【DS】Java实现顺序表
![]() ✨博客主页: XIN-XIANG荣
✨博客主页: XIN-XIANG荣
✨系列专栏:【Java实现数据结构】
✨一句短话: 难在坚持,贵在坚持,成在坚持!
推荐一款模拟面试、刷题神器 、从基础到大厂面试题:点击跳转刷题网站进行注册学习
![]()
文章目录
- 一. 线性表中的顺序表
- 二. 顺序表的全局实现
-
- MyArrayLisst.java
- EmptyException.java(空指针异常)
- PosWrongfulException.java(越界异常)
- TestList.java(测试部分)
- 测试结果
- 三. 顺序表功能的具体分析
-
- 1. 顺序表的定义
- 2. 获取顺序表长度
- 3. 新增元素,在数组最后添加
- 4. 在指定位置插入元素
- 5. 判断是否包含某个元素
- 6. 查找某个元素所在位置
- 7. 获取指定位置的元素
- 8. 修改指定位置的元素
- 9. 删除第一次出现的元素key
- 10. 清空顺序表
- 11. 打印顺序表(不属于顺序表功能)
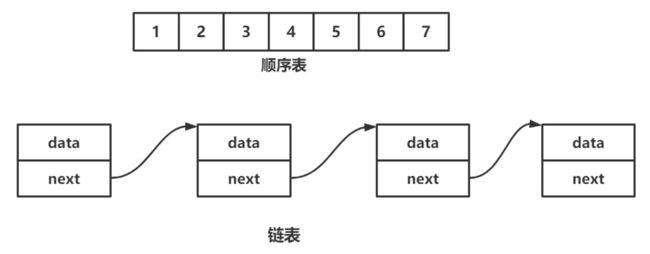
一. 线性表中的顺序表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
二. 顺序表的全局实现
MyArrayLisst.java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList {
private int[] elem;//数组
private int usedSize;//记录有效数据个数
private static final int DEFAYLT_SIZE = 10;
//构造方法
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAYLT_SIZE];
}
// 打印顺序表
//注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
}
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) {
//1.判断数组是否满了
if(Full()) {
System.out.println("空间满!");
//2.满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2*this.elem.length);
System.out.println("扩容完成!");
}
//3.将数据放入
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
//4.更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize++;
}
//1.
public boolean Full() {
return this.size() >= this.elem.length;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) throws PosWrongfulException{
//1.判断数组是否满了
if(Full()) {
System.out.println("空间满!");
//2.满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2*this.elem.length);
System.out.println("扩容完成!");
}
//判断pos位置是否合法,不合法抛出异常
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("add参数中,pos位置不合法");
}
//pos合法,从pos位置开始的元素向都后挪一个位置,让pos位置空出来
for (int i = this.usedSize; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
//在pos位置插入数据
this.elem[pos] = data;
//更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize++;
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) throws EmptyException{
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//判断pos是否合法
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("get获取元素时,pos位置不合法");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size() == 0;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) {
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//判断pos是否合法
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("set设置元素时,pos位置不合法");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//查找要删除元素的位置
int index = this.indexOf(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的元素"+toRemove);
return;
}
//删除元素,从后往前进行覆盖
for (int i = index; i < this.size(); i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
//更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize--;
}
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
}
EmptyException.java(空指针异常)
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException() {
}
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
PosWrongfulException.java(越界异常)
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException() {
}
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
TestList.java(测试部分)
public class TestList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
System.out.println("在顺序表最后一个位置添加元素");
myArrayList.add(1);
myArrayList.add(2);
myArrayList.add(3);
myArrayList.add(4);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("插入元素");
try {
myArrayList.add(0,6);
myArrayList.add(6,10);
} catch (PosWrongfulException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("顺序表是否包含某个元素");
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(2));
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(66));
System.out.println("获取元素位置");
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf(3));
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf(88));
System.out.println("获取pos位置的元素");
try {
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(1));
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(10));
}catch (PosWrongfulException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更改pos位置的元素值");
try {
myArrayList.set(0,99);
myArrayList.set(10,10);
}catch (PosWrongfulException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("删除第一次出现的数值");
myArrayList.remove(3);
myArrayList.remove(999);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println();
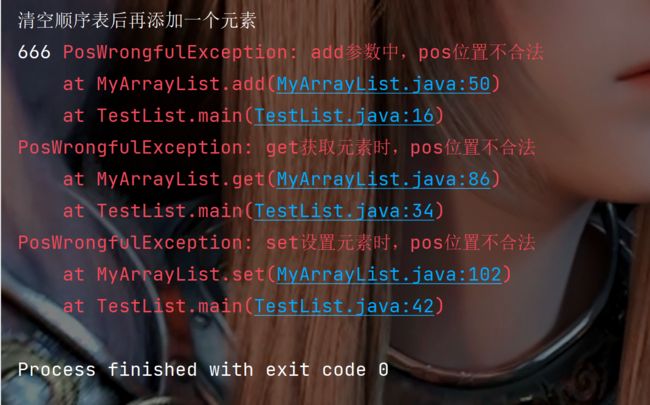
System.out.println("清空顺序表后再添加一个元素");
myArrayList.clear();
myArrayList.add(666);
myArrayList.display();
}
}
测试结果
三. 顺序表功能的具体分析
1. 顺序表的定义
顺序表本质上是基于数组进行操作的, 所以顺序表成员中定义一个数组elem来存放数据, 这里的顺序表实现以整形为例, 顺序表中的元素可以是其他类型,实现方法类似.
