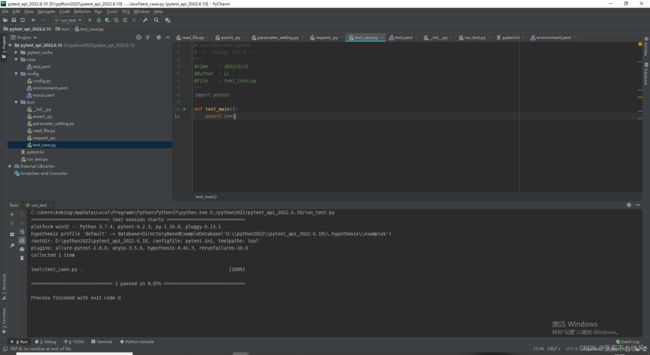
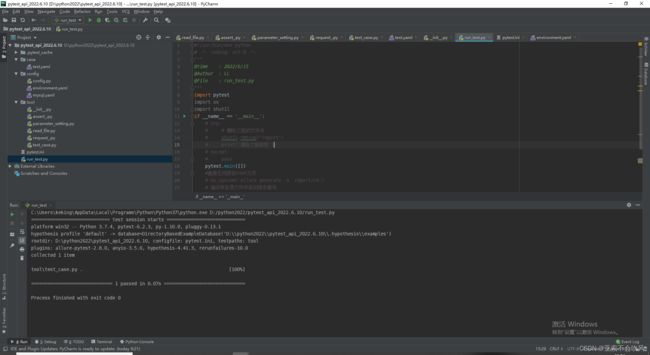
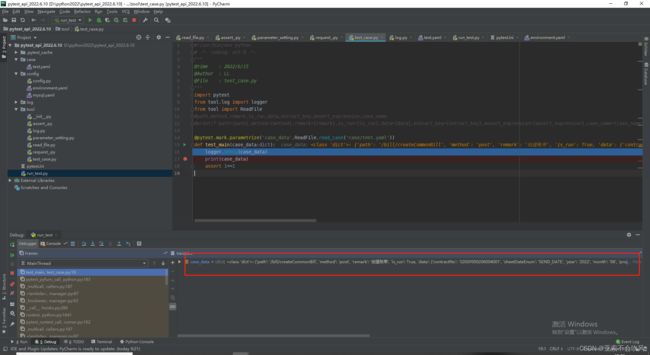
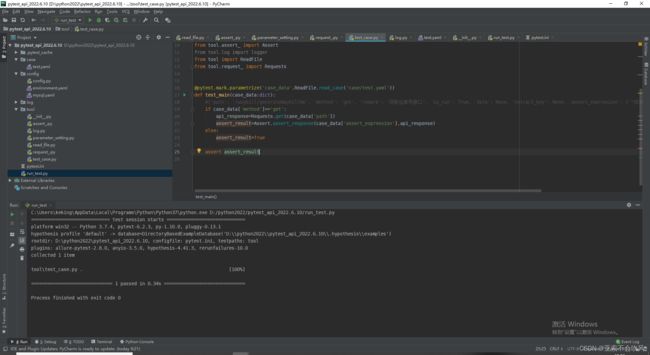
pytest+yaml设计接口自动化框架过程记录(一步一步记录如何设计,完结撒花),源码提供,视频教程
pytest+yaml设计接口自动化框架过程记录
-
- 框架简介
- 框架运行演示和功能介绍视频
- pytest+yaml框架环境配置和使用教程
- 0.去年也写了一个测试框架,不过用例需要用代码来编写
- 1.第一步我先写一个环境配置文件
- 2.我写一个读取文件的类
-
- 方法测试:
- 3.环境配置总开关
- 4.写一个读取并处理配置文件信息的方法,使用我之前写的读取ymal的方法,把数据组合起来
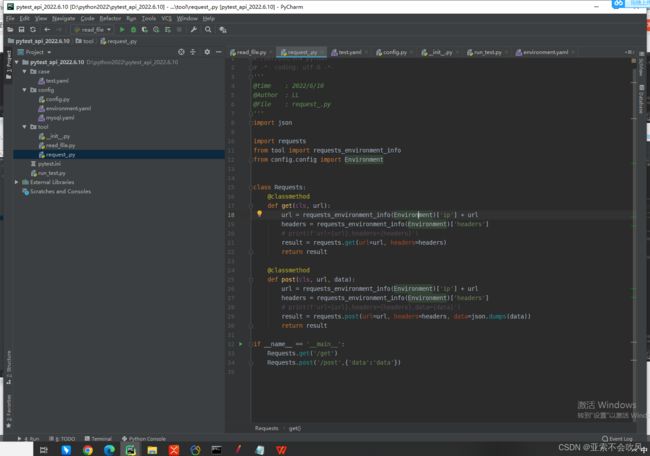
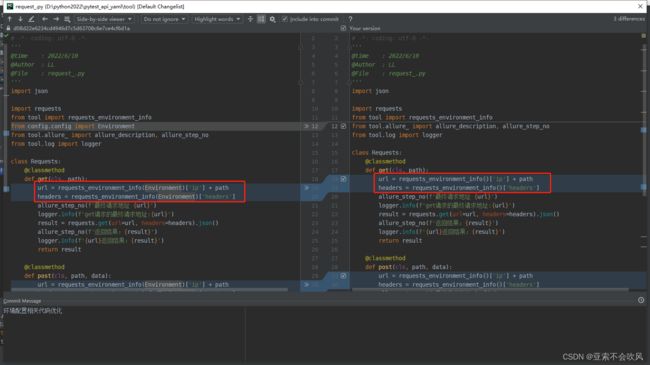
- 5.初步封装requests方法,大部分接口都是这2个请求场景,针对公司接口格式封装
-
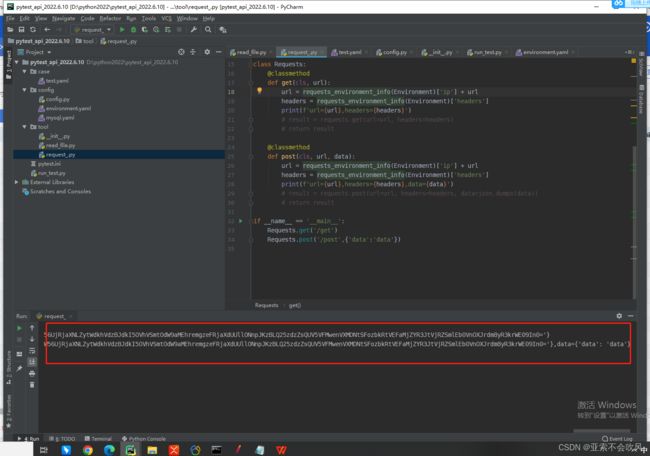
- 测试请求数据读取情况,读出来最终url,headers,data
- 6.yaml格式用例设计
-
- 测试读取,按照注释的格式来(设计时各种报错)
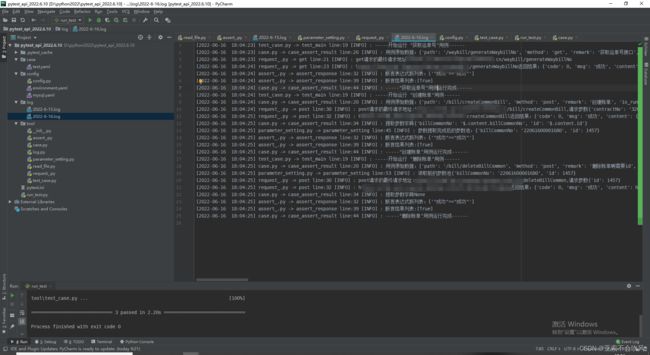
- 7.编写用例请求参数依赖方法(接口返回值提取和接口参数依赖),一个图截不下啊
-
- 保存到参数池需要明确的数值,需要提前把提取表达式处理下
- 搞个代码
- 测试
- 8.写一个读取用例数据的迭代器,可以判断是否需要执行,把请求参数表达式替换为具体的值,测试结果也截图了,但是这个方法只能读取单个文件的数据,后续处理多个文件。或者直接读取整个文件,还可以设置排除用例文件的方式运行
-
- 测试代码这里使用了生成器来一条一条的返回
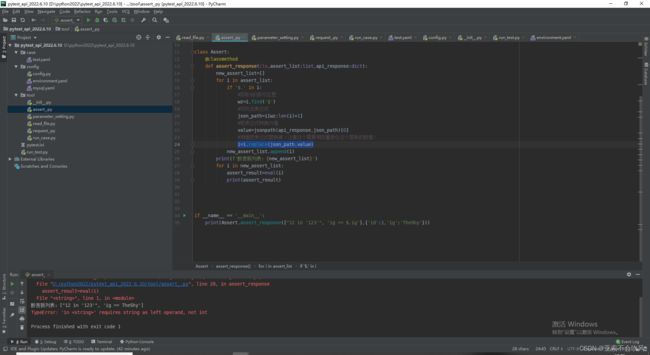
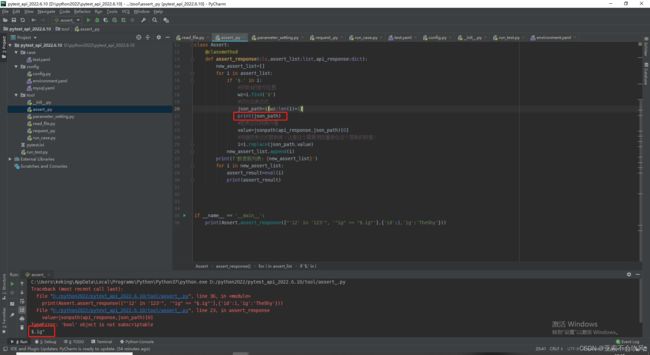
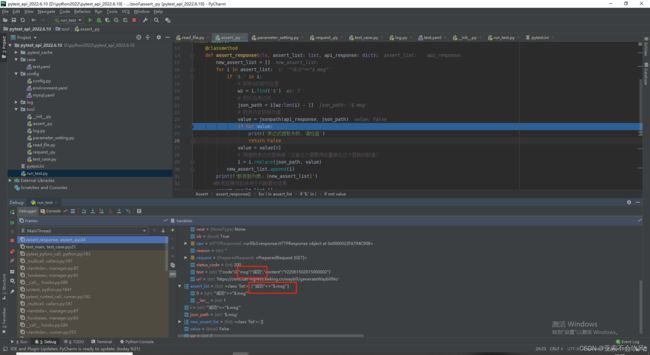
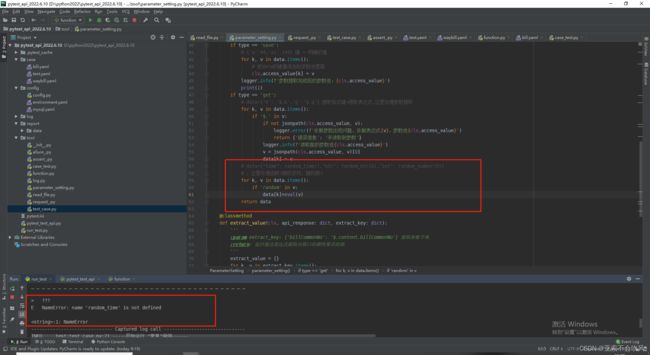
- 9.设计处理断言列表的方法,这里我发现没有替换成功,i=i.replace(json_path,value)需要把值接住才可以
-
- 我把新列表(已经把json表达式替换成了值)遍历解析每一个断言元素时遇到 requires string as left operand, not int报错,大概意思就是
- 我在把这个12加上了单引号["'12' in '123'", 'ig == $.ig'], 然后后面的 'ig == $.ig'又出现了新问题,ig变量未定义,ig本来是‘ig’为字符串,但是被eval()函数处理后就会变成ig,是一个变量
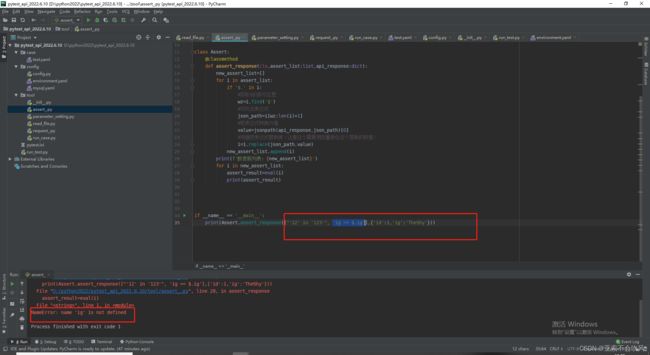
- 于是我又给ig加上了引号
- 可是被替换为值的TheShy被eval()函数处理后又成了变量,我想着给"$.ig"加上引号,可是在jsonpath提取时出现了问题
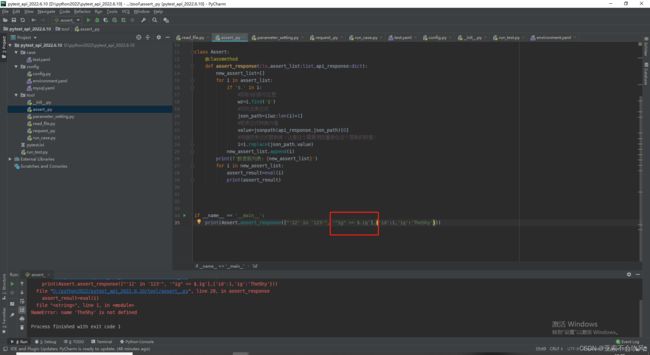
- 打印下我的提取表达式提取表达式格式错误了,没取到值。发现我给之前的表达式加上了引号,我提取表达式是通过符号的索引位置到最后一个索引位置,现在我只能取倒数第二个索引位置
- 经过我的一顿操作,勉强解决问题,需要完善一下这个方法
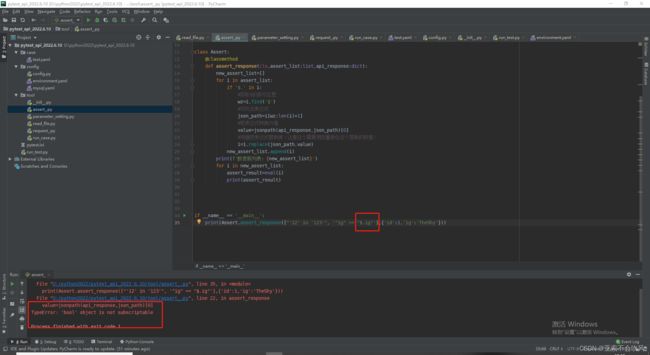
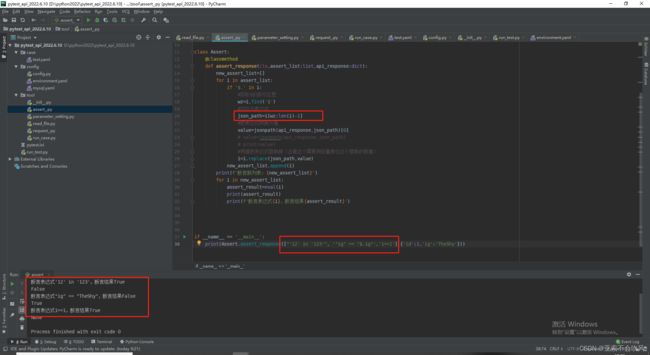
- 方法完善,大改一波,测试结果,但是这里出现的问题,不得不修改用例模板断言列表的编写格式
- 代码
- 10.用例格式更改,还是使用原始列表格式写断言列表
- 11.pytest初次登场
-
- pytest.ini 配置pytest运行规则,要位于项目根目录下
- 我准备写一个主方法(结合之前写的参数处理,断言处理等方法)来运行从yaml里面读取的用例数据
- 运行pytest文件
- 12.pytest 获取用例参数
- 13.日志文件以前写过直接拿来用
- 14.实现get请求用例
-
- 发现个问题,我使用jsonpath时提取了非json的数据
- 解决方案:对返回结果进行了处理,后续还得考虑非json格式返回的问题
- 15.实现post请求和使用参数提取和参数依赖(好多坑,裂开)
-
- 处理用例执行返回断言结果
- 测试post请求时接口一直报错,查日志发现是传参格式的问题,之前在headers里面没有设置,补充一下
- 16.出现bug参数池保存完成后,下次读取时参数池重置
-
- 排除问题查看池子信息提取信息
- 忙活了半天,猜测估计是一个类方法在2个py页面使用时使用的参数池就不是一样的了,下一个使用的是重置的参数池
- 后来我把这个参数替换和参数提取放着了一个方法里面,这样就是共用一个参数池了
- 17.日志写到该写的地方(日志不要太复杂)
-
- 看下最终走进了的请求信息,判断接口失败或者成功的信息
- 这个方法又运行接口和处理参数提取
- 断言方法,通过接口返回结果和断言表达式列表来处理
- 主方法,加个用例开始执行,这个方法越简洁越好
- 日志的最终效果
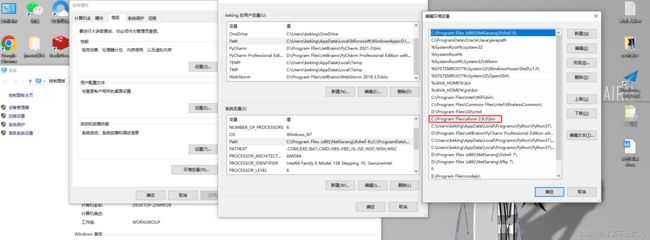
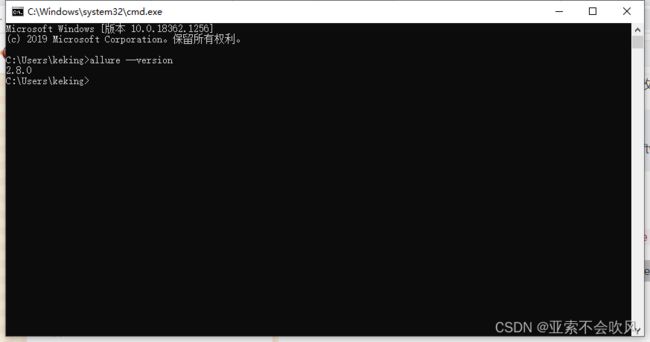
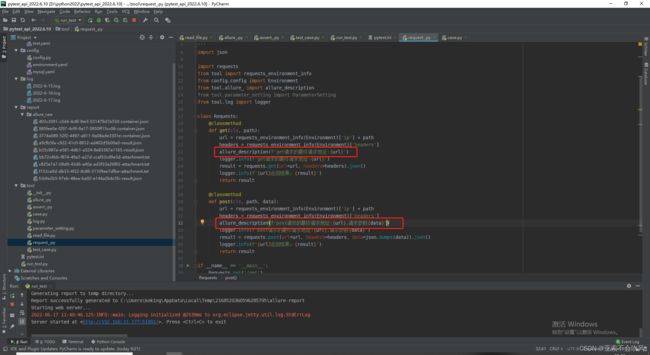
- 18.使用allure(配置环境)
-
- 配置环境
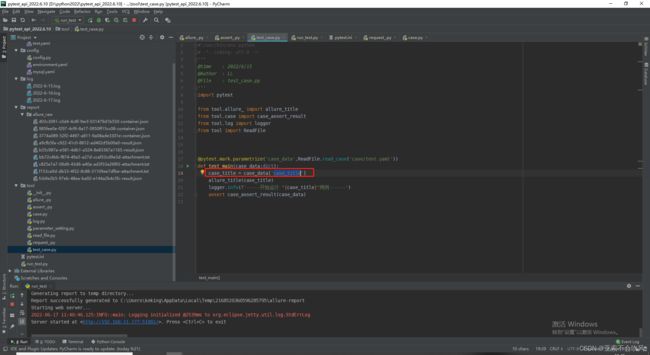
- 18.allure简单封装并使用
-
- 使用记录用例标题
- 最终请求信息使用报告描述记录
- 这里记录下用例数据里面的描述信息
- 19.allure报告生成
-
- 运行启动文件,清空之前的文件,直接打开报告
- 20.allure生成本地报告(命令解析)
-
- pytest运行后产生了report目录和data目录然后开始运行os.system('allure generate report/data -o report/html --clean')直接生成html目录(里面包含了html文件)
- 21.发现bug(因为之前get请求方法里面没有写处理参数提取的,导致使用get请求没有到提取参数)
-
- 给get请求也加上参数提取处理,我看都加的话代码看起来好丑,直接封装为一个方法,直接用好一点
- 代码
- 22.使用一个用到框架比较多的用例(3个接口,我自己fastapi写的)
-
- 其中一个接口,另外几个看我写的fastapi的那个文章
- 测试结果
- 23.增加随机几位数字、字符,获取当前时间的方法,并写在用例里面使用
-
- 3个方法
- 在参数提取这里加上一个函数处理,但是一开始没有导入这几个方法报错了
- 导入方法,虽然是灰色的,但是在运行过程中会使用到
- 用例文件使用
- 最终运行结果,函数已经替换为了具体的时间,数字和字符
- 用例模板更新一下(加入函数使用)
- 24.多目录多文件用例处理,实现一个通过目录和文件排除一些用例文件的方法,来返回要运行测试用例文件
-
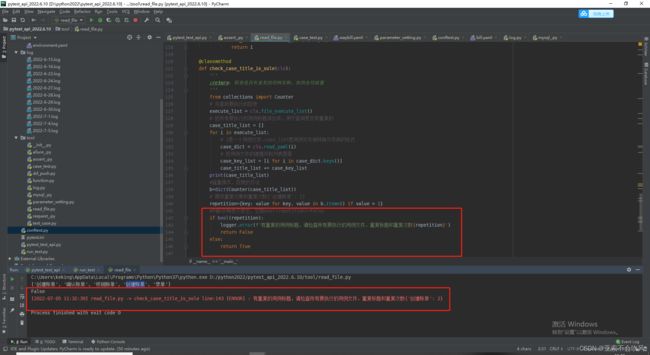
- 第一版(有bug)
- 最新读取文件的方法代码(有点bug)
- 第二版
- bug修复后代码
- 使用(细节)
- 字典拼接知识点
- 当前最终读取文件代码
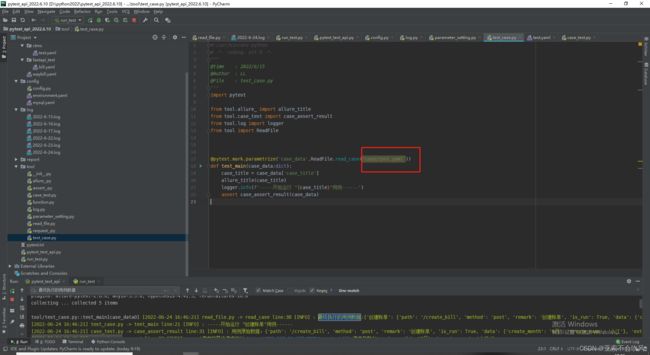
- test_case文件ReadFile.read_case()方法的参数注意去掉
- 报告,最终运行了2个文件下的用例,但是现在没有标识用例出自于那个文件
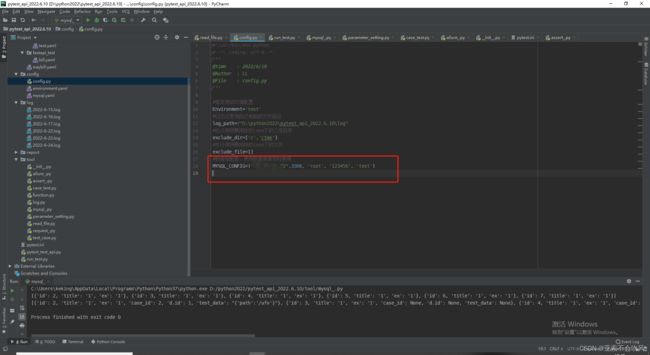
- 25.增加mysql数据库操作
-
- 代码
- 代码测试
- 数据库配置
- 26.mysql使用(前置sql,(请求参数sql,断言sql有问题))bug修复完成
-
- sql有2大类,一个是查询有返回值,一个是增删改无返回值,前置sql为无返回值类型
- 有bug时的用例设计和代码
- bug修复时的用例设计和代码
- 27.源码上传
-
- 代码下拉后首次启动的4个坑
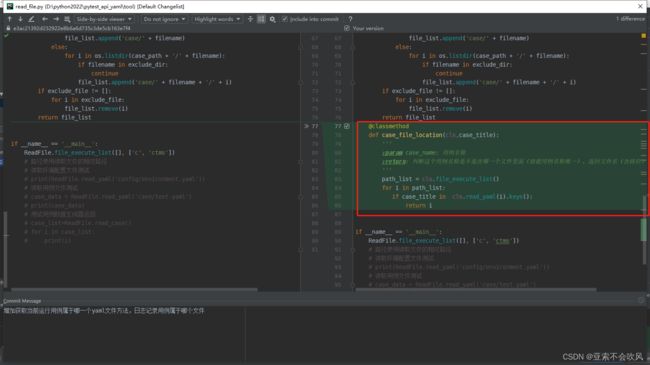
- 28.增加获取当前运行用例属于哪一个yaml文件方法,日志记录用例属于哪个文件
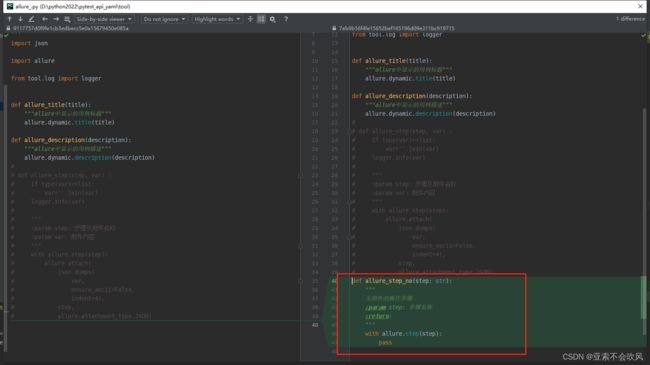
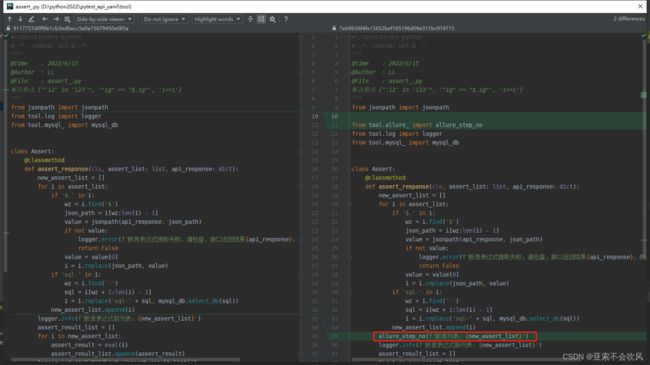
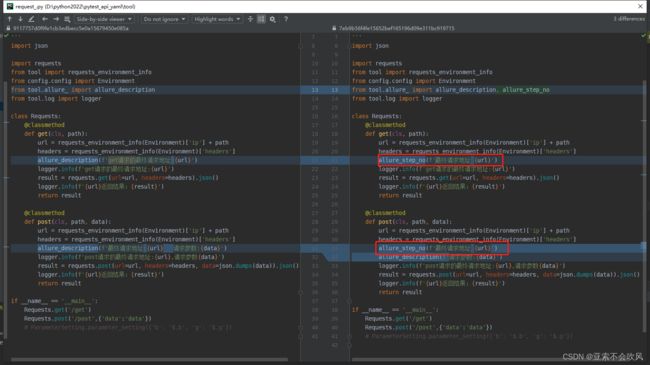
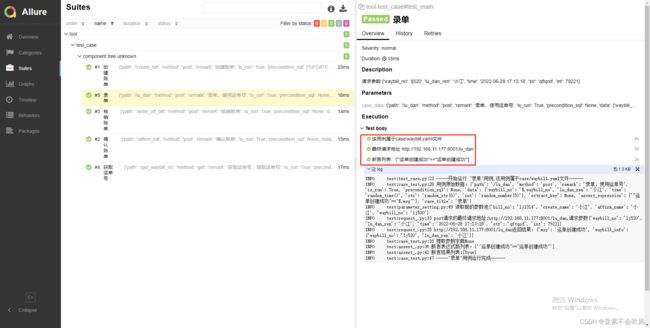
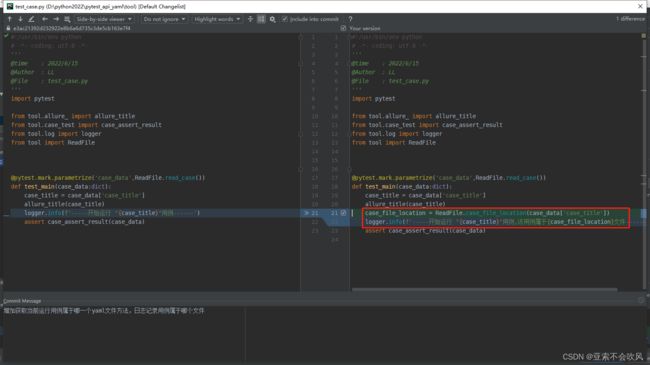
