逻辑:主要是从 request 对象中将 Cookie 对象取出来,获得登录凭证 String ticket = CookieUtil.getValue(request, "ticket"); if (ticket != null) { // 表示存在登录凭证 LoginTicket loginTicket = userService.getLoginTicket(ticket); // 检查登录凭证是否失效 if (loginTicket != null && loginTicket.getStatus() == 0 & loginTicket.getExpired().after(new Date())) { // 根据凭证查询用户 User user = userService.findUserById(loginTicket.getUserId()); // 在本次请求中持有用户,使用 ThreadLocal 存储用户 hostHolder.setUser(user); } } return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { // 在处理 Controller 之后,获取用户对象,然后将用户对象填充到模板引擎中 User user = hostHolder.getUser(); if (user != null && modelAndView != null) { modelAndView.addObject("loginUser", user); } } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // 在视图渲染之后执行,此时已经可以将 ThreadLocal 中的对象清除 hostHolder.removeUser(); } }之后再使用配置类对这个拦截器进行相关的配置:
@Autowired private LoginTicketInterceptor loginTicketInterceptor; @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 除了静态资源都需要拦截 registry.addInterceptor(loginTicketInterceptor) .excludePathPatterns("/**/*.css", "/**/*.js", "/**/*.png", "/**/*.jpg", "/**/*.jpeg"); }一、在请求开始时查询登录用户:
public class CookieUtil { public static String getValue(HttpServletRequest request, String name) { if (request == null || name == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数为空!"); } Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); if (cookies != null) { // 不为空才能开始遍历 for (Cookie cookie : cookies) { if (cookie.getName().equals(name)) { return cookie.getValue(); } } } return null; } }这一阶段的任务主要是针对 request 对象,从 request 对象中将目标 Cookie 值拿出来。通过 Cookie 值拿到登录凭证,判断凭证是否合法,再根据凭证查询到用户,根据不同的线程将用户存储进 ThreadLocal 中。再从 Thread Local 中将用户对象取出来,填充到页面中的目标地方。
二、在本次请求中持有用户数据
@Component public class HostHolder { private final ThreadLocal<User> users = new ThreadLocal<>(); public void setUser(User user) { users.set(user); } public User getUser() { return users.get(); } public void removeUser() { users.remove(); } }三、在模板视图上显示用户数据
@Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { // 在处理 Controller 之后,获取用户对象,然后将用户对象填充到模板引擎中 User user = hostHolder.getUser(); if (user != null && modelAndView != null) { modelAndView.addObject("loginUser", user); } }通过前端的显示逻辑,将一些前端元素的判定规则修改:
<li class="nav-item ml-3 btn-group-vertical"> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/index}">首页a> li> <li class="nav-item ml-3 btn-group-vertical" th:if="${loginUser!=null}"> <a class="nav-link position-relative" href="site/letter.html">消息<span class="badge badge-danger">12span>a> li> <li class="nav-item ml-3 btn-group-vertical" th:if="${loginUser==null}"> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/register}">注册a> li> <li class="nav-item ml-3 btn-group-vertical" th:if="${loginUser==null}"> <a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/login}">登录a> li><li class="nav-item ml-3 btn-group-vertical dropdown" th:if="${loginUser!=null}"> <a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href="#" id="navbarDropdown" role="button" data-toggle="dropdown" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false"> <img th:src="${loginUser.headerUrl}" class="rounded-circle" style="width:30px;"/> a> <div class="dropdown-menu" aria-labelledby="navbarDropdown"> <a class="dropdown-item text-center" href="site/profile.html">个人主页a> <a class="dropdown-item text-center" href="site/setting.html">账号设置a> <a class="dropdown-item text-center" th:href="@{/logout}">退出登录a> <div class="dropdown-divider">div> <span class="dropdown-item text-center text-secondary" th:utext="${loginUser.username}">nowcoderspan> div> li>四、在请求结束时清理用户数据
@Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // 在视图渲染之后执行,此时已经可以将 ThreadLocal 中的对象清除 hostHolder.removeUser(); }账号设置
账号设置主要针对的是修改用户头像。修改用户头像的时候,通过 IO 流将图片从本地写入到服务端,保存在服务端,之后将头像的访问路径修改成 web 端的路径,对应的数据项也应该修改,这样就完成了头像的更改。
-
上传文件
- 请求:必须是POST请求
- 表单:enctype= “multipart/form-data”
- Spring MVC:通过 MultipartFile 处理上传文件
-
开发步骤
-
访问账号设置页面
-
上传头像
-
获取头像
-
前端显示页面需要修改访问路径以及表单的一些属性,如下:
<form class="mt-5" method="post" th:action="@{/user/upload}" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <div class="form-group row mt-4"> <label for="head-image" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label text-right">选择头像:label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <div class="custom-file"> <input type="file" accept="image/png" th:class="|custom-file-input ${error!=null?'is-invalid':''}|" id="head-image" name="headerImage" lang="es" required=""> <label class="custom-file-label" for="head-image" data-browse="文件">选择一张图片label> <div class="invalid-feedback" th:text="${error}"> 文件格式不正确! div> div> div> div> <div class="form-group row mt-4"> <div class="col-sm-2">div> <div class="col-sm-10 text-center"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-info text-white form-control">立即上传button> div> div> form>首先在 UserMapper 中添加
int updateHeader(int id, String headerUrl);方法,然后添加对应的映射 sql 语句,如下:<update id="updateHeader"> update user set header_url = #{headerUrl} where id = #{id} update>然后修改 UserService 类,添加 updateHeader 方法,传入 userId 和 header 参数:
public int updateHeader(int userId, String header) { return userMapper.updateHeader(userId, header); }通过 Controller 方法将表单的请求方法进行映射,处理:
@LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/upload", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String uploadHeader(MultipartFile headerImage, Model model) { // 异常情况处理 if (headerImage == null) { model.addAttribute("error", "您还没有添加图片!"); return "/site/setting"; } // 获取文件名 String filename = headerImage.getOriginalFilename(); String filetype = ""; // 判断文件类型 if (!StringUtils.isBlank(filename)) { // 生成的文件后缀名格式一般为 .jpg / .png / .jpeg 格式 filetype = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".")); } // 文件格式正确性判断 if (StringUtils.isBlank(filetype)) { /*if ("jpg".equals(filetype) || "jpeg".equals(filetype) || "png".equals(filetype)) { } else { }*/ model.addAttribute("error", "文件格式不正确!"); return "/site/setting"; } // 生成随机文件名 filename = CommunityUtil.generatorUUID() + filetype; // 确定文件存放的路径 File file = new File(uploadPath + "/" + filename); // 将文件存储到目标文件夹中 try { headerImage.transferTo(file); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("头像图片存储失败:" + e.getMessage()); throw new RuntimeException("上传头像失败!服务器异常发生异常", e); } // 存储成功之后要更新用户的头像路径 // 更新之后的路径应该为 web 访问路径 // http://localhost:8080/community/user/header/xxx.jpg User user = hostHolder.getUser(); user = userService.findUserById(user.getId()); String headerUrl = domain + contextPath + "/user/header/" + filename; // 输出测试头像路径 // System.out.println("更新之后的头像路径: " + headerUrl); int updateHeader = userService.updateHeader(user.getId(), headerUrl); /*if (updateHeader == 1) { model.addAttribute("message", "头像修改成功!"); }*/ // 重定向会重新执行 Controller 中的 RequestMapping 映射请求 return "redirect:/index"; } @LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/header/{fileName}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public void getHeaderUrl(@PathVariable("fileName") String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) { // 服务器存放路径 fileName = uploadPath + "/" + fileName; // 获得 .jpg / .png / .jpeg 类型的字符串,文件后缀名 String fileType = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1); // 响应文件类型 response.setContentType("image/" + fileType); // 将图片使用输出流写入 response 对象 try ( OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream(); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName); ) { byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int b = 0; while ((b = fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) { outputStream.write(buffer, 0, b); } } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("读取头像失败:" + e.getMessage()); } }修改密码
- 修改密码
- 请求:必须是 POST 请求
- 将密码使用 POST 请求加密传输,验证原始密码之后使用新的密码更新数据库
- 生成新的 salt 值,将 salt 值重新传进数据库
- 验证密码
- 使用新的密码登录
- 使用原始密码登录应该是失败的
在 UserMapper 下编写
int updatePassword(int id, String password);接口,并且在对应的 xm 中编写新的 sql 语句:<update id="updatePassword"> update user set password = #{password} where id = #{id} update>在 Service 层 UserService 对传入的密码进行操作:
public int updatePassword(int userId, String password) { return userMapper.updatePassword(userId, password); }对密码的加密以及检验在 Controller 层进行:
@LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/updatePassword", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String updatePassword(String oldPassword, String newPassword, String confirmPassword, Model model) { // 判断两次输入的新密码是否相等,是否合法 if (!StringUtils.isBlank(newPassword) || !StringUtils.isBlank(confirmPassword)) { if (!newPassword.equals(confirmPassword)) { // 两次密码不相等 model.addAttribute("confirmPasswordError", "确认密码不一致!请重新输入!"); return "/site/setting"; } }/* else { // 前端界面做了判断,不需要这里的处理 if (StringUtils.isBlank(newPassword)) { model.addAttribute("newPasswordError", "新密码为空!请重新输入!"); } else { model.addAttribute("confirmPasswordError", "确认密码为空!请重新输入!"); } return "/site/setting"; }*/ // 获得原始密码,判断初始密码是否正确 User user = hostHolder.getUser(); if (oldPassword.length() == 0) { // 原始密码为空,应该添加提示信息 model.addAttribute("initialError", "原密码为空!请重新输入!"); return "/site/setting"; } oldPassword = CommunityUtil.md5(oldPassword + user.getSalt()); if (!StringUtils.isBlank(oldPassword)) { if (!oldPassword.equals(user.getPassword())) { model.addAttribute("initialError", "原密码错误!请重新输入!"); return "/site/setting"; } } // 更新密码 userService.updatePassword(user.getId(), CommunityUtil.md5(newPassword + user.getSalt())); // 修改成功重定向至登录界面,并且设置原有的 LoginTicket 失效 return "redirect:/logout"; }检查登录状态
登录状态下,往往能够比非登录状态下进行更多的操作,比如修改一些个人信息等。如果现在一个未登录用户,要进行个人信息的修改操作,那么应该是不可完成的,我们就要借助拦截器来对非登录用户的一些操作进行拦截。
未登录状态下的越权操作,应该是被禁止的。这个时候就需要进行一些检测操作,在需要登录才能进行的操作上,使用自定义的注解,然后针对所有的请求进行检查,查看是否存在用户处于登录状态,使用拦截器实现即可。
@Component public class LoginRequiredInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 主要是判断用户是否登录,以及请求的方法上是否带有 @LoginRequired 注解 if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod(); LoginRequired annotation = method.getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class); if (annotation != null && hostHolder.getUser() == null) { // 此种情况表示存在注解但是用户并没有登录,应该拦截请求 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/login"); return false; } } return true; } }- 使用拦截器
- 在方法前标注自定义注解
- 拦截所有请求,只处理带有该注解的方法
- 自定义注解
- 常用的元注解:
@Target:描述注解的使用范围
@Retention:描述注解保留的时间范围,分为源文件保留、编译器保留、运行期保留
@Documented:描述在使用 javadoc 工具为类生成帮助文档时是否要保留其注解信息
@Inherited:使被它修饰的注解具有继承性。也就是添加了 @Inherited 注解的类的子类也会保留该注解。 - 如何读取注解:
