【数据结构初阶】一个队列怎么实现栈~~OJ
目录
1.用两个队列实现栈
变式:如何用一个队列实现栈
2.用两个栈实现队列
1.用两个队列实现栈
用队列实现栈
思路:主要是“入栈”和“出栈”
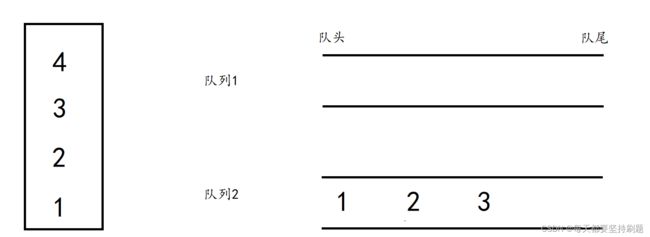
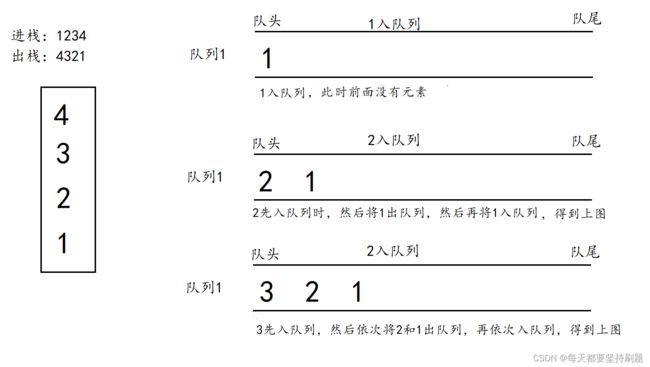
左边的是栈,假设1234依次进栈,那么如果要用右边的两个队列实现栈的功能,就应该按照4321的次序出栈,按照题目要求得用两个队列实现4321出数据的形式,并且完成栈的初始化,判空,销毁等功能。
第一步:实现“入栈”,我们将要入的每一个数据都入在其中一个队列,而保持另一个为空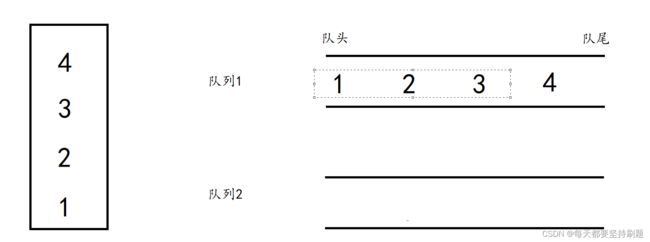
第二步:实现“出栈步骤1”,因为每出一个数据都要来回倒腾数据,使得这次这个队列为空,下一次就是另一个为空,所以这里为了方便,我们就不关心q1和q2谁为空,而是用空队列和非空队列来描述操作。
我们先取非空队列里的队头数据入到之前预留好的空队列中,然后将非空队列里队头数据出队列,依次类推,直到原来的非空队列中只剩一个元素,此时,原来非空队列里的前size-1个数据都保留到了原来的空队列中。
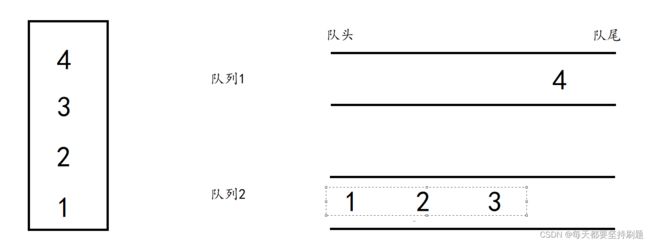 第三步:实现“出栈步骤2”,将原来的非空队列中的唯一一个数据4出队列,即完成一次出队列的过程。
第三步:实现“出栈步骤2”,将原来的非空队列中的唯一一个数据4出队列,即完成一次出队列的过程。
这里有很多细节值得我们的注意:
1.模拟初始化栈的时候,在定义MyStack时不能定义一个局部变量,然后返回局部变量的地址,这是经典的返回栈空间地址的错误。(下面是错误的写法)
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack obj;
//...
return &obj;
}2.模拟出栈的时候,我们为了方便,定义出empty和noempty两个队列的指针,而非拷贝!
