Flutter学习第十三课:文本组件Text
一:文本组件Text
//文本
const Text(
String this.data, {//data必填项文本信息
Key? key,
this.style,//文本样式
this.strutStyle,//文本字体样式
this.textAlign,//文本应如何水平对齐
this.textDirection,//相对TextAlign中的start、end而言有用(当start使用了ltr相当于end使用了rtl,也相当于TextAlign使用了left)
this.locale,
this.softWrap,//某一行中文本过长,是否需要换行。默认为true,
this.overflow,//如何处理视觉溢出//TextOverflow.fade:将溢出的文本淡化为透明。TextOverflow.clip:剪切溢出的文本以修复其容器。TextOverflow.ellipsis:使用省略号表示文本已溢出。
this.textScaleFactor,//每个逻辑像素的字体像素数
this.maxLines,//本要跨越的可选最大行数
this.semanticsLabel,
this.textWidthBasis,
this.textHeightBehavior,
}) : assert(
data != null,
'A non-null String must be provided to a Text widget.',
),
textSpan = null,
super(key: key);
//富文本
const Text.rich(
InlineSpan this.textSpan, {
Key? key,
this.style,
this.strutStyle,
this.textAlign,
this.textDirection,
this.locale,
this.softWrap,
this.overflow,//如何处理视觉溢出//TextOverflow.fade:将溢出的文本淡化为透明。TextOverflow.clip:剪切溢出的文本以修复其容器。TextOverflow.ellipsis:使用省略号表示文本已溢出。
this.textScaleFactor,//textScaleFactor字体显示倍率
this.maxLines,//maxLines文字显示最大行数
this.semanticsLabel,
this.textWidthBasis,
this.textHeightBehavior,
}) : assert(
textSpan != null,
'A non-null TextSpan must be provided to a Text.rich widget.',
),
data = null,
super(key: key);
文本样式属性TextStyle
const TextStyle({
this.inherit = true,//是否将null值替换为祖先文本样式中的值(例如,在TextSpan树中)。如果为false,则没有显式值的属性将恢复为默认值:白色,字体大小为10像素,采用无衬线字体。
this.color,//文本颜色。如果指定了foreground,则此值必须为null。如自定义颜色:Color.fromRGBO(155, 155, 155, 1) 也可以使用Colors类里面自带的属性
this.backgroundColor,//文本的背景颜色
this.fontSize,//字体大小,默认14像素
this.fontWeight,//字体厚度,可以使文本变粗或变细
//FontWeight.bold 常用的字体重量比正常重。即w700
//FontWeight.normal 默认字体粗细。即w400
//FontWeight.w100 薄,最薄
//FontWeight.w200 特轻
//FontWeight.w300 轻
//FontWeight.w400 正常/普通/平原
//FontWeight.w500 较粗
//FontWeight.w600 半粗体
//FontWeight.w700 加粗
//FontWeight.w800 特粗
//FontWeight.w900 最粗
this.fontStyle,//字体风格:
//FontStyle.italic 使用斜体
//FontStyle.normal 使用直立
this.letterSpacing,//水平字母之间的空间间隔(逻辑像素为单位)。可以使用负值来让字母更接近。
this.wordSpacing,//单词之间添加的空间间隔(逻辑像素为单位)。可以使用负值来使单词更接近。
this.textBaseline,//对齐文本的水平线:
//TextBaseline.alphabetic:文本基线是标准的字母基线
//TextBaseline.ideographic:文字基线是表意字基线;
//如果字符本身超出了alphabetic 基线,那么ideograhpic基线位置在字符本身的底部。
this.height,//文本行与行的高度,作为字体大小的倍数(取值1~2,如1.2)
this.leadingDistribution,
this.locale,
this.foreground,
this.background,
this.shadows,//文本的阴影可以利用列表叠加处理,例如shadows: [Shadow(color:Colors.black,offset: Offset(6, 3), blurRadius: 10)], color即阴影的颜色, offset即阴影相对文本的偏移坐标,blurRadius即阴影的模糊程度,越小越清晰
this.fontFeatures,
this.decoration,//文字的线性装饰,比如 TextDecoration.underline 下划线, //TextDecoration.lineThrough删除线
this.decorationColor,//文本装饰线的颜色
this.decorationStyle,//文本装饰线的风格
this.decorationThickness,
this.debugLabel,
String? fontFamily,
List? fontFamilyFallback,
String? package,
this.overflow,
}) : fontFamily = package == null ? fontFamily : 'packages/$package/$fontFamily',
_fontFamilyFallback = fontFamilyFallback,
_package = package,
assert(inherit != null),
assert(color == null || foreground == null, _kColorForegroundWarning),
assert(backgroundColor == null || background == null, _kColorBackgroundWarning); textAlign