Method.getDeclaredAnnotations()
Method.getAnnotation(Class annotationClass)
- 常用的元注解:
实现的自定义注解如下:
/** * @author : Real * @date : 2021/11/27 15:49 * @description : 登录检查注解 */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 规定书写的位置为方法上 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 规定生效的时机为运行时 public @interface LoginRequired { }六、开发社区核心功能
社区的核心功能,主要包括帖子的发布,用户的评论等。
过滤敏感词
- 前缀树
- 名称:Trie 、字典树、查找树
- 特点:查找效率高,消耗内存大
- 应用:字符串检索、词频统计、字符串排序等
- 敏感词过滤器
- 定义前缀树
- 根据敏感词,初始化前缀树
- 编写过滤敏感词的方法
过滤敏感词我们使用前缀树这样的数据结构来实现。这种树的特点是根节点不存储信息,其他每个节点只存储一个字符。遍历的时候从根节点开始,往下遍历其他的所有节点,判断是否匹配。每次遍历到末尾节点表示符合预设的敏感词,于是将词汇进行替换。整个过程需要用到三个指针,第一个指向前缀树,第二个指向匹配的子串开头处,第三个指向匹配的子串末尾处。每次匹配完成就将后两个指针下移,然后将第一个指针移动至根节点。
敏感词过滤器在实现的时候需要定义前缀树,之后根据预设的敏感词初始化前缀树,最后使用匹配算法将敏感词替换返回。
前缀树的结构:
/** * 设定一个 前缀树节点类,用来存放每个节点 */ private static class TrieNode { // 是否为末尾节点 private boolean isKeywordEnd = false; // 节点的孩子节点 private final Map<Character, TrieNode> childrenNode = new HashMap<>(); public boolean isKeywordEnd() { return isKeywordEnd; } public void setKeywordEnd(boolean keywordEnd) { isKeywordEnd = keywordEnd; } public TrieNode getChildrenNode(Character c) { return childrenNode.get(c); } public void setChildrenNode(Character c, TrieNode node) { childrenNode.put(c, node); } }在实际的开发中,我们将敏感词合集存储在一个 txt 文件中,然后通过读取 txt 文件构造出一个敏感词前缀树。
/** * 读取敏感词 */ @PostConstruct public void init() { try (InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("sensitive-words.txt"); InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); ) { String keyword; while ((keyword = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { this.addKeyWord(keyword); } } catch (IOException exception) { logger.error("敏感词文件读取失败:" + exception.getMessage()); } } /** * 将敏感词添加到前缀树中 * * @param keyword 待添加的敏感词 */ private void addKeyWord(String keyword) { TrieNode tempNode = rootNode; // 需要构建树形结构 char[] chars = keyword.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) { TrieNode childrenNode = tempNode.getChildrenNode(chars[i]); if (childrenNode == null) { // 初始化子节点 childrenNode = new TrieNode(); tempNode.setChildrenNode(chars[i], childrenNode); } // 将临时节点下移至子节点位置 tempNode = childrenNode; // 判断是否为末尾节点 if (i == chars.length - 1) { childrenNode.setKeywordEnd(true); } } }之后过滤使用的算法:
/** * 过滤文本,输出过滤之后的字符串 * * @param text 待过滤的文本 * @return 过滤后的文本 */ public String filter(String text) { if (StringUtils.isBlank(text)) { return null; } // 设定三个指针,分别指向前缀树、起始匹配字符、末尾匹配字符 TrieNode tempNode = rootNode; int begin = 0, end = 0; StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); while (begin < text.length()) { char c = text.charAt(end); // 跳过符号 if (isSymbol(c)) { if (tempNode == rootNode) { result.append(c); begin++; } end++; continue; } // 检查下级节点 tempNode = tempNode.getChildrenNode(c); if (tempNode == null) { // 以 begin 开头的字符不是敏感词 result.append(text.charAt(begin)); // 进入下一个位置 end = ++begin; // 重新指向根节点 tempNode = rootNode; } else if (tempNode.isKeywordEnd()) { // 发现敏感词,将 begin ~ end 之间的字符替换为常量 result.append(StringUtils.repeat(REPLACEMENT, end - begin + 1)); // 进入下一个节点 begin = ++end; // 重新指向根节点 tempNode = rootNode; } else { // 检查下一个字符 if (end < text.length() - 1) { end++; } else { end = begin; } } } // 将最后的字符计入 result.append(text.substring(begin)); return result.toString(); } /** * 判断是否为符号 * * @param character 字符判断 * @return 输出是否需要跳过 */ private boolean isSymbol(Character character) { // 0x2E80 ~ 0x9FFF 是东亚文字 return !CharUtils.isAsciiAlphanumeric(character) && (character < 0x2E80 || character > 0x9FFF); }发布帖子
- AJAX
- Asynchronous JavaScript and XML
- 异步的 JavaScript 与 XML ,不是一门新技术,只是一个新的术语。
- 使用 AJAX ,网页能够将增量更新呈现在页面上,而不需要刷新整个页面。
- 虽然 X 代表 XML ,但目前 JSON 的使用比 XML 更加普遍。
- Ajax - Web 开发者指南 | MDN (mozilla.org)
- 示例
- 使用 jQuery 发送 AJAX 请求
此处使用 Ajax 发送 POST 请求,编写 post 方法,传入三个参数:访问 URL 路径、JSON 字符串值、回调函数。
function send() { $.post( "/community/Hello/ajax", {"age":20, "name":"张三"}, function (data) { /*回调函数*/ console.log(typeof (data)); console.log(data); data = $.parseJSON(data); console.log(typeof (data)); console.log(data.code); console.log(data.message); } ) }最终调用的时候,点击相关按钮,调用该函数,会实现异步发送 post 请求。然后在 Controller 层进行一些处理:
/** * 发送 ajax 请求实例 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/ajax", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String testAjax(String name, int age) { System.out.println(name); System.out.println(age); return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, "操作成功!"); }- 实践
- 采用 AJAX 请求,实现发布帖子的功能
要实现发布帖子,首先需要在数据库的层面上实现发布的功能。在 UserMapper 中添加抽象方法:
/** * 插入新的讨论帖子 * @param discussPost 讨论帖对象 * @return 插入的提示符 */ int insertDiscussPost(DiscussPost discussPost);在 xml 文件中添加对应的方法映射:
<insert id="insertDiscussPost" parameterType="discussPost"> insert into discuss_post(<include refid="insertFields">include>) values(#{userId}, #{title}, #{content}, #{type}, #{status}, #{createTime}, #{commentCount}, #{score}) insert>之后在 web 页面中实现 ajax 异步发布功能:
$(function(){ $("#publishBtn").click(publish); }); function publish() { $("#publishModal").modal("hide"); // 获取标题和正文 let title = $("#recipient-name").val(); let content = $("#message-text").val(); // 发送异步请求, POST 请求 $.post( CONTEXT_PATH + "/discuss/add", {"title": title, "content": content}, function (data) { data = $.parseJSON(data); // 在提示框中显示提示消息 $("#hintBody").text(data.message); // 显示提示框 $("#hintModal").modal("show"); // 显示提示框之后 2s 隐藏 setTimeout(function(){ $("#hintModal").modal("hide"); // 刷新页面,判断是否成功 if (data.code === 0) { window.location.reload(); } }, 2000); } ); }点击发布按钮默认触发
publish()方法,然后在其中编写 ajax 中的 post 方法,回调方法中设置弹出框的显示逻辑。在 Service 层处理 post 发布之后的存储逻辑,要针对帖子进行过滤操作:
/** * 添加讨论帖 * * @param discussPost 讨论帖 * @return 插入结果 */ public int addDiscussPost(DiscussPost discussPost) { if (discussPost == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!"); } // 转义 HTML 标签 discussPost.setTitle(HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(discussPost.getTitle())); discussPost.setContent(HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(discussPost.getContent())); // title 以及 content 需要进行敏感词过滤 discussPost.setTitle(sensitiveFilter.filter(discussPost.getTitle())); discussPost.setContent(sensitiveFilter.filter(discussPost.getContent())); return discussPostMapper.insertDiscussPost(discussPost); }在 Controller 处理用户登录检查以及讨论帖的数据库插入操作:
@RequestMapping(path = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String addDiscussPost(String title, String content) { User user = hostHolder.getUser(); if (user == null) { return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(403, "您还没有登录哦~"); } // 构造讨论贴 DiscussPost discussPost = new DiscussPost(); discussPost.setUserId(user.getId()); discussPost.setTitle(title); discussPost.setContent(content); discussPost.setCreateTime(new Date()); discussPostService.addDiscussPost(discussPost); // 异常情况统一处理 return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, "发布成功!"); }帖子详情
- DiscussPostMapper
- DiscussPostService
- DiscussPostController
- index.html
- 在帖子标题上增加访问详情页面的链接
- discuss-detail.html
- 处理静态资源的访问路径
- 复用 index.html 的 header 区域以及分页区域
- 显示标题、作者、发布时间、帖子正文等内容
在开发之前,要了解帖子的数据表结构,包括
id帖子 ID 主键、user_id帖子的作者 ID 、title帖子的标题、content帖子的内容、type帖子的类型( 0 对应普通,1 对应置顶)、status帖子的状态( 0 代表正常, 1 代表精华, 2 代表拉黑)、create_time帖子的发布时间、comment_count评论的数量(冗余存储,避免数据库联合查询带来的压力)、score帖子的评分。开发步骤:一、Mapper 编写查询方法接口:
/** * 查询帖子详情 * @param id 根据帖子 id * @return 帖子 */ DiscussPost selectDiscussPostById(int id);之后在对应的 xml 文件中添加对应的方法实现:
<select id="selectDiscussPostById" resultType="discussPost"> select <include refid="selectFields"></include> from discuss_post where id = #{id} </select>二、Service 层添加查询的方法:
@Autowired private DiscussPostMapper discussPostMapper; public List<DiscussPost> findDiscussPosts(int userId, int offset, int limit) { return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPosts(userId, offset, limit); } public int findDiscussPostRows(int userId) { return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPostRows(userId); }三、Controller 将帖子的详情进行分页处理,复用 index 页面中的分页
/** * 获取帖子详情,包括帖子详情、作者、帖子评论 * * @param id 帖子 ID * @param model model对象 * @return 帖子详情页面 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/detail/{discussPostId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getDiscussPost(@PathVariable("discussPostId") int id, Model model, Page page) { // 帖子详情 DiscussPost discussPost = discussPostService.findDiscussPostById(id); model.addAttribute("post", discussPost); // 帖子作者 User user = userService.findUserById(discussPost.getUserId()); model.addAttribute("user", user); // 评论分页信息 page.setLimit(5); page.setPath("/discuss/detail/" + id); page.setRows(discussPost.getCommentCount()); return "/site/discuss-detail"; }前端的处理中,在
标签添加属性th:utext="${#dates.format(post.createTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"之后可以将创建时间进行格式化。其余的地方直接取 post 或者 user 对象的属性值。事务管理
- 什么是事务
- 事务是由 N 步数据库操作序列组成的逻辑执行单元,这系列操作要么全执行,要么全放弃执行
- 事务的特性(ACID)
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务是应用中不可再分的最小执行体
- 一致性(Consistency):事务执行的结果,须使数据从一个一致性状态,变为另一个-致性状态
- 隔离性(Isolation):各个事务的执行互不干扰,任何事务的内部操作对其他的事务都是隔离的
- 持久性(Durability):事务一旦提交,对数据所做的任何改变都要记录到永久存储器中
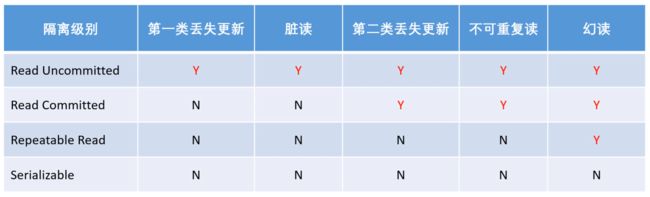
事务中主要需要处理的就是隔离性的问题,包括:
- 常见的并发异常
- 第一类丢失更新:某一个事务回滚,导致另一个事务已经更新的数据丢失
- 第二类丢失更新:某一个事务提交,导致另一个事务已经更新的数据丢失
- 脏读、不可重复读、幻读。
- 常见的隔离级别:
- Read Uncommitted:读未提交
- Read Committed:读已提交
- Repeatable Read:可重复读
- Serializable:串行化
隔离级别的实现方式:
- 悲观锁(数据库)
- 共享锁(S 锁)
- 事务 A 对某数据加了共享锁后,其他事务只能对该数据加共享锁,但不能加排他锁
- 排他锁(X 锁)
- 事务 A 对某数据加了排他锁后,其他事务对该数据既不能加共享锁,也不能加排他锁
- 乐观锁(自定义)
- 版本号、时间戳等
- 在更新数据前,检查版本号是否发生变化。若变化则取消本次更新,否则就更新数据(版本号 +1 )
在开发的过程中,通常借助 Spring 提供的声明式事务来实现事务管理:
- 声明式事务
- 通过 xml 配置,声明某方法的事务特征
- 通过注解,声明某方法的事务特征
- 编程式事务
- 通过 TransactionTemplate 管理事务,并通过它执行数据库的操作
声明式事务示例:在 Service 层创建方法,标注事务管理注解,实现声明式事务管理。
/** * 演示事务管理,声明式事务 * 事务传播行为 * REQUIRED:支持当前事务 (外部事务),如果不存在则创建新事务 * REQUIRES_NEW:创建一个新事务,并且暂停当前事务(外部事务) * NESTED:如果当前存在事务(外部事务),则嵌套在该事务中执行(独立的提交和回滚),否则就会和 REQUIRED 一样 * @return 字符串格式对象 */ @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public Object save1() { User user = new User(); user.setUsername("alpha"); user.setEmail("[email protected]"); user.setHeaderUrl("http://image.nowcoder.com/head/99t.png"); user.setCreateTime(new Date()); user.setSalt(CommunityUtil.generatorUUID().substring(0, 5)); user.setPassword(CommunityUtil.md5("123" + user.getSalt())); userMapper.insertUser(user); DiscussPost discussPost = new DiscussPost(); discussPost.setUserId(user.getId()); discussPost.setTitle("Hello!"); discussPost.setContent("新人报道"); discussPost.setCreateTime(new Date()); discussPostMapper.insertDiscussPost(discussPost); Integer.valueOf("abc"); return "OK"; }这个时候因为标注了事务隔离级别以及事务传播行为的级别,所以在事务运行的时候出现错误的时候会自动视为事务执行失败。可以避免将错误的数据传入数据库进行了持久化操作。
