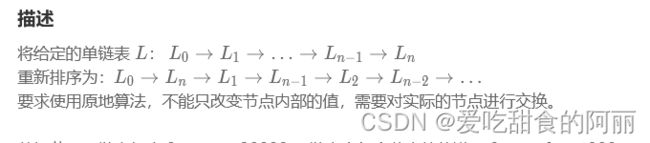牛客网面试高频题top100(71~80)
面试高频算法题top100(71~80)java实现
71.数字字符串转化为IP地址
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {
search(s,0,"","");
return res;
}
public void search(String s,int len,String pre,String cur){
if(pre!="" && judge(pre))
return;
if(len==4 && s.length()==0){
if(!res.contains(cur)){
res.add(cur.substring(0,cur.length()-1));
}
}
if(s.length()>=1)
search(s.substring(1,s.length()),len+1,s.substring(0,1),cur+s.substring(0,1)+'.');
if(s.length()>=2)
search(s.substring(2,s.length()),len+1,s.substring(0,2),cur+s.substring(0,2)+'.');
if(s.length()>=3)
search(s.substring(3,s.length()),len+1,s.substring(0,3),cur+s.substring(0,3)+'.');
}
public boolean judge(String pre){
int num = Integer.parseInt(pre);
if(num>=0 && num<=255 && String.valueOf(num).equals(pre))
return false;
return true;
}
}
72.设计LFU缓存结构
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
class node{
int key;
int val;
int time;
node(int k,int v,int t){
this.key = k;
this.val = v;
this.time = t;
}
}
int min_time = 0;
int size = 0;
HashMap<Integer,node> map = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Integer,LinkedList<node>> map_time = new HashMap<>();
// 更新node的使用频次,同时根据使用频次freq更新node在链表中的位置
public void update(node n){
LinkedList<node> t = map_time.get(n.time);
t.remove(n);
if(t.isEmpty() && min_time==n.time) {
min_time++;
}
n.time ++;
if(!map_time.containsKey(n.time))
map_time.put(n.time,new LinkedList<>());
LinkedList<node> tmp = map_time.get(n.time);
tmp.addLast(n);
}
public int get(int key){
if(!map.containsKey(key)) return -1;
node temp = map.get(key);
update(temp);
return temp.val;
}
// put过程
public void put(int key, int val, int k){
// 已经使用过该key,map替换value值并增加使用频次
if(map.containsKey(key)){
node tmp=map.get(key);
tmp.val=val;
update(tmp);
map.put(key, tmp);
return;
}
LinkedList<node>list=map_time.get(min_time);
// 第一次使用到这个key,需要判断map容量,容量不足,需要淘汰key
if(size==k){
node tmp=list.remove();
map.remove(tmp.key);
}else {
size++;
}
node no=new node(key, val, 1);
map.put(key, no);
if(!map_time.containsKey(1)){
map_time.put(1, new LinkedList<node>());
}
map_time.get(1).addLast(no);
min_time=1;
}
public int[] LFU (int[][] operators, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++){
if (operators[i][0] == 1){
put(operators[i][1], operators[i][2], k);
}else{
res.add(get(operators[i][1]));
}
}
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
}
}
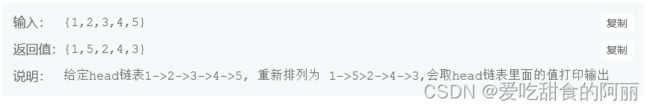
73.重排链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return;
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p4 = head;
ListNode left = p1;
while(p4.next!=null)
p4 = p4.next;
ListNode right = p4;
while(p1!=p4 && p1.next!=p4){
left = p1.next;
right = p1;
while(right.next!= p4)
right = right.next;
p1.next = p4;
p4.next = left;
p1 = left;
p4 = right;
}
right.next = null;
}
}
74.删除有序链表中重复的元素(一)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return null;
ListNode dummy = head;
while(head!=null){
ListNode next = head.next;
