springboot2初期笔记存档
SpringBoot2
1 springboot简介
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。
该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。
通过这种方式,Spring Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
简单来说就是SpringBoot其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架 。
- springboot优点
- 创建独立Spring应用
- 内嵌web服务器
- 自动starter依赖,简化构建配置
- 自动配置Spring以及第三方功能
- 提供生产级别的监控、健康检查及外部化配置
- 无代码生成、无需编写XML
- springboot缺点
- 人称版本帝,迭代快,需要时刻关注变化
- 封装太深,内部原理复杂,不容易精通
- 官方文档
springBoot2.4.4开发手册
- 什么是微服务?
- 微服务是一种架构风格
- 一个应用拆分为一组小型服务
- 每个服务运行在自己的进程内,也就是可独立部署和升级
- 服务之间使用轻量级HTTP交互
- 服务围绕业务功能拆分
- 可以由全自动部署机制独立部署
- 去中心化,服务自治。服务可以使用不同的语言、不同的存储技术
- 微服务的痛点
- 运维要求高: 更多的服务意味着要投入更多的运维。
- **分布式固有的复杂性:**使用微服务构建的是分布式系统。对于一个分布式系统,系统容错、网络延迟、分布式事务等都会带来巨大的问题。
- **接口调整成本高:**微服务之间通过接口进行通信。如果修改某一个微服务的API,可能所有用到这个接口的微服务都需要进行调整。
- 远程调用、服务发现、负载均衡、服务容错、配置管理、服务监控、链路追踪、日志管理、任务调度……
2 springboot入门
2.1 环境准备及maven设置
1、环境要求
- Java 8 & 兼容java14
- Maven 3.3+
- idea 2019.1.2
1.1、Maven设置
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyunid>
<mirrorOf>centralmirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyunname>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/publicurl>
mirror>
mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>trueactiveByDefault>
<jdk>1.8jdk>
activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
properties>
profile>
profiles>
注意:
本人是IDEA2020,在打包的时候出现Process terminated。经过一番折腾,删除
2 HelloWorld
**需求:**浏览发送/hello请求,响应 Hello,Spring Boot 2
2.1 创建maven工程
2.2 引入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASEversion>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.3 创建主程序
/**
* 主程序类
* @SpringBootApplication:这是一个SpringBoot应用
* @SpringBootConfiguration
* @EnableAutoConfiguration
* @ComponentScan("priv.zwh")
* @SpringBootApplication等同于这三个注解,@ComponentScan默认扫描的是MainApplication的包目录
* 如果其他包与MainApplication不是同级目录,则@ComponentScan需要指定扫描到其共有的包路径
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
2.4 编写业务
在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
//@Controller---组件声明
//@ResponseBody---表示传字符串到前端
// RestController包含上面两个注解
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01() {
return "Hello SpringBoot2 你好";
}
}
2.5 测试
运行main方法即可,localhost:8080/hello
2.6 简化配置
application.properties(一般放在resources下面),作用是对某些组件的修改,例如tomcat端口号等。
server.port=8888
2.7 简化部署
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
把项目打成jar包,直接在目标服务器执行即可。
- 选中maven的Lifecycle下面的clean和package,执行
- 在工程的target文件夹下面会得到一个jar文件
- 在文件夹找到这个xxx.jar文件,命令行执行
java -jar xxx.jar - 在没有运行主程序的情况下测试8080端口的hello连接。(正常运行)
注意:
命令行执行时,鼠标点击到了正在执行的命令时,会特别慢,解决方法。取消掉cmd的快速编辑模式(鼠标右键)
2.8 自定义banner
- 到项目下的 resources 目录下新建一个banner.txt 即可。
- https://www.bootschool.net/ascii 这个网站生成,然后拷贝到文件中即可!
2.9 修改依赖版本号
springboot有版本仲裁机制,默认parent中加入了开发的大多数依赖。
以mysql为例,springboot默认是mysql8,那么相应的数据库也得更新成mysql8才能使用!
为了解决这个问题,我们也可以手动版本切换!
