Node.js基础知识点
1.什么是Node.js
Node.js 是运行在服务端的JavaScript。
Node.js 是一个基于Chrome JavaScript运行时建立的一个平台。
Node.js是一个事件驱动 I/O 服务端JavaScript 环境,基于Google的V8引擎,V8引擎执行Javascript 的速度非常快,性能非常好。
2.创建一个应用
2.1引入required模块
我们使用require 指令来载入 http模块,并将实例化的 HTTP赋值给变量http
var http = require("http")2.2创建服务器
接下来我们使用 http.createserver()方法创建服务器,并使用 listen方法绑定8888端口。函数通过request、response参数来接收和响应数据。
//创建服务器
http.createServer(function(requeest,response){
}).listen(8888)
//终端打印启动信息
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8888/')2.3 接收请求与响应请求
//引入http模块
var http = require('http')
//创建服务器
http.createServer(function(request,response){
//发送响应头
response.writeHead(200,{'Content-Type':"text/plain"})
//输出响应内容
response.write("hello world")
response.end()
}).listen(8888)
console.log('我的服务器已经启动,访问:http://127.0.0.1:8888');3.模块系统
为了让Node.js的文件可以相互调用,Node.js提供了一个简单的模块系统。
模块是Node.js 应用程序的基本组成部分,文件和模块是一一对应的。换言之,一个 Node.js 文件就是一个模块,这个文件可能是JavaScript 代码、JSON 或者编译过的C/C++ 扩展。
方法一:
文件1:hello.js
exports.world = function(){
console.log("Hello Node.js");
}
文件2:main.js
//导入模块
var hello=require('./hello')
//调用hello中的方法
hello.world() 方法二
文件1:hello.js
function Hello(){
let name;
this.setName=function(theName){
name=theName
}
this.sayHello=function(){
console.log(`你好,${name}`);
}
}
module.exports=Hello;
文件2:main.js
//导入模块
var Hello=require('./hello');
let hello=new Hello();
hello.setName("刘");
hello.sayHello()
4.url模块提供的方法
url.parse(urlStr[, parseQueryString][, slashesDenoteHost]):输入URL字符串,返回一个对象。
第二个参数为true时,使用querystring 来解析查询字符串。如果为true,query 属性将会一直赋值为对象,并且search属性将会一直是字符串(可能为空)。默认为false.
第三个参数为true,把//foo/bar当做{ host: 'foo',pathname: '/bar'},而不是( pathname : ' / /foo/bar'}。默认为false。
const url = require('url')
const reqUrl = 'http://user:[email protected]:8080/p/a/t/h?query=string#hash';
const urlObj = url.parse(reqUrl)
// console.log(urlObj);
// //获取当前url的端口
// console.log(urlObj.port);
// //获取主机
// console.log(urlObj.host)
//获取查询参数
console.log(urlObj.query);
//URL模块提供的方法
const reqUrl="//foo/bar"
const urlObj1 = url.parse(reqUrl,false);
console.log(urlObj1.host,urlObj1.pathname);
const urlObj2 = url.parse(reqUrl,false,true);
console.log(urlObj2.host,urlObj2.pathname);5.回调函数
Node.js 异步编程的直接体现就是回调。
回调函数在完成任务后就会被调用,Node使用了大量的回调函数,Node所有API都支持回调函数
文件1:main.js
const fs = require("fs")
//阻塞代码(同步)
let data = fs.readFileSync('./index.txt')
console.log(data.toString());
console.log("程序执行成功");
//非阻塞代码(异步)
//以上程序中 fs.readFile()是异步函数用于读取文件。如果在读取文件过程中发生错误,错误err对象就会输出错误信息。如果没发生错误,readFile跳过err对象的输出,文件内容就通过回调函数输出
fs.readFile('./index.txt',function(err,data){
if(err){
console.error(err.stack);
return
}
console.log(data.toString());
})
console.log("程序执行成功");
文件2:index.txt(根据自己的需要)
啥都好说就肯定会6.事件循环
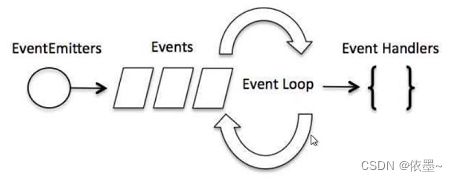
Node.js 是单进程单线程应用程序,但是通过事件和回调支持并发。所以性能非常高。
Node.js的每一个API都是异步的,并作为一个独立线程运行,使用异步函数调用,并处理并发。
Node.js基本上所有的事件机制都是用设计模式中观察者模式实现。
Node.js单线程类似进入一个while(true)的事件循环,直到没有事件观察者退出,每个异步事件都生成一个事件观察者,如果有事件发生就调用该回调函数。
6.1事件驱动程序
Node.js,使用事件驱动模型,当web server接收到请求,就把它关闭然后进行处理,然后去服务下一个web请求。
当这个请求完成,它被放回处理队列,当到达队列开头,这个结果被返回给用户。
这个模型非常高效可扩展性非常强,因为webserver一直接受请求而不等待任何读写操作。(这也被称之为非阻塞式IO或者事件驱动lO)|
在事件驱动模型中,会生成一个主循环来监听事件,当检测到事件时触发回调函数。
整个事件驱动的流程就是这么实现的,非常简洁。有点类似于观察者模式,事件相当于一个主题(Subject),而所有注册到这个事件上的处理函数相当于观察者(Observer) .
//引入events模块
const events = require("events")
//实例化对象
let eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter()
//on事件绑定
eventEmitter.on("demo",function(){
console.log("我是执行的方法--demo");
})
//emit触发事件
eventEmitter.emit("demo")
console.log("程序执行结束")练习:
var events = require("events")
let eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter()
//定义connection事件
let connectionHandler=function(){
console.log("连接成功。。。");
//触发其他事件data_recived
eventEmitter.emit("data_recived")
}
//绑定connection事件
eventEmitter.on("connection",connectionHandler)
//绑定data_rectived事件
eventEmitter.on("data_recived",function(){
console.log("数据接收成功");
})
//触发connection事件
eventEmitter.emit("connection")
console.log("程序执行完毕");jQuery怎样注册事件
1. $().click() 2. on("click",fn) 3. bind("click",fn) 4.live("click") 5. delegate("click")