编程式事务管理:在 Service 层注入 TransactionTemplate 对象,通过该对象设置事务隔离级别和事务传播行为,调用提供的 execute 方法中的回调接口可以构造事务的具体实现。
@Autowired private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate; /** * 编程式事务管理,使用 TransactionTemplate 进行事务管理 * @return 对象 */ public Object save2() { transactionTemplate.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED); transactionTemplate.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED); return transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback<Object>() { @Override public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) { User user = new User(); user.setUsername("beta"); user.setEmail("[email protected]"); user.setHeaderUrl("http://image.nowcoder.com/head/999t.png"); user.setCreateTime(new Date()); user.setSalt(CommunityUtil.generatorUUID().substring(0, 5)); user.setPassword(CommunityUtil.md5("123" + user.getSalt())); userMapper.insertUser(user); DiscussPost discussPost = new DiscussPost(); discussPost.setUserId(user.getId()); discussPost.setTitle("你好!"); discussPost.setContent("Hello World"); discussPost.setCreateTime(new Date()); discussPostMapper.insertDiscussPost(discussPost); Integer.valueOf("abc"); return "OK"; } }); }显示评论
- 数据层
- 根据实体查询一页评论数据
- 根据实体查询评论的数量
- 业务层
- 处理查询评论的业务
- 处理查询评论数量的业务
- 表现层
- 显示帖子详情数据,同时显示该帖子所有的评论数据
显示评论的功能的主要难点在于处理帖子的评论,选用合适的数据类型存储。使用 List 数据结构存储评论,评论的每一条信息使用 Map 来存储。之后将封装的整体 List 添加进 Model 对象,使用 Thymeleaf 将对象渲染到页面上,完成页面表现层的处理。
首先要看评论表 Comment 的结构,包括字段:
id评论 ID 主键、user_id评论发表用户、entity_type评论的类型(帖子的评论/用户的回复)、entity_id评论的目标是哪一个帖子/回复、target_id评论的对象用户、content评论的内容、status评论的状态( 0 表示评论有效)、create_time评论的时间。一、首先编辑数据层,新建一个 CommentMapper 类:
@Mapper public interface CommentMapper { /** * 分页查询评论 */ List<Comment> selectCommentsByEntity(int entityId, int entityType, int offset, int limit); /** * 查询评论的数量 */ int selectCountByEntity(int entityId, int entityType); /** * 添加评论 * @param comment 评论对象 * @return 插入的行数 */ int insertComment(Comment comment); }二、在对应的 Mybatis 映射文件中添加方法对应的 Sql 语句:
<sql id="selectFields"> id, user_id, entity_type, entity_id, target_id, content, status, create_time sql> <sql id="insertFields"> user_id, entity_type, entity_id, target_id, content, status, create_time sql> <select id="selectCommentsByEntity" resultType="Comment"> select <include refid="selectFields">include> from comment where status = 0 and entity_id = #{entityId} and entity_type = #{entityType} order by create_time asc limit #{offset}, #{limit} select> <select id="selectCountByEntity" resultType="int"> select count(id) from comment where status = 0 and entity_id = #{entityId} and entity_type = #{entityType} select> <insert id="insertComment" parameterType="Comment" keyProperty="id"> insert into comment(<include refid="insertFields">include>) values (#{userId}, #{entityType}, #{entityId}, #{targetId}, #{content}, #{status}, #{createTime}) insert>三、在 Service 层新建一个 CommentService 的类:
@Service public class CommentService { @Autowired private CommentMapper commentMapper; public List<Comment> findCommentsByEntity(int entityId, int entityType, int offset, int limit) { return commentMapper.selectCommentsByEntity(entityId, entityType, offset, limit); } public int findCommentsCount(int entityId, int entityType) { return commentMapper.selectCountByEntity(entityId, entityType); } }在这个类中添加了分页查询以及查询评论数量的功能。分页查询返回的是一个 List 的类型,其中存储的是 Comment 评论的实体类。
四、在 DiscussPostController 控制层中添加显示帖子详情的方法,包括显示帖子的内容,显示该帖子对应的所有评论、用户的回复并且进行分页。
/** * 获取帖子详情,包括帖子详情、作者、帖子评论 * * @param id 帖子 ID * @param model model对象 * @return 帖子详情页面 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/detail/{discussPostId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getDiscussPost(@PathVariable("discussPostId") int id, Model model, Page page) { // 帖子详情 DiscussPost discussPost = discussPostService.findDiscussPostById(id); model.addAttribute("post", discussPost); // 帖子作者 User user = userService.findUserById(discussPost.getUserId()); model.addAttribute("user", user); // 评论分页信息 page.setLimit(5); page.setPath("/discuss/detail/" + id); page.setRows(discussPost.getCommentCount()); // 评论:帖子的评论 // 回复:评论的评论 // 评论列表 List<Comment> commentList = commentService.findCommentsByEntity(discussPost.getId(), ENTITY_TYPE_POST, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit()); // 评论 VO 列表 List<Map<String, Object>> commentVOList = new ArrayList<>(); if (commentList != null) { for (Comment comment : commentList) { Map<String, Object> commentVO = new HashMap<>(); commentVO.put("comment", comment); commentVO.put("user", userService.findUserById(comment.getUserId())); // 回复列表 List<Comment> replyList = commentService.findCommentsByEntity(comment.getId(), ENTITY_TYPE_COMMENT, 0, Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 回复 VO 列表 List<Map<String, Object>> replyVOList = new ArrayList<>(); if (replyList != null) { for (Comment reply : replyList) { Map<String, Object> replyVO = new HashMap<>(); // 回复 replyVO.put("reply", reply); // 回复者 replyVO.put("user", userService.findUserById(reply.getUserId())); // 回复的目标 User target = reply.getTargetId() == 0 ? null : userService.findUserById(reply.getTargetId()); replyVO.put("target", target); replyVOList.add(replyVO); } } commentVO.put("reply", replyVOList); // 回复数量 int commentsCount = commentService.findCommentsCount(comment.getId(), ENTITY_TYPE_COMMENT); commentVO.put("replyCount", commentsCount); commentVOList.add(commentVO); } } model.addAttribute("comments", commentVOList); return "/site/discuss-detail"; }对于显示帖子详情,尤其是显示帖子的评论,处理的关键点在于对于帖子的 Comment 的处理。处理帖子的详情,首先要将帖子的作者信息以及帖子的标题内容进行处理。使用 URL 将帖子的 ID 传入,之后使用根据 ID 查询到帖子对象,获得作者的 ID 查询到作者的其他信息即可。
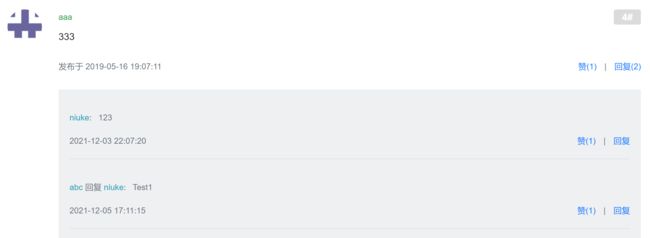
首先, Comment 分为两种类型,一种是对于帖子的直接评论,我们直接称之为评论;另一种,对于帖子的评论的回复,我们称为回复。创建一个 VOList 最终用于显示层中,List 中使用 Map 存储 Comment 对象中需要显示的数据。
一条评论包含的部分如图所示。其中,一条评论下可能包含多条回复,直接回复层主的帖子没有显示回复层级关系,回复其他用户则会显示回复逻辑关系。首先查询所有的评论(根据评论类型 Entity_Type 可以指定查询到的是帖子的评论) Comment 用 List 进行保存,然后遍历其中的 Comment ,之后根据评论的 ID (Entity_Id)和 Comment 的类型(指定为评论的回复,即“回复”)查询出这条评论对应有哪些回复,存放在一个
List对象中(这里的查询是一对多的查询,一条评论对应多个回复,是具有层级关系的,但是考虑到设计的复杂性以及效率,在 Comment 数据表中存储有冗余字段用来表示 Comment 的类型以及回复的对象等)。再指定一个List对象,查询回复对象中是否存在有效的 Target_Id 可以得知是否需要显示 “回复” 字样。根据 Map 对象,可以很轻松利用 Thymeleaf 从 Map 对象中取值渲染。<div class="container mt-3"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-8"> <h6><b class="square">b> <i th:text="${post.commentCount}">30i>条回帖h6> div> <div class="col-4 text-right"> <a href="#replyform" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm"> 回 帖 a> div> div> <ul class="list-unstyled mt-4"> <li class="media pb-3 pt-3 mb-3 border-bottom" th:each="cvo:${comments}"> <a href="profile.html"> <img th:src="${cvo.user.headerUrl}" class="align-self-start mr-4 rounded-circle user-header" alt="用户头像" > a> <div class="media-body"> <div class="mt-0"> <span class="font-size-12 text-success" th:utext="${cvo.user.username}">掉脑袋切切span> <span class="badge badge-secondary float-right floor"> <i th:text="${page.offset + cvoStat.count}">1i># span> div> <div class="mt-2" th:utext="${cvo.comment.content}"> 这开课时间是不是有点晚啊。。。 div> <div class="mt-4 text-muted font-size-12"> <span>发布于 <b th:text="${#dates.format(cvo.comment.createTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">2019-04-15 15:32:18b>span> <ul class="d-inline float-right"> <li class="d-inline ml-2"><a href="#" class="text-primary">赞(1)a>li> <li class="d-inline ml-2">|li> <li class="d-inline ml-2"><a href="#" class="text-primary">回复(<i th:text="${cvo.replyCount}">2i>)a>li> ul> div> <ul class="list-unstyled mt-4 bg-gray p-3 font-size-12 text-muted"> <li class="pb-3 pt-3 mb-3 border-bottom" th:each="rvo:${cvo.reply}"> <div> <span th:if="${rvo.target==null}"> <b class="text-info" th:text="${rvo.user.username}">寒江雪b>: span> <span th:if="${rvo.target!=null}"> <i class="text-info" th:text="${rvo.user.username}">sisii> 回复 <b class="text-info" th:text="${rvo.target.username}">寒江雪b>: span> <span th:utext="${rvo.reply.content}">这个是直播时间哈,觉得晚的话可以直接看之前的完整录播的~span> div> <div class="mt-3"> <span th:text="${#dates.format(rvo.reply.createTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">2019-04-15 15:32:18span> <ul class="d-inline float-right"> <li class="d-inline ml-2"><a href="#" class="text-primary">赞(1)a>li> <li class="d-inline ml-2">|li> <li class="d-inline ml-2"><a th:href="|#huifu-${rvoStat.count}|" data-toggle="collapse" class="text-primary">回复a>li> ul> <div th:id="|huifu-${rvoStat.count}|" class="mt-4 collapse"> <form method="post" th:action="@{|/comment/add/${post.id}|}"> <div> <input type="text" class="input-size" name="content" th:placeholder="|回复${rvo.user.username}|"/> <input type="hidden" name="entityType" value="2"> <input type="hidden" name="entityId" th:value="${cvo.comment.id}"> <input type="hidden" name="targetId" th:value="${rvo.user.id}"> div> <div class="text-right mt-2"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="#"> 回 复 button> div> form> div> div> li> ul> div> li> ul> div>添加评论
- 数据层
- 增加评论数据
- 修改帖子的评论数量
- 业务层
- 处理添加评论的业务
- 先增加评论,再更新帖子的评论数量
- 表现层
- 处理添加评论数据的请求
- 设置添加评论的表单
一、根据之前的评论数据表,在 DAO 层中添加新增评论的方法
/** * 添加评论 * @param comment 评论对象 * @return 插入的行数 */ int insertComment(Comment comment);二、在 DiscussPostMapper.xml 文件中添加对应的 sql 语句
<insert id="insertComment" parameterType="Comment" keyProperty="id"> insert into comment(<include refid="insertFields">include>) values (#{userId}, #{entityType}, #{entityId}, #{targetId}, #{content}, #{status}, #{createTime}) insert>三、在 Service 层中添加处理方法,同时需要修改 DiscussPost 表格中的 CommentCount 字段的数据
/** * 添加评论,需要保证在一个事务当中 * CommentService 层中 * @param comment 评论实体 * @return 添加的评论条数 */ @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public int addComment(Comment comment) { // 需要对评论的内容进行一些过滤 if (comment == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("评论不能为空!"); } // 过滤 html 标签 comment.setContent(HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(comment.getContent())); // 评论进行过滤 comment.setContent(sensitiveFilter.filter(comment.getContent())); // 添加评论 int rows = commentMapper.insertComment(comment); // 更新帖子评论数量 if (comment.getEntityType() == CommunityConstant.ENTITY_TYPE_POST) { int count = commentMapper.selectCountByEntity(comment.getEntityId(), comment.getEntityType()); discussPostService.updateCommentCount(comment.getEntityId(), count); } return rows; } public int updateCommentCount(int id, int commentCount) { return discussPostMapper.updateCommentCount(id, commentCount); }四、Controller 层处理添加评论