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.47mysql.version>
properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
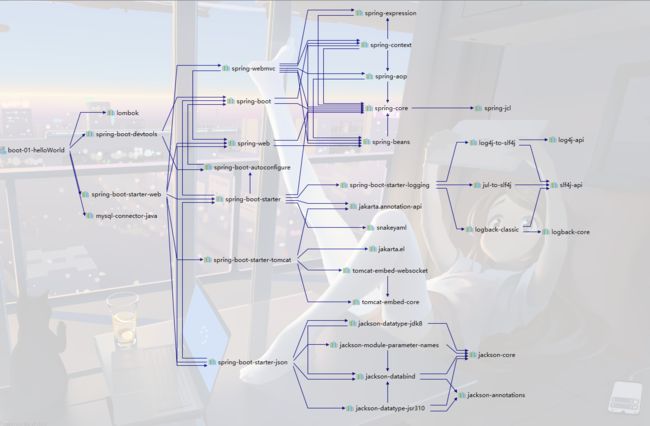
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bj1qZqG7-1621126786457)(C:\Users\33132\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210512125708939.png)]
3 自动配置原理了解
3.1 springboot依赖管理特点
- 父项目做依赖管理
依赖管理,主要是管理项目的资源过滤及插件!
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASEversion>
parent>
点进去可以发现他的他的父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASEversion>
parent>
几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖的版本号,无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁
引入依赖默认都可以不写版本,引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
- 开发导入starter场景启动器
1、见到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就某种场景
2、只要引入starter,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖我们都自动引入
3、SpringBoot所有支持的场景:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
4、见到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方为我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。
5、所有场景启动器最底层的依赖(spring-boot-starter):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASEversion>
<scope>compilescope>
dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件
***–spring-boot-starter:**这些是第三方给我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什
么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 ;我们未来也可以自己自定义 starter;
SpringBoot所有支持的场景
3.2 容器功能
组件添加
1、@Configuration
Configuration使用:
- 配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认是单实例的(@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true))
- 配置类本身也是组件
- Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
- Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
Full模式与Lite模式的最佳实战:
- 配置 类组件之间无依赖关系用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
- 配置类组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式
2、@Import
// 给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件、默认组件的名字就是全类名
@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
public class MyConfig {
}
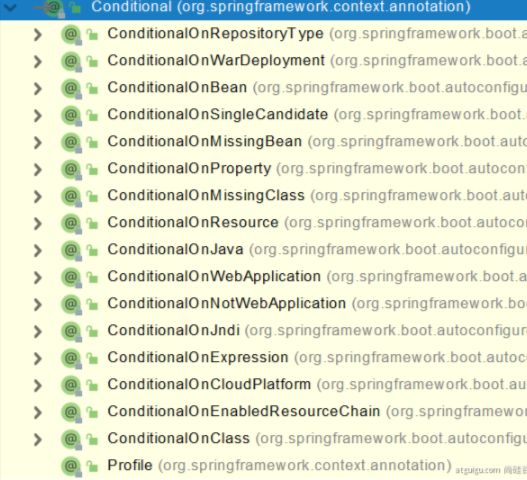
3、@Conditional
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入
4、@ImportResource(原生配置文件引入)
基于大多数公司还是基于xml配置bean
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="haha" class="priv.zwh.boot.bean.Student">
<property name="name" value="haha">property>
bean>
beans>
于是springboot使用@ImportResource可以将xml的数据导入到配置文件。
只需在你的配置类加上即可。
("classpath:bean.xml")
public class MyConfig {
}
5、@ConfigurationProperties(配置绑定)
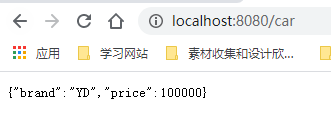
假设配置文件的配置为(那么该怎么给Car对象进行绑定呢):
mycar.brand=YD
mycar.price=100000
- @Component + @ConfigurationProperties
/**
* 只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有SpringBoot提供的强大功能
*/
@ToString
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
- @EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
@ToString
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
//1、开启Car配置绑定功能
//2、把这个Car这个组件自动注册到容器中
public class MyConfig {
}
- 测试
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
Car car;
@RequestMapping("/car")
public Car testCar() {
return car;
}
}
小结:
后者是没有@Component注解,但需要在配置类上加上@EnableConfigurationProperties注解,好处在于我可以引入第三方jar。
总不可能我们拿到第三方的jar给它加入到容器中(@Component)
3.3 自动配置原理入门
@SpringBootApplication详解
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
1、@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration。代表当前是一个配置类。
2、@ComponentScan
指定扫描哪些,Spring注解;
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
1、@AutoConfigurationPackage
自动配置包?指定了默认的包规则
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) //给容器中导入一个组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {}
//利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件
//将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来?MainApplication 所在包下。
2、@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
1、利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
2、调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类
3、利用工厂加载 Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件
4、从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。