if(next==null) break;
if(next.val!=head.val)
head = head.next;
else{
while(next!=null && next.val==head.val)
next = next.next;
head.next = next;
head = next;
}
}
return dummy;
}
}
75.有重复项数字的全排列
给出一组可能包含重复项的数字,返回该组数字的所有排列。结果以字典序升序排列。

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
Allsort(num,0);
Collections.sort(res,new Comparator<ArrayList<Integer>>(){
@Override
public int compare(ArrayList<Integer> a1,ArrayList<Integer> a2){
int i=0;
while(i<a1.size()){
if(a1.get(i)==a2.get(i))
i++;
else
break;
}
return a1.get(i)-a2.get(i);
}
});
return res;
}
public void Allsort(int[] num,int index){
if(index==num.length-1){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int t:num)
list.add(t);
if(!res.contains(list))
res.add(list);
}
for(int i=index;i<num.length;i++){
swap(num,i,index);
Allsort(num,index+1);
swap(num,i,index);
}
}
public void swap(int[] num,int i,int j){
int temp = num[i];
num[i] = num[j];
num[j] = temp;
}
}
76.滑动窗口的最大值
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(size==0 || num.length<size) return list;
Deque<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0;i<num.length;i++){
while(!que.isEmpty() && i-que.peek()+1>size) que.pop();
while(!que.isEmpty() && num[i]>=num[que.getLast()]) que.removeLast();
que.add(i);
if(i+1>=size) list.add(num[que.peek()]);
}
return list;
}
}
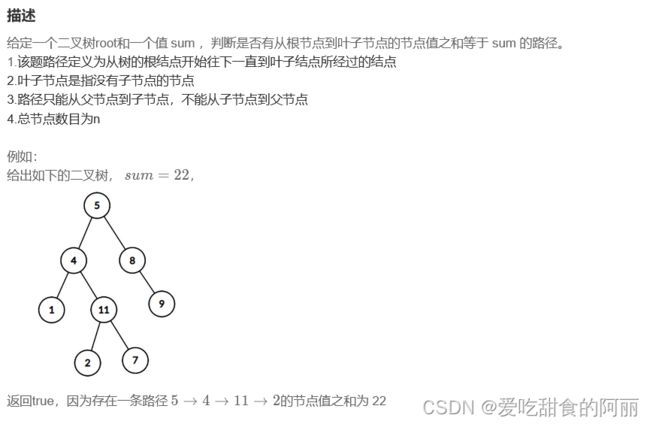
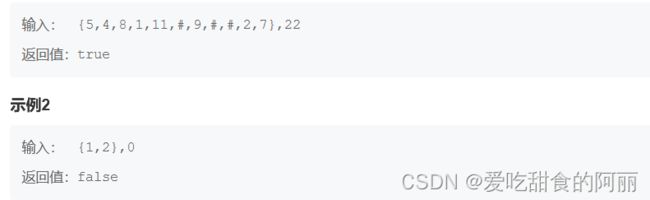
77.二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum - root.val == 0)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
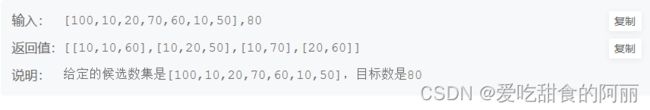
78.加起来和为目标值的组合(二)
给出一组候选数 c 和一个目标数 t ,找出候选数中起来和等于 t 的所有组合。c 中的每个数字在一个组合中只能使用一次。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] num, int target) {
Arrays.sort(num);
Add(num,target,0,new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
public void Add(int[] num,int tar,int index,ArrayList<Integer> list){
if(tar<0) return;
if(tar==0){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
for(int i=index;i<num.length;i++){
if(tar<num[i]) break;
if(i>index && num[i]==num[i-1]) continue;
list.add(num[i]);
Add(num,tar-num[i],i+1,list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
}
79.最长的括号子串
给出一个长度为 n 的,仅包含字符 ‘(’ 和 ‘)’ 的字符串,计算最长的格式正确的括号子串的长度。

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses (String s) {
if(s.length()<2) return 0;
int num = 0;
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(-1);
for(int i=0;i<cs.length;i++){
String temp = "";
if(cs[i]=='(' )
stack.push(i);
else{
stack.pop();
if(stack.empty())
stack.push(i);
else
num = Math.max(num,i-stack.peek());
}
}
return num;
}
}
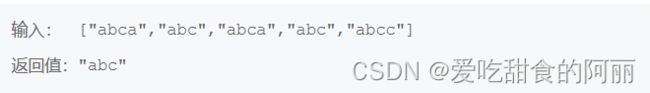
80.最长公共前缀
给你一个大小为 n 的字符串数组 strs ,其中包含n个字符串 , 编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀,返回这个公共前缀。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) {
if(strs.length==0) return "";
String str = strs[0];
for(int i=1;i<strs.length;i++){
while(strs[i].indexOf(str)!=0)
str = str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
}
return str;
}
}