@Controller @RequestMapping("/comment") public class CommentController { @Autowired private CommentService commentService; @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; /** * 添加评论 * @param discussionPostId 帖子 ID * @param comment 评论实体对象 * @return 帖子详情页面,重定向 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/add/{discussPostId}", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String addComment(@PathVariable("discussPostId") int discussionPostId, Comment comment) { // 需要得知发表评论的用户,评论的类型,评论的对象 comment.setUserId(hostHolder.getUser().getId()); comment.setStatus(0); comment.setCreateTime(new Date()); commentService.addComment(comment); return "redirect:/discuss/detail/" + discussionPostId; } }之后再处理前端页面中的相关数据即可。
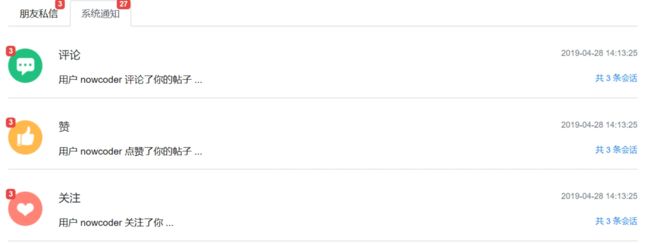
私信列表
- 私信列表
- 查询当前用户的会话列表,每个会话只显示一条最新的私信
- 支持分页显示
- 私信详情
- 查询某个会话所包含的私信
- 支持分页显示
私信列表的处理方法类似于帖子的详情列表的处理方式,主要处理逻辑都是创建一个 List 列表存储多个 Map 集合用来将各种需要渲染的信息保存,最后将 List 对象添加到 Model 对象中,编写好相应的 ThymeLeaf 表达式取值即可。
一、首先编写 MessageMapper 类接口
/** * 分页查询会话列表 * * @param userId * @param offset * @param limit * @return */ List<Message> selectConversations(int userId, int offset, int limit); /** * 查询用户会话数量 * * @param userId 用户 ID * @return 会话数量 */ int selectConversationsCount(int userId); /** * 查询一个会话中所有的私信列表 * * @param conversationId 会话 ID * @param offset 起始 * @param limit 分页数量 * @return 私信集合列表 */ List<Message> selectLetters(String conversationId, int offset, int limit); /** * 查询一个会话中消息的数量 * * @param conversationId 会话 ID * @return 数量 */ int selectedLetterCount(String conversationId); /** * 查询未读消息的数量,包含一个会话列表中的未读数量,该用户对应的所有私信的未读数量 * 在编写 Sql 的时候需要动态传递 conversationId ,决定使用哪一种 * * @param userId 用户 ID * @param conversationId 会话 ID * @return 私信列表中未读消息的数量 */ int selectLetterUnreadCount(int userId, String conversationId);二、编写相应的 mapper.xml 文件实现对应的 sql 语句
<sql id="selectFields"> id, from_id, to_id, conversation_id, content, status, create_time sql> <sql id="insertFields"> from_id, to_id, conversation_id, content, status, create_time sql> <select id="selectConversations" resultType="Message"> select <include refid="selectFields">include> from message where id in ( select max(id) from message where status != 2 and from_id != 1 and (from_id = #{userId} or to_id = #{userId}) group by conversation_id ) order by id desc limit #{offset}, #{limit} select> <select id="selectConversationsCount" resultType="int"> select count(m.maxid) from ( select max(id) as maxid from message where status != 2 and from_id != 1 and (from_id = #{userId} or to_id = #{userId}) group by conversation_id ) as m select> <select id="selectLetters" resultType="Message"> select <include refid="selectFields">include> from message where status != 2 and from_id != 1 and conversation_id = #{conversationId} order by id desc limit #{offset}, #{limit} select> <select id="selectedLetterCount" resultType="int"> select count(id) from message where status != 2 and from_id != 1 and conversation_id = #{conversationId} select> <select id="selectLetterUnreadCount" resultType="int"> select count(id) from message where status = 0 and from_id != 1 and to_id = #{userId} <if test="conversationId != null"> and conversation_id = #{conversationId} if> select>三、在 Service 层中编写对应的数据库操作方法
@Autowired private MessageMapper messageMapper; @Autowired private SensitiveFilter sensitiveFilter; public List<Message> findConversations(int userId, int offset, int limit) { return messageMapper.selectConversations(userId, offset, limit); } public int findConversationsCount(int userId) { return messageMapper.selectConversationsCount(userId); } public List<Message> findLetters(String conversationId, int offset, int limit) { return messageMapper.selectLetters(conversationId, offset, limit); } public int findLettersCount(String conversationId) { return messageMapper.selectedLetterCount(conversationId); } public int findLetterUnreadCount(int userId, String conversationId) { return messageMapper.selectLetterUnreadCount(userId, conversationId); }四、在 Controller 编写对应的页面请求处理逻辑
@Autowired private MessageService messageService; @Autowired private UserService userService; @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; /** * 显示私信列表 * 处理的时候应该判断用户是否登录,获取用户的一些状态 * * @param model model对象 * @param page 分页显示对象 * @return 私信列表页面 */ @LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/letter/list", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getLetterList(Model model, Page page) { // 获取用户对象 User user = hostHolder.getUser(); // 设置分页的一些信息 page.setLimit(5); page.setPath("/letter/list"); page.setRows(messageService.findConversationsCount(user.getId())); // 会话列表 List<Message> conversationsList = messageService.findConversations(user.getId(), page.getOffset(), page.getLimit()); List<Map<String, Object>> conversations = new ArrayList<>(); // 还需要显示的信息包含:未读消息总条数,单次会话消息的未读数量、总数量,会话对象相关信息 if (conversationsList != null) { for (Message message : conversationsList) { // 查询每一条消息的其他相关信息 Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("conversation", message); // 查询会话中消息的总数 map.put("letterCount", messageService.findLettersCount(message.getConversationId())); // 查询未读消息的数量 map.put("unreadCount", messageService.findLetterUnreadCount(user.getId(), message.getConversationId())); // 查询会话列表的目标用户 ID ,需要显示会话中对方的信息 int targetId = user.getId() == message.getFromId() ? message.getToId() : message.getFromId(); User targetUser = userService.findUserById(targetId); map.put("target", targetUser); conversations.add(map); } } model.addAttribute("conversations", conversations); // 查询用户未读消息总数量,显示在会话 header 位置 int letterUnreadCount = messageService.findLetterUnreadCount(user.getId(), null); model.addAttribute("letterUnreadCount", letterUnreadCount); return "/site/letter"; } /** * 处理会话列表的详情 * 显示一个会话中的所有对话信息,同时处理的时候取消未读消息 * * @param conversationId 会话 ID ,使用 URL 传递参数 * @param model model 对象 * @return 会话详情页面 */ @LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/letter/detail/{conversationId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getLetterDetail(@PathVariable("conversationId") String conversationId, Page page, Model model) { User user = hostHolder.getUser(); // 设置分页的一些参数 page.setRows(messageService.findLettersCount(conversationId)); page.setPath("/letter/detail/" + conversationId); page.setLimit(5); // 获取会话对象 List<Message> letters = messageService.findLetters(conversationId, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit()); List<Map<String, Object>> letterList = new ArrayList<>(); if (letters != null) { for (Message letter : letters) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); // int targetId = letter.getFromId() == user.getId() ? letter.getToId() : letter.getFromId(); // User target = userService.findUserById(targetId); // map.put("target", target); map.put("letter", letter); map.put("fromUser", userService.findUserById(letter.getFromId())); letterList.add(map); } } // 私信详情列表 model.addAttribute("letters", letterList); // 私信目标用户 model.addAttribute("target", getTargetUser(conversationId)); // 设置已读 List<Integer> unreadConversationId = getUnreadConversationId(letters); if (!unreadConversationId.isEmpty()) { messageService.readMessage(unreadConversationId); } return "/site/letter-detail"; }发送私信
- 发送私信
- 采用异步的方式发送私信
- 发送成功后刷新私信列表
- 设置已读
- 访问私信详情时,将显示的私信设置为已读状态
关键点:发送私信的方法应该使用 Ajax 的方式进行操作,避免频繁地进行全局刷新耗费数据库资源。
一、在 DAO 层编写数据库添加私信方法
/** * 插入私信,新增私信 * @param message message 对象 * @return 新增行数 */ int insertMessage(Message message); /** * 批量修改私信的状态 * @param ids 一次性修改多条私信,目标私信的 ID 列表 * @param status 修改的目标状态 * @return 修改行数 */ int updateStatus(List<Integer> ids, int status);二、在数据库中编写相应的 update 以及 insert 的 sql 语句
<insert id="insertMessage" parameterType="message" keyProperty="id"> insert into message(<include refid="insertFields">include>) values (#{fromId}, #{toId}, #{conversationId}, #{content}, #{status}, #{createTime}) insert> <update id="updateStatus" parameterType="int"> update message set status = #{status} where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{id} foreach> update>三、在 Service 层添加对应的数据操作,要注意私信需要经过敏感词过滤操作
public int findLetterUnreadCount(int userId, String conversationId) { return messageMapper.selectLetterUnreadCount(userId, conversationId); } public int addMessage(Message message) { // 需要对私信的内容进行过滤,避免影响用户阅读 message.setContent(HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(message.getContent())); message.setContent(sensitiveFilter.filter(message.getContent())); return messageMapper.insertMessage(message); } /** * 读取消息,将消息状态变为已读 * * @param ids 会话的 ID 集合 * @return 更新状态的行数 */ public int readMessage(List<Integer> ids) { return messageMapper.updateStatus(ids, 1); }四、在 Controller 层中添加处理逻辑
/** * 获取私信用户对象 * * @param conversationId 会话 ID * @return 对方用户 */ private User getTargetUser(String conversationId) { // conversationId 是使用双方的 id 中间拼接 _ 符号构成的 String[] split = conversationId.split("_"); int user1 = Integer.parseInt(split[0]); int user2 = Integer.parseInt(split[1]); // 获取当前登录的用户,返回对方用户 if (hostHolder.getUser().getId() == user1) { return userService.findUserById(user2); } else { return userService.findUserById(user1); } } /** * 获取集合中未读消息的状态 * * @param letters * @return */ private List<Integer> getUnreadConversationId(List<Message> letters) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if (letters != null) { for (Message letter : letters) { if (hostHolder.getUser().getId() == letter.getToId() && letter.getStatus() == 0) { // 只有当接收者是一个未读的状态,才会改变消息的状态 list.add(letter.getId()); } } } return list; } /** * 发送私信的方法 * * @param toName 发送的用户名 * @param content 发送的私信内容 * @return 发送之后的页面,刷新的私信列表 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/letter/send", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String sendLetter(String toName, String content) { User target = userService.findUserByName(toName); if (target == null) { return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(1, "目标用户不存在!"); } // 利用目标用户以及私信内容构建一个 Message 对象 Message message = new Message(); message.setFromId(hostHolder.getUser().getId()); message.setToId(target.getId()); message.setContent(content); message.setCreateTime(new Date()); if (message.getFromId() < message.getToId()) { message.setConversationId(message.getFromId() + "_" + message.getToId()); } else { message.setConversationId(message.getToId() + "_" + message.getFromId()); } messageService.addMessage(message); // 表示处理成功 return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0); }五、在前端中设置 ajax 的实现,发送数据要异步操作
