中断系统中的设备树
目录
- 一、中断概念的引入与处理流程
-
- 1、何为中断?
- 2、处理流程
- 3、SoC对中断的实现机制:异常向量表
- 4、异常和中断的区别和联系
- 二、Linux对中断处理的框架及代码流程简述
-
- a. 异常向量入口: arch\arm\kernel\entry-armv.S
- b. 中断向量: vector_irq
- c. __irq_usr/__irq_svc
- d. irq_handler: 将会调用C函数 handle_arch_irq
- e. handle_arch_irq的处理过程
- 三、中断号的演变与irq_domain
-
- 1、以前的中断处理过程
- 2、使用设备树后的中断处理过程
- 四、示例_在S3C2440上使用设备树描述中断体验
- 五、内核对设备树中断信息的处理过程
-
- (1) 中断处理过程如何触发?
- (2) root irq controller的驱动调用过程:
- (3) pinctrl系统中gpf/gpg irq controller的驱动调用过程:
- (4) 使用中断的驱动调用过程:
本文章参考学习阅读:
基于设备树的TQ2440的中断(1)
https://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/6847685.html
基于设备树的TQ2440的中断(2)
https://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/6848851.html
基於tiny4412的Linux內核移植 --- 实例学习中断背后的知识(1)
http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/6349209.html
linux kernel的中断子系统之:GIC代码分析
http://www.wowotech.net/irq_subsystem/interrupt_subsystem_architecture.html
本篇文章所用内核源码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/14WfehP9gF2GLrrCdxWG7yg
提取码:gymq
--来自百度网盘超级会员V6的分享
一、中断概念的引入与处理流程
1、何为中断?
中断是为单片机具有对外部或内部随机发生的事件实时处理而设置的。为了便于大家理解中断概念,给大家举一个例子:

至于能看这篇文章,各位应该都是单片机和嵌入式老手了,中断应该都懂,给大家简要回忆下就行了。
(1)中断的发明是用来解决宏观上的并行需要的。宏观就是从整体上来看,并行就是多件事情都完成了。
(2)微观上的并行,就是指的真正的并行,就是精确到每一秒甚至每一刻,多个事情都是在同时进行的。宏观上面的并行并不等于微观上的并行,有时候宏观上是并行的,微观上是串行的。
(3)例子中一个人在看电影,快递来了暂停电影跑去收快递,收完快递继续回来看电影,这个例子就是宏观上的并行和微观上的串行。例子中一个人等同于SoC中1个CPU(也就是单核CPU),这个CPU看电影就不能收快递,收快递就不能看电影(也就是说不能真正的并行)。单核心CPU在微观角度是串行的,但是因为CPU很快,所以在宏观看来可以并行。
(4)上例中大部分时间在看电影,中间少量时间去收快递,那么类比于CPU来说,看电影就应该是CPU的常规任务,而收快递则应该是中断例程。也就是说CPU平时一直在进行看电影任务,等快递来了(中断发生了)快递员(类似于中断源)会打电话叫人去收快递(中断源会触发中断通知CPU去处理中断),人收到电话(CPU收到中断信号)后会暂定电影(CPU保存常规任务的现场)跑去收快递(CPU去执行中断处理程序ISR处理中断),收完快递(执行完ISR)回来继续看电影(CPU恢复常规任务的现场,继续执行常规任务)
(5)为什么需要中断?因为单核CPU实际无法并行的,但是通过中断机制,可以实现假并行(宏观上的并行,微观上实际还是串行的)。
2、处理流程
(1)保存现场
(2)处理异常
(3)恢复现场
3、SoC对中断的实现机制:异常向量表
(1)异常向量表是CPU中某些特定地址的特定定义。当中断发生的时候,中断要想办法通知CPU去处理中断,怎么做到?这就要靠异常向量表。
(2)在CPU设计时,就事先定义了CPU中一些特定地址作为特定异常的入口地址(譬如定义0x00000000地址为复位异常向量地址,则发生复位异常时CPU会自动跳转到0x00000000地址去执行指令。又譬如外部中断对应的异常向量地址为0x30000008,则发生外部中断后,CPU会硬件自动跳转到0x30000008地址去执行指令)
(3)以上讲的是CPU硬件设计时对异常向量表的支持,下来就需要软件支持了。硬件已经决定了发生什么异常CPU自动跳转PC到哪个地址去执行,软件需要做的就是把处理这个异常的代码的首地址填入这个异常向量地址。
(4)异常向量表中各个向量的相对位置是固定的,但是他们的起始地址是不固定的,各种SoC可以不一样,而且复杂ARM中还可以让用户来软件设置这个异常向量表的基地址。
(5)扩展到所有架构的CPU中:所有架构(譬如51单片机、PIC单片机)的CPU实现中断都是通过异常向量表实现的,这个机制是不变的;但是不同CPU异常向量表的构造和位置是不同的。

4、异常和中断的区别和联系
(1)针对SoC来说,发生复位、软中断、中断、快速中断、取指令异常、数据异常等,我们都统一叫异常。所以说:中断其实是异常的一种。
(2)异常的定义就是突发事件,打断了CPU的正常常规业务,CPU不得不跳转到异常向量表中去执行异常处理程序;中断是异常的一种,一般特指SoC内的内部外设产生的打断SoC常规业务,或者外部中断(SoC的GPIO引脚传回来的中断)。
中断可以被屏蔽,但异常不可以
二、Linux对中断处理的框架及代码流程简述
a. 异常向量入口: arch\arm\kernel\entry-armv.S
.section .vectors, "ax", %progbits
.L__vectors_start:
W(b) vector_rst
W(b) vector_und
W(ldr) pc, .L__vectors_start + 0x1000
W(b) vector_pabt
W(b) vector_dabt
W(b) vector_addrexcptn
W(b) vector_irq
W(b) vector_fiq
b. 中断向量: vector_irq
/*
* Interrupt dispatcher
*/
vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, 4 // 相当于 vector_irq: ...,
// 它会根据SPSR寄存器的值,
// 判断被中断时CPU是处于USR状态还是SVC状态,
// 然后调用下面的__irq_usr或__irq_svc
.long __irq_usr @ 0 (USR_26 / USR_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 1 (FIQ_26 / FIQ_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 2 (IRQ_26 / IRQ_32)