文本应如何水平对齐enum:
| 可选值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| TextAlign.center | 将文本对齐容器的中心 |
| TextAlign.end | 对齐容器后缘上的文本 |
| TextAlign.start | 对齐容器前缘上的文本 |
| TextAlign.justify | 拉伸以结束的文本行以填充容器的宽度。即使用了decorationStyle才起效 |
| TextAlign.left | 对齐容器左边缘的文本 |
| TextAlign.right | 对齐容器右边缘的文本 |
栗子:
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
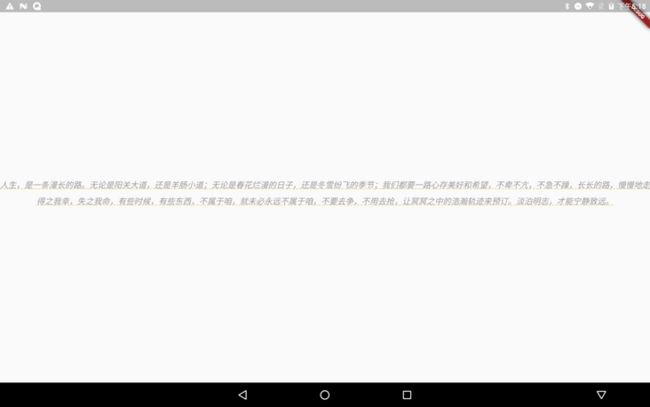
child: Text("人生,是一条漫长的路。无论是阳关大道,还是羊肠小道;无论是春花烂漫的日子,还是冬雪纷飞的季节;我们都要一路心存美好和希望,不卑不亢,不急不躁,长长的路,慢慢地走得之我幸,失之我命,有些时候,有些东西,不属于咱,就未必永远不属于咱,不要去争,不用去抢,让冥冥之中的浩瀚轨迹来预订。淡泊明志,才能宁静致远。",
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w500,//字体厚度
fontStyle: FontStyle.italic,//斜体
color: Color.fromRGBO(155, 155, 155, 1),//字体颜色
height: 2,//文本行与行的高度,作为字体大小的倍数(取值1~2,如1.2)
decoration: TextDecoration.underline,//下划线
decorationColor: Colors.orange,
decorationStyle: TextDecorationStyle.dashed//虚线
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,//对齐方式,居中对齐
),
),
);在上面的例子中,Text的所有文本内容只能按同一种样式,如果我们需要对一个Text内容的不同部分按照不同的样式显示,这时就可以使用TextSpan,它代表文本的一个“片段”。我们看看TextSpan的定义:
TextSpan用于指定文本片段的风格及手势交互
const TextSpan({
this.text,//显示文本的组件
this.children,////子组件
TextStyle? style,//文本的样式
this.recognizer,//指定手势交互
recognizer: TapGestureRecognizer()..onTap = () {},可以监听点击事件
MouseCursor? mouseCursor,
this.onEnter,
this.onExit,
this.semanticsLabel,
this.locale,
this.spellOut,
}) : mouseCursor = mouseCursor ??
(recognizer == null ? MouseCursor.defer : SystemMouseCursors.click),
assert(!(text == null && semanticsLabel != null)),
super(style: style);栗子:
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: RichText(
textScaleFactor: 5,//字体显示倍率
overflow: TextOverflow.fade,//TextOverflow.fade:将溢出的文本淡化为透明。TextOverflow.clip:剪切溢出的文本以修复其容器。TextOverflow.ellipsis:使用省略号表示文本已溢出。
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
textAlign: TextAlign.left,//对齐方式
text: TextSpan(
children: [
TextSpan(
text: "保证不对外公开或向第三方提供单个用户的注册资料及用户在使用网络服务时存储",
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
),
recognizer: TapGestureRecognizer()..onTap = () {}),
TextSpan(text: "安全协议",
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.red,
),
//点击事件
recognizer: TapGestureRecognizer()..onTap = () {
print("点击了安全协议");
})
]
),
),
),
)
-----------------------------------------------------
//另一种方式实现父文本文本组装使用Text.rich()
//InlineSpan 是默认必须得加的
InlineSpan span = TextSpan(children: [
TextSpan(
text: "保证不对外公开或向第三方提供单个用户的注册资料及用户在使用网络服务时存储",
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
),
recognizer: TapGestureRecognizer()..onTap = () {}),
TextSpan(
text: "安全协议",
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.red,
),
//点击事件
recognizer: TapGestureRecognizer()
..onTap = () {
print("点击了安全协议");
})
]);
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Text.rich(
span,
textScaleFactor: 5,
//字体显示倍率
overflow: TextOverflow.fade,
//TextOverflow.fade:将溢出的文本淡化为透明。TextOverflow.clip:剪切溢出的文本以修复其容器。TextOverflow.ellipsis:使用省略号表示文本已溢出。
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
textAlign: TextAlign.left, //对齐方式
),
),
);