function send_letter() { $("#sendModal").modal("hide"); let name = $("#recipient-name").val(); let text = $("#message-text").val(); $.post( CONTEXT_PATH + "/letter/send", {"toName":name,"content":text}, function (data) { data = $.parseJSON(data); if (data.code === 0) { $("#hintBody").text("发送成功!"); } else { $("#hintBody").text(data.message); } $("#hintModal").modal("show"); setTimeout(function(){ $("#hintModal").modal("hide"); location.reload(); }, 2000); } ); }统一异常处理
- @ControllerAdvice
- 用于修饰类,表示该类是 Controller 的全局配置类
- 在此类中,可以对 Controller 进行如下三种全局配置:
- 异常处理方案、绑定数据方案、绑定参数方案
- @ ExceptionHandler
- 用于修饰方法,该方法会在 Controller 出现异常后被调用,用于处理捕获到的异常
- @ ModelAttribute
- 用于修饰方法,该方法会在 Controller 方法执行前被调用,用于为 Model 对象绑定参数
- @DataBinder
- 用于修饰方法,该方法会在 Controller 方法执行前被调用,用于绑定参数的转换器
编写统一的异常处理,使用 @ControllerAdvice 注解统一对标注了 @Controller 注解的类进行统一处理,遇见异常直接使用 logger 进行异常信息记录。
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = Controller.class) // 规定只扫描标注了 Controller 注解的类 public class ExceptionAdvice { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionAdvice.class); /** * 处理异常情况 * * @param e exception 对象 * @param request 请求 * @param response 应答 */ @ExceptionHandler({Exception.class}) public void handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { logger.error("服务器发生异常:" + e.getMessage()); // 遍历发生异常之时的调用栈,并进行记录 for (StackTraceElement element : e.getStackTrace()) { logger.error(element.toString()); } // 判断请求的类型并且做出相应的处理 String requestHeader = request.getHeader("x-requested-with"); if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(requestHeader)) { // 表示该请求返回的是 JSON 格式的字符串 response.setContentType("application/plain;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter responseWriter = response.getWriter(); // 将异常信息输出给 response 对象 responseWriter.write(CommunityUtil.getJSONString(1, "服务器异常!")); } else { response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error"); } } }统一记录日志
统一记录日志,应该使用 AOP 来完成。该功能独立于业务功能之外,且属于系统级别集成的功能,使用 AOP 来实现可以降低耦合性,更容易进行扩展。
之前的记录日志,分为两种:① 直接在各个类中添加 Logger 对象,然后记录 Exception 级别的日志; ② 使用拦截器对所有的请求进行拦截,然后使用 Logger 进行日志记录。第一种方式比较繁琐,而且高耦合;第二种方式仅限针对 Controller 中的方法,并没有对 Service 以及 DAO 进行覆盖。所以使用 AOP 对于业务层代码进行切面,集成日志,分割了业务层代码和系统级功能代码是一种合适的解决方案。
AOP 的术语简介:
AOP 的实现方式分为两种:
- AspectJ
- AspectJ 是语言级的实现,它扩展了 Java 语言,定义了 AOP 语法
- AspectJ 在编译期织入代码,它有一个专门的编译器,用来生成遵守 Java 字节码规范的 class 文件
- Spring AOP
- Spring AOP 使用纯 Java 实现,它不需要专门的编译过程,也不需要特殊的类装载器
- Spring AOP 在运行时通过代理的方式织入代码,只支持方法类型的连接点
- Spring 支持对 AspectJ 的集成
AOP 的原理: AOP 是通过动态代理实现的。
- JDK 动态代理
- Java 提供的动态代理技术,可以在运行时创建接口的代理实例
- Spring AOP 默认采用此种方式,在接口的代理实例中织入代码
- CGLib 动态代理
- 采用底层的字节码技术,在运行时创建子类代理实例
- 当目标对象不存在接口时, Spring AOP 会采用此种方式,在子类实例中织入代码
统一记录日志,主要依赖于 AOP 中的 AspectJ 实现方式。
要实现对于 Service 层中的所有方法的访问进行记录,实现步骤:① 针对 Service 中的所有方法进行切点; ② 对切点进行增强, 标注 @Before 或者 @After 注解进行记录。
@Component @Aspect public class ServiceLogAspect { public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceLogAspect.class); @Pointcut("execution(* com.nowcoder.community.service.*.*(..))") public void pointcut() { } @Before("pointcut()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { // 记录格式:用户[1.2.3.4]在[HH:mm:ss]访问了[com.nowcoder.community.service.xxx()]功能 ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); HttpServletRequest request = requestAttributes.getRequest(); String host = request.getRemoteHost(); String date = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()); String method = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); logger.info(String.format("用户[%s],在[%s],访问了[%s]", host, date, method)); } }切点在进行配置的时候,使用的是 execution 表达式进行匹配。第一个
*代表的是方法的返回值类型,匹配任意类型;后面写的是方法的全限定名,*表示匹配任意路径;最后一个*代表的是任意的方法名,后面的(..)匹配的是任意数量任意类型的参数列表。七、Redis 优化
Redis 入门
- Redis 是一款基于键值对的 NoSQL 数据库,它的值支持多种数据结构:字符串(strings)、哈希(hashes)、列表(lists)、 集合(sets)、 有序集合(sorted sets)等
- Redis 将所有的数据都存放在内存中,所以它的读写性能十分惊人。同时,Redis 还可以将内存中的数据以快照或日志的形式保存到硬盘上,以保证数据的安全性
- Redis 典型的应用场景包括:缓存、排行榜、计数器、社交网络、消息队列等
启动的时候,在本机上直接点击 redis-server.exe 会直接闪退,正确的打开方式为:
在文件管理中输入 cmd D:\Java\Redis-x64-3.2.100 ,之后弹出 cmd 窗口,在窗口中输入 redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf 指令即可正常运行。Spring 整合 Redis
-
引入依赖
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis
-
配置 Redis
- 配置数据库参数
- 编写配置类,构造 RedisTemplate
-
访问Redis
-
redisTemplate.opsForValue()
-
redisTemplate.opsForHash()
-
redisTemplate.opsForList()
-
redisTemplate.opsForSet()
-
redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
-
一、导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId> dependency>二、进行配置
编写 Redis 配置参数
spring: # redis 配置 redis: database: 11 host: localhost port: 6379编写 Redis 配置类
@Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory); // 设置 key 的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string()); // 设置 value 的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.json()); // 设置 hash 的 key 序列化方式 redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string()); // 设置 hash 的 value 序列化方式 redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.json()); // 触发参数生效 redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } }三、访问 Redis ,使用 Spring Boot 整合 redis 的方式访问
@SpringBootTest @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class) public class RedisTests { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Test public void testStrings() { String redisKey = "test:count"; redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(redisKey, 1); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(redisKey)); } @Test public void testHashes() { String redisKey = "test:user"; redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(redisKey, "id", 1); redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(redisKey, "username", "zhangsan"); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(redisKey, "id")); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(redisKey, "username")); } @Test public void testLists() { String redisKey = "test:ids"; redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(redisKey, 101); redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(redisKey, 102); redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(redisKey, 103); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().size(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().index(redisKey, 0)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().range(redisKey, 0, 2)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(redisKey)); } @Test public void testSets() { String redisKey = "test:teachers"; redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(redisKey, "张三", "李四", "王五"); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForSet().pop(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(redisKey)); } @Test public void testZSets() { String redisKey = "test:students"; redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(redisKey, "张三", 30); redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(redisKey, "李四", 40); redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(redisKey, "王五", 50); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().size(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(redisKey)); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(redisKey, "张三")); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rank(redisKey, "张三")); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRank(redisKey, "张三")); System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().range(redisKey, 0, 1)); } @Test public void testKeys() { redisTemplate.delete("test:user"); System.out.println(redisTemplate.hasKey("test:user")); redisTemplate.expire("test:student", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } /** * 测试多次访问同一个 Key */ @Test public void testBoundOperations() { String redisKey = "test:count"; BoundValueOperations operations = redisTemplate.boundValueOps(redisKey); operations.increment(); operations.increment(); operations.increment(); operations.increment(); operations.increment(); System.out.println(operations.get()); } @Test public void testTransactional() { Object execute = redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() { @Override public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException { String redisKey = "test:tx"; operations.multi(); operations.opsForSet().add(redisKey, "zahngsan"); operations.opsForSet().add(redisKey, "lisi"); operations.opsForSet().add(redisKey, "wangwu"); System.out.println(operations.opsForSet().members(redisKey)); return operations.exec(); } }); System.out.println(execute); } }直接 redisTemplate 模板对象提供的方法,可以针对五种基本数据类型进行各种操作。
点赞功能
- 点赞
- 支持对帖子、评论点赞
- 第一次点赞,第二次取消点赞
- 首页点赞数量
- 统计帖子的点赞数量
- 详情页点赞数量
- 统计点赞数量
- 显示点赞状态
点赞功能属于一个高频实时的功能,使用 redis 能够实现低延迟高性能,如果使用 MySQL 则会导致表的 IO 次数过高,用 Redis 读取内存比 MySQL 读硬盘更快。在数据库上挑选 Redis 能够实现比 MySQL 效率更高、性能更好的结果。
设计使用的 Redis 数据结构,对于点赞功能,我们需要得知一个用户对于一个实体(帖子/评论/回复)是否进行了点赞操作,以此来对应界面上的点赞按钮的显示以及点赞数量的显示。所以针对这样的情况,使用 Set 集合保存对于某个实体对象的点赞用户 ID ,保存的是点赞的用户 ID 。需要得知用户是否进行了点赞,只需要对 Redis 中该对象的 Set 集合查询,存在 ID ,则代表进行过点赞;没有则代表未点赞。实体的点赞数量,则查询 set 集合的元素个数即可。
like:entity:entityType:entityId -> set(userId)这样的设计,可以很轻松查询点赞的用户有哪些以及添加点赞的用户、查询点赞的状态。
点赞的功能一共涵盖三处:对帖子进行点赞,对评论进行点赞,对评论的回复进行点赞。
在点赞的时候,我们需要知道点赞的目标对象、点赞的状态、点赞的数量。
设计一个新的 Service 类,用于处理点赞的业务。