- 29.增加allure步骤描述,描述用例所属文件,请求地址,断言列表(都自定义)
-
- 报告效果
- 30.钉钉推送测试报告,全局前后置配置(公司局域网内都可访问)
-
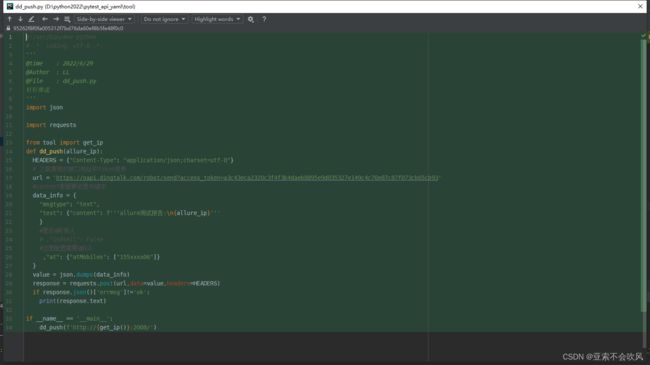
- python操作钉钉机器人推送消息
- 新增钉钉dd_push.py,现在的内容就是发送个链接并且@我自己
- 固定allurl报告服务启动的端口
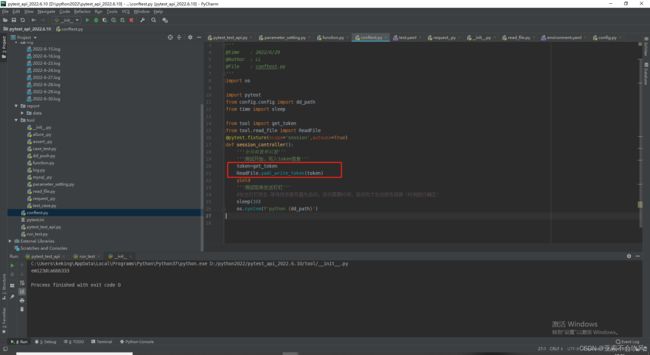
- 配置conftest.py实现全局前后置(后置推送钉钉消息)
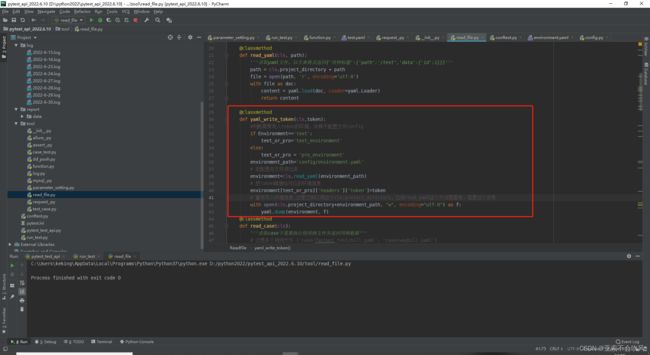
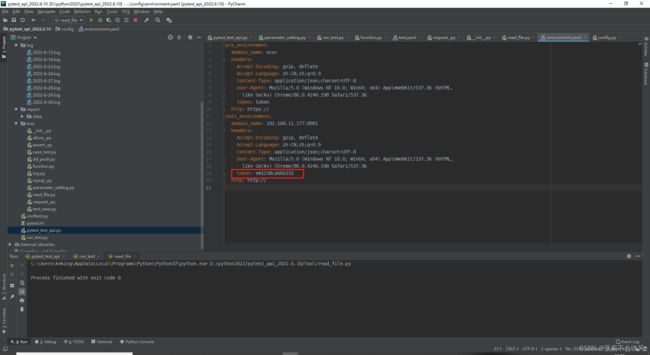
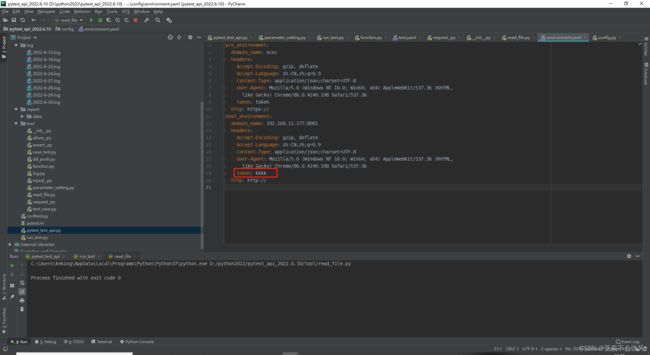
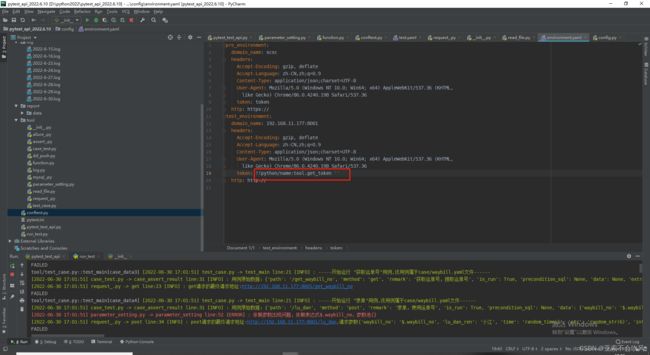
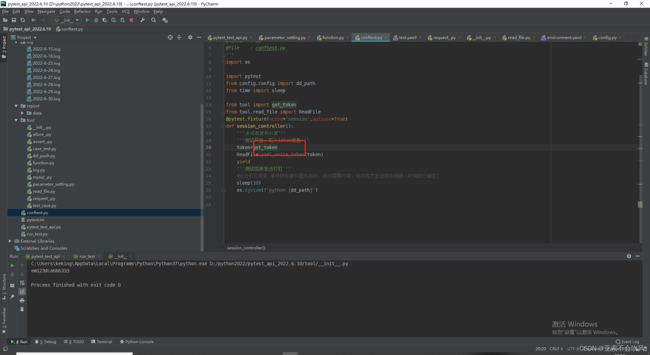
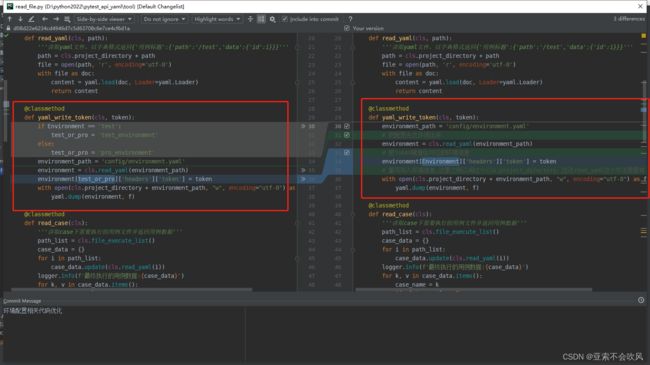
- 31.token前置写入到测试环境配置文件
-
- 先写一个写入token到yaml文件的方法
- 测试
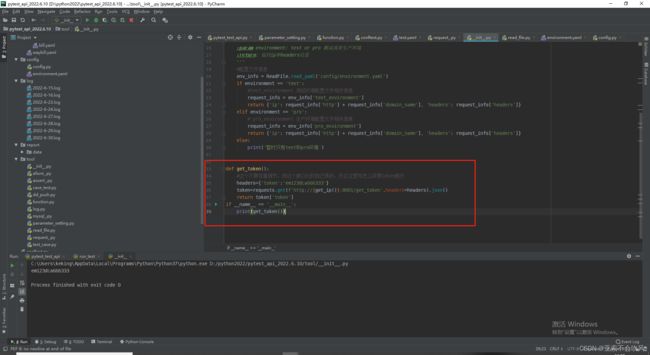
- 写个获取token的方法
- 配合@pytest.fixture前置写入token
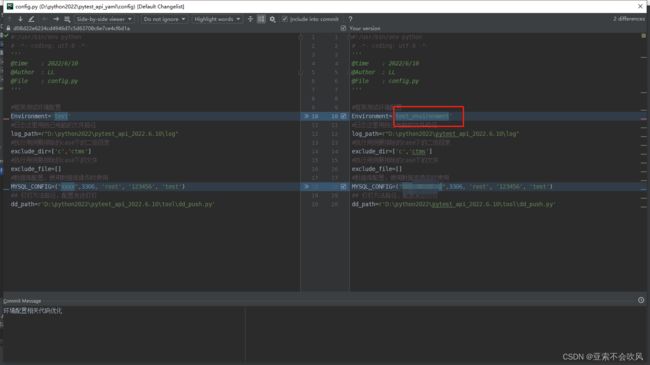
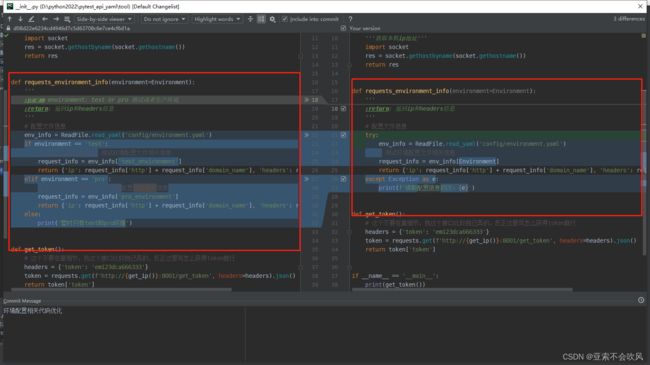
- 32.环境配置相关代码优化(直接使用配置的数据)
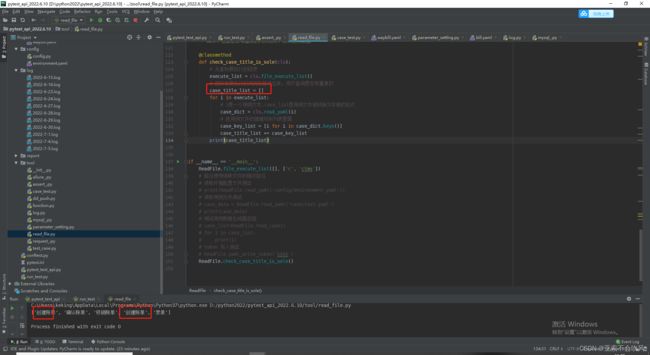
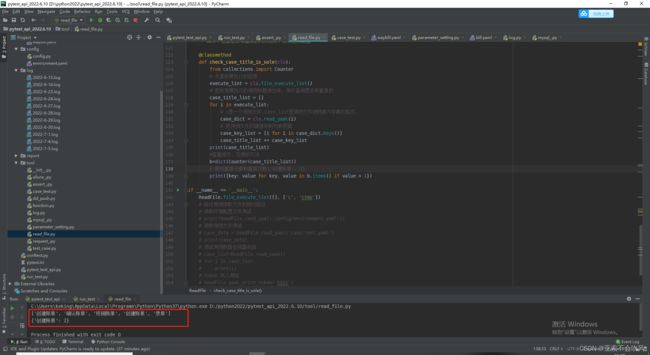
- 33.判断所有用例执行的文件是否有重复的标题
-
- 查询列表的重复元素和出现重复的次数
- 知识点:判断字典是否为空
- 判断是否有重复元素,有就日志打印出重复元素和出现的次数
- 使用@pytest.mark.skipif
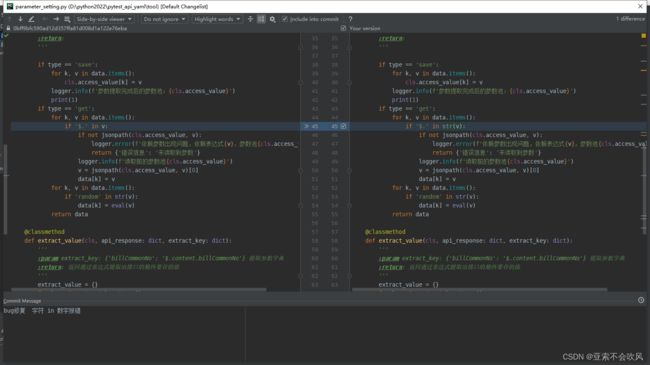
- 34.bug修复
- 35.处理请求参数嵌套的情况
-
- 新增2个方法
- 方法使用
- 测试(暂时只支持这种嵌套[{},{},{}])
- bug发现
- bug解决
- 解决嵌套参数中的随机函数使用问题
- 36.解决请求参数是数组(列表)格式的问题
框架简介
'''
基于pytest+yaml+allure+requests搭建的接口自动化框架(提供测试接口基于fastapi)
tool功能:
__init__: 读取具体的环境配置信息给requests_使用
requests_请求接口:requests二次封装,自动获取headers和域名信息
read_file文件读取:读取目录下yaml文件,支持排除指定文件和目录,最终返回字典格式的用例数据
parameter_setting参数设置:提供参数池,支持接口返回参数提取保存和接口请求参数提取(解决参数依赖)
log日志:保存运行日志记录
function函数:支持随机几位数的字符,数字和当前时间函数,直接在用例文件中使用
assert_断言操作:处理多个断言表达式,返回最终断言结果
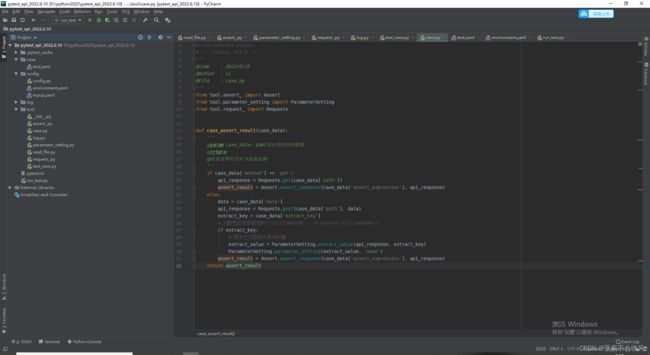
case_test用例执行:处理从read_file读取出的原始用例数据,使用parameter_setting进行参数存储和提取,使用assert_进行断言,最后返回用例执行结果
allure_报告定制:allure.dynamic动态属性的简单封装
mysql_:数据库操作,用于前置sql,请求参数sql,断言sql
'''
框架运行演示和功能介绍视频
框架运行演示和功能介绍视频述
pytest+yaml框架环境配置和使用教程
pytest+yaml框架环境配置和使用教程
0.去年也写了一个测试框架,不过用例需要用代码来编写
基于pytest搭建接口自动化测试框架,提供源码
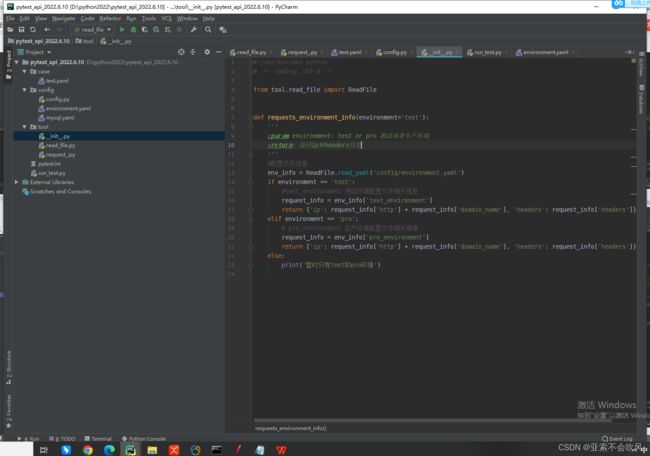
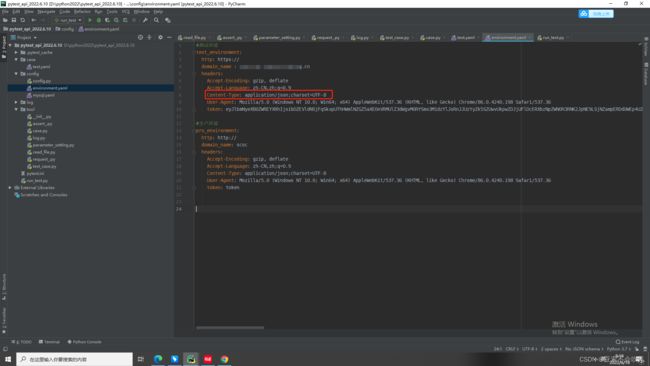
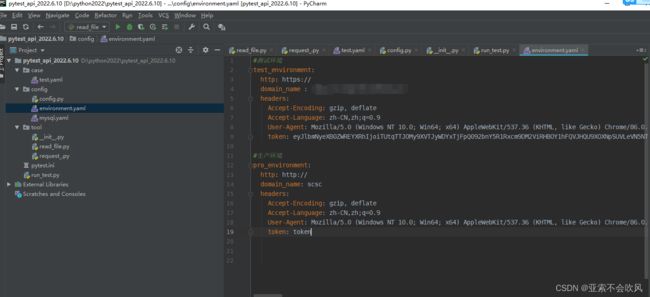
1.第一步我先写一个环境配置文件
按自己公司环境配置,我这边只有测试和生产环境,配置协议,域名和headers。后续我只有提供地址和请求参数就可以发起接口访问
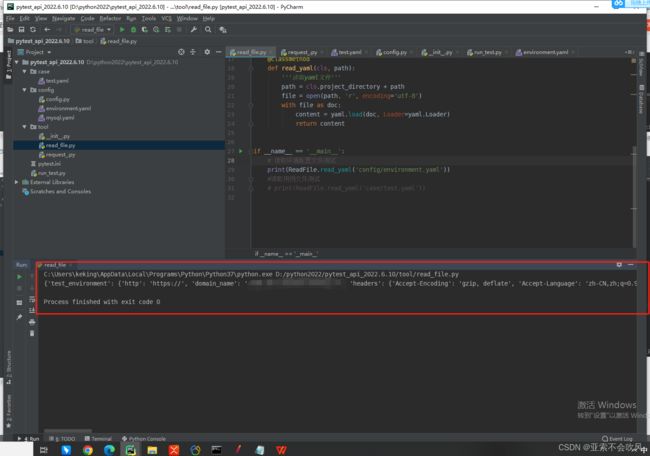
2.我写一个读取文件的类
准备用于处理文件相关,现在只有读取yaml问的方法,后续准备写读取execl、execl和yaml用例数据转换,用例数据处理。
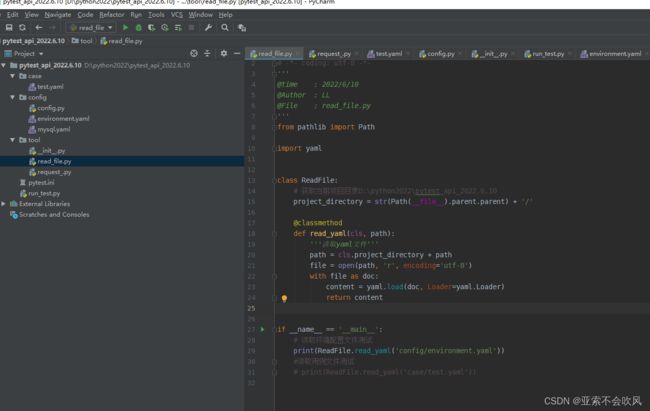
方法测试:
3.环境配置总开关
一开始我是想把环境这个参数放着请求时填写的,最后发现比较麻烦,一切以简单明了为好

4.写一个读取并处理配置文件信息的方法,使用我之前写的读取ymal的方法,把数据组合起来
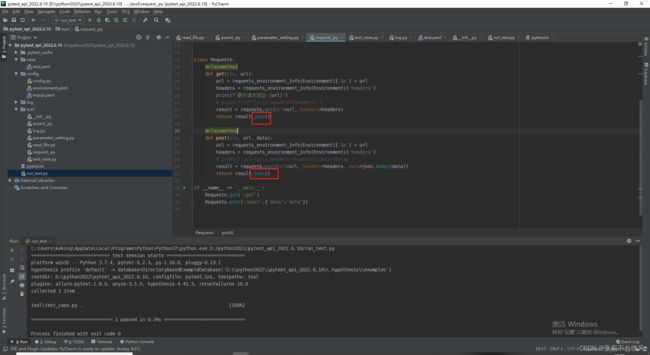
5.初步封装requests方法,大部分接口都是这2个请求场景,针对公司接口格式封装
测试请求数据读取情况,读出来最终url,headers,data
6.yaml格式用例设计
测试读取,按照注释的格式来(设计时各种报错)
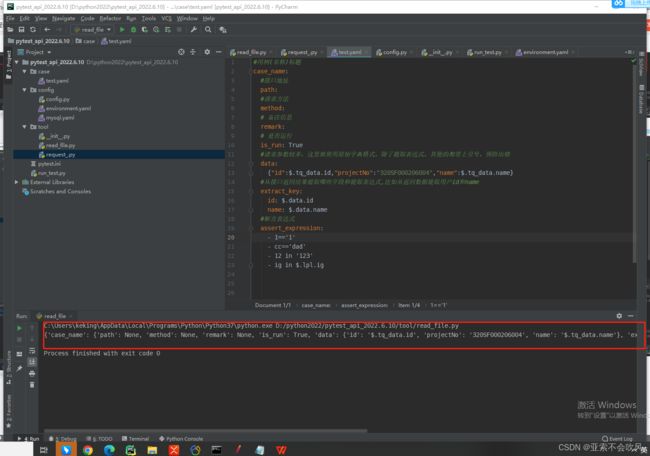
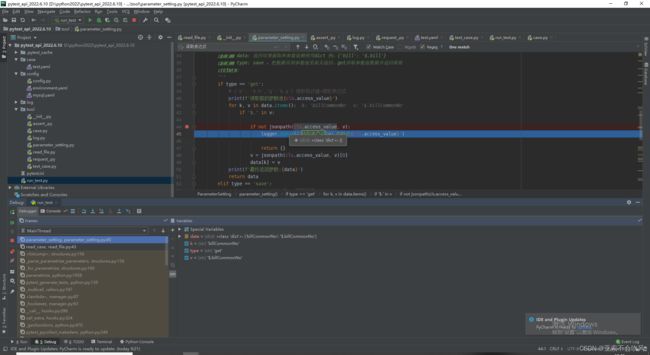
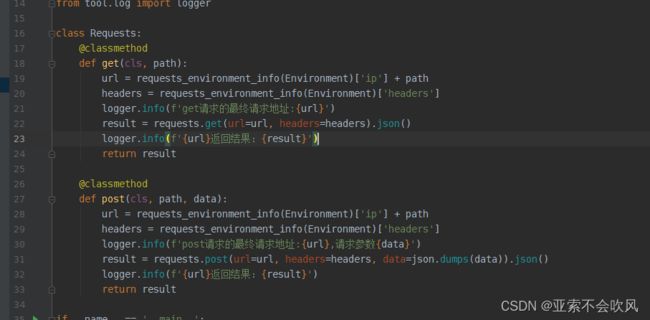
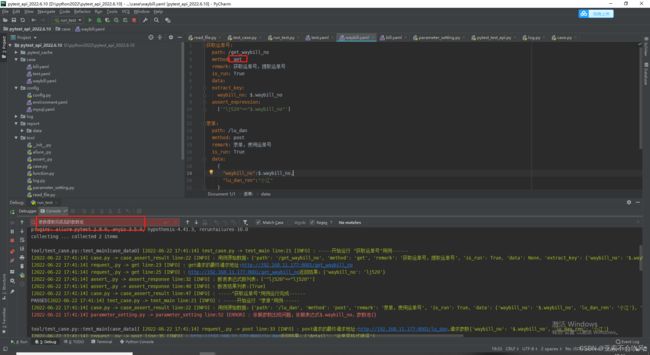
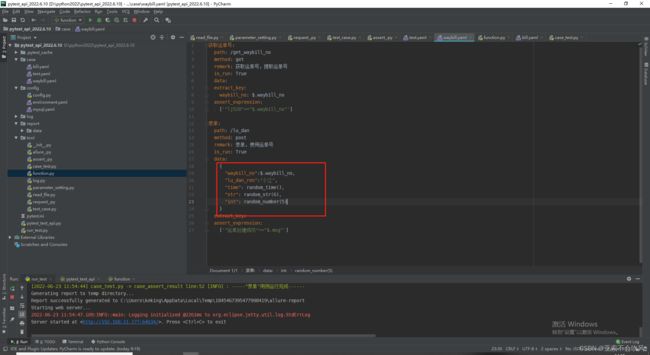
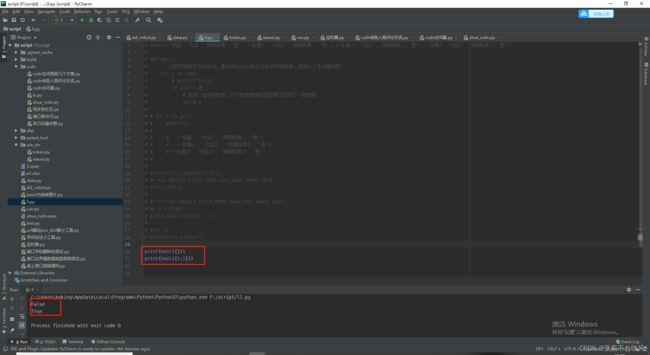
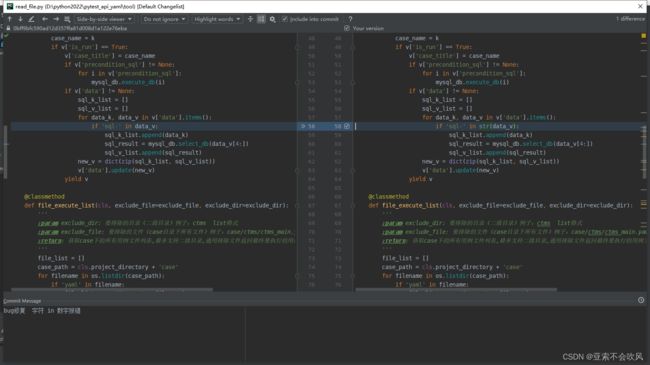
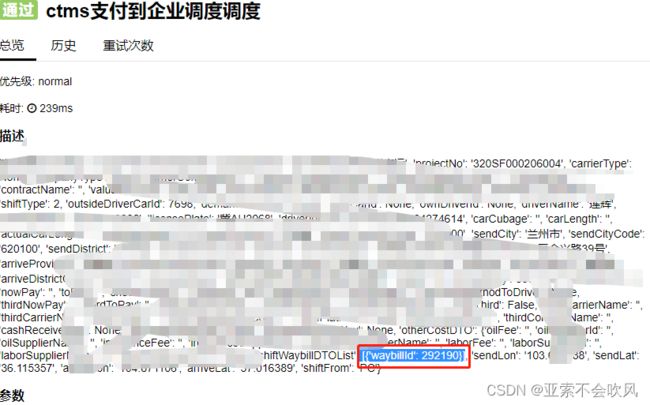
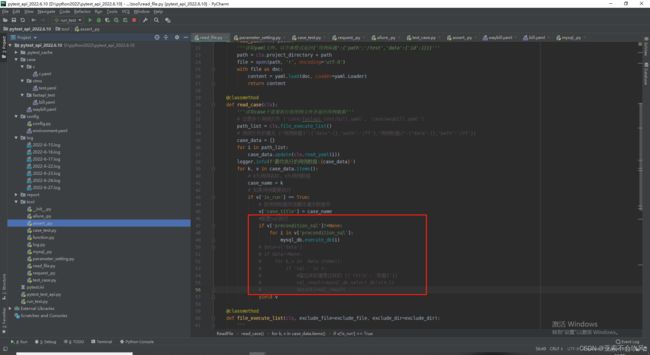
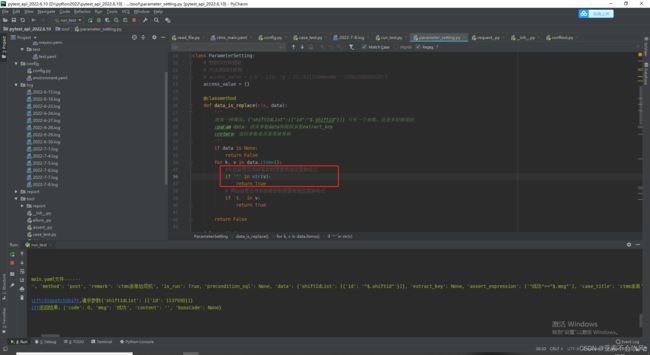
7.编写用例请求参数依赖方法(接口返回值提取和接口参数依赖),一个图截不下啊
data_is_replace()判断数据需不需要替换,data有可能是空,因为一些接口不需要请求参数,或者不需要提取接口返回值
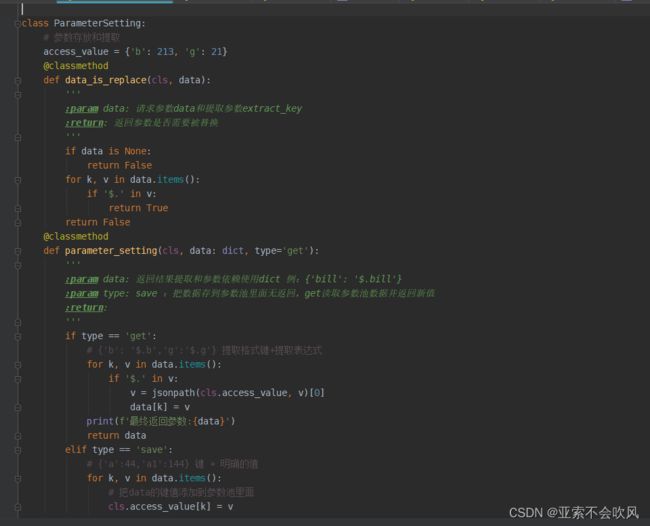
保存到参数池需要明确的数值,需要提前把提取表达式处理下
![]()
搞个代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/14
@Author : LL
@File : parameter_setting.py
参数处理
'''
from jsonpath import jsonpath
from tool.log import logger
#运行中会调用这些方法
from tool.function import random_time,random_str,random_number
class ParameterSetting:
# 参数存放和提取
# 方法测试时使用
# access_value = {'b': 213, 'g': 21,'billCommonNo':'22061500001629'}
access_value = {}
@classmethod
def data_is_replace(cls, data):
'''
:param data: 请求参数data和提取参数extract_key
:return: 返回参数是否需要被替换
'''
if data is None:
return False
for k, v in data.items():
if '$.' in v:
return True
return False
@classmethod
def parameter_setting(cls, data: dict, type='get'):
'''
:param data: 返回结果提取和参数依赖使用dict 例:{'bill': '$.bill'}
:param type: save :把数据存到参数池里面无返回,get读取参数池数据并返回新值
:return:
'''
if type == 'save':
# {'a':44,'a1':144} 键 + 明确的值
for k, v in data.items():
# 把data的键值添加到参数池里面
cls.access_value[k] = v
logger.info(f'参数提取完成后的参数池:{cls.access_value}')
print(1)
if type == 'get':
# data={'b': '$.b','g':'$.g'} 提取格式键+提取表达式,这里处理参数提取
for k, v in data.items():
if '$.' in v:
if not jsonpath(cls.access_value, v):
logger.error(f'依赖参数出现问题,依赖表达式{v},参数池{cls.access_value}')
return {'错误信息': '未读取到参数'}
logger.info(f'读取前的参数池{cls.access_value}')
v = jsonpath(cls.access_value, v)[0]
data[k] = v
# data={"time": random_time(),"str": random_str(6),"int": random_number(5)}
# ,这里处理函数(随机字符,随机数)
for k, v in data.items():
if 'random' in str(v):
data[k]=eval(v)
return data
@classmethod
def extract_value(cls, api_response: dict, extract_key: dict):
'''
:param extract_key: {'billCommonNo': '$.content.billCommonNo'} 提取参数字典
:return: 返回通过表达式提取出接口的最终要存的值
'''
extract_value = {}
for k, v in extract_key.items():
# 把表达式通过接口返回的数据变成值,通过字典添加到extract_value里面返回
extract_value[k] = jsonpath(api_response, v)[0]
return extract_value
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 测试参数存储
ParameterSetting.parameter_setting({'a': 44, 'a1': 144, 'b': 1, 'g': 'wbg'}, 'save')
# 测试参数读取
ParameterSetting.parameter_setting({'b': '$.b', 'g': '$.g'})
print(f'最终的参数池{ParameterSetting.access_value}')
# 测试提取参数字典转换为值
# print(ParameterSetting.extract_value({'data':{'id':'1'}},{'id':'$.data.id'}))
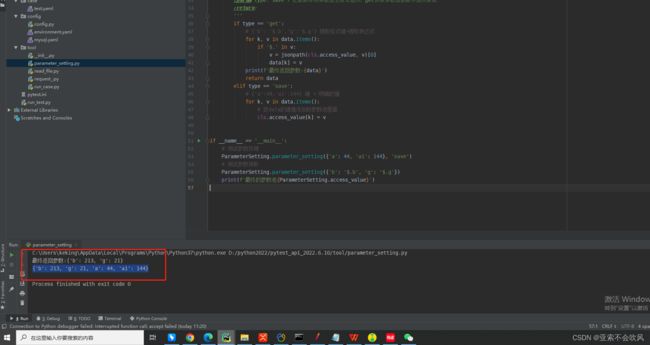
测试
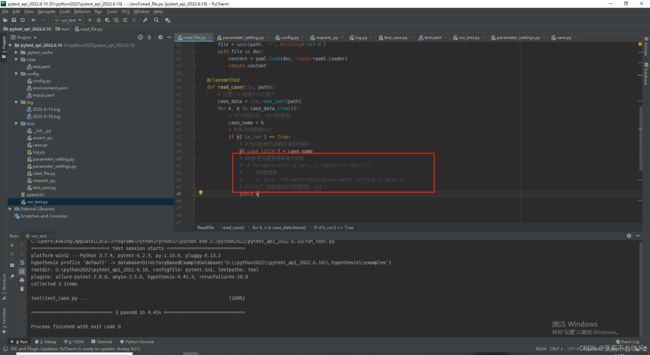
8.写一个读取用例数据的迭代器,可以判断是否需要执行,把请求参数表达式替换为具体的值,测试结果也截图了,但是这个方法只能读取单个文件的数据,后续处理多个文件。或者直接读取整个文件,还可以设置排除用例文件的方式运行
测试代码这里使用了生成器来一条一条的返回
生成器我之前写过一篇 python生成器+pytest实现参数化
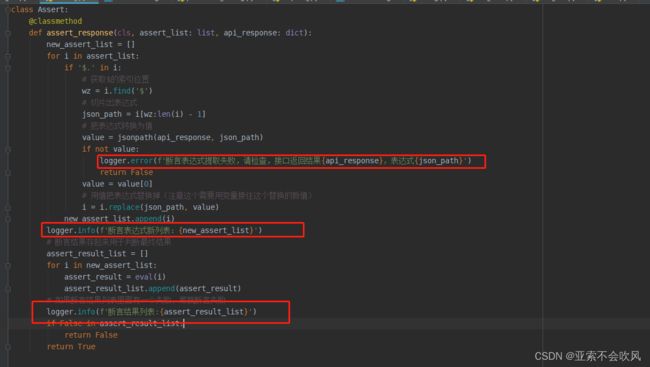
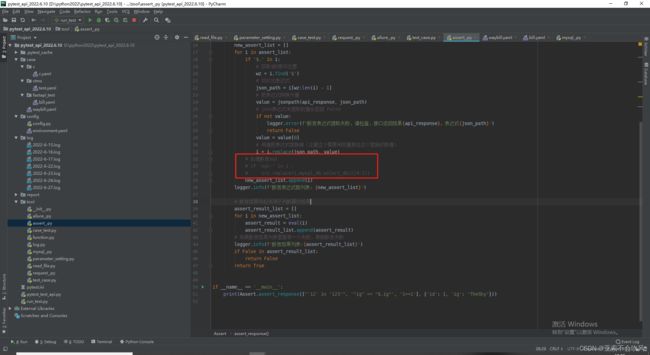
9.设计处理断言列表的方法,这里我发现没有替换成功,i=i.replace(json_path,value)需要把值接住才可以
我把新列表(已经把json表达式替换成了值)遍历解析每一个断言元素时遇到 requires string as left operand, not int报错,大概意思就是
我在把这个12加上了单引号[“‘12’ in ‘123’”, ‘ig == $.ig’], 然后后面的 'ig == $.ig’又出现了新问题,ig变量未定义,ig本来是‘ig’为字符串,但是被eval()函数处理后就会变成ig,是一个变量
于是我又给ig加上了引号
可是被替换为值的TheShy被eval()函数处理后又成了变量,我想着给"$.ig"加上引号,可是在jsonpath提取时出现了问题
打印下我的提取表达式提取表达式格式错误了,没取到值。发现我给之前的表达式加上了引号,我提取表达式是通过符号的索引位置到最后一个索引位置,现在我只能取倒数第二个索引位置
经过我的一顿操作,勉强解决问题,需要完善一下这个方法
方法完善,大改一波,测试结果,但是这里出现的问题,不得不修改用例模板断言列表的编写格式
代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/15
@Author : LL
@File : assert_.py
断言格式 ["1=='1'", "cc=='dad'", "12 in '123'", 'ig in $.lpl.ig']
'''
from jsonpath import jsonpath
class Assert:
@classmethod
def assert_response(cls, assert_list: list, api_response: dict):
new_assert_list = []
for i in assert_list:
if '$.' in i:
# 获取$的索引位置
wz = i.find('$')
# 切片出表达式
json_path = i[wz:len(i) - 1]
# 把表达式转换为值
value = jsonpath(api_response, json_path)
if not value:
print('表达式提取失败,请检查')
return False
value = value[0]
# 用值把表达式替换掉(注意这个需要用变量接住这个替换的新值)
i = i.replace(json_path, value)
new_assert_list.append(i)
print(f'断言新列表:{new_assert_list}')
#判断每个断言的成功或者失败
assert_result_list=[]
for i in new_assert_list:
assert_result = eval(i)
print(f'断言表达式{i},断言结果{assert_result}')
assert_result_list.append(assert_result)
#如果断言结果列表里面有一个失败,那就断言失败
if False in assert_result_list:
return False
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(Assert.assert_response(["'12' in '123'", '"ig" == "$.ig"', '1==1'], {'id': 1, 'ig': 'TheShy'}))
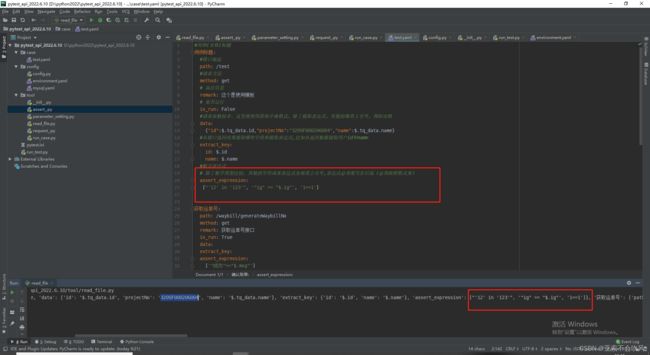
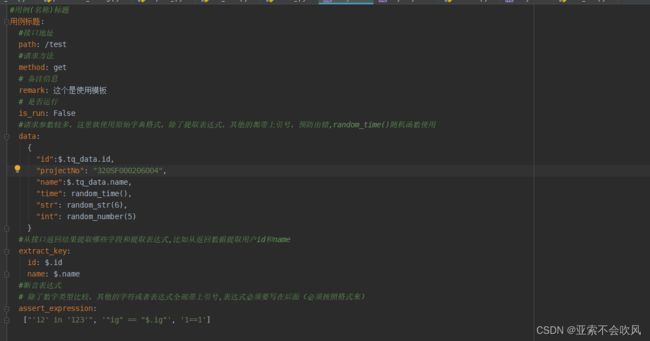
10.用例格式更改,还是使用原始列表格式写断言列表
感谢 yilidou1005 提出的bug ,这里的参数池只有一层的。
最新的用例模板,这里下面的几个模板现在不用管,后面会介绍的
#用例(名称)标题
用例标题:
#接口地址
path: /test
#请求方法
method: post
# 备注信息
remark: 这个是使用模板
# 是否运行
is_run: True
# 前置sql:sql有2大类,一个是查询有返回值,一个是增删改无返回值,前置sql为无返回值类型
precondition_sql:
- UPDATE case_test SET title = '标题2', ex = '44' WHERE id = 2
- UPDATE case_test SET title = '标题3', ex = '55' WHERE id = 3
#请求参数较多,这里就使用原始字典格式,除了提取表达式,其他的都带上引号,预防出错,random_time()随机函数使用
data:
{
"id":$.id,
"projectNo": "320SF000206004",
"name":$.name,
"time": random_time(),
"str": random_str(6),
"int": random_number(5),
# 请求参数sql为有返回值查询
"sql": sql-SELECT title FROM case_test where id=2
}
#从接口返回结果提取哪些字段和提取表达式,比如从返回数据提取用户id和name
extract_key:
id: $.id
name: $.name
#断言表达式
# 除了数字类型比较,其他的字符或者表达式全部带上引号,表达式必须要写在后面(必须按照格式来)
assert_expression:
# 断言sql为有返回值查询
["'12' in '123'", '"ig" == "$.ig"', '1=="sql-SELECT title FROM case_test where id=2"']
参数list:
path: /list
method: post
remark: 参数list的参数替换模板
is_run: True
precondition_sql:
data:
#list请求参数使用和json的无区别
[$.waybillid,random_number(5)]
extract_key:
assert_expression:
['"成功"=="$.msg"']
参数嵌套替换:
path: /ccsstthh
method: post
remark: ctms发车
is_run: True
precondition_sql:
data:
{
#参数嵌套的不影响之前的参数替换使用
"a":$.a,
"b":"bba",
"shiftIdList":[
{
#参数嵌套这种格式暂时只支持[{},{},{}],在参数嵌套里面使用需要加上^^
"id":^$.shiftid^,
"sendTime":^random_time()^
},
{
"waybillId":^$.waybillid^
}
]
}
extract_key:
assert_expression:
['"成功"=="$.msg"']
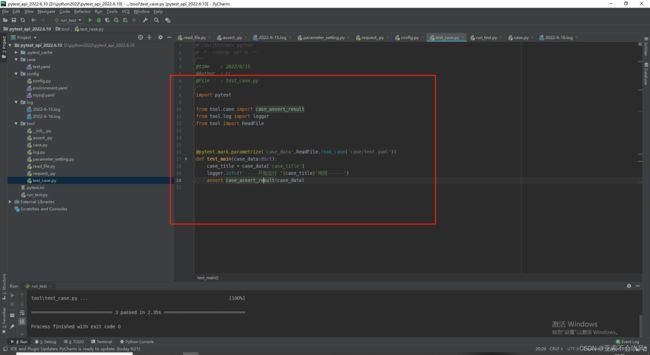
11.pytest初次登场
pytest.ini 配置pytest运行规则,要位于项目根目录下
我准备写一个主方法(结合之前写的参数处理,断言处理等方法)来运行从yaml里面读取的用例数据
运行pytest文件
12.pytest 获取用例参数
13.日志文件以前写过直接拿来用
logging 学习最终版-配置的不同级别日志打印的颜色
14.实现get请求用例
发现个问题,我使用jsonpath时提取了非json的数据
解决方案:对返回结果进行了处理,后续还得考虑非json格式返回的问题
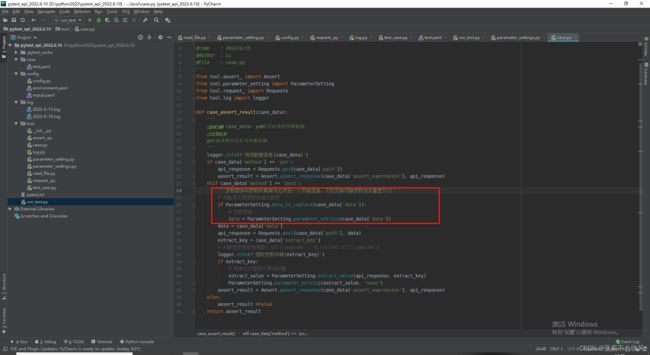
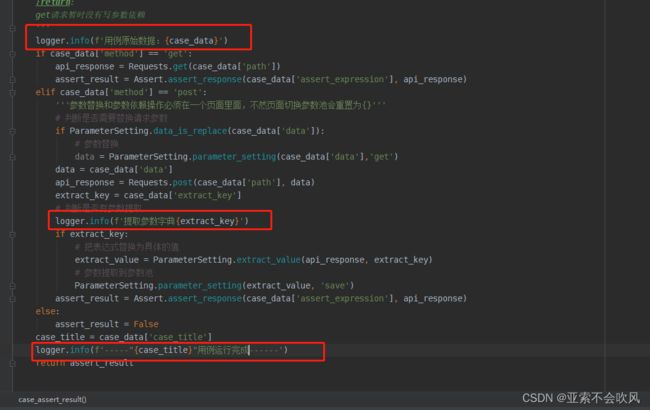
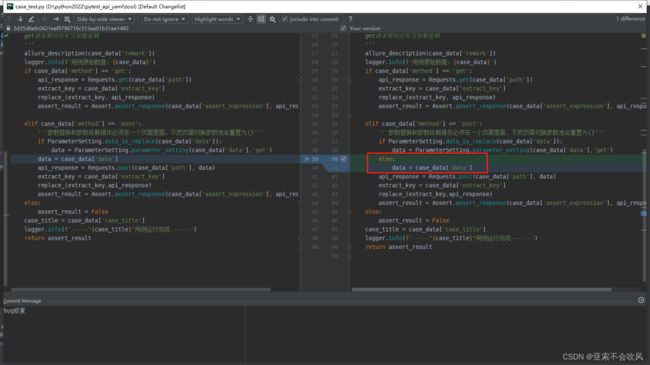
15.实现post请求和使用参数提取和参数依赖(好多坑,裂开)
这个方法还是要简洁,不然断言失败时pytest的日志里面会带上这个方法的代码,不利于查看错误,我把用例请求和参数提取和参数依赖和断言写在了一个方法里面,这里只需要给一个用例数据就行了
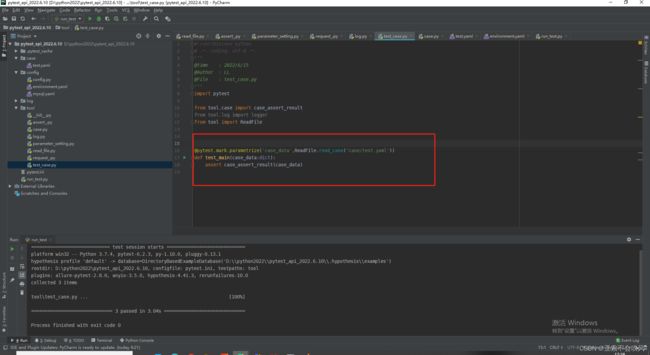
处理用例执行返回断言结果
测试post请求时接口一直报错,查日志发现是传参格式的问题,之前在headers里面没有设置,补充一下
16.出现bug参数池保存完成后,下次读取时参数池重置
排除问题查看池子信息提取信息
忙活了半天,猜测估计是一个类方法在2个py页面使用时使用的参数池就不是一样的了,下一个使用的是重置的参数池
后来我把这个参数替换和参数提取放着了一个方法里面,这样就是共用一个参数池了
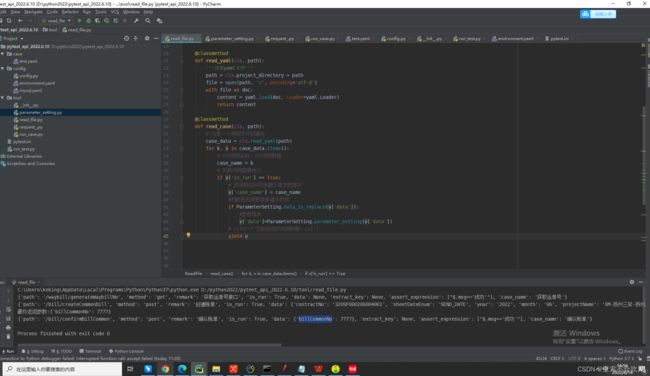
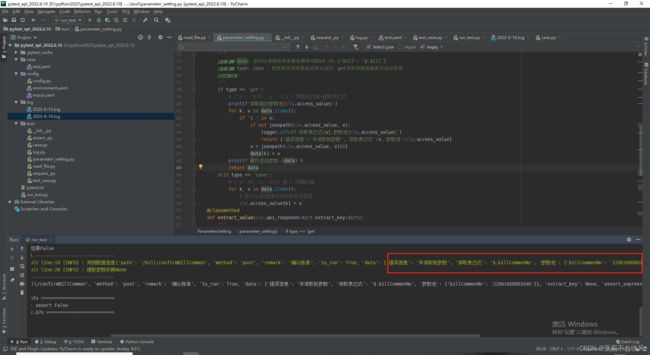
17.日志写到该写的地方(日志不要太复杂)
可以查看参数池情况,提取失败查找具体原因
![]()
看下最终走进了的请求信息,判断接口失败或者成功的信息
这个方法又运行接口和处理参数提取
断言方法,通过接口返回结果和断言表达式列表来处理
主方法,加个用例开始执行,这个方法越简洁越好
日志的最终效果
18.使用allure(配置环境)
allure报告文件,2.8版本,0积分下载(应该是免费把),我自己上传的资源
配置环境
18.allure简单封装并使用
这是allure.dynamic动态使用,不需要装饰器,装饰器不适应这种框架,这个动态的想放在哪里都行
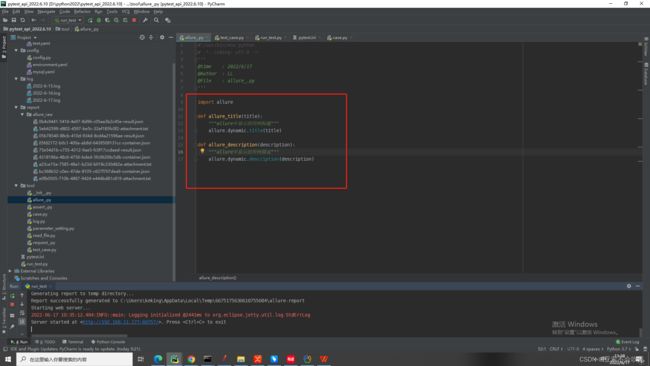
使用记录用例标题
最终请求信息使用报告描述记录
这里记录下用例数据里面的描述信息
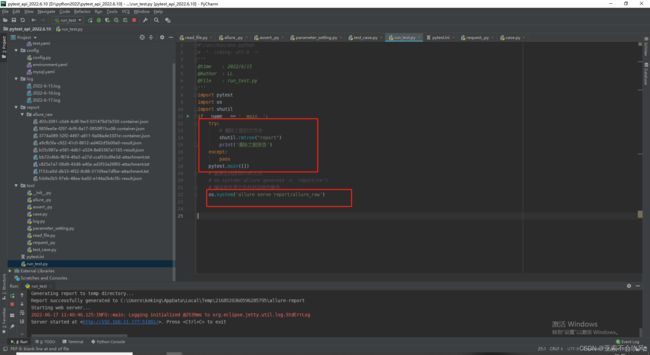
19.allure报告生成
运行启动文件,清空之前的文件,直接打开报告
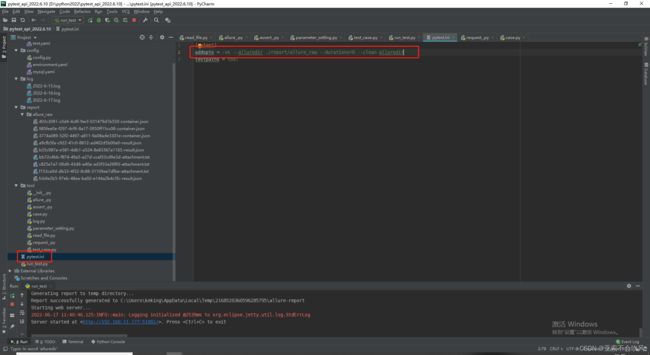
20.allure生成本地报告(命令解析)
这个addopts =是配置pytest的运行命令
–alluredir ./report/data 是生成report目录和data目录,data里面存放的用例执行的相关数据
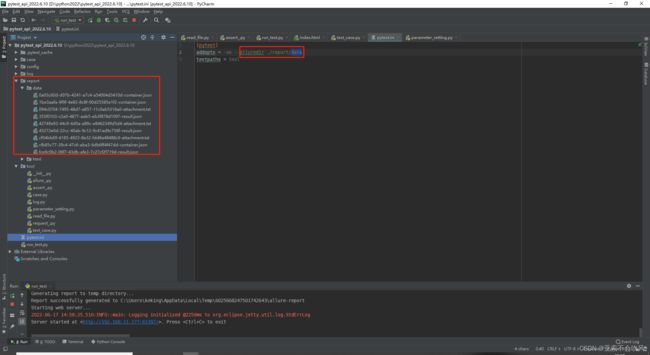
pytest运行后产生了report目录和data目录然后开始运行os.system(‘allure generate report/data -o report/html --clean’)直接生成html目录(里面包含了html文件)
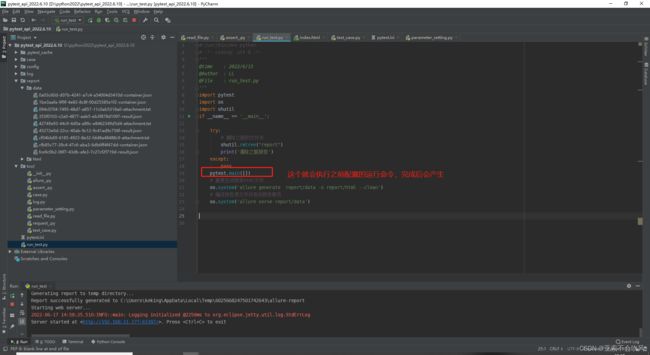
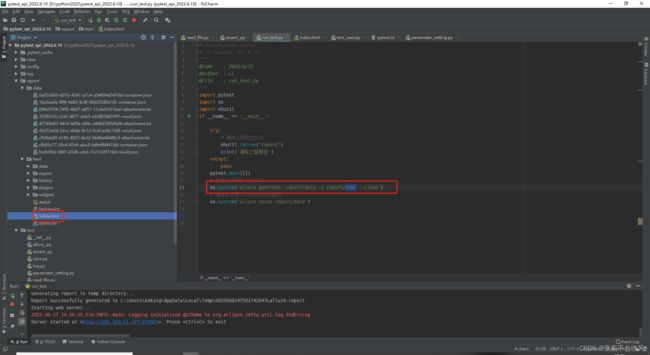
os.system(‘allure serve report/data’) 这个命令是处理data目录下的数据直接以服务器的形式启动报告,不生成文件,这个报告地址在公司局域网内都是可以打开的。
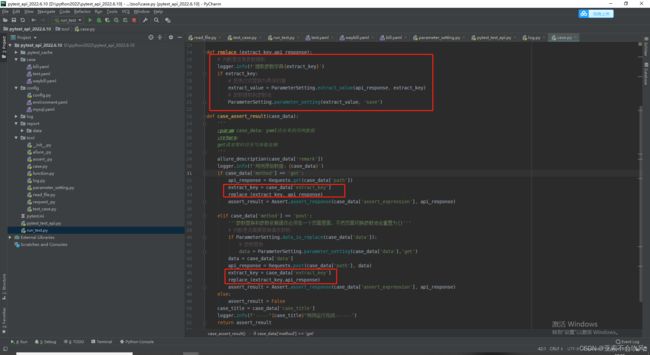
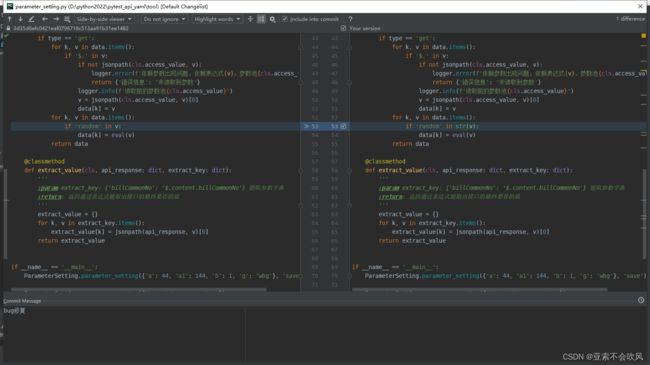
21.发现bug(因为之前get请求方法里面没有写处理参数提取的,导致使用get请求没有到提取参数)
给get请求也加上参数提取处理,我看都加的话代码看起来好丑,直接封装为一个方法,直接用好一点
代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/15
@Author : LL
@File : case.py
'''
from tool.allure_ import allure_description
from tool.assert_ import Assert
from tool.parameter_setting import ParameterSetting
from tool.request_ import Requests
from tool.log import logger
def replace_(extract_key,api_response):
'''参数提取处理'''
# 判断是否有参数提取
logger.info(f'提取参数字典{extract_key}')
if extract_key:
# 把表达式替换为具体的值
extract_value = ParameterSetting.extract_value(api_response, extract_key)
# 参数提取到参数池
ParameterSetting.parameter_setting(extract_value, 'save')
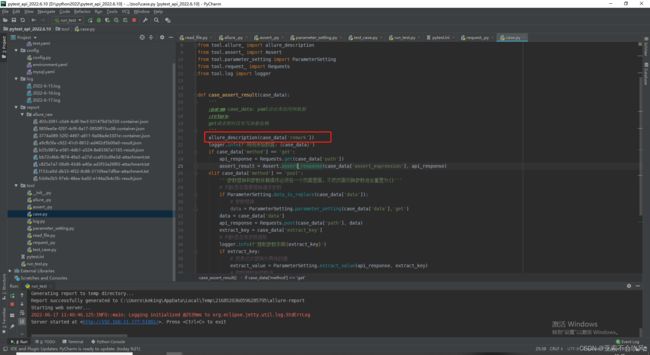
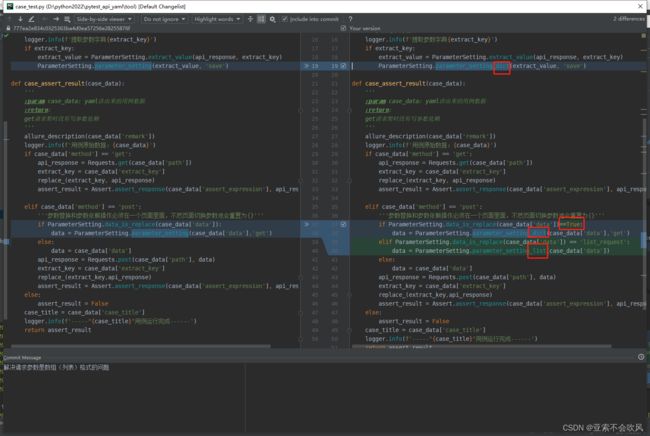
def case_assert_result(case_data):
'''
:param case_data: yaml读出来的用例数据
:return:
get请求暂时没有写参数依赖
'''
allure_description(case_data['remark'])
logger.info(f'用例原始数据:{case_data}')
if case_data['method'] == 'get':
api_response = Requests.get(case_data['path'])
extract_key = case_data['extract_key']
replace_(extract_key, api_response)
assert_result = Assert.assert_response(case_data['assert_expression'], api_response)
elif case_data['method'] == 'post':
'''参数替换和参数依赖操作必须在一个页面里面,不然页面切换参数池会重置为{}'''
# 判断是否需要替换请求参数
if ParameterSetting.data_is_replace(case_data['data']):
# 参数替换
data = ParameterSetting.parameter_setting(case_data['data'],'get')
data = case_data['data']
api_response = Requests.post(case_data['path'], data)
extract_key = case_data['extract_key']
replace_(extract_key,api_response)
assert_result = Assert.assert_response(case_data['assert_expression'], api_response)
else:
assert_result = False
case_title = case_data['case_title']
logger.info(f'-----"{case_title}"用例运行完成------')
return assert_result
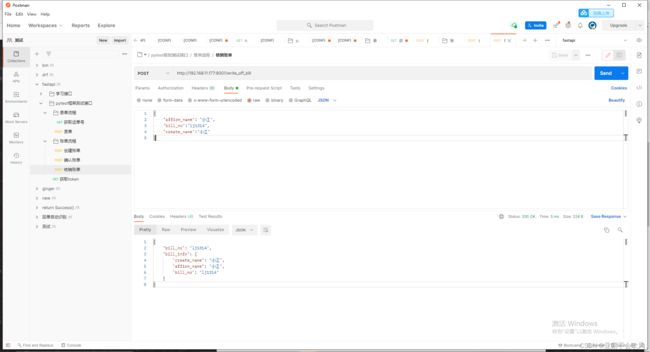
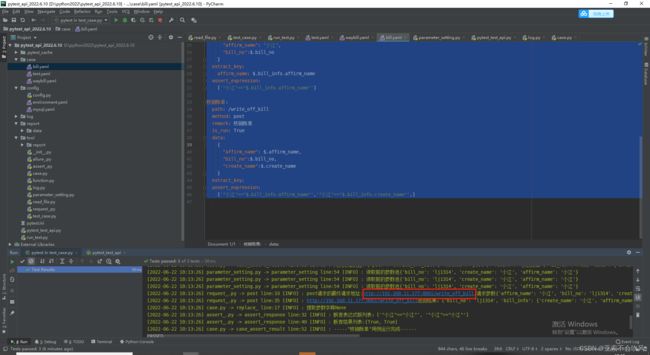