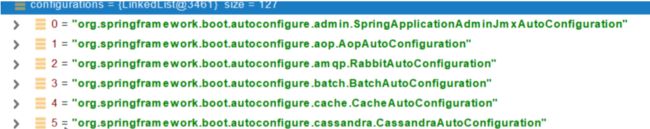
默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories
文件里面写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器中加载的所有配置类
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
按需开启自动配置类
- 虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载。xxxxAutoConfiguration
- 按照条件装配规则(@Conditional)只有条件满足,最终才会按需配置。
- 当导入相应jar,才会按需加载
修改默认配置
@Bean
//容器中有这个类型组件
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
//容器中没有这个名字 multipartResolver 的组件
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
//给@Bean标注的方法传入了对象参数,这个参数的值就会从容器中找。
//SpringMVC multipartResolver。防止有些用户配置的文件上传解析器不符合规范
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
给容器中加入了文件上传解析器;
SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件。但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
}
总结:
-
SpringBoot先加载所有的自动配置类 xxxxxAutoConfiguration
-
每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。xxxxProperties里面拿。xxxProperties和配置文件进行了绑定
-
生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
-
只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
-
定制化配置
-
- 用户直接自己@Bean替换底层的组件
- 用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改。
xxxxxAutoConfiguration —> 组件 —> xxxxProperties里面拿值 ----> application.properties
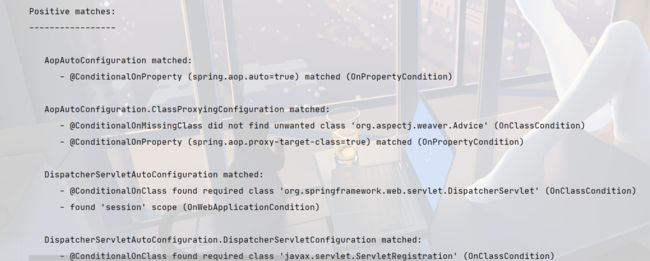
开启自动配置报告
配置文件中debug=true。Negative(不生效)、Positive(生效)
3.4 开发小技巧
lombok
简化JavaBean开发
- idea中搜索安装lombok插件,安装
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
Slf4j(lombok下自带)
简化日志开发
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(@RequestParam("name") String name){
log.info("请求进来了....");
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!"+"你好:"+name;
}
}
dev-tools
省去实时运行(热加载、日更新),只需ctrl+F9
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
spring initailizr(项目初始化向导)
- 选择我们需要开发的场景
-
自动依赖注入
-
自动创建项目结构
-
自动编写好主配置类
4 yml配置文件
1、文件类型
1.1、properties
同以前的application.properties作用相同。
1.2、yaml
1.2.1、简介
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。
在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件
1.2.2、基本语法
- key: value;kv之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,单引号与双引号表示字符串内容 会被 转义/不转义(双引号不会转义,单引号会转义)。
1.2.3、数据类型
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
k: v
- 对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
行内写法: k: {k1:v1,k2:v2,k3:v3}
#或
k:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
行内写法: k: [v1,v2,v3]
#或者
k:
- v1
- v2
- v3
1.2.4、示例
- 对象
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String name;
private Double weight;
}
- 使用yaml给对象赋值
person:
userName: zhangsan
boss: false
birth: 2019/12/12 20:12:33
age: 18
pet:
name: tomcat
weight: 23.4
interests: [篮球,游泳]
animal:
- jerry
- mario
score:
english:
first: 30
second: 40
third: 50
math: [131,140,148]
chinese: {first: 128,second: 136}
salarys: [3999,4999.98,5999.99]
allPets:
sick:
- {name: tom}
- {name: jerry,weight: 47}
health: [{name: mario,weight: 47}]
2、配置提示
- 使用yaml时没有关键字提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
- 打包部署时
spring-boot-configuration-processor不进行打包
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
exclude>
excludes>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
5 Web开发
5.1 简单功能分析
5.1.1 静态资源访问
静态资源目录
springboot静态资源约定路径(类路径下即可resources/):
- META-INF/resources
- resources
- static
- public
静态资源访问:
当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名 。localhost:8080/xxx.jpg
原理:
静态映射/**,请求进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理。不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
改变默认的静态资源路径:
在springboot2.4.2版本,此方法被移除,划上了删除线
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/others/]
静态资源默认访问路径优先级:
当每个文件夹的文件名相同时,访问的是哪个文件夹下的文件。(由大到小排序)
- META-INF/resources
- resources
- static
- public
静态资源访问前缀
静态资源默认是无前缀,当然也可以自定义前缀(application.yaml下)。
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /img/**
访问:
当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名
webjar
自动映射 /webjars/**
https://www.webjars.org/
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjarsgroupId>
<artifactId>jqueryartifactId>
<version>3.5.1version>
dependency>
访问地址:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js 后面地址要按照依赖里面的包路径
5.1.2 欢迎页支持