@Service public class LikeService { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /** * 点赞功能,包括对评论/回复点赞,也包括对用户的点赞 * * @param userId 点赞的执行者 * @param entityType 点赞目标的类型:帖子/评论 * @param entityId 点赞目标的 ID * @param entityUserId 实体的作者 ID ,要查询用户主页的点赞数量 */ public void like(int userId, int entityType, int entityId, int entityUserId) { redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() { @Override public Object execute(RedisOperations redisOperations) throws DataAccessException { String entityLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getEntityLikeKey(entityType, entityId); String userLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserLikeKey(entityUserId); // 查询不能放在事务中,需要将查询放在事务之外 Boolean isMember = redisOperations.opsForSet().isMember(entityLikeKey, userId); redisOperations.multi(); if (isMember) { // 如果存在该用户点赞的记录,再次点赞应该是取消点赞了 redisOperations.opsForSet().remove(entityLikeKey, userId); redisOperations.opsForValue().decrement(userLikeKey); } else { // 不存在点赞记录,则应该向列表中添加点赞记录(记录的是点赞的用户名单) redisOperations.opsForSet().add(entityLikeKey, userId); redisOperations.opsForValue().increment(userLikeKey); } return redisOperations.exec(); } }); } /** * 查询实体被点赞的数量 * * @param entityType 实体类型:帖子/评论 * @param entityId 实体 ID * @return 实体被点赞的数量 */ public long findEntityLikeCount(int entityType, int entityId) { String entityLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getEntityLikeKey(entityType, entityId); // 返回 Key 值对应的 Value 的数量:存取的是点赞的用户 ID return redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(entityLikeKey); } /** * 查询某个人对于某个帖子是否进行了点赞/踩/无操作 * * @param userId 用户 ID * @param entityType 实体类型 * @param entityId 实体 ID * @return 状态对应的 ID 值, 1 对应点赞, 0 对应无操作, -1 对应踩 */ public int findEntityLikeStatus(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) { String entityLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getEntityLikeKey(entityType, entityId); Boolean isMember = redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(entityLikeKey, userId); return isMember ? 1 : 0; } /** * 查询某个用户获得的赞的数量 * 查询的逻辑是该用户拥有多少个赞,包括发帖/评论获得的赞 * * @param userId 用户 ID * @return 收到赞的个数 */ public int findUserLikeCount(int userId) { String userLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserLikeKey(userId); Integer count = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(userLikeKey); return count == null ? 0 : count; } }在处理完点赞的业务层之后,我们需要将点赞的数据渲染到页面上,这就需要我们编写一个新的控制层来处理点赞的业务了。
@Controller public class LikeController { @Autowired private LikeService likeService; @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; @Autowired private EventProducer eventProducer; /** * 点赞功能的实现 * * @param entityType 实体类型 * @param entityId 实体 ID * @return JSON 字符串,返回点赞数量以及用户的点赞状态 */ @LoginRequired @RequestMapping(path = "/like", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String like(int entityType, int entityId, int entityUserId, int postId) { User user = hostHolder.getUser(); // 点赞 likeService.like(user.getId(), entityType, entityId, entityUserId); // 获取点赞数量以及点赞状态 long likeCount = likeService.findEntityLikeCount(entityType, entityId); int likeStatus = likeService.findEntityLikeStatus(user.getId(), entityType, entityId); // 封装 JSON 字符串 Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("likeCount", likeCount); map.put("likeStatus", likeStatus); // 触发点赞事件,点赞触发通知,取消不触发 if (likeStatus == 1) { Event event = new Event() .setTopic(CommunityConstant.TOPIC_LIKE) .setUserId(hostHolder.getUser().getId()) .setEntityType(entityType) .setEntityId(entityId) .setEntityUserId(entityUserId) .setData("postId", postId); eventProducer.fireEvent(event); } return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, null, map); } }用户收到的赞
- 重构点赞功能
- 以用户为 key ,记录点赞数量
- increment(key) , decrement(key)
- 开发个人主页
- 以用户为 key ,查询点赞数量
用户收到的赞统计的是该用户的帖子以及评论收到的点赞数量之和,统计的是该用户所有操作被点赞的数量。在之前的点赞功能中,传递的只有点赞的用户以及实体类型、实体 ID ,并不包含被点赞的用户。要想实现统计用户被点赞的数量,就需要将实体的发布者 ID 传入,并且点赞与统计用户被点赞的数量两个操作需要并入同一个事务之间进行处理,否则将会出现问题。
关注/取关
- 需求
- 开发关注、取消关注功能
- 统计用户的关注数、粉丝数
- 关键
- 若 A 关注了 B ,则 A 是 B 的 Follower (粉丝), B 是 A 的 Followee (目标)
- 关注的目标可以是用户、帖子、题目等,在实现时将这些目标抽象为实体。
用户在进行使用社区的时候,肯定会存在关注用户与取关用户的操作。这部分操作在平时的使用中频率比较高,且对时效性的要求也比较高,使用 Redis 来完成这一部分功能是一个非常不错的选择。
要想完成关注与取关,必须要得知的两个因素:用户与关注对象。传入的参数也包含这两个,以用户 ID 为主键,关注列表中存储关注对象的用户 ID ,这样设计既可以比较方便的得知关注的对象是哪些,也可以比较及时统计出关注的用户数量。
要设计关注与取关的 Redis 数据格式,需要了解关注与取关的功能组成。关注与取关功能一共存在两个 Set 集合。第一个包括用户关注了哪些对象,第二个包含的是哪些人关注了用户;分别对应“偶像”列表与“粉丝”列表。
设计的 Redis 的 Key 结构分别为:
构造某个用户关注的实体对象的 Key 值,按照时间排序 格式:followee:userId:entityType -> zset(entityId,now) 某个实体的粉丝数量,按照时间排序 格式:follower:entityType:entityId -> zset(userId, now)存储的 Value 值均为用户 ID ,表示具体的用户。在关注和取关操作的时候要注意事务操作,关注列表和粉丝列表需要同时进行更新。
关注/粉丝列表
- 业务层
- 查询某个用户关注的人,支持分页
- 查询某个用户的粉丝,支持分页
- 表现层
- 处理"查询关注的人”、“查询粉丝” 请求
- 编写“查询关注的人”、“查询粉丝” 模板
优化登录模块
- 使用 Redis 存储验证码
- 验证码需要频繁的访问与刷新,对性能要求较高
- 验证码不需永久保存,通常在很短的时间后就会失效
- 分布式部署时,存在 Session 共享的问题
- 使用 Redis 存储登录凭证
- 处理每次请求时,都要查询用户的登录凭证,访问的频率非常高
- 使用 Redis 缓存用户信息
- 处理每次请求时,都要根据凭证查询用户信息,访问的频率非常高
注意验证码暂存在 redis 中的时候,设置了一个生效时间,我们在处理的时候需要将前台的验证码按时间也进行刷新。
function refresh_kaptcha() { var path = CONTEXT_PATH + "/kaptcha?p=" + Math.random(); $("#kaptcha").attr("src", path); } setInterval(refresh_kaptcha, 120000);设置刷新每 120s 刷新一次,无限循环刷新。这样前台的验证码显示的就是在当前时间内可用的验证码,只要用户当前点击登录的时候,框内的验证码和验证码图片一致,不会出现用户输入的验证码失效的情况。
缓存登录凭证的时候,使用 String 类型存储对象序列化字段。这样的存储方式与 MySQL 存储字段相比,都能实现需求,且 Redis 更快的查询效率能够适配更多场景。
八、 Kafka 异步消息队列
在整个项目中,有系统级别的用户通知,而且消息积累,是按照发送时间堆积的。所以使用队列来优化这一部分是比较合适的。可以利用 Queue 的数据结构来存放系统通知。
阻塞队列
- BlockingQueue
- 解决线程通信的问题
- 阻塞方法:put 、 take
- 生产者消费者模式
- 生产者:产生数据的线程
- 消费者:使用数据的线程
- 实现类
- ArrayBlockingQueue
- LinkedBlockingQueue
- PriorityBlockingQueue、SynchronousQueue、 DelayQueue 等
Kafka 入门
- Kafka 简介
- Kafka 是一个分布式的流媒体平台
- 应用:消息系统、日志收集、用户行为追踪、流式处理
- Kafka 特点
- 高吞吐量、消息持久化、高可靠性、高扩展性
- Kafka 术语
- Broker、Zookeeper
- Topic、Partition、 Offset
- Leader Replica、Follower Replica
Kafka 下载地址:Apache Downloads
Kafka 主要被用来充当消息队列,可以处理 TB 级别的数据量。原因是对比于传统的阻塞队列, Kafka 可以将消息进行持久化操作,存储到硬盘中。虽然内存的速度普遍要快于硬盘,但是因为 Kafka 对于持久化消息的特殊处理,持久化的消息在硬盘上是有序的。所以 Kafka 对于硬盘上的持久化的消息可以顺序读写,相比于对内存的随机读写,硬盘的顺序读写速度并不比内存相差很大。
下载完成之后,对压缩文件进行解压缩处理。
打开 config 目录下的 zookeeper.properties 文件以及 server.properties 文件,分别修改其中的属性:
dataDir=D:/Java/IdeaProjects/community/log/zookeeper log.dirs=D:/Java/IdeaProjects/community/log/kafka-logs修改的目的是修改其日志以及数据文件的存放目录。
配置完成之后,进入到 kafka_2.13-3.0.0 目录下,启动 cmd 窗口,指定以 zookeeper.properties 配置文件启动 zookeeper 服务:
bin\windows\zookeeper-server-start.bat config\zookeeper.properties启动完成会有相应的提示。
启动 kafka 的方式也类似,进入到安装目录之后,输入 bin\windows\kafka-server-start.bat config\server.properties 启动 kafka ,之后报错:提示 ERROR Disk error while writing log start offsets checkpoint in directory 。查询解决方法,两种可能:① jdk 版本过低(安装的 14 ,原因除外);② 更换 Kafka 版本,按照提示,更换成 kafka_2.12-2.8.1 版本。下载链接:https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.8.1/kafka_2.12-2.8.1.tgz ,下载之后,修改两个配置文件,重新启动 zookeeper 以及 Kafka ,启动成功。
成功启动在末尾可以看到 started 的字样,启动命令:
bin\windows\kafka-server-start.bat config\server.properties之后再启动一个 cmd 窗口,进入 Kafka 安装目录下的 \bin\windows 目录,输入
kafka-topics.bat --create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic test参数意义:–replication-factor 指的是主题的副本数量,副本位于集群中不同的 Broker 上,也就是该参数的大小不能超过 Broker 的数量,否则会创建失败。 partitions 指的是主题分区数量, Kafka 通过分区策略,将不同的分区分配在一个集群的 Broker 上,通常会是不同的 Broker 。分区数量越多,可以提高 Kafka 的并发执行能力,提高一定的吞吐量。
创建一个名为 test 的主题,之后可以使用
--list命令指定查看哪一台机器上的主题。创建主题,就相当于创建了一个消息队列。此时我们就可以向这个 test 的主题中发送生产者消息了。发送消息使用指令:
kafka-console-producer.bat --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test之后会出现
>符号,我们直接输入需要发送的消息即可:消息队列中的消息要想消费,也需要相应的操作,我们再启动一个窗口,输入指令消费消息队列中的消息:
kafka-console-consumer.bat --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test --from-beginning在此之后,我们在生产者中输入新的消息,消费者窗口就能同步查看到同样的消息。测试发现,目前只能直接发送英文消息,输入中文会造成编码错误,源于 GBK 字符集与 Unicode 字符集之间的转换问题。
其中出现问题, zk 启动报错: Unexpected exception exiting abnormally java.io.eofexception 。解决方法:找到 zoo.conf 中配置的 dataDir 和 dataLogDir 路径,然后删除两个文件夹下的 version -2 文件夹,重新启动即可。
Spring 整合 Kafka
- 引入依赖
- spring-kafka
- 配置 Kafka
- 配置 server 、 consumer
- 访问 Kafka
- 生产者:
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, data) ; - 消费者:
@KafkaListener(topics={"test"})
public void handleMessage(ConsumerRecord record)
- 生产者:
一、导入 Kafka 依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kafkagroupId> <artifactId>spring-kafkaartifactId> dependency>二、配置 Kafka 相关参数,在 application.yml 文件中进行配置:
spring: # Kafka 配置 kafka: bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092 consumer: group-id: community-consumer-group enable-auto-commit: true auto-commit-interval: 3000其中,group-id 配置的是消费者的分组 Id ,这个 ID 位于 Kafka 安装目录配置文件下的 consumer.properties 文件中,我们根据项目将其进行修改即可。维持两者一致即可。另外两个参数配置的是自动提交与否和自动提交的时间间隔。
三、编写测试类
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener; import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; /** * @author : Real * @date : 2021/12/11 15:22 * @description : Kafka 测试类 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest @ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class) public class KafkaTests { @Autowired private KafkaProducer kafkaProducer; @Test public void testKafka() throws InterruptedException { kafkaProducer.sendMessage("test", "Hello, World!"); Thread.sleep(10000); } } @Component class KafkaProducer { @Autowired private KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate; public void sendMessage(String topic, String content) { kafkaTemplate.send(topic, content); } } @Component class KafkaConsumer { @KafkaListener(topics = {"test"}) public void handleMessage(String message) { System.out.println(message); } }编写完测试类,运行的时候发生以下错误:
java: 程序包org.apache.kafka.clients.producer不存在。
经检查,发现并不存在导错依赖的情况,因为只需要导一个依赖。后面经过 IDEA 中的 Maven 管理,clean compile install 均得不到解决。最后查询得知解决方法,文件管理中前往项目的文件夹下,运行 cmd 指令:mvn idea:module可以重新将丢失的包文件加载进来。这个操作会重新编译 Maven 工程,整个时间大约持续半分钟,相比 IDEA 中自带的时间要长了不少,但是能够解决问题。 IDEA 中进行缓存清理、重新 clean install 等操作均不能解决。
最后运行结果:
发送系统通知
- 触发事件
- 评论后,发布通知
- 点赞后,发布通知
- 关注后,发布通知
- 处理事件
- 封装事件对象
- 开发事件的生产者
- 开发事件的消费者
在整个项目中,对于自己发布的帖子、评论、回复等,收到点赞或回复,系统会给用户发送通知,提醒被其他用户点赞;包括用户新增粉丝,系统同样会发送通知,我们使用 Kafka 来完成系统通知整个模块。
系统通知的形式比较相似,我们直接利用一个方法将所有类型的通知全部抽象起来。
分为三种类型的通知:评论、点赞、关注。我们利用不同的 Topic 处理不同的通知消息。
显示系统通知
- 通知列表
- 显示评论、点赞、关注三种类型的通知
- 显示页面中,显示的是每一种通知的最新消息,每一类型的通知的数量
- 通知详情
- 分页显示某一类主题所包含的通知
- 未读消息
- 在页面头部显示所有的未读消息数量
九、Elasticsearch 分布式搜索
Elasticsearch 是一款分布式搜索引擎,可以实现实时搜索,支持处理 PB 级别的数据
Elasticsearch 入门
- Elasticsearch 简介
- 一个分布式的、 Restful 风格的搜索引擎
- 支持对各种类型的数据的检索
- 搜索速度快,可以提供实时的搜索服务
- 便于水平扩展,每秒可以处理 PB 级海量数据
- Elasticsearch 术语
- 索引、类型、文档、字段
- 集群、节点、分片、副本
官方网站:Elasticsearch:官方分布式搜索和分析引擎 | Elastic
推荐下载 6.4.3 版本:Elasticsearch 6.4.3 | Elastic一、下载和安装
根据提供的网站下载好对应的系统版本,解压缩即可。
二、配置
进入到安装目录下的 config 目录中,打开 elasticsearch.yml 文件,配置其中的集群名字、data 数据文件夹、 logs 文件夹:
cluster.name: community path.data: D:\Java\IdeaProjects\community\log\Elaticsearch-6.4.3\data path.logs: D:\Java\IdeaProjects\community\log\Elaticsearch-6.4.3\logsES 在启动的时候,默认申请 1G 的内存空间,我们可以指定分配的内存大小,打开 config 目录下的 jvm.options 文件,修改其中的参数:
第一个调整的是初始内存,第二个调整的是最大内存。分别调小一点就可以。
三、分词插件
由于中文词义比较复杂,搜索的时候分词并不像英文一样以空格为分隔。所以需要将中文检索词进行分词,需要下载一个分词插件。分词插件为 IK 分词插件。
下载地址:GitHub - medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik: The IK Analysis plugin integrates Lucene IK analyzer into elasticsearch, support customized dictionary.
