A-Level经济真题(2)
1.Whichone of the following is not the role of investment banks?
A take in deposits from customers
B helping firms to issue shares and raisefinance
C assisting with mergers and acquisitions
D investment management
2.Whichone of the following is correct?
A banks can not engage in both commercial andinvestment banking activities
B banks create deposits by providing loans
C investment banks take in deposits fromcustomers
D commercial banks and investmentbanks have no risks
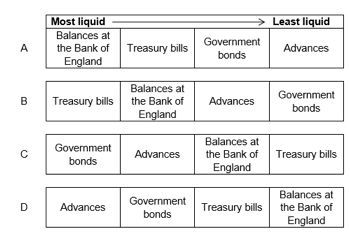
3.Three aims of commercial banks are liquidity, profitability andsecurity.To achieve these aims, the banks hold a range of assets. Which one of the following shows a list ofbanks’ assets ranging from the most liquid to the least liquid?
4.Whichone of the following is not the difference between Investment Bank andCommercial Bank?
A Deposits
B Loans and lending services
C The number of consumers
D Can not exist in one bank
5.Whichone of the following is not the risk of Investment Banks?
A Legal Risk
B Credit Risk
C Reputation Risk
D Price Risk
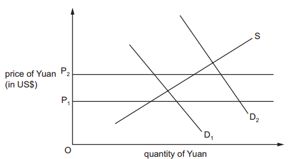
6.Assume the Chinese monetary authorities arecommitted to maintaining the exchange rate of China’s currency, the Yuan,against the US$ between P1 and P2 on the diagram.
What might they do if demand changed from D1 to D2?
A. impose controls on Chineseinvestment overseas
B. increase interest rates $
C. sell US$ from foreign exchangereserves
D. sell Yuan on the foreign exchange markets
7.What is usually a characteristic of low incomedeveloping countries?
A. an absenceof government intervention in the economy
B. low birthrates
C. lowtertiary sector output as a percentage of GDP
D. zero tariffs on imports
8.Which policy is likely to promote economicdevelopment in a developing economy but may lead to a decline in the rate ofeconomic growth?
A. a policy to increase female participation in thelabour market
B. a policy to increase immunisation rates
C. a policy to reverse environmental degradation
D. a policy to promoteexports
9.The Sri Lankan government decides to offerfinancial support to local firms. Of what is this an example?
A. a quota
B. a subsidy
C. a tariff
D. exchange control
10.Drinks producers in India are resisting plans toremove tariffs on imported drinks. They claim that a reduction in tariffs woulddestroy the emerging drinks industry with large-scale imports of cheap drinks.Which argument for protectionism are they putting forward?
A. thedeclining industry argument
B. the infantindustry argument
C. thestrategic industry argument
D. the sunset industry argument