.long __irq_svc @ 3 (SVC_26 / SVC_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 4
.long __irq_invalid @ 5
.long __irq_invalid @ 6
.long __irq_invalid @ 7
.long __irq_invalid @ 8
.long __irq_invalid @ 9
.long __irq_invalid @ a
.long __irq_invalid @ b
.long __irq_invalid @ c
.long __irq_invalid @ d
.long __irq_invalid @ e
.long __irq_invalid @ f
c. __irq_usr/__irq_svc
__irq_usr:
usr_entry
kuser_cmpxchg_check
irq_handler
get_thread_info tsk
mov why, #0
b ret_to_user_from_irq
UNWIND(.fnend )
ENDPROC(__irq_usr)
.ltorg
.align 5
__irq_svc:
svc_entry
irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT
ldr r8, [tsk, #TI_PREEMPT] @ get preempt count
ldr r0, [tsk, #TI_FLAGS] @ get flags
teq r8, #0 @ if preempt count != 0
movne r0, #0 @ force flags to 0
tst r0, #_TIF_NEED_RESCHED
blne svc_preempt
#endif
svc_exit r5, irq = 1 @ return from exception
UNWIND(.fnend )
ENDPROC(__irq_svc)
.ltorg
这2个函数的处理过程类似:
保存现场
调用 irq_handler
恢复现场
d. irq_handler: 将会调用C函数 handle_arch_irq
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
ldr r1, =handle_arch_irq
mov r0, sp
badr lr, 9997f
ldr pc, [r1]
#else
arch_irq_handler_default
#endif
9997:
.endm
e. handle_arch_irq的处理过程
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
void (*handle_arch_irq)(struct pt_regs *) __ro_after_init;
#endif
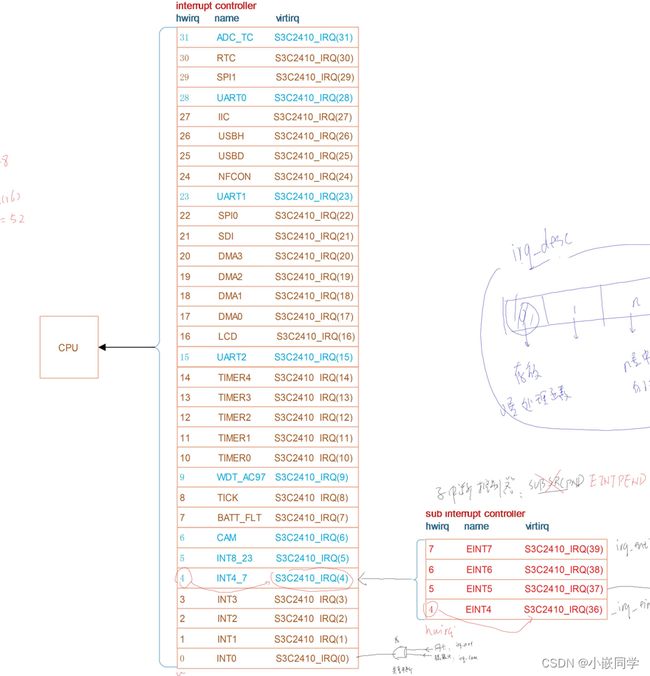
(1)读取寄存器获得中断信息: hwirq(hardware irq)
(2)把hwirq(硬件中断号)转换为virq(虚拟中断号),一个硬件中断号可能会对应多个
虚拟中断号,因为存在多个硬件共享一个硬件中断号,但具有不同的虚拟中断号。通过调用
irq_desc[virq].handle_irq实现二者的转换
对于S3C2440, s3c24xx_handle_irq 是用于处理中断的C语言入口函数
假设中断结构如下:
sub interrupt controller(子中断控制器) ---> interrupt controller(中断控制器) ---> cpu
发生中断时,
cpu跳到"vector_irq", 保存现场, 调用C函数handle_arch_irq
handle_arch_irq:
a. 读 interrupt controller, 得到hwirq
b. 根据hwirq得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
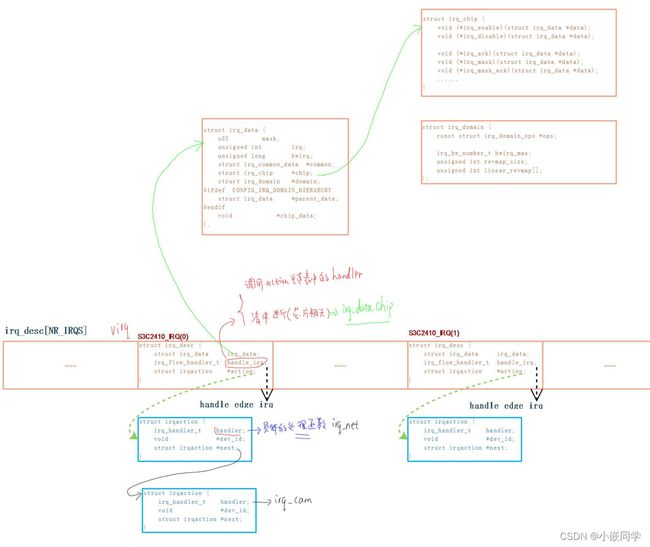
如果该中断没有子中断, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 取出irq_desc[virq].action 链表 中的每一个handler, 执行它
b. 使用irq_desc[virq].irq_data.chip的函数清中断
如果该中断是由子中断产生, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 读 sub interrupt controller, 得到hwirq
b. 根据hwirq得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
/**
* struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor
* @irq_common_data: per irq and chip data passed down to chip functions
* @kstat_irqs: irq stats per cpu
* @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler
* @preflow_handler: handler called before the flow handler (currently used by sparc)
* @action: the irq action chain
* @status: status information
* @core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it: core internal status information
* @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls
* @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple irq_set_irq_wake() callers
* @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs
* @last_unhandled: aging timer for unhandled count
* @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts
* @threads_handled: stats field for deferred spurious detection of threaded handlers
* @threads_handled_last: comparator field for deferred spurious detection of theraded handlers