(下面是错误的写法)
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue empty=obj->q1;
Queue noempty=obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
empty=obj->q2;
noempty=obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(&noempty)>1)
{
QueuePush(&empty,QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(&noempty);
}
int ret=QueueFront(&noempty);
QueuePop(&noempty);
return ret;
}3.模拟销毁栈的时候 ,不能直接free(obj),这样释放掉的仅仅是MyStack这个结构体的变量,而结构体变量里的一些指针所指向的动态开辟的空间并不会被释放掉!!(下面是错误的写法)
而将QueueDestory(&obj->q1);QueueDestory(&obj->q2);调用Queue的函数一个一个将链表结点释放才能真正达到释放的目的~~
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
free(obj);
}下面是完整的正确的代码~~
typedef int QDateType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDateType val;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* head;
QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* ps);
void QueuePush(Queue* ps, QDateType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* ps);
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* ps);
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* ps);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps);
int QueueSize(Queue* ps);
void QueueDestory(Queue* ps);
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
QueueNode* cur = ps->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
}
//入队列:尾插
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail.");
exit(-1);
}
if (ps->tail == NULL)
{
ps->head = ps->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
ps->tail->next = newnode;
ps->tail = ps->tail->next;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
if (ps->head == ps->tail)
{
free(ps->head);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QueueNode* next = ps->head->next;
free(ps->head);
ps->head = next;
}
}
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
return ps->head->val;
}
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
return ps->tail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->tail == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int size = 0;
QueueNode* cur = ps->head;
while(cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
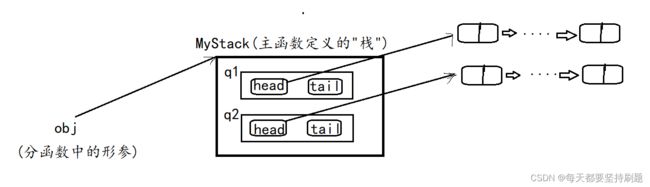
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//代码书写方式1:
// Queue* empty=&obj->q1;
// Queue* noempty=&obj->q2;
// if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
// {
// empty=&obj->q2;
// noempty=&obj->q1;
// }
// QueuePush(noempty,x);
//代码书写方式2:
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* empty=&obj->q1;
Queue* noempty=&obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
empty=&obj->q2;
noempty=&obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(noempty)>1)
{
QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(noempty);
}
int ret=QueueFront(noempty);
QueuePop(noempty);
return ret;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}变式:如何用一个队列实现栈
typedef struct {
Queue q;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
QueuePush(&obj->q,x);
for(int i=0;iq)-1;i++)
{
QueuePush(&obj->q,QueueFront(&obj->q));
QueuePop(&obj->q);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
int top=QueueFront(&obj->q);
QueuePop(&obj->q);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueFront(&obj->q);
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestory(&obj->q);
free(obj);
} 2.用两个栈实现队列
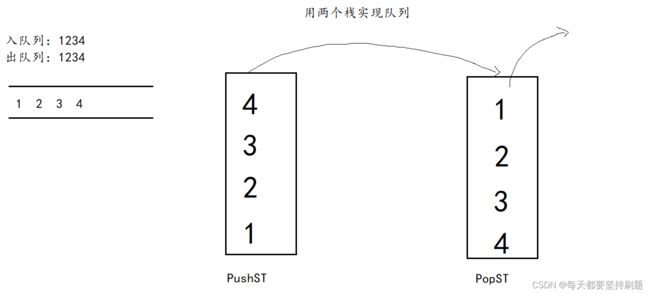
用两个栈实现队列
思路:两个栈,一个用作入数据PushST,一个用作出数据PopST,在栈内倒转两次就变成正序了~~
“队列”入数据:直接入PushST栈
"队列"出数据:如果PopST栈为空,则将PushST栈内的数据先全部倒到PopST中,然后再在PopST中出数据;
如果PopST栈不为空,则直接在PopST中出数据。
需要特别注意的是:"队列"出数据的时候,如果PopST栈不为空,则直接在PopST中出数据。这样可以避免123先入栈后,出了一个3后,再入数据4的情况出错!
typedef struct {
Stack PushST;
Stack PopST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&obj->PushST);
StackInit(&obj->PopST);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
StackPush(&obj->PushST,x);
}
//未复用myQueuePeek代码的书写代码方式1:
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->PopST))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->PushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->PopST,StackTop(&obj->PushST));
StackPop(&obj->PushST);
}
}
int top=StackTop(&obj->PopST);
StackPop(&obj->PopST);
return top;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj);
//复用myQueuePeek代码的书写代码方式2:
// int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
// // if(StackEmpty(&obj->PopST))
// // {
// // while(!StackEmpty(&obj->PushST))
// // {
// // StackPush(&obj->PopST,StackTop(&obj->PushST));
// // StackPop(&obj->PushST);
// // }
// // }
// int top=myQueuePeek(obj);
// StackPop(&obj->PopST);
// return top;
// }
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->PopST))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->PushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->PopST,StackTop(&obj->PushST));
StackPop(&obj->PushST);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->PopST);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->PushST)&&StackEmpty(&obj->PopST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestory(&obj->PushST);
StackDestory(&obj->PopST);
free(obj);
}