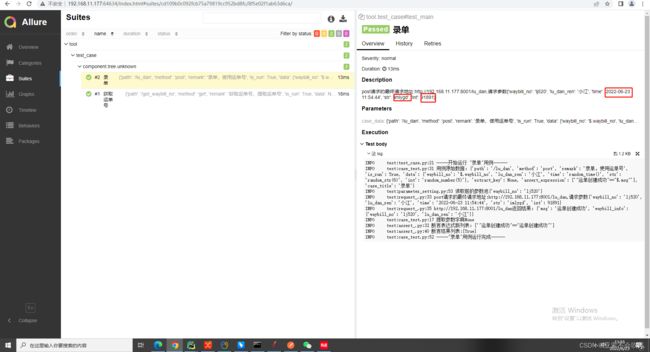
22.使用一个用到框架比较多的用例(3个接口,我自己fastapi写的)
基于fastapi实现6个接口(token拦截, 2个业务流程,接口参数依赖校验)
用例文件 yaml文件
创建账单:
path: /create_bill
method: post
remark: 创建账单
is_run: True
data:
{
"create_month": "6月",
"create_name": "小江"
}
extract_key:
bill_no: $.bill_no
create_name: $.bill_info.create_name
assert_expression:
['"lj1314"=="$.bill_no"']
确认账单:
path: /affirm_bill
method: post
remark: 确认账单
is_run: True
data:
{
"affirm_name": "小江",
"bill_no":$.bill_no
}
extract_key:
affirm_name: $.bill_info.affirm_name
assert_expression:
['"小江"=="$.bill_info.affirm_name"']
核销账单:
path: /write_off_bill
method: post
remark: 核销账单
is_run: True
data:
{
"affirm_name": $.affirm_name,
"bill_no":$.bill_no,
"create_name":$.create_name
}
extract_key:
assert_expression:
['"小江"=="$.bill_info.affirm_name"','"小江"=="$.bill_info.create_name"',]
其中一个接口,另外几个看我写的fastapi的那个文章
测试结果
23.增加随机几位数字、字符,获取当前时间的方法,并写在用例里面使用
3个方法
在参数提取这里加上一个函数处理,但是一开始没有导入这几个方法报错了
导入方法,虽然是灰色的,但是在运行过程中会使用到
用例文件使用
最终运行结果,函数已经替换为了具体的时间,数字和字符
用例模板更新一下(加入函数使用)
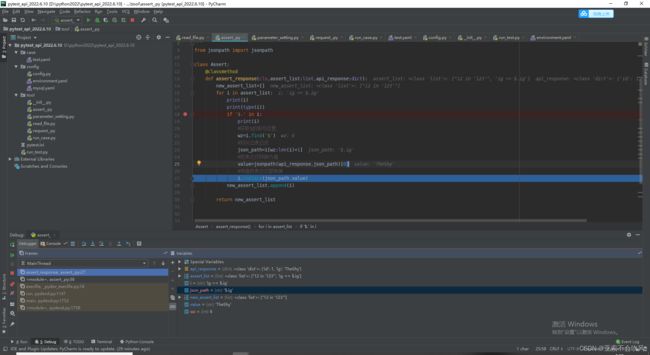
24.多目录多文件用例处理,实现一个通过目录和文件排除一些用例文件的方法,来返回要运行测试用例文件
第一版(有bug)
这个是初级版本,直接返回case目录下的所有文件(最多支持2级目录)
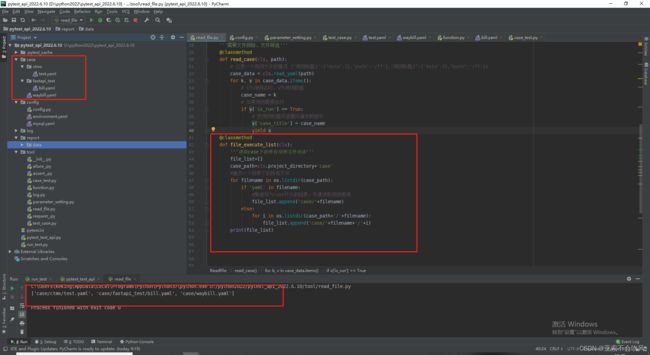
最终版本
:param exclude_dir: 要排除的目录(二级目录)例子:ctms
:param exclude_file: 要排除的文件(case目录下所有文件)例子:case/ctms/test.yaml case/waybill.yaml
:return: 获取case下的所有用例文件列表,最多支持二级目录,通用排除文件返回最终要执行的用例文件
注意看我的目录结构
最新读取文件的方法代码(有点bug)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/10
@Author : LL
@File : read_file.py
'''
from pathlib import Path
import yaml
from tool.parameter_setting import ParameterSetting
import os
class ReadFile:
# 获取当前项目目录D:\python2022\pytest_api_2022.6.10
project_directory = str(Path(__file__).parent.parent) + '/'
@classmethod
def read_yaml(cls, path):
'''读取yaml文件'''
path = cls.project_directory + path
file = open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
with file as doc:
content = yaml.load(doc, Loader=yaml.Loader)
return content
'''需要文件排除,文件筛选'''
@classmethod
def read_case(cls, path):
# 这是一个用例文件的情况 {"用例标题1":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'},"用例标题2":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'}}
case_data = cls.read_yaml(path)
for k, v in case_data.items():
# k为用例名称,v为用例数据
case_name = k
# 如果用例需要执行
if v['is_run'] == True:
# 把用例标题写进最终请求数据中
v['case_title'] = case_name
yield v
@classmethod
def file_execute_list(cls, exclude_file: list, exclude_dir: list):
'''
:param exclude_dir: 要排除的目录(二级目录)例子:ctms
:param exclude_file: 要排除的文件(case目录下所有文件)例子:case/ctms/test.yaml case/waybill.yaml
:return: 获取case下的所有用例文件列表,最多支持二级目录,通用排除文件返回最终要执行的用例文件
'''
file_list = []
case_path = cls.project_directory + 'case'
# case目录下的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(case_path):
if 'yaml' in filename:
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用
file_list.append('case/' + filename)
else:
# 遍历case下面的二级目录
for i in os.listdir(case_path + '/' + filename):
# 检查这个二级目录是否需要被排除
if filename in exclude_dir:
continue
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用,这是二级目录得把二级目录拼接上
file_list.append('case/' + filename + '/' + i)
#找出要排除的文件和已经找出来的文件的并集
exclude_file = list(set(exclude_file) & set(file_list))
#最后把它踢出去
file_list.remove(exclude_file[0])
print(file_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ReadFile.file_execute_list(['case/waybill.yaml'], ['ctms'])
# 路径使用读取文件的相对路径
# 读取环境配置文件测试
# print(ReadFile.read_yaml('config/environment.yaml'))
# 读取用例文件测试
# case_data = ReadFile.read_yaml('case/test.yaml')
# print(case_data)
# 测试用例数据生成器返回
# case_list=ReadFile.read_case('case/test.yaml')
# for i in case_list:
# print(i)
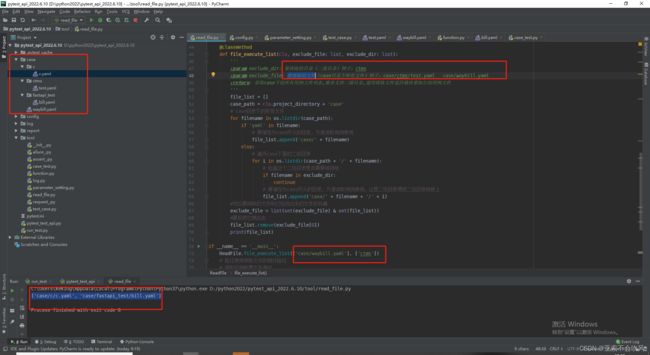
第二版
bug修复后代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/10
@Author : LL
@File : read_file.py
'''
from pathlib import Path
import yaml
from tool.parameter_setting import ParameterSetting
import os
class ReadFile:
# 获取当前项目目录D:\python2022\pytest_api_2022.6.10
project_directory = str(Path(__file__).parent.parent) + '/'
@classmethod
def read_yaml(cls, path):
'''读取yaml文件'''
path = cls.project_directory + path
file = open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
