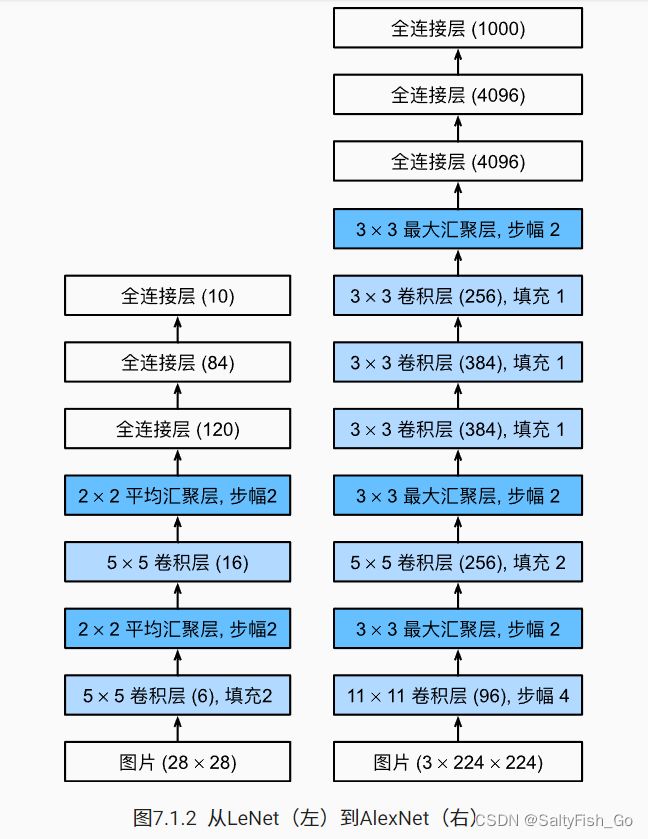
卷积神经网络LeNet和深度卷积神经网络AlexNet的区别与实现
目录
LeNet
LeNet的实现
AlexNet——更大更深的LeNet
AlexNet和LeNet的区别:
AlexNet的实现
LeNet
总体来看,LeNet(LeNet-5)由两个部分组成:
每个卷积层使用5×55×5卷积核和一个sigmoid激活函数。这些层将输入映射到多个二维特征输出,通常同时增加通道的数量。第一卷积层有6个输出通道,而第二个卷积层有16个输出通道。每个2×22×2池操作(步骤2)通过空间下采样将维数减少4倍。
LeNet的稠密块有三个全连接层,分别有120、84和10个输出。因为我们在执行分类任务,所以输出层的10维对应于最后输出结果的数量。
LeNet的实现
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10))
X = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:
X=layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28]) AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 14, 14]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10]) AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 5, 5]) Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 400]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 120]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 120]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 84]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 84]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
AlexNet——更大更深的LeNet
AlexNet网络是更大更深的LeNet网络,前者的计算参数是后者的10倍,计算复杂度是260倍。
AlexNet由八层组成:五个卷积层、两个全连接隐藏层和一个全连接输出层。
AlexNet和LeNet的区别:
AlexNet是更大更深的LeNet,主要的改进:
· 使用丢弃法来正则(在全连接层后),做模型的控制
· ReLu作为激活函数,不再是sigmoid
· 用MaxPooling而不是AvgPooling
更大的核窗口和步长,因为图片大小变大了,这样每次能多看一点
使用了更大的池化窗口
目录
LeNet
LeNet的实现
AlexNet——更大更深的LeNet
AlexNet和LeNet的区别:
AlexNet的实现
更多的通道,以为图片大了,要更多的识别模式
增加了三个卷积层和一个池化层,能更好的提取特征,更深
隐藏层(全连接层)的节点数变多,更胖
数据增强:对一幅图片进行截取,亮度、色温等进行改变,增加训练数据,可以减小卷积神经网络对图片位置、颜色等信息的敏感性
AlexNet的实现
net = nn.Sequential(
# 这里,我们使用一个11*11的更大窗口来捕捉对象。
# 同时,步幅为4,以减少输出的高度和宽度。
# 另外,输出通道的数目远大于LeNet
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口。
# 除了最后的卷积层,输出通道的数量进一步增加。
# 在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用于减少输入的高度和宽度
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
#拉成2D形状
# 这里,全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍。使用dropout层来减轻过拟合
nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
# 最后是输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10))看一下各个类的输出类型
X = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:
X=layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 54, 54]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 54, 54]) MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 26, 26]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26]) MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12]) MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 5, 5]) Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 6400]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])