当我们访问localhost:8080时就可以默认打开欢迎页。
实现:
-
静态资源路径下:index.html
-
不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
spring: # mvc: # static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致welcome page功能失效 resources: static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
5.1.3 自定义Favicon
当我们访问页面时,自动引入icon图标。
实现步骤:
- 将favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下
- 不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
注意点:当我们引入后应该先关闭当前会话再操作才能实现效果。
5.1.4 静态资源配置原理
-
SpringBoot启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)
-
SpringMVC功能的自动配置类 WebMvcAutoConfiguration,生效
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {}
- 给容器中配了什么。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {}
- 配置文件的相关属性和xxx进行了绑定。WebMvcPropertiesspring.mvc、ResourcePropertiesspring.resources
配置类只有一个有参构造器
//有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中确定
//ResourceProperties resourceProperties;获取和spring.resources绑定的所有的值的对象
//WebMvcProperties mvcProperties 获取和spring.mvc绑定的所有的值的对象
//ListableBeanFactory beanFactory Spring的beanFactory
//HttpMessageConverters 找到所有的HttpMessageConverters
//ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer 找到 资源处理器的自定义器。=========
//DispatcherServletPath
//ServletRegistrationBean 给应用注册Servlet、Filter....
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(ResourceProperties resourceProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
ObjectProvider<ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
}
资源处理的默认规则
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
//webjars的规则
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
//
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
禁用所有静态资源规则:
spring:
resources:
add-mappings: false 禁用所有静态资源规则
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
/**
* Locations of static resources. Defaults to classpath:[/META-INF/resources/,
* /resources/, /static/, /public/].
*/
private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
欢迎页的处理规则
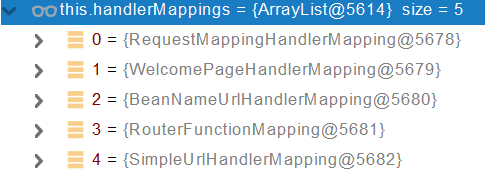
HandlerMapping:处理器映射。保存了每一个Handler能处理哪些请求。
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext, Optional<Resource> welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage.isPresent() && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
//要用欢迎页功能,必须是/**
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage.get());
setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
}
else if (welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
// 调用Controller /index
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
setRootViewName("index");
}
}
favicon
5.3 请求参数处理
5.3.1 请求映射
rest使用与原理
- 之前的SSM中使用为XXXMapping
- 核心Filter;HiddenHttpMethodFilte
用法:
- 在controller进行配置
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/user")
public String getUser() {
return "GET-张三";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping("/user")
public String saveUser() {
return "POST-张三";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/user")
public String putUser() {
return "PUT-张三";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping(value = "/user")
public String deleteUser() {
return "DELETE-张三";
}
- 前端进行绑定
<form action="/user" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="REST-GET 提交">
form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="REST-POST 提交">
form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
<input type="submit" value="REST-DELETE 提交">
form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_m" value="PUT">
<input type="submit" value="REST-PUT 提交">
form>
- 在配置文件中手动开启rest风格
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true #开启页面表单的Rest功能
- 扩展:如何把_method 这个名字换成我们自己喜欢的。
//自定义filter
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter methodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
methodFilter.setMethodParam("_m");
return methodFilter;
}
Rest原理(表单提交要使用REST的时候)
-
表单提交会带上**_method=PUT**
-
请求过来被HiddenHttpMethodFilter拦截
-
- 请求是否正常,并且是POST
-
-
- 获取到**_method**的值。
- 兼容以下请求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH
- 原生request(post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的值。