下载之后,将文件解压缩到 ES 安装目录的 plugins 目录中,在此新建一个 ik 文件夹,解压缩至此即可。注意需要新建一个文件夹,之后再将插件解压缩,否则会出现错误。
IK 分词插件是根据 config 目录下的 dic 词典文件进行分词操作的,但是因为新词语的出现,原有的词典并不一定能满足所有需要。用户可以在 config 目录下的 IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml 文件中自己配置一些新的词语。
之后,我们需要安装 postman 软件,使用 postman 软件对其中的一些功能进行测试。
下载地址:Download Postman | Get Started for Free
启动 ElasticSearch 的时候,出现了一些错误。
An exception was caught and reported. Message: access denied ("java.lang.RuntimePermission" "accessClassInPackage.jdk.internal.vm.annotation") at _unknown_查找原因得知,错误发生的原因是 jdk 版本过高,导致 ElasticSearch 不兼容。之后重新装上 JDK 11,配置好新的 Java 环境变量,重新启动 ES ,最后启动成功。
启动成功的运行状态:
可以从中看到,ES 默认占用端口 9200 。
由于已经调整 ES 占用内存为默认的 1G 内存,打开任务管理器可以看到非常高的内存占用。
现在就可以直接使用命令行查看 ES 的一些状态了。
D:\Java\elasticsearch-6.4.3\bin>进入 bin 目录下,输入命令行查看 ES 的健康状态。
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/health?v"
输入命令行查看 ES 的节点状态。
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v"输入命令行查看 ES 的索引。
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"这种状态表示没有索引存在。
创建索引命令:
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/test"表示在 localhost:9200 这台机器上创建一个名为 test 的索引。
再次输入命令查看索引,可以看到:
输入指令删除索引。
curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/test"再次查询就不存在 test 索引了。
同样,我们可以利用 postman 发送不同的 web 请求,包括 GET 、PUT 、 DELETE 等。测试的方法以及结果与命令行的结果一样,只是测试流程会更加简单。
发送创建索引的请求:
发送删除索引的请求:
我们现在需要往索引中插入数据,指定提交的路径之后,我们添加 JSON 格式的字符串即可。
PUT 请求的路径格式:【localhost:9200/test/_doc/1】端口号 / 索引名 / 类型 / ID ,之后我们在 Body 中添加 JSON 格式的字符串,添加完毕之后发送请求,可以得到:
{ "_index": "test", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 0, "_primary_term": 1 }查询该数据,只需要将请求类型修改为 GET 即可,一样的请求路径,得到:
删除数据与查询一致,只需要将请求方式修改为 DELETE 即可,返回的结果为删除操作成功与否的提示。
至此,对于 ES 的操作,我们可以大致了解到步骤:创建索引,之后向索引中添加索引,并且针对这些索引中的内容进行增删改查。
我们可以创建更多的 _doc 类型的数据,添加更多的文字信息。使用命令可以进行搜索指定关键字、指定位置(标题/内容)。
使用查询命令,可以查到标题中有关键字的数据:
localhost:9200/test/_search?q=title:互联网我们可以从查询结果中的 hits 列中看到命中的数据:
如果我们既要针对标题也要针对内容进行匹配,就需要更复杂的操作。在 Body 中提交 JSON 字符串数据,发送一些更加复杂的请求命令。
{ "query":{ "multi_match":{ "query":"互联网", "fields":["title","content"] } } }这样的请求方式,我们就既可以查到标题中有关键字的数据,也可以查到内容中有关键字的数据。
Spring 整合 ElasticSearch
- 引入依赖
- spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch
- 配置 Elasticsearch
- cluster-name、cluster-nodes
- Spring Data Elasticsearch
- ElasticsearchTemplate
- ElasticsearchRepository
一、引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearchartifactId> dependency>二、有些版本需要处理 Netty 与 ES 的启动冲突
在 Spring Boot 项目的启动类中添加一个后置构造方法,如下:
/** * 解决 Netty 和 ES 的启动冲突,设置初始化后置方法 */ @PostConstruct public void init() { // 解决 Netty 启动冲突 // see Netty4Utils.setAvailableProcessors System.setProperty("es.set.netty.runtime.available.processors", "false"); }三、配置 ES 的一些参数
# ElasticSearch Properties 配置 spring: data: elasticsearch: cluster-name: community cluster-nodes: localhost:9300四、在需要搜索的实体类上加以改造,将数据添加进 ES 服务器中。
@Document(indexName = "discusspost", type = "_doc" ,shards = 6, replicas = 3) public class DiscussPost { /** * 帖子 ID */ @Id private int id; /** * 发表帖子用户 ID */ @Field(type = FieldType.Integer) private int userId; /** * 帖子标题,设置存储时候的解析器以及 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word", searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart") private String title; /** * 帖子内容 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word", searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart") private String content; /** * 帖子类型 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Integer) private int type; /** * 帖子状态 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Integer) private int status; /** * 帖子创建时间 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Date) private Date createTime; /** * 帖子评论数量,这里直接存储不关联其他表是为了避免频繁的查询 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Integer) private int commentCount; /** * 帖子分数 */ @Field(type = FieldType.Double) private double score; }其余的 Get 以及 Set 方法不需要做任何的修改。在想要添加进检索的字段上添加注解 @Field 即可,指定字段的类型。
五、编写 ES 需要的接口 DiscussPostRepository 接口
/** * @author : Real * @date : 2021/12/13 17:43 * @description : 创建 DiscussPost 的接口供 ES 使用 * 泛型声明为 数据类型 + 主键数据类型 */ @Repository public interface DiscussPostRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<DiscussPost, Integer> { }接口需要继承自特定的接口,泛型选择的添加进的实体类型以及主键类型。
六、解决 ES 与 Netty 的启动冲突
在启动类中添加后置构造增强方法,设置固定的参数@SpringBootApplication @EnableElasticsearchRepositories(basePackages = "com.nowcoder.community.elasticsearch") public class CommunityApplication { /** * 解决 Netty 和 ES 的启动冲突,设置初始化后置方法 */ @PostConstruct public void init() { // 解决 Netty 启动冲突 // see Netty4Utils.setAvailableProcessors System.setProperty("es.set.netty.runtime.available.processors", "false"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(CommunityApplication.class, args); } }七、创建测试类进行测试
遇到的问题:因为 Spring Boot 版本不一致问题,导致导入的 ES 版本无法和本地安装的 ES 进行配置。在实体类上标注 type 属性找不到该 value 值,最后在 maven 仓库找到教程中 2.1.5 版本的 Spring Boot 对应的 ES 依赖版本为 3.1.8.RELEASE 版本,在 ES 依赖上标注即可。
查找版本对应的关系可以在网站:Maven Repository: org.springframework.boot » spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch » 2.1.5.RELEASE (mvnrepository.com) 找到。
重新配置版本依赖之后,依然会出现 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name ‘discussPostRepository’ 错误的提示。更换 Spring Boot 的版本为 2.1.5.RELEASE 版本。之后出现插件加载错误:Cannot resolve plugin org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-site-plugin:3.7.1 提示。解决办法:向 pom.xml 文件中添加依赖:
org.apache.maven.plugins maven-site-plugin 3.7.1 重新下载一下指定的依赖。
之后还是发生了依赖错误的问题,最终降级 Spring Boot 版本,将 Spring Boot 版本降级到 2.1.5.RELEASE 得以解决。降级的时候不只修改
之后测试的时候又出现错误:mapper [createTime] of different type, current_type [long], merged_type [date] 导致整个服务不能正常启动。查看提示发现是类型不匹配导致的,但是检查发现实体类代码不存在错误。clean install 清除缓存都尝试了之后还是不行,最后重新启动 ES 服务器,通过 postman 将已经存在的 ES 索引删除,之后重新进行测试,成功!
原因:ES 中的索引和映射发生了改变
解决:删除 ES 中已经存在的索引和映射,重新导入至此,ES 导致的错误全部解决了。
社区搜索功能
- 搜索服务
- 将帖子保存至 Elasticsearch 服务器
- 从 Elasticsearch 服务器删除帖子
- 从 Elasticsearch 服务器搜索帖子
- 发布事件
- 发布帖子时,将帖子异步的提交到 Elasticsearch 服务器
- 增加评论时,将帖子异步的提交到 Elasticsearch 服务器
- 在消费组件中增加一个方法,消费帖子发布事件
- 显示结果
- 在控制器中处理搜索请求,在 HTML 上显示搜索结果
十、 Spring Security 应用安全
在整个项目中,我们可以使用 Spring Security 框架来保证 Web 的应用安全性。
Spring Security 入门
- 简介
- Spring Security 是一个专注于为Java应用程序提供
- 身份认证和授权的框架,它的强大之处在于它可以轻松扩展以满足自定义的需求
- 特征
- 对身份的认证和授权提供全面的、可扩展的支持
- 防止各种攻击,如会话固定攻击、点击劫持、 csrf 攻击等
- 支持与 Servlet API 、 Spring MVC 等 Web 技术集成
在 Java EE 体系以及 Spring 的体系中,过滤器、拦截器之间的关系如下:
在实际实现中, Spring Security 算是底层非常复杂的,因为涉及到的层面比较多。
参考网站:Spring Cloud 从入门到精通 | 程序猿DD (didispace.com)
社区 Spring Security 从入门到进阶系列教程 | Spring For All (spring4all.com)
可以从 Spring4all 社区进行相关资料的查看。Spring Security 一旦引入,即刻生效,会对整个系统的安全进行管理。
重定向和转发
重定向:
服务器原先的组件推荐浏览器重新去请求新的组件,浏览器开始新的请求,避免组件之间产生直接耦合。相当于是两次请求,且两者之间没有直接的关联,所以在传递参数的时候略微复杂。
弊端在于 A 组件与 B 组件之间不方便传数据,要想实现数据之间的传输,需要使用 Cookie 和 Session 的方式来完成组件之间的传参。
转发:
浏览器向服务器发出请求,最终请求完成需要 A 和 B 组件一起协作完成,那么 A 组件会向 B 组件发起调用,会造成组件之间的耦合。整个过程是在一个请求之间完成的,在组件之间传参很容易实现。
权限管理
- 登录检查
- 之前采用拦截器实现了登录检查,这是简单的权限管理方案,现在废弃
- 授权配置
- 对当前系统内包含的所有的请求,分配访问权限(普通用户、版主、管理员)
- 认证方案
- 绕过 Security 认证流程,采用系统原来的认证方案
- CSRF 配置
- 防止 CSRF 攻击的基本原理,以及表单、 AJAX 相关的配置
整个过程的目的在于对系统进行权限管理,所以需要引入 Security 实现。
一、引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency>二、注释掉原先配置的 LoginRequired 拦截器
三、常量表中添加新的权限角色常量
/** * 权限:普通用户 */ String AUTHORITY_USER = "user"; /** * 权限:管理员 */ String AUTHORITY_ADMIN = "admin"; /** * 权限:版主 */ String AUTHORITY_MODERATOR = "moderator";四、新增 Security 配置类
七、CSRF 攻击以及避免
CSRF 攻击简单来说就是用户的 Cookie 被用户访问的其他网站窃取,造成 Cookie 中的 ticket 泄漏。其他用户使用 Cookie 来向服务器发起伪造请求,达到伪造请求获取用户信息的目的。
Security 的解决方案,是在返回 Cookie 的时候向 Cookie 中添加一个 Hidden 的 Token 字段,Cookie 被窃取可以获得 Ticket 但是无法获得 Token ,所以最终无法造成 CSRF 攻击。
之前的配置中,在使用了 Security 进行了上述的配置之后,我们在一个带有表单的页面中,打开源代码可以看到 Security 针对 CSRF 攻击自动生成了一个隐藏的值,也就是 CSRF 令牌。
这样的处理方式是针对同步请求的,但是对于异步请求,我们还需要做更多的处理。
按照首页的发帖功能为例,我们使用的是异步方式进行发帖的处理的。在 index.html 中的
标签中添加生成 csrf 令牌的头部以及值标签。<meta name="_csrf" th:content="${_csrf.token}"> <meta name="_csrf_header" th:content="${_csrf.headerName}">之后我们修改发帖的时候的 js 代码,在发送异步请求之前让 xhr 将 csrf 令牌携带。
处理请求的时候,我们查看页面源代码,可以看到在首页生成了 CSRF 令牌。
使用浏览器进行网络请求记录,查看 CSRF 令牌的传输,可以看到:
请求方式是异步请求,且可以看到 CSRF 令牌值。
之后,依次在关注/取关、点赞、评论、发私信模块中添加对于各种请求的处理。
置顶/加精/删除
- 功能实现
- 点击置顶按钮,修改帖子的类型
- 点击加精、删除,修改帖子的状态
- 权限管理
- 版主可以执行帖子置顶、加精操作
- 管理员可以执行删除操作
- 按钮显示
- 版主可以看到置顶、加精按钮
- 管理员可以看到删除按钮
置顶、删除、加精三个操作涉及到对不同身份的角色进行权限管理,所以我们使用 Security 进行了授权管理之后,设计这三个功能将更加顺畅。
一、导入新的依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5artifactId> dependency>取消加精、置顶操作
加精、置顶操作因为是版主操作,但是在实际的项目使用中,通常应该对不同的帖子进行加精或者置顶,以替换掉一些时间比较长的帖子,所以应该存在对帖子加精、置顶操作进行撤销。
编写思路:根据帖子的状态,将操作按钮文字设置为特定的字符,之后根据字符显示判断应该触发的 js 操作,绑定不同的 js 事件即可。
Redis 高级数据结构
- HyperLogLog (超级日志)
- 采用一种基数算法,用于完成独立总数的统计,统计不同数字的个数