* @lock: locking for SMP
* @affinity_hint: hint to user space for preferred irq affinity
* @affinity_notify: context for notification of affinity changes
* @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts
* @threads_oneshot: bitfield to handle shared oneshot threads
* @threads_active: number of irqaction threads currently running
* @wait_for_threads: wait queue for sync_irq to wait for threaded handlers
* @nr_actions: number of installed actions on this descriptor
* @no_suspend_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with
* IRQF_NO_SUSPEND set
* @force_resume_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with
* IRQF_FORCE_RESUME set
* @rcu: rcu head for delayed free
* @kobj: kobject used to represent this struct in sysfs
* @request_mutex: mutex to protect request/free before locking desc->lock
* @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry
* @debugfs_file: dentry for the debugfs file
* @name: flow handler name for /proc/interrupts output
*/
struct irq_desc {
struct irq_common_data irq_common_data;
struct irq_data irq_data;
unsigned int __percpu *kstat_irqs;
irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_PREFLOW_FASTEOI
irq_preflow_handler_t preflow_handler;
#endif
struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */
unsigned int status_use_accessors;
unsigned int core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it;
unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */
unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */
unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */
unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */
unsigned int irqs_unhandled;
atomic_t threads_handled;
int threads_handled_last;
raw_spinlock_t lock;
struct cpumask *percpu_enabled;
const struct cpumask *percpu_affinity;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
const struct cpumask *affinity_hint;
struct irq_affinity_notify *affinity_notify;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
cpumask_var_t pending_mask;
#endif
#endif
unsigned long threads_oneshot;
atomic_t threads_active;
wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads;
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
unsigned int nr_actions;
unsigned int no_suspend_depth;
unsigned int cond_suspend_depth;
unsigned int force_resume_depth;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
const char *dev_name;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
struct mutex request_mutex;
int parent_irq;
struct module *owner;
const char *name;
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
typedef void (*irq_flow_handler_t)(struct irq_desc *desc);
/**
* struct irqaction - per interrupt action descriptor
* @handler: interrupt handler function
* @name: name of the device
* @dev_id: cookie to identify the device
* @percpu_dev_id: cookie to identify the device
* @next: pointer to the next irqaction for shared interrupts
* @irq: interrupt number
* @flags: flags (see IRQF_* above)
* @thread_fn: interrupt handler function for threaded interrupts
* @thread: thread pointer for threaded interrupts
* @secondary: pointer to secondary irqaction (force threading)