定义变量usedSize用来记录顺序表中的元素个数; 定义常量并给出构造方法以方便在创建顺序表时给数组分配默认空间.
public class MyArrayList {
private int[] elem;//数组
private int usedSize;//记录有效数据个数
private static final int DEFAYLT_SIZE = 10;
//构造方法
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAYLT_SIZE];
}
}
2. 获取顺序表长度
获取顺序表中记录数组中有效数据个数的成员即可
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
3. 新增元素,在数组最后添加
在添加元素前要判断数组空间是否满了, 如果满了要先进行扩容然后再添加, 添加成功后要记得更新数据的有效个数
public void add(int data) {
//1.判断数组是否满了
if(Full()) {
System.out.println("空间满!");
//2.满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2*this.elem.length);
System.out.println("扩容完成!");
}
//3.将数据放入
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
//4.更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize++;
}
//1.
public boolean Full() {
return this.size() >= this.elem.length;
}
4. 在指定位置插入元素
先判断数组空间是不是满了, 然后判断要插入位置的法性, 注意插入数据只能在以经存放了数剧的范围内进行插入, 也就是插入的位置相邻位置要有元素, 不能空着插;
如果位置不合法, 为了使出现问题的地方更突出以便于追踪和解决问题, 我们可以让报异常来达到目的, 我们去自定义异常, 如果位置不合法抛出异常, 让程序进行捕获和处理.
添加成功后要记得更新数据的有效个数, 异常的实现在上文中已经给出.
public void add(int pos, int data) throws PosWrongfulException{
//1.判断数组是否满了
if(Full()) {
System.out.println("空间满!");
//2.满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2*this.elem.length);
System.out.println("扩容完成!");
}
//判断pos位置是否合法,不合法抛出异常
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("add参数中,pos位置不合法");
}
//pos合法,从pos位置开始的元素向都后挪一个位置,让pos位置空出来
for (int i = this.usedSize; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
//在pos位置插入数据
this.elem[pos] = data;
//更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize++;
}
5. 判断是否包含某个元素
遍历数组将每个元素逐一比较即可
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind)
return true;
}
return false;
}
6. 查找某个元素所在位置
遍历数组比较即可
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
7. 获取指定位置的元素
如果顺序表中没有存放元素的话是不能去获取元素的, 这里同样可以去声明一个异常去解决问题; 同时要判断位置的合法性,
上面两个条件都没问题的话就可以通过下标去获取元素了
public int get(int pos) throws EmptyException{
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//判断pos是否合法
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("get获取元素时,pos位置不合法");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
8. 修改指定位置的元素
和6中的代码属于一份代码, 在最后将获取元素返回改为赋值即可
public void set(int pos, int value) {
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//判断pos是否合法
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
//抛出自定义异常,要注意去声明异常以便继续抛出
throw new PosWrongfulException("set设置元素时,pos位置不合法");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
9. 删除第一次出现的元素key
判断顺序表是否为空, 不为空则先找到要删除元素的位置, 将key之后的元素逐一往前覆盖, 将key覆盖便达到了删除的效果; 最后要记得元素的有效个数要减1;
需要注意的是,这里删除的基本数据类型的数据, 删除后相对于删除前数组的最后一个位置, 虽然那个位置还留有原来的值, 但这个值不置为0并不会有什么影响;
而如果顺序表中放置的是引用类型, 此时这个位置必须置空(置为null), 否则会有内存泄漏的问题存在.
public void remove(int toRemove) {
//判断顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");
}
//查找要删除元素的位置
int index = this.indexOf(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的元素"+toRemove);
return;
}
//删除元素,从后往前进行覆盖
for (int i = index; i < this.size(); i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
//更新有效数据个数
this.usedSize--;
}
10. 清空顺序表
将数组的有效元素个数赋值为0即可;
同样的, 要注意如果顺序表中的元素是引用类型的话, 要将数组中的每个元素都置为null.
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
11. 打印顺序表(不属于顺序表功能)
遍历数组打印即可, 要注意的是顺序表中是没有这个功能的, 只是为了测试, 方便观察调试所设.
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
}