- 占据空间小,无论统计多少个数据,只占 12K 的内存空间
- 不精确的统计算法,标准误差为 0.81%
- Bitmap (位图)
- 不是一种独立的数据结构,实际上就是字符串
- 支持按位存取数据,可以将其看成是 byte 数组
- 适合存储索大量的连续的数据的布尔值
HyperLogLog 方便我们统计网站的独立访客数量,通常称之为 UV ,同一个客户端在一天之内的多次访问只会被计算一次,而 HyperLogLog 通常就是我们用来统计 UV 的数据结构。 bitmap 用于统计同一用户在每天的访问情况,通常用于快速检索关键字状态。
网站数据统计
- UV (Unique Visitor)
- 独立访客,需通过用户 IP 排重统计数据
- 每次访问都要进行统计
- HyperLogLog ,性能好,且存储空间小
- DAU (Daily Active User)
- 日活跃用户,需通过用户 ID 排重统计数据
- 访问过一次,则认为其活跃
- Bitmap ,性能好、且可以统计精确的结果
针对于 UV 和 DAU 的统计,我们需要设计符合使用需求的 redis 的 key 值。
/** * 获取当日 UV 的 Key 值 * 格式: uv:date */ public static String getUVKey(String date) { return PREFIX_UV + SPLIT + date; } /** * 获取区间之间的 UV */ public static String getUVKey(String startDate, String endDate) { return PREFIX_UV + SPLIT + startDate + SPLIT + endDate; } /** * 获取当日的 DAU 的 key 值 */ public static String getDAUKey(String date) { return PREFIX_DAU + SPLIT + date; } /** * 获取区间之间的 DAU 数据 */ public static String getDAUKey(String startDate, String endDate) { return PREFIX_DAU + SPLIT + startDate + SPLIT + endDate; }设计完成之后,我们需要开发相关的数据访问层。
在 Service 层中,我们需要添加一个新的类 DataService 来进行编写新的数据统计的方法。
@Service public class DataService { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /** * 实例化日期格式化对象 */ private final SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd"); /** * 记录 IP 值至 HLL 中 * * @param ip ip 地址值 */ public void recordUV(String ip) { String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUVKey(sf.format(new Date())); redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().add(redisKey, ip); } /** * 统计指定日期范围内的 UV * * @param start 开始日期 * @param end 结束日期 * @return UV 值 ( 不同的 IP 总数和) */ public long calculateUV(Date start, Date end) { if (start == null || end == null || start.after(end)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("日期输入错误!"); } // 整理日期范围内的 Key 值 List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>(); Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.setTime(start); while (!calendar.getTime().after(end)) { // 从开始时间至结束时间将 key 值存入 List 中 String uvKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUVKey(sf.format(calendar.getTime())); redisKeys.add(uvKey); // 将日期进行 + 1 处理 calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, 1); } // 设置合并之后的 Key 值 String uvKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUVKey(sf.format(start), sf.format(end)); // 传入 key 的集合,将合并结果存入 uvKey 中 redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().union(uvKey, redisKeys.toArray()); // 返回统计结果 return redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().size(uvKey); } /** * 将指定用户记录到 DAU */ public void recordDAU(int userId) { String dauKey = RedisKeyUtil.getDAUKey(sf.format(new Date())); redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(dauKey, userId, true); } public long calculateDAU(Date start, Date end) { // 输入日期判断 if (start == null || end == null || start.after(end)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("日期输入错误!"); } // 整理日期范围内的 Key 值 List<byte[]> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>(); Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.setTime(start); while (!calendar.getTime().after(end)) { // 从开始时间至结束时间将 key 值存入 List 中 String dauKey = RedisKeyUtil.getDAUKey(sf.format(calendar.getTime())); redisKeys.add(dauKey.getBytes()); // 将日期进行 + 1 处理 calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, 1); } // 进行 OR 运算 return (long) redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback) redisConnection -> { String dauKey = RedisKeyUtil.getDAUKey(sf.format(start), sf.format(end)); redisConnection.bitOp(RedisStringCommands.BitOperation.OR, dauKey.getBytes(), redisKeys.toArray(new byte[0][0])); return redisConnection.bitCount(dauKey.getBytes()); }); } }进行运算之后,我们可以计算出 UV 以及 DAU 的数据。
但是我们在计算数据之前还需要有相关的数据进行记录,我们可以新建一个新的拦截器进行拦截,将用户的 IP 地址以及用户的 ID 记录到 Redis 中,用 HyperLogLog 以及 Bitmap 记录。
@Component public class DataInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Autowired private HostHolder hostHolder; @Autowired private DataService dataService; @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 统计 UV String host = request.getRemoteHost(); dataService.recordUV(host); // 统计 DAU User user = hostHolder.getUser(); if (user != null) { dataService.recordDAU(user.getId()); } return true; } }拦截器编写完成之后,需要将拦截器进行配置,添加进去。
对于数据的 Controller 层,我们创建一个新的处理数据的控制层类。
@Controller public class DataController { @Autowired private DataService dataService; /** * 获取统计页面,为了方便转发,需要加上 POST 请求 * * @return 数据页面 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/data", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}) public String getDataPage() { return "/site/admin/data"; } /** * 统计 UV 数据 * * @param start 开始时间 * @param end 结束时间 * @param model model 对象 * @return 转发至统计页面 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/data/uv", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String getUV(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date start, @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date end, Model model) { long uv = dataService.calculateUV(start, end); model.addAttribute("uvResult", uv); model.addAttribute("uvStartDate", start); model.addAttribute("uvEndDate", end); return "forward:/data"; } /** * 统计活跃用户 * * @param start 开始时间 * @param end 结束时间 * @param model model 对象 * @return 转发至数据页面 */ @RequestMapping(path = "/data/dau", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String getDAU(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date start, @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date end, Model model) { long dau = dataService.calculateDAU(start, end); model.addAttribute("dauResult", dau); model.addAttribute("dauStartDate", start); model.addAttribute("dauEndDate", end); return "forward:/data"; } }之后我们将数据渲染到页面中即可。
任务执行和调度
- JDK线程池
- ExecutorService
- ScheduledExecutorService
- Spring线程池
- ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
- ThreadPoolTaskScheduler
- 分布式定时任务
- Spring Quartz
任务调度在整个系统中是不可或缺的一部分,主要用于调整每一天的一些定时任务,维护系统的正常运行。通常处理的服务包括:系统重新计算帖子排名、系统定时清理不必要的内存等等。这其中需要用到多线程来处理这些任务。
热帖排行
- Hacker News
- Score = (P-1) / (T+2) ^ G
- StackOverflow
- (log (Qviews) *4) + ( (Qanswers * Qscore) /5) + sum (Ascores)
- ( (QageInHours + 1) - ( (QageInHours - Qupdated) /2)) ^ 1.5
- Nowcoder
- log (精华分+评论数 X10 +点赞数 X2 +收藏数X2) + (发布时间 - 牛客纪元)
根据网站对于帖子的权重值计算公式,在帖子的权重改变操作发生时,比如加精、评论、点赞、收藏、发布操作进行后,将帖子 ID 添加进 redis 中,计算一个新的分数。
计算分数的时候,需要注意分数的曲线设置为平缓,避免造成恶意刷分情况。
对应的方法在 DiscussPostController 中,将其中的发帖、加精方法添加对应的帖子 ID 添加进 Redis 的 Set 中。
CommentController 中的添加评论方法、 LikeController 中的 like 方法,都需要添加对应的计算帖子分数方法,处理的第一步就是将帖子的 ID 转存进 set 集合中。
// 计算帖子分数 String postScoreKey = RedisKeyUtil.getPostScoreKey(); redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(postScoreKey, discussionPostId);生成长图
-
wkhtmltopdf
- wkhtmltopdf url file
- wkhtmltoimage url file
-
java
Runtime.getRuntime().exec()
生成长图的功能主要用于在 APP 端分享帖子,在分享的时候,我们需要生成一个分享图,方便其他用户查看到分享的内容。
我们主要使用工具来完成网页转换成 image / pdf 的功能,使用的工具就是 wkhtmltopdf ,下载网址为:wkhtmltopdf 。下载完工具之后,我们进行安装即可。在安装的时候,我们需要记住安装的位置。我们届时需要调用的是安装目录下的 bin 目录中的两个程序。
优化网站性能
- 本地缓存
- 将数据缓存在应用服务器上,性能最好。
- 常用缓存工具:Ehcache 、 Guava 、 Caffeine 等。
- 分布式缓存
- 将数据缓存在 NoSQL 数据库上,跨服务器
- 常用缓存工具: MemCache 、 Redis 等
- 多级缓存
- 一级缓存(本地缓存) > 二级缓存(分布式缓存) > DB
- 避免缓存雪崩(缓存失效,大量请求直达 DB ),提高系统的可用性
提升网站性能最有效的手段就是使用缓存。
本地缓存与分布式缓存 Redis 的对比:
本地缓存与 app 是存储在同一台服务器上的,由于没有服务器之间的请求应答,所以访问速度更快。但是分布式缓存可以处理多台服务器之间的缓存需求,使用上更加广泛。
如果服务端部署了一级缓存与二级缓存,在使用上,一级缓存是要优先于二级缓存的。如果两次缓存访问均未命中目标数据,那么就要将请求打到数据库上。由于命中了数据库,那么新的数据应该更新到缓存中,更新的过程是需要先更新二级缓存,再更新一级缓存。
我们在项目中使用缓存,主要使用的是 Caffeine 来将查询到的热点帖子进行缓存,并不缓存新发布的帖子,而是发布按照热度排序的帖子。主要原因是新发布的帖子数据多变,实际使用比较少;而热度比较高的帖子在一段事件内都是比较稳定的,可以有效避免数据库频繁查询带来的性能开销。
使用步骤
一、引入依赖文件
项目监控
- Spring Boot Actuator
- Endpoints:监控应用的入口, Spring Boot 内置了很多端点,也支持自定义端点
- 监控方式: HTTP 或 JMX
- 访问路径:例如 “/actuator/health”
- 注意事项:按需配置暴露的端点,并对所有端点进行权限控制
默认开放的有两个端点,包括: /actuator/health 、 /actuator/info
十一、项目总结
核心功能
- 发帖、评论、私信、转发;
- 点赞、关注、通知、搜索;
- 权限、统计、调度、监控;
核心技术
- Spring Boot、SSM
- Redis、Kafka、ElasticSearch
- Spring Security、Quatz、Caffeine
项目亮点
- 项目构建在 Spring Boot + SSM 框架之上,并统一的进行了状态管理、事务管理、异常处理;
- 利用 Redis 实现了点赞和关注功能,单机可达 5000TPS;
- 利用 Kafka 实现了异步的站内通知,单机可达 7000TPS;
- 利用 ElasticSearch 实现了全文搜索功能,可准确匹配搜索结果,并高亮显示关键词;
- 利用 Caffeine + Redis 实现了两级缓存,并优化了热门帖子的访问,单机可达 8000QPS;
- 利用 Spring Security 实现了权限控制,实现了多重角色、URL级别的权限管理;
- 利用 HyperLogLog 、Bitmap 分别实现了 UV 、 DAU 的统计功能,100万用户数据只需数 M 内存空间;
- 利用 Quartz 实现了任务调度功能,并实现了定时计算帖子分数、定时清理垃圾文件等功能;
- 利用 Actuator 对应用的 Bean 、缓存、日志、路径等多个维度进行了监控,并通过自定义的端点对数据库连接进行了监控。
未开发功能:
忘记密码:forget 已开发 12.21
我的帖子:my-post 已开发 12.21
我的回复:my-reply 已开发 12.22