- 过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper。以后的方法调用getMethod是调用****requesWrapper的。
-
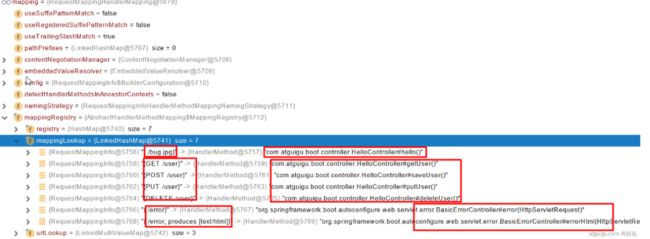
请求映射原理
SpringMVC功能分析都从 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet-》doDispatch()
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 找到当前请求使用哪个Handler(Controller的方法)处理
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//HandlerMapping:处理器映射。/xxx->>xxxx
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:保存了所有@RequestMapping 和handler的映射规则。
所有的请求映射都在HandlerMapping中。
-
SpringBoot自动配置欢迎页的 WelcomePageHandlerMapping 。访问 /能访问到index.html;
-
SpringBoot自动配置了默认 的 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
-
请求进来,挨个尝试所有的HandlerMapping看是否有请求信息。
-
- 如果有就找到这个请求对应的handler
- 如果没有就是下一个 HandlerMapping
-
我们需要一些自定义的映射处理,我们也可以自己给容器中放HandlerMapping。自定义 HandlerMapping
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
5.3.2 普通参数与基本注解
@PathVariable:动态获取路径变量的值/car/${id}/owner/${name}
@RequestHeader:获取请求头信息
@RequestAttribute:获取request域属性
@MatrixVariable:获取矩阵变量的值
@RestController
public class ParameterTestController {
@GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}")
public Map<String, Object> getCar(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("username") String name,
@PathVariable Map<String, Object> pv,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@RequestHeader Map<String, Object> header,
@RequestParam("age") Integer age,
@RequestParam("sex") String sex,
@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params
) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("name", name);
map.put("pv", pv);
// map.put("userAgent", userAgent);
// map.put("header", header);
map.put("age", age);
map.put("sex", sex);
map.put("params", params);
// map.put("cookie", cookie);
return map;
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public Map postMethod(@RequestBody String context) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("context", context);
return map;
}
//1、语法: /cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd
//2、springboot默认是禁用了矩阵变量的功能,
// 手动开启:原理。对于路径的处理。UrlPathHelper进行解析。
// removeSemicolonContent(移除分号内容)支持矩阵变量的
// 3、矩阵变量必须有url路径变量才能被解析
@GetMapping("/cars/{path}")
public Map carsSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,
@MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand,
@PathVariable("path") String path) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("low", low);
map.put("brand", brand);
map.put("path", path);
return map;
}
// /boss/1;age=20/2;age=10
@GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}")
public Map boss(@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("bossAge", bossAge);
map.put("empAge", empAge);
return map;
}
}
5.4 数据响应与内容协商
SpringMVC到底支持哪些返回值:
ModelAndView
Model
View
ResponseEntity
ResponseBodyEmitter
StreamingResponseBody
HttpEntity
HttpHeaders
Callable
DeferredResult
ListenableFuture
CompletionStage
WebAsyncTask
有 @ModelAttribute 且为对象类型的
@ResponseBody 注解 ---> RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor;
5.5 视图解析与模板引擎
视图解析:SpringBoot默认不支持 JSP,需要引入第三方模板引擎技术实现页面渲染。
1 视图解析原理流程
1、目标方法处理的过程中,所有数据都会被放在 ModelAndViewContainer 里面。包括数据和视图地址
2、方法的参数是一个自定义类型对象(从请求参数中确定的),把他重新放在 ModelAndViewContainer
3、任何目标方法执行完成以后都会返回 ModelAndView(数据和视图地址)。
4、processDispatchResult 处理派发结果(页面改如何响应)
-
1、render(mv, request, response); 进行页面渲染逻辑
-
- 1、根据方法的String返回值得到 View 对象【定义了页面的渲染逻辑】
-
-
- 1、所有的视图解析器尝试是否能根据当前返回值得到View对象
- 2、得到了 redirect:/main.html --> Thymeleaf new RedirectView()
- 3、ContentNegotiationViewResolver 里面包含了下面所有的视图解析器,内部还是利用下面所有视图解析器得到视图对象。
- 4、view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); 视图对象调用自定义的render进行页面渲染工作
-
-
-
-
- RedirectView 如何渲染【重定向到一个页面】
- 1、获取目标url地址
- 2、response.sendRedirect(encodedURL);
-
-
视图解析:
-
- 返回值以 forward: 开始: new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl); --> 转发request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request, response);
- 返回值以 redirect: 开始: new RedirectView() --》 render就是重定向
- 返回值是普通字符串: new ThymeleafView()—>
2 模板引擎-Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments,
capable of processing HTML, XML, JavaScript, CSS and even plain text.