* @thread_flags: flags related to @thread
* @thread_mask: bitmask for keeping track of @thread activity
* @dir: pointer to the proc/irq/NN/name entry
*/
struct irqaction {
irq_handler_t handler;
void *dev_id;
void __percpu *percpu_dev_id;
struct irqaction *next;
irq_handler_t thread_fn;
struct task_struct *thread;
struct irqaction *secondary;
unsigned int irq;
unsigned int flags;
unsigned long thread_flags;
unsigned long thread_mask;
const char *name;
struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
三、中断号的演变与irq_domain
1、以前的中断处理过程
以前中断号(virq)跟硬件密切相关,现在的趋势是中断号跟硬件无关, 仅仅是一个标号而已。以前, 对于每一个硬件中断(hwirq)都预先确定它的中断号(virq),这些中断号一般都写在一个头文件里, 比如arch\arm\mach-s3c24xx\include\mach\irqs.h

使用时,
a. 执行 request_irq(virq, my_handler) :
内核根据virq可以知道对应的硬件中断, 然后去设置、使能中断等
b. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取硬件信息, 确定hwirq, 反算出virq,
然后调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq, 最终会用到my_handler
怎么根据hwirq计算出virq?
硬件上有多个intc(中断控制器), 对于同一个hwirq数值, 会对应不同的virq,所以在讲hwirq时,应该强调"是哪一个中断控制器的hwirq",在描述hwirq转换为virq时, 引入一个概念: irq_domain, 域, 在这个域里hwirq转换为某一个virq
/**
* struct irq_domain - Hardware interrupt number translation object
* @link: Element in global irq_domain list.
* @name: Name of interrupt domain
* @ops: pointer to irq_domain methods
* @host_data: private data pointer for use by owner. Not touched by irq_domain
* core code.
* @flags: host per irq_domain flags
* @mapcount: The number of mapped interrupts
*
* Optional elements
* @fwnode: Pointer to firmware node associated with the irq_domain. Pretty easy
* to swap it for the of_node via the irq_domain_get_of_node accessor
* @gc: Pointer to a list of generic chips. There is a helper function for
* setting up one or more generic chips for interrupt controllers
* drivers using the generic chip library which uses this pointer.
* @parent: Pointer to parent irq_domain to support hierarchy irq_domains
* @debugfs_file: dentry for the domain debugfs file
*
* Revmap data, used internally by irq_domain
* @revmap_direct_max_irq: The largest hwirq that can be set for controllers that
* support direct mapping
* @revmap_size: Size of the linear map table @linear_revmap[]
* @revmap_tree: Radix map tree for hwirqs that don't fit in the linear map
* @linear_revmap: Linear table of hwirq->virq reverse mappings
*/
struct irq_domain {
struct list_head link;
const char *name;
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops;
void *host_data;
unsigned int flags;
unsigned int mapcount;
/* Optional data */
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token;
struct irq_domain_chip_generic *gc;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
struct irq_domain *parent;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
#endif
/* reverse map data. The linear map gets appended to the irq_domain */
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max;
unsigned int revmap_direct_max_irq;
unsigned int revmap_size;
struct radix_tree_root revmap_tree;
struct mutex revmap_tree_mutex;
unsigned int linear_revmap[];
};
当中断控制器越来越多、当中断越来越多,上述方法(virq和hwirq固定绑定)有缺陷:
a. 增加工作量, 你需要给每一个中断确定它的中断号, 写出对应的宏, 可能有成百上千个
b. 你要确保每一个硬件中断对应的中断号互不重复
有什么方法改进?
