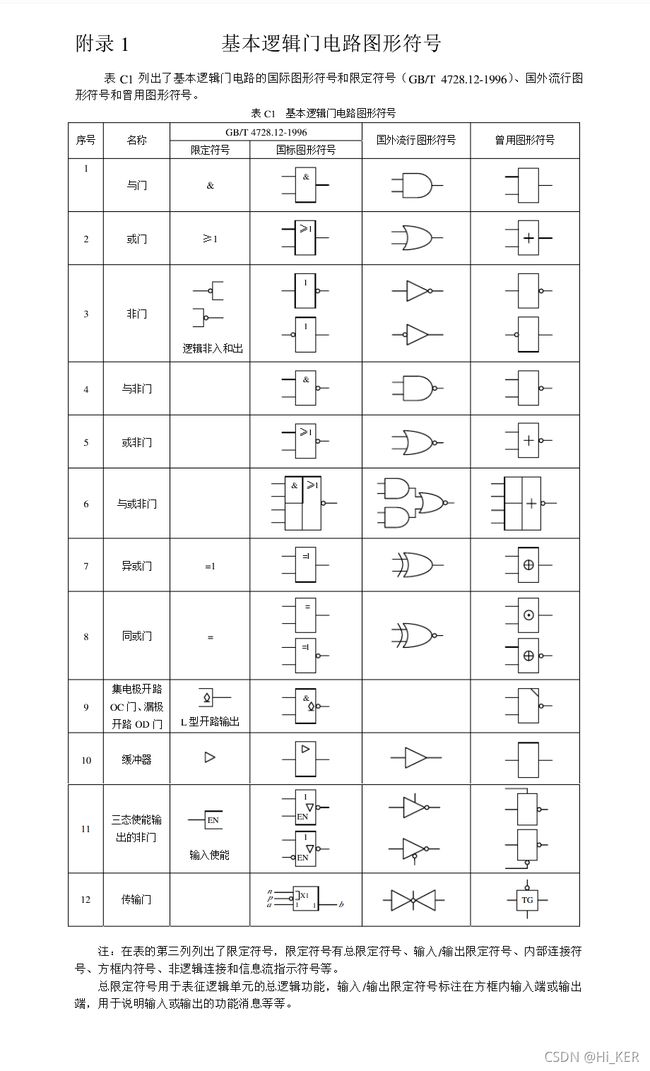
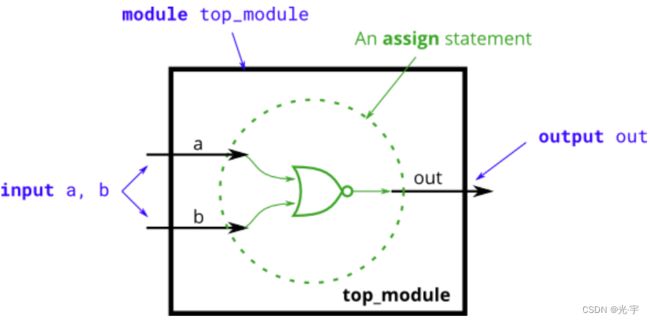
HDLbits exercises 1 (开头到vector5节选题)
目录
LET'S LEARN SOMETHING:
1\ ANDGATE
2\ NORGATE
3\ VECTOR1
4\VECTORGATES
5\ GATES4
6\ VECTOR4
7\ VECTOR5
LET'S LEARN SOMETHING:
In verilog, bitwise-NOT is ~ , logical-NOT is !, and is &(bitwise) or &&( logical), or is |(bitwise) or ||( logical), xnor(同或=异或非) is !(a^b), xor is ^
1\ ANDGATE
HINT:
Verilog has separate bitwise-AND (&) and logical-AND (&&) operators, like C. Since we're working with a one-bit here, it doesn't matter which we choose.
ERRO:
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output out );
assign out=a+b;
endmodule
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output out );
assign out=a&b;
endmodule
2\ NORGATE
HINT:
Verilog has separate bitwise-OR (|) and logical-OR (||) operators, like C. Since we're working with a one-bit here, it doesn't matter which we choose.
ERRO:
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output out );
assign out=!(a+b);
endmodule
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output out );
assign out=!(a | b);
endmodule
3\ VECTOR1
向量的声明:以下全部合法
wire [7:0] w; // 8-bit wire reg [4:1] x; // 4-bit reg output reg [0:0] y; // 1-bit reg that is also an output port (this is still a vector) input wire [3:-2] z; // 6-bit wire input (negative ranges are allowed) output [3:0] a; // 4-bit output wire. Type is 'wire' unless specified otherwise. wire [0:7] b; // 8-bit wire where b[0] is the most-significant bit.
向量的使用:
w[3:0] // Only the lower 4 bits of w
x[1] // The lowest bit of x
x[1:1] // ...also the lowest bit of x
z[-1:-2] // Two lowest bits of z
b[3:0] // Illegal. Vector part-select must match the direction of the declaration.
b[0:3] // The *upper* 4 bits of b.
assign w[3:0] = b[0:3]; // Assign upper 4 bits of b to lower 4 bits of w. w[3]=b[0], w[2]=b[1], etc.
ERRO:
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi=in[8:15];
assign out_lo=in[0:7];
endmodule
CORRECT:
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi=in[15:8];
assign out_lo=in[7:0];
endmodule
4\VECTORGATES
HINT:
Even though you cannot assign to a wire more than once, you can use a part select on the left-hand-side of an assign. You don't need to assign to the entire vector all in one statement.
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise=a|b;
assign out_or_logical=a||b;
assign out_not={~b,~a}; //assign out_not[2:0] = ~a; assign out_not[5:3] = ~b;
endmodule
本题注意按位或与逻辑或的区别,前者为&后者为&&。
5\ GATES4
ERRO:
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and=in && in;
assign out_or=in || in;
assign out_xor=in ^^ in;
endmodule
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = & in;
assign out_or = | in;
assign out_xor = ^in;
endmodule
注意,变量前面只有符号时,说明是对它自己进行符号的操作,比如&in是对in自己进行按位与的操作。
6\ VECTOR4
WAHT YOU SHOULD KNOW:
Examples:
{5{1'b1}} // 5'b11111 (or 5'd31 or 5'h1f)
{2{a,b,c}} // The same as {a,b,c,a,b,c}
{3'd5, {2{3'd6}}} // 9'b101_110_110. It's a concatenation of 101 with
// the second vector, which is two copies of 3'b110.
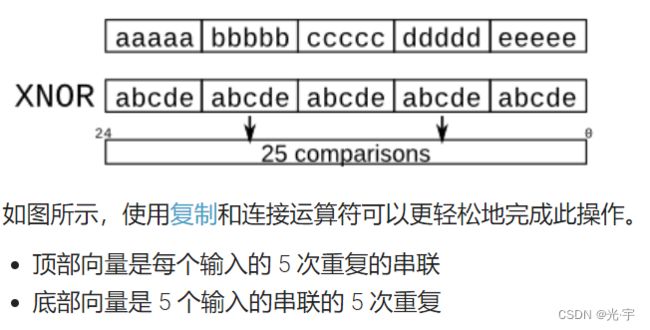
7\ VECTOR5
CORRECT:
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out );
wire [24:0] top, bottom;
assign top = { {5{a}}, {5{b}}, {5{c}}, {5{d}}, {5{e}} };
assign bottom = {5{a,b,c,d,e}};
assign out = ~top ^ bottom; // Bitwise XNOR
endmodule