现代化、服务端Java模板引擎
1、表达式
| 表达式名字 | 语法 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 变量取值 | ${…} | 获取请求域、session域、对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{…} | 获取上下文对象值 |
| 消息 | #{…} | 获取国际化等值 |
| 链接 | @{…} | 生成链接 |
| 片段表达式 | ~{…} | jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
2、字面量
文本值: ‘one text’ , ‘Another one!’ **,…**数字: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 **,…**布尔值: true , false
空值: null
变量: one,two,… 变量不能有空格
3、文本操作
字符串拼接: +
变量替换: |The name is ${name}|
4、数学运算
运算符: + , - , * , / , %
5、布尔运算
运算符: and , or
一元运算: ! , not
6、比较运算
比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le **)**等式: == , != ( eq , ne )
7、条件运算
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
8、特殊操作
无操作: _
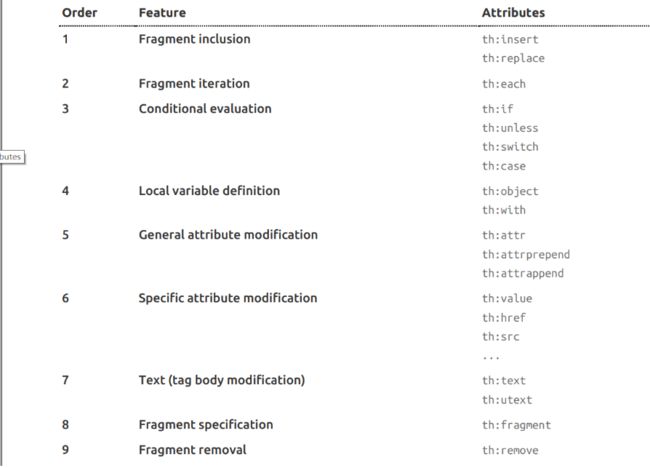
9、设置属性值-th:attr
设置单个值
<form action="subscribe.html" th:attr="action=@{/subscribe}">
<fieldset>
<input type="text" name="email" />
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:attr="value=#{subscribe.submit}"/>
fieldset>
form>
设置多个值
<img src="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
以上两个的代替写法 th:xxxx
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:value="#{subscribe.submit}"/>
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">
所有h5兼容的标签写法
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#setting-value-to-specific-attributes
10、迭代
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd>
tr>
<tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd>
tr>
11、条件运算
<a href="comments.html"
th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">viewa>
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administratorp>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a managerp>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thingp>
div>
12、属性优先级
3、thymeleaf使用
1、引入Starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
2、自动配置好了thymeleaf
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThymeleafProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass({ TemplateMode.class, SpringTemplateEngine.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter({ WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class })
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration { }
自动配好的策略
- 1、所有thymeleaf的配置值都在 ThymeleafProperties
- 2、配置好了 SpringTemplateEngine
- 3、配好了 ThymeleafViewResolver
- 4、我们只需要直接开发页面
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; //xxx.html
3、页面开发
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${msg}">哈哈h1>
<h2>
<a href="www.atguigu.com" th:href="${link}">去百度a> <br/>
<a href="www.atguigu.com" th:href="@{link}">去百度2a>
h2>
body>
html>
5.6 拦截器
5.6.1 实现HandlerInterceptor接口
/**
* 登录检查
* 1、配置好拦截器要拦截哪些请求
* 2、把这些配置放在容器中
*/
@Slf4j
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 目标方法执行之前
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("preHandle拦截的请求路径是{}",requestURI);
//登录检查逻辑
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser");
if(loginUser != null){
//放行
return true;
}
//拦截住。未登录。跳转到登录页
request.setAttribute("msg","请先登录");
// re.sendRedirect("/");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request,response);
return false;
}
/**
* 目标方法执行完成以后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.info("postHandle执行{}",modelAndView);
}
/**
* 页面渲染以后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param ex
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.info("afterCompletion执行异常{}",ex);
}
}
5.6.2 配置拦截器
/**
* 1、编写一个拦截器实现HandlerInterceptor接口
* 2、拦截器注册到容器中(实现WebMvcConfigurer的addInterceptors)
* 3、指定拦截规则【如果是拦截所有,静态资源也会被拦截】
*/
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") //所有请求都被拦截包括静态资源
.excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**"); //放行的请求
}
}
5.7 文件上传
5.7.1 表单规范