with file as doc:
content = yaml.load(doc, Loader=yaml.Loader)
return content
'''需要文件排除,文件筛选'''
@classmethod
def read_case(cls, path):
# 这是一个用例文件的情况 {"用例标题1":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'},"用例标题2":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'}}
case_data = cls.read_yaml(path)
for k, v in case_data.items():
# k为用例名称,v为用例数据
case_name = k
# 如果用例需要执行
if v['is_run'] == True:
# 把用例标题写进最终请求数据中
v['case_title'] = case_name
yield v
@classmethod
def file_execute_list(cls, exclude_file: list, exclude_dir: list):
'''
:param exclude_dir: 要排除的目录(二级目录)例子:ctms
:param exclude_file: 要排除的文件(case目录下所有文件)例子:case/ctms/test.yaml case/waybill.yaml
:return: 获取case下的所有用例文件列表,最多支持二级目录,通用排除文件返回最终要执行的用例文件
'''
file_list = []
case_path = cls.project_directory + 'case'
# case目录下的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(case_path):
if 'yaml' in filename:
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用
file_list.append('case/' + filename)
else:
# 遍历case下面的二级目录
for i in os.listdir(case_path + '/' + filename):
# 检查这个二级目录是否需要被排除
if filename in exclude_dir:
continue
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用,这是二级目录得把二级目录拼接上
file_list.append('case/' + filename + '/' + i)
#文件列表不为空的话一个一个的排除掉这些文件
if exclude_file !=[]:
for i in exclude_file:
file_list.remove(i)
print(file_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ReadFile.file_execute_list(['case/ctms/test.yaml'],[])
# 路径使用读取文件的相对路径
# 读取环境配置文件测试
# print(ReadFile.read_yaml('config/environment.yaml'))
# 读取用例文件测试
# case_data = ReadFile.read_yaml('case/test.yaml')
# print(case_data)
# 测试用例数据生成器返回
# case_list=ReadFile.read_case('case/test.yaml')
# for i in case_list:
# print(i)
使用(细节)
之前都是单文件用例处理,现在变成了多文件,我取消了之前的path参数,现在路径是一个路径列表,需要把列表里的路径循环遍历的都读取一遍,读出每个文件的数据{“用例标题1”:{“data”:{},“path”:‘/ff’},“用例标题2”:{“data”:{},“path”:‘/ff’}},然后把这些文件的数据拼接成一个字典,搞出最终要执行的用例数据
[2022-06-24 16:46:21] read_file.py -> read_case line:38 [INFO] : 最终执行的用例数据:{
'创建账单': {'path': '/create_bill', 'method': 'post', 'remark': '创建账单', 'is_run': True, 'data': {'create_month': '6月', 'create_name': '小江'}, 'extract_key': {'bill_no': '$.bill_no', 'create_name': '$.bill_info.create_name'}, 'assert_expression': ['"lj1314"=="$.bill_no"']},
'确认账单': {'path': '/affirm_bill', 'method': 'post', 'remark': '确认账单', 'is_run': True, 'data': {'affirm_name': '小江', 'bill_no': '$.bill_no'}, 'extract_key': {'affirm_name': '$.bill_info.affirm_name'}, 'assert_expression': ['"小江"=="$.bill_info.affirm_name"']},
'核销账单': {'path': '/write_off_bill', 'method': 'post', 'remark': '核销账单', 'is_run': True, 'data': {'affirm_name': '$.affirm_name', 'bill_no': '$.bill_no', 'create_name': '$.create_name'}, 'extract_key': None, 'assert_expression': ['"小江"=="$.bill_info.affirm_name"', '"小江"=="$.bill_info.create_name"']},
'获取运单号': {'path': '/get_waybill_no', 'method': 'get', 'remark': '获取运单号,提取运单号', 'is_run': True, 'data': None, 'extract_key': {'waybill_no': '$.waybill_no'}, 'assert_expression': ['"lj520"=="$.waybill_no"']},
'录单': {'path': '/lu_dan', 'method': 'post', 'remark': '录单,使用运单号', 'is_run': True, 'data': {'waybill_no': '$.waybill_no', 'lu_dan_ren': '小江', 'time': 'random_time()', 'str': 'random_str(6)', 'int': 'random_number(5)'}, 'extract_key': None, 'assert_expression': ['"运单创建成功"=="$.msg"']}}
字典拼接知识点
#字典拼接
d={}
for i in [{1:1},{2:2},{3:3,4:4}]:
d.update(i)
print(d) #{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3, 4: 4}
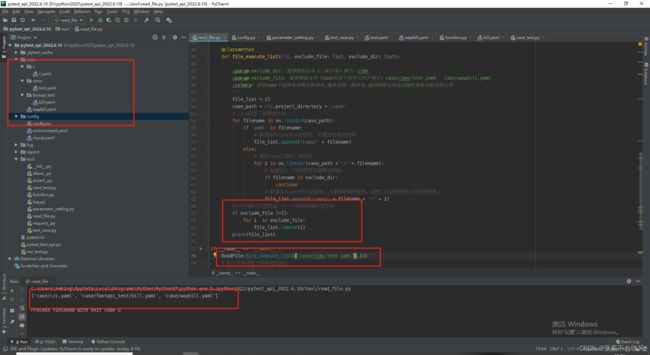
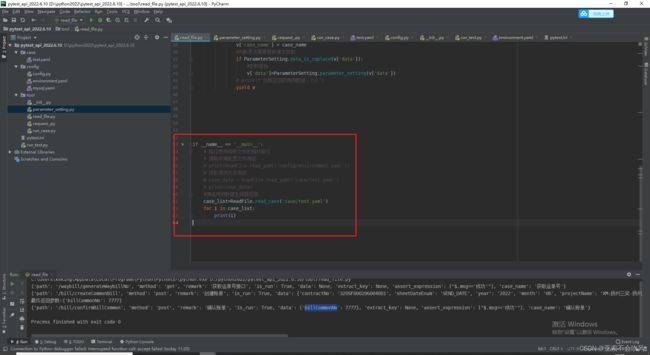
当前最终读取文件代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/10
@Author : LL
@File : read_file.py
'''
from pathlib import Path
from tool.log import logger
import yaml
from config.config import exclude_file, exclude_dir
from tool.parameter_setting import ParameterSetting
import os
class ReadFile:
# 获取当前项目目录D:\python2022\pytest_api_2022.6.10
project_directory = str(Path(__file__).parent.parent) + '/'
@classmethod
def read_yaml(cls, path):
'''读取yaml文件,以字典格式返回{'用例标题':{'path':'/test','data':{'id':1}}}'''
path = cls.project_directory + path