a. hwirq跟virq之间不再绑定
b. 要使用某个hwirq时,
先在irq_desc数组中找到一个空闲项, 它的位置就是virq
再在irq_desc[virq]中放置处理函数
2、使用设备树后的中断处理过程
a.以前是request_irq发起,
现在是先在设备树文件中声明想使用哪一个中断(哪一个中断控制器下的哪一个中断)
b. 内核解析设备树时,
会根据"中断控制器"确定irq_domain,
根据"哪一个中断"确定hwirq,
然后在irq_desc数组中找出一个空闲项, 它的位置就是virq
并且把virq和hwirq的关系保存在irq_domain中:
irq_domain.linear_revmap[hwirq] = virq;
c. 驱动程序 request_irq(virq, my_handler)
d. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取硬件信息, 确定hwirq, 确定 virq = irq_domain.linear_revmap[hwirq];
然后调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq, 最终会用到my_handler
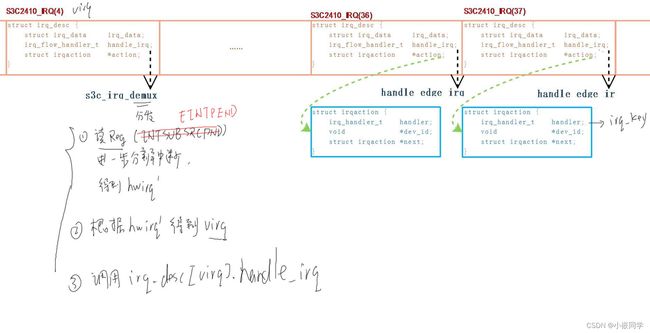
假设要使用子中断控制器(subintc)的n号中断, 它发生时会导致父中断控制器(intc)的m号
中断:
1. 设备树表明要使用<subintc n>
subintc表示要使用<intc m>
2. 解析设备树时,
会为<subintc n>找到空闲项 irq_desc[virq'], sub irq_domain.linear_revmap[n] = virq';
会为<intc m> 找到空闲项 irq_desc[virq], irq_domain.linear_revmap[m] = virq;
并且设置它的handle_irq为某个分析函数demux_func
3. 驱动程序 request_irq(virq', my_handler)
d. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取intc硬件信息, 确定hwirq = m, 确定 virq = irq_domain.linear_revmap[m];
然后调用 irq_desc[m].handle_irq, 即demux_func
e. demux_func:
读取sub intc硬件信息, 确定hwirq = n, 确定 virq' = sub irq_domain.linear_revmap[n];
然后调用 irq_desc[n].handle_irq, 即my_handler
四、示例_在S3C2440上使用设备树描述中断体验
a. 某个设备要使用中断, 需要在设备树中描述中断, 如何描述?
它要用哪一个中断? 这个中断连接到哪一个中断控制器去?
即: 使用哪一个中断控制器的哪一个中断?
至少有有2个属性:
interrupts // 表示要使用哪一个中断, 中断的触发类型等等
interrupt-parent // 这个中断要接到哪一个设备去? 即父中断控制器是谁
b. 上述的interrupts属性用多少个u32来表示?