<form method="post" action="/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
5.7.2 文件上传代码
/**
* MultipartFile 自动封装上传过来的文件
* @param email
* @param username
* @param headerImg
* @param photos
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("email") String email,
@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headerImg,
@RequestPart("photos") MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException {
log.info("上传的信息:email={},username={},headerImg={},photos={}",
email,username,headerImg.getSize(),photos.length);
if(!headerImg.isEmpty()){
//保存到文件服务器,OSS服务器
String originalFilename = headerImg.getOriginalFilename();
headerImg.transferTo(new File("H:\\cache\\"+originalFilename));
}
if(photos.length > 0){
for (MultipartFile photo : photos) {
if(!photo.isEmpty()){
String originalFilename = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("H:\\cache\\"+originalFilename));
}
}
}
return "main";
}
5.8 异常处理
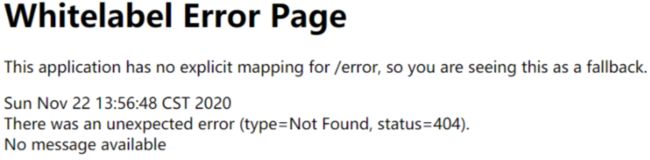
5.8.1 默认规则
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot提供
/error处理所有错误的映射 - 对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。
- 对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据
5.8.2 定制错误处理
- templates下面的error/下的4xx,5xx页面会被自动解析;
5.9 web原生组件注入
5.9.1 使用Servlet API
- 主程序入口加上:@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = “pri.zwh.admin”)
// 过滤器
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/css/*", "/images/*"})
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
}
// servlet
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/my")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
}
// 监听器
@WebListener
public class MySwervletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
}
5.9.2 使用RegistrationBean
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)// 保证都是单实例对象
public class MyRegistConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet() {
MyServlet myServlet = new MyServlet();
return new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet, "/my01", "/my02");
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter() {
MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter();
// return new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter,myServlet());
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/my01", "/css/*"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener() {
MySwervletContextListener mySwervletContextListener = new MySwervletContextListener();
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(mySwervletContextListener);
}
}
6 数据访问
6.1 SQL
- 场景导入
// 注意,默认支持的的版本是mysql8,要修改则手动加上版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
想要修改版本
1、直接依赖引入具体版本(maven的就近依赖原则)
2、重新声明版本(maven的属性的就近优先原则)
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.49mysql.version>
properties>
6.1.1 jdbcTemplate
- 修改配置项
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 测试
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class Boot05WebAdminApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from account_tbl", Long.class);
log.info("记录总数:{}",aLong);
}
}
6.1.2 Druid数据源tarter整合
- 引入druid-sstarter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.1.17version>
dependency>
- 配置示例
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
druid:
aop-patterns: com.atguigu.admin.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true
login-username: admin
login-password: admin
resetEnable: false
web-stat-filter: # 监控web
enabled: true
urlPattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
slow-sql-millis: 1000
logSlowSql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false
SpringBoot配置示例
配置项列表
6.1.3 整合mybatis
- mybatis-starter引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.4version>
dependency>
- yml
# 配置mybatis规则
mybatis:
# config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml #mybatis之前的写法,还需要写mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 可以不写全局;配置文件,所有全局配置文件的配置都放在configuration配置项中即可
**注意:**编写mapper接口时,标注@Mapper注解,注意命名空间的绑定
最佳实战:
- 引入mybatis-starter
- 配置application.yaml中,指定mapper-location位置即可
- 编写Mapper接口并标注@Mapper注解
- 简单方法直接注解方式
- 复杂方法编写mapper.xml进行绑定映射
- @MapperScan(“pri.zwh.admin.mapper”)简化,其他的接口就可以不用标注@Mapper注解
6.1.4 整合mybatis-plus
- starter引入
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
- 自动配置分析
SqlSessionFactory 自动配置好。底层是容器中默认的数据源
mapperLocations 自动配置好的,有默认值,*classpath\*:/mapper/\**/\*.xml任意包的类路径下的所有mapper文件夹下任意路径下的所有xml都是sql映射文件。 建议以后sql映射文件,放在 mapper下
@Mapper 标注的接口也会被自动扫描;建议直接 @MapperScan(“com.zwh.admin.mapper”) 批量扫描就行
只需要我们的Mapper继承 BaseMapper 就可以拥有crud能力
- CRUD
@GetMapping("/user/delete/{id}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Long id,
@RequestParam(value = "pn",defaultValue = "1")Integer pn,
RedirectAttributes ra){
userService.removeById(id);
ra.addAttribute("pn",pn);
return "redirect:/dynamic_table";
}
@GetMapping("/dynamic_table")
public String dynamic_table(@RequestParam(value="pn",defaultValue = "1") Integer pn,Model model){
//表格内容的遍历
// response.sendError
// List users = Arrays.asList(new User("zhangsan", "123456"),
// new User("lisi", "123444"),
// new User("haha", "aaaaa"),
// new User("hehe ", "aaddd"));
// model.addAttribute("users",users);
//
// if(users.size()>3){
// throw new UserTooManyException();
// }
//从数据库中查出user表中的用户进行展示
//构造分页参数
Page<User> page = new Page<>(pn, 2);
//调用page进行分页
Page<User> userPage = userService.page(page, null);
// userPage.getRecords()
// userPage.getCurrent()
// userPage.getPages()
model.addAttribute("users",userPage);
return "table/dynamic_table";
}
6.2 NoSQL
- redis-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
- RedisTemplate与Lettuce
@Test
void testRedis(){
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set("hello","world");
String hello = operations.get("hello");
System.out.println(hello);
}
- 切换成jedis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
dependency>
- yml
spring:
redis:
host: r-bp1nc7reqesxisgxpipd.redis.rds.aliyuncs.com
port: 6379
password: zwh:123456
client-type: jedis
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 10
7 单元测试
7.1 Junit5的变化
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库。
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform: Junit Platform是在JVM上启动测试框架的基础,不仅支持Junit自制的测试引擎,其他测试引擎也都可以接入。
JUnit Jupiter: JUnit Jupiter提供了JUnit5的新的编程模型,是JUnit5新特性的核心。内部 包含了一个测试引擎,用于在Junit Platform上运行。
JUnit Vintage: 由于JUint已经发展多年,为了照顾老的项目,JUnit Vintage提供了兼容JUnit4.x,Junit3.x的测试引擎。
SpringBoot 2.4 以上版本移除了默认对 Vintage 的依赖。如果需要兼容junit4需要自行引入(不能使用junit4的功能 @Test)
JUnit 5’s Vintage Engine Removed from spring-boot-starter-test,如果需要继续兼容junit4需要自行引入vintage
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.hamcrestgroupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-coreartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
7.2 Junit5常用注解
JUnit5的注解与JUnit4的注解有所变化
**@Test *表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
**@ParameterizedTest *表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍
**@RepeatedTest *表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍
**@DisplayName *为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
**@BeforeEach *表示在每个单元测试之前执行
**@AfterEach *表示在每个单元测试之后执行
**@BeforeAll *表示在所有单元测试之前执行
**@AfterAll *表示在所有单元测试之后执行
**@Tag *表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
**@Disabled *表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
**@Timeout *表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
**@ExtendWith *为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
雷神springboot2文档
狂神springboot2文档