file = open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
with file as doc:
content = yaml.load(doc, Loader=yaml.Loader)
return content
@classmethod
def read_case(cls):
'''读取case下需要执行的用例文件并返回用例数据'''
# 这是多个用例文件 ['case/fastapi_test/bill.yaml', 'case/waybill.yaml']
path_list = cls.file_execute_list()
# 用例文件的情况 {"用例标题1":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'},"用例标题2":{"data":{},"path":'/ff'}}
case_data = {}
for i in path_list:
case_data.update(cls.read_yaml(i))
logger.info(f'最终执行的用例数据:{case_data}')
for k, v in case_data.items():
# k为用例名称,v为用例数据
case_name = k
# 如果用例需要执行
if v['is_run'] == True:
# 把用例标题写进最终请求数据中
v['case_title'] = case_name
yield v
@classmethod
def file_execute_list(cls, exclude_file=exclude_file, exclude_dir=exclude_dir):
'''
:param exclude_dir: 要排除的目录(二级目录)例子:ctms list格式
:param exclude_file: 要排除的文件(case目录下所有文件)例子:case/ctms/test.yaml case/waybill.yaml list格式
:return: 获取case下的所有用例文件列表,最多支持二级目录,通用排除文件返回最终要执行的用例文件
'''
file_list = []
case_path = cls.project_directory + 'case'
# case目录下的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(case_path):
if 'yaml' in filename:
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用
file_list.append('case/' + filename)
else:
# 遍历case下面的二级目录
for i in os.listdir(case_path + '/' + filename):
# 检查这个二级目录是否需要被排除
if filename in exclude_dir:
continue
# 要储存为case开头的目录,方便读取用例使用,这是二级目录得把二级目录拼接上
file_list.append('case/' + filename + '/' + i)
# 文件列表不为空的话一个一个的排除掉这些文件
if exclude_file != []:
for i in exclude_file:
file_list.remove(i)
return file_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
ReadFile.file_execute_list([], ['c', 'ctms'])
# 路径使用读取文件的相对路径
# 读取环境配置文件测试
# print(ReadFile.read_yaml('config/environment.yaml'))
# 读取用例文件测试
# case_data = ReadFile.read_yaml('case/test.yaml')
# print(case_data)
# 测试用例数据生成器返回
# case_list=ReadFile.read_case('case/test.yaml')
# for i in case_list:
# print(i)
test_case文件ReadFile.read_case()方法的参数注意去掉
报告,最终运行了2个文件下的用例,但是现在没有标识用例出自于那个文件
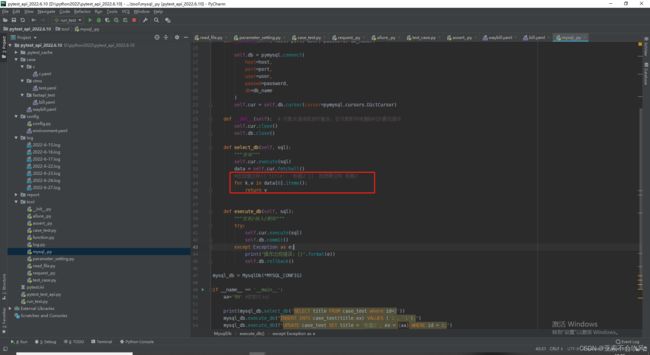
25.增加mysql数据库操作
代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@time : 2022/6/27
@Author : LL
@File : mysql_.py
'''
import pymysql
from config.config import MYSQL_CONFIG
class MysqlDb():
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name):
self.db = pymysql.connect(
host=host,
port=port,
user=user,
passwd=password,
db=db_name
)
self.cur = self.db.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
def __del__(self): # 对象资源被释放时触发,在对象即将被删除时的最后操作
self.cur.close()
self.db.close()
def select_db(self, sql):
"""查询"""
self.cur.execute(sql)
data = self.cur.fetchall()
return data
def execute_db(self, sql):
"""更新/插入/删除"""
try:
self.cur.execute(sql)
self.db.commit()
except Exception as e:
print("操作出现错误:{}".format(e))
self.db.rollback()
mysql_db = MysqlDb(*MYSQL_CONFIG)
if __name__ == '__main__':
aa='99' #参数化sql
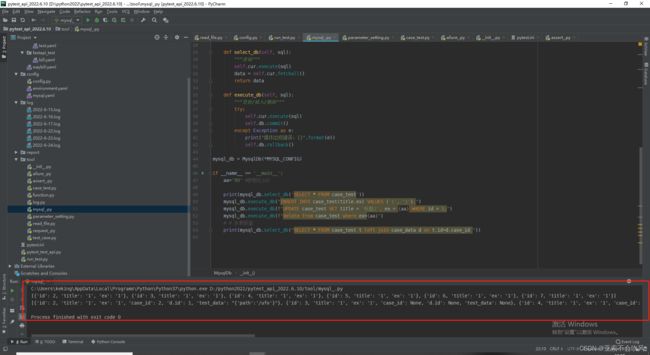
print(mysql_db.select_db('SELECT * FROM case_test'))
mysql_db.execute_db("INSERT INTO case_test(title,ex) VALUES ('1', '1');")
mysql_db.execute_db(f"UPDATE case_test SET title = '标题2', ex = {aa} WHERE id = 1;")
mysql_db.execute_db(f"delete from case_test where ex={aa}")
# # 多表联查
print(mysql_db.select_db("SELECT * FROM case_test t left join case_data d on t.id=d.case_id "))
代码测试
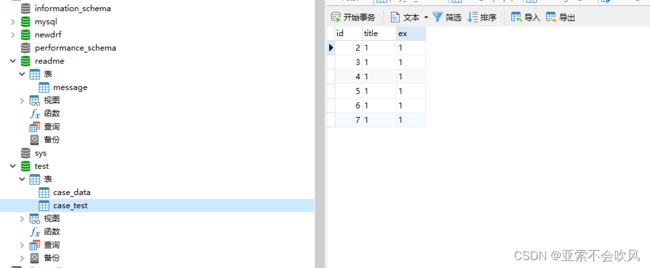
数据库配置
26.mysql使用(前置sql,(请求参数sql,断言sql有问题))bug修复完成
sql有2大类,一个是查询有返回值,一个是增删改无返回值,前置sql为无返回值类型
暂时使用场景:
1.断言时使用sql(有返回值)
2.请求参数使用sql(有返回值)
3.前置sql(无返回值)
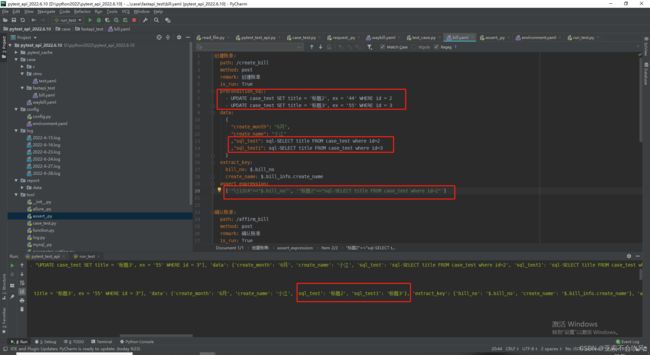
有bug时的用例设计和代码
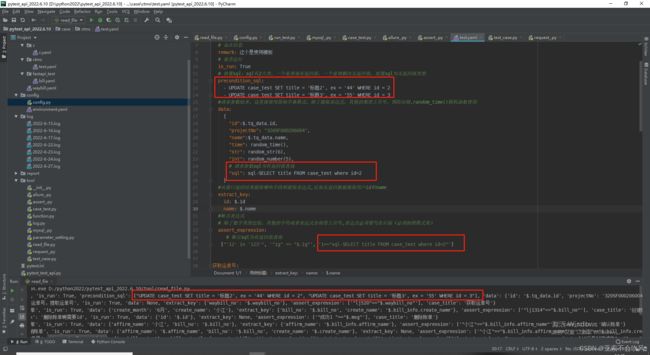
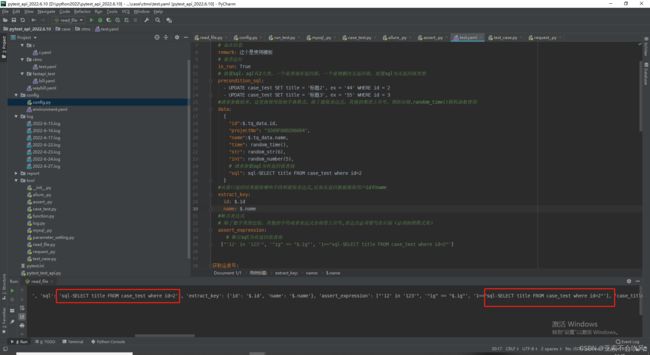
我把前置sql和请求参数sql写在了读取文件里面,但是这个请求参数sql在运行到请求参数没有sql的时候会报错
断言sql写在了断言方法里,也用不了
mysql查询的返回参数格式我改了一下,debug时请求参数sql确实替换成数据库里面读出来的值了,但是别的会报错
bug修复时的用例设计和代码
前置sql处理和请求参数sql处理,如果需要后置sql的话代码思路和前置sql一样,但是需要写在用例执行完成之和
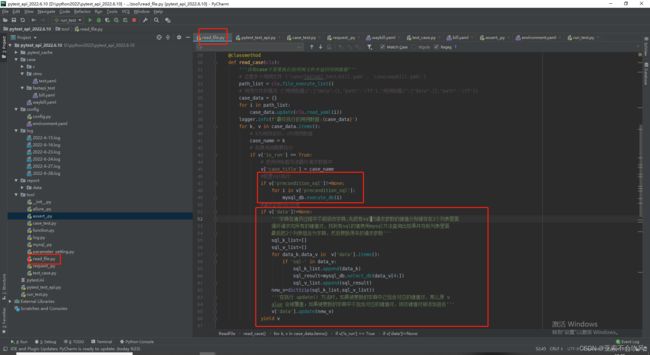
断言sql处理
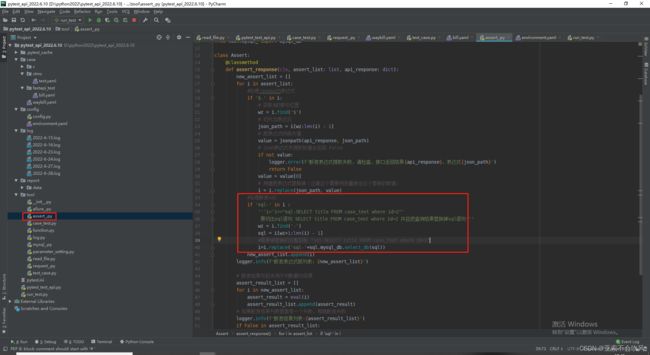
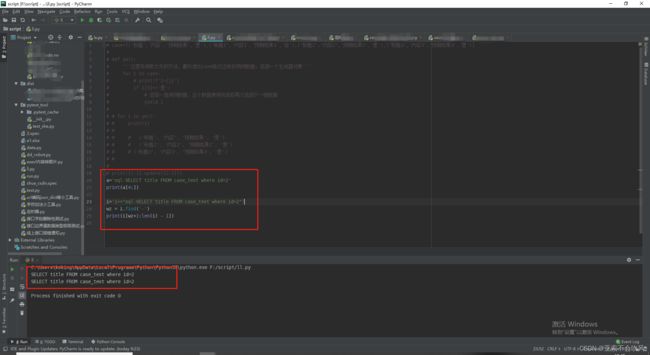
sql切片小测试
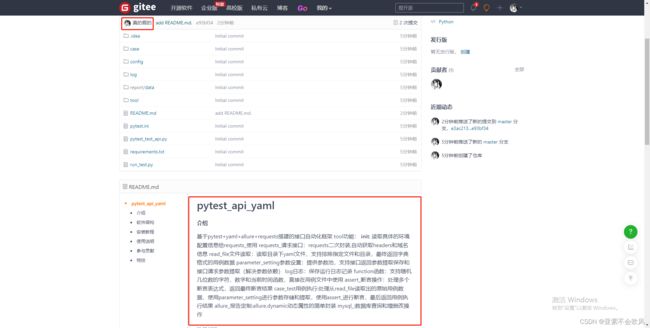
27.源码上传
设置开源需要审核,我以前写的框架应该可以访问
https://gitee.com/jianglisha/pytest_api_yaml
代码下拉后首次启动的4个坑
1.pip install allure-pytest 这个也使用2.8版本
2.windows安装allure 和系统变量配置(还需要配置jdk)(我这个allure是2.8),如果pycharm打开项目后配置的allure路径,一定要重启pycharm
3.日志文件位置,改为当前项目日志文件夹的绝对路径
4.mock接口的地址,要改成当前mock接口地址
我在csdn资源里面上传一份带注释版的(vx 一五五七六一五二零零六)
28.增加获取当前运行用例属于哪一个yaml文件方法,日志记录用例属于哪个文件
设计思路:
每个yaml文件读出来时初始的键值就是每个用例的标题,只要判断下当前标题在某个文件下时就可以确定属于哪个文件(用例标题得唯一,不然就只会找到第一个)
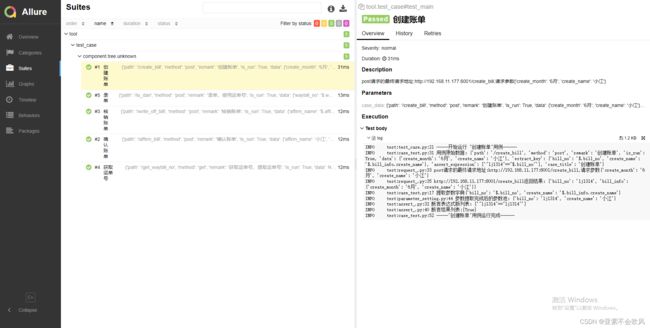
报告效果截图
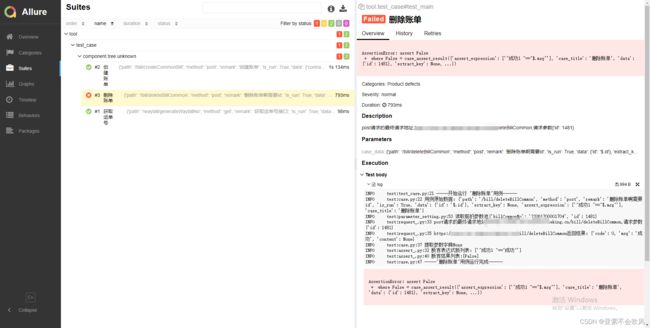
29.增加allure步骤描述,描述用例所属文件,请求地址,断言列表(都自定义)
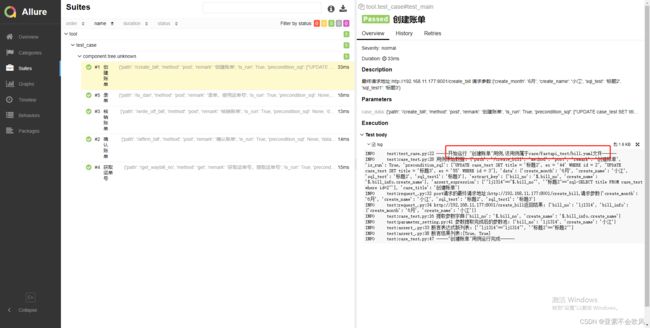
报告效果
30.钉钉推送测试报告,全局前后置配置(公司局域网内都可访问)
python操作钉钉机器人推送消息
python操作钉钉机器人推送消息
新增钉钉dd_push.py,现在的内容就是发送个链接并且@我自己
我通过直接运行dd_push.py文件来发送钉钉消息,需要配置下这个文件的绝对路径
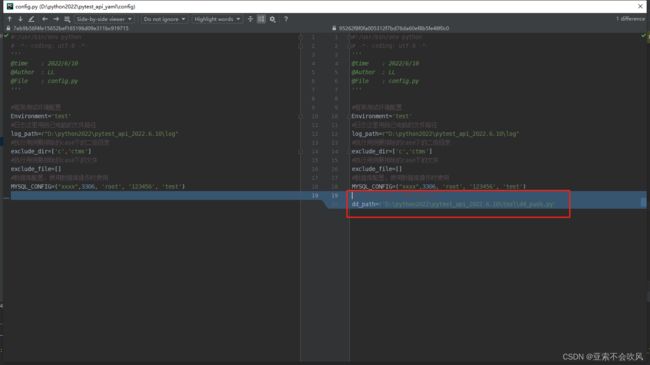
固定allurl报告服务启动的端口
allurl报告服务启动的端口是随机的,我改成了固定的,方便钉钉消息链接推送
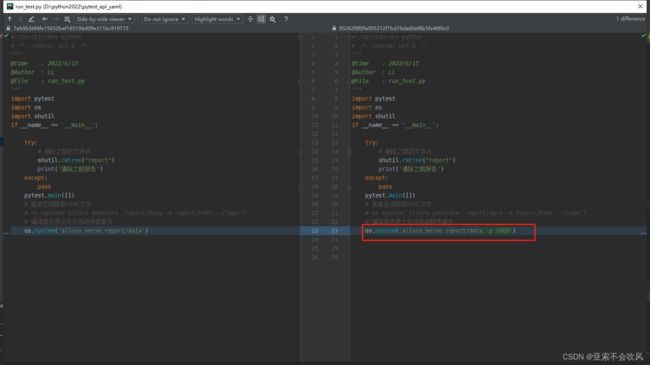
配置conftest.py实现全局前后置(后置推送钉钉消息)
conftest.py这个文件要建立在当前项目的根目录下,这个文件名是写死的。pytest规定的,可以配合fixture写前后置,全局参数等。我这里用来写前后置,作用范围是整个测试活动(所有用例执行开始前和执行完成后运行),我在所有用例完成后执行了钉钉推送
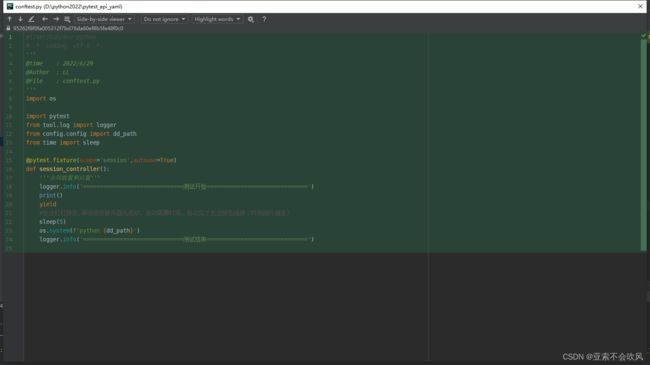
31.token前置写入到测试环境配置文件
先写一个写入token到yaml文件的方法
测试
写个获取token的方法
配合@pytest.fixture前置写入token
32.环境配置相关代码优化(直接使用配置的数据)
33.判断所有用例执行的文件是否有重复的标题
把所有文件转为字典,把键拿出来存在列表
查询列表的重复元素和出现重复的次数
知识点:判断字典是否为空
判断是否有重复元素,有就日志打印出重复元素和出现的次数
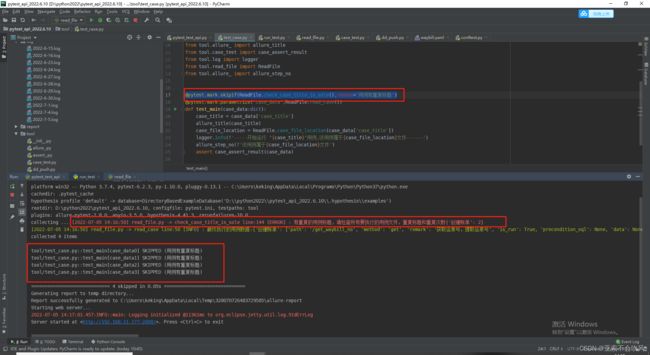
使用@pytest.mark.skipif
使用@pytest.mark.skipif(ReadFile.check_case_title_is_sole(),reason=‘用例有重复标题’),跳过所有的用例,但是现在这种情况还是会启动报告,但是钉钉不会发送了
34.bug修复
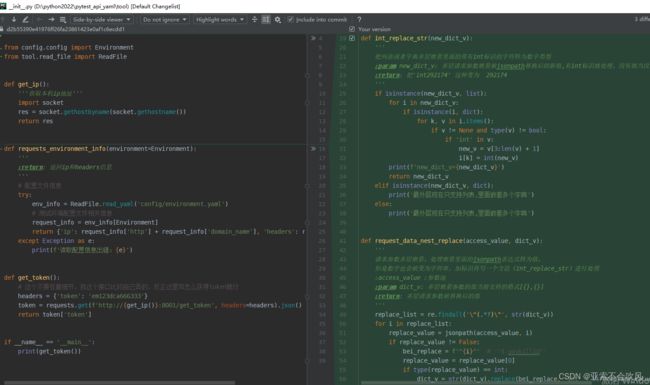
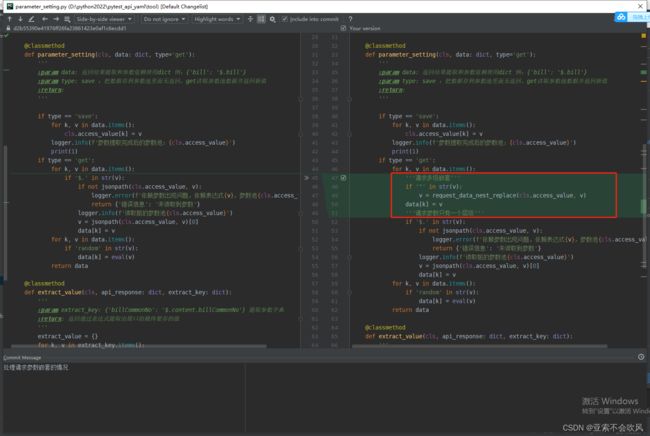
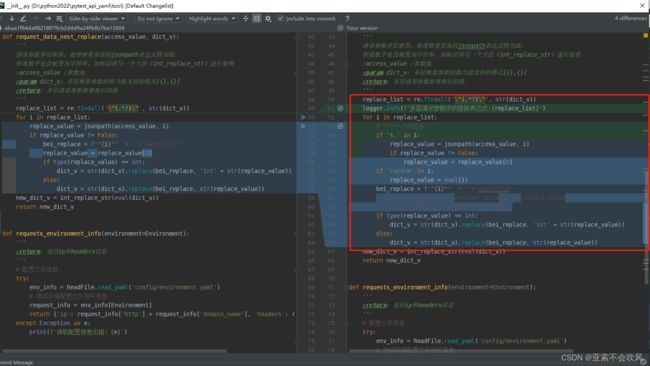
35.处理请求参数嵌套的情况
新增2个方法
'''
request_data_nest_replace()方法设计思路:
1.找出多层嵌套的请求参数里面的多个jsonpatn表达式,放在列表里面
2.循环使用这些表达式从参数池里面替换为值
3.把值和多层嵌套的请求参数里的jsonpatn表达式进行替换
4.因为replace(字符串替换方法)只能用字符串,数字必须要以字符的格式替换,数字类型的先给个标记int后续处理转为数字
int_replace_str()方法设计思路:
现在只兼容最外层现在只支持列表,里面嵌套多个字典的请求参数(有新的得加一个)
遍历列表找出字典里面值带有int标识的,把字符'int292174'里面的int去掉,并转为int类型重新赋值
'''
'''
现在只兼容最外层现在只支持列表,里面嵌套多个字典的请求参数(有新的得加一个)
遍历列表找出字典里面值带有int标识的,把字符'int292174'里面的int去掉,并转为int类型重新赋值
'''
def int_replace_str(new_dict_v):
'''
把列表或者字典多层嵌套里面的带有int标识的字符转为数字类型
:param new_dict_v: 多层请求参数嵌套被jsonpath替换后的新值,有int标识就处理,没有就当没运行这方法
:return: 把'int292174' 这种变为 292174
'''
if isinstance(new_dict_v,list):
for i in new_dict_v:
if isinstance(i,dict):
# print(f'i={i}')
for k,v in i.items():
# print(f'k={k},v={v}')
if v !=None and type(v)!=bool:
if 'int' in v:
new_v=v[3:len(v)+1]
i[k]=int(new_v)
print(f'new_dict_v={new_dict_v}')
return new_dict_v
elif isinstance(new_dict_v,dict):
print('最外层现在只支持列表,里面嵌套多个字典')
else:
print('最外层现在只支持列表,里面嵌套多个字典')
'''
1.找出多层嵌套的请求参数里面的多个jsonpatn表达式,放在列表里面
2.循环使用这些表达式从参数池里面替换为值
3.把值和多层嵌套的请求参数里的jsonpatn表达式进行替换
4.因为replace只能用字符串,数字类型的先给个标记int后续处理转为数字
'''
def request_data_nest_replace(access_value,dict_v):
'''
请求参数多层嵌套,处理嵌套里面的jsonpath表达式转为值,
但是数字也会被变为字符串,加标识再写一个方法(int_replace_str)进行处理
:access_value :参数池
:param dict_v: 多层嵌套参数的值当前支持的格式[{},{}]
:return: 多层请求参数被替换后的值
'''
print(f'原始的v={dict_v}')
#通过正则找出要替换的jsonpath表达式
replace_list = re.findall('\^(.*?)\^', str(dict_v))
for i in replace_list:
#一个一个的替换
replace_value = jsonpath(access_value, i)
if replace_value != False:
bei_replace=f'^{i}^'#'^$.waybillid^'
replace_value=replace_value[0]
# print(f'值类型:{type(replace_value)},值{replace_value}')
#如果是数字类型后续还需要处理,先加个int标识
if type(replace_value)==int:
dict_v = str(dict_v).replace(bei_replace, 'int'+str(replace_value))
else:
dict_v = str(dict_v).replace(bei_replace, str(replace_value))
new_dict_v=int_replace_str(eval(dict_v))
return new_dict_v
方法使用
测试(暂时只支持这种嵌套[{},{},{}])
bug发现
当请求参数为只有一个参数,而且还是嵌套参数时,之前写的一个判断是否需要参数依赖的方法无法检测到这种情况,遇到后会认为不需要参数依赖,其实是需要的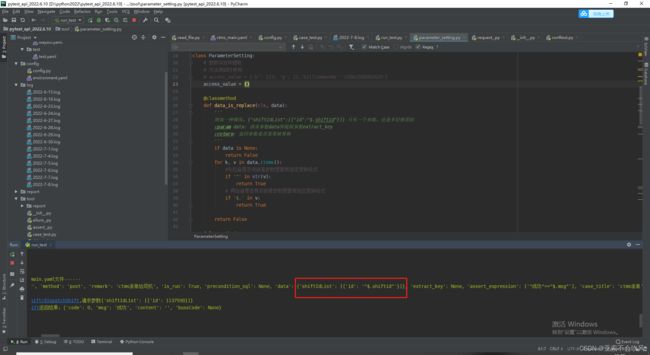
bug解决
先检查是否有嵌套参数里面有指定替换格式,有的话就是需要参数依赖,如果没检测到,再去检测非嵌套参数
解决嵌套参数中的随机函数使用问题
36.解决请求参数是数组(列表)格式的问题
优化一下判断参数是否需要依赖方法的代码,然后增加处理参数是数组的代码
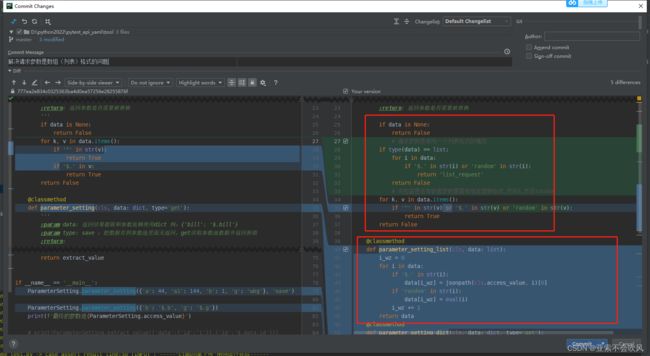
还增加一个处理数组参数依赖的方法
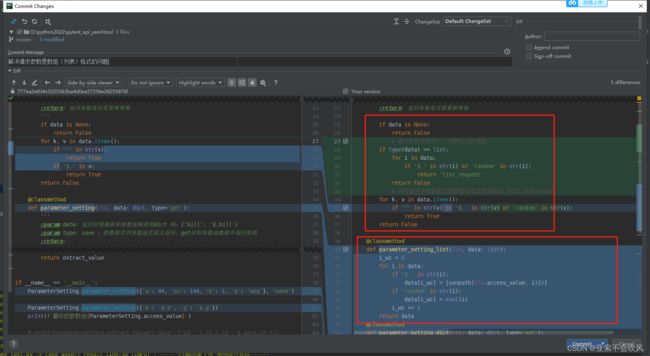
这一个处理json一个处理数组,我把方法改了下名字(记得把使用这个方法的地方也改掉)

这里下面的代码是使用的字典的方法,不能是列表(数组)类型,得判断下
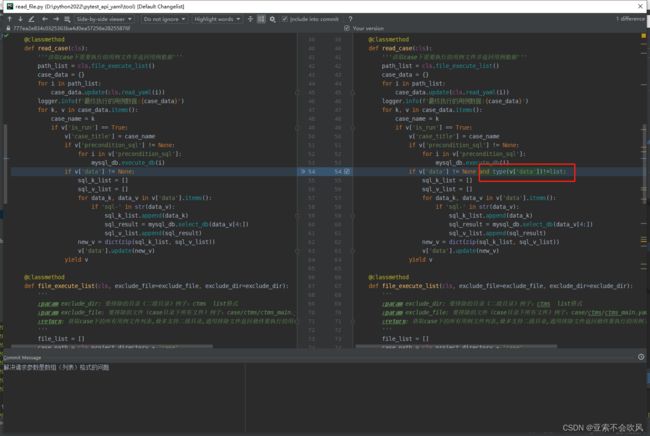
增加处理列表格式的请求参数,先判断是否是列表并且是否需要依赖,然后调用相应的方法进行参数处理。这里_dict之前改的方法名,记得这里也要改,加上等于True之所以加了这个,因为if 后面只要有值就是算通过,我判断列表返回的list_request也是值,就会去走处理字典的方法,会报错,所有直接加上等于True,这样避免list_request使用parameter_setting_dict()方法的问题