这应该由它的父中断控制器来描述,
在父中断控制器中, 至少有2个属性:
interrupt-controller; // 表示自己是一个中断控制器
#interrupt-cells // 表示自己的子设备里应该有几个U32的数据来描述中断
在设备树的设备节点中描述"中断的硬件信息",表明使用了"哪一个中断控制器里的哪一个中断, 及中断触发方式",
设备节点会被转换为 platform_device, “中断的硬件信息” 会转换为"中断号", 保存在platform_device的"中断资源"里,驱动程序从platform_device的"中断资源"取出中断号, 就可以request_irq了。
实验:
a. jz2440_irq.dts" 放入内核 arch/arm/boot/dts目录,
在内核根目录下执行:make dtbs // 得到 arch/arm/boot/dts/jz2440_irq.dtb
使用这个jz2440_irq.dtb启动内核;
b. 编译、测试驱动:
b.1 把 buttons_drv 上传到ubuntu
b.2 编译驱动:
export PATH=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/work/system/gcc-linaro-4.9.4-2017.01-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabi/bin
cd buttons_drv
make // 得到 buttons.ko
b.3 编译测试程序:
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/usr/local/arm/4.3.2/bin
cd buttons_drv
arm-linux-gcc -o buttons_test buttons_test.c
b.4 测试:
insmod buttons.ko
./buttons_test &
然后按键
button.c文件
#include 设备树文件
/dts-v1/;
/ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440", "samsung,smdk2440";
interrupt-parent = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
model = "JZ2440";
aliases {
pinctrl0 = "/pinctrl@56000000";
serial0 = "/serial@50000000";
serial1 = "/serial@50004000";
serial2 = "/serial@50008000";
i2c1 = "/i2c-gpio-1";
};
interrupt-controller@4a000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-irq";
reg = <0x4a000000 0x100>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x4>;
phandle = <0x1>;
};
pinctrl@56000000 {
reg = <0x56000000 0x1000>;
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl";
wakeup-interrupt-controller {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-wakeup-eint";
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x0 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x1 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x2 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x3 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x4 0x4 0x0 0x0 0x5 0x4>;
};
gpa {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpb {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0xd>;
};
gpc {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpd {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpe {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x7>;
};
gpf {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x6>;
};
gpg {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0xe>;
};
gph {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpj {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
uart0-data {
samsung,pins = "gph-0", "gph-1";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x3>;
};
i2c0-bus {
samsung,pins = "gpe-14", "gpe-15";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x4>;
};
nand_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpa-17", "gpa-18", "gpa-19", "gpa-20", "gpa-22";
samsung,pin-function = <0x1>;
phandle = <0x5>;
};
lcd_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpc-8", "gpc-9", "gpc-10", "gpc-11", "gpc-12", "gpc-13", "gpc-14", "gpc-15", "gpd-0", "gpd-1", "gpd-2", "gpd-3", "gpd-4", "gpd-5", "gpd-6", "gpd-7", "gpd-8", "gpd-9", "gpd-10", "gpd-11", "gpd-12", "gpd-13", "gpd-14", "gpd-15", "gpc-1", "gpc-2", "gpc-3", "gpc-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x8>;
};
lcd_backlight {
samsung,pins = "gpg-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x3>;
phandle = <0x9>;
};
uda1340_codec_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpb-4", "gpb-3", "gpb-2";
samsung,pin-function = <0x1>;
phandle = <0xc>;
};
s3c2440_iis_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpe-0", "gpe-1", "gpe-2", "gpe-3", "gpe-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0xa>;
};
};
timer@51000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-pwm";
reg = <0x51000000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0xa 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xb 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xc 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xd 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xe 0x3>;
#pwm-cells = <0x4>;
clock-names = "timers";
clocks = <0x2 0x19>;
};
serial@50000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-uart";
reg = <0x50000000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x1c 0x0 0x4 0x1 0x1c 0x1 0x4>;
status = "okay";
clock-names = "uart";
clocks = <0x2 0x10>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x3>;
};
serial@50004000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-uart";
reg = <0x50004000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x17 0x3 0x4 0x1 0x17 0x4 0x4>;
status = "disabled";
};
serial@50008000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-uart";
reg = <0x50008000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0xf 0x6 0x4 0x1 0xf 0x7 0x4>;
status = "disabled";
};
watchdog@53000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-wdt";
reg = <0x53000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x9 0x1b 0x3>;
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x2 0x6>;
clock-names = "watchdog";
};
rtc@57000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-rtc";
reg = <0x57000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1e 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x8 0x3>;
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x2 0x1a>;
clock-names = "rtc";
};
i2c@54000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-i2c";
reg = <0x54000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1b 0x3>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
status = "disabled";
clocks = <0x2 0x13>;
clock-names = "i2c";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x4>;
};
cpus {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
cpu {
compatible = "arm,arm920t";
};
};
xti_clock {
compatible = "fixed-clock";
clock-frequency = <0xb71b00>;
clock-output-names = "xti";
#clock-cells = <0x0>;
};
clock-controller@4c000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-clock";
reg = <0x4c000000 0x20>;
#clock-cells = <0x1>;
phandle = <0x2>;
};
nand@4e000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-nand";
reg = <0x4e000000 0x40>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x18 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x23>;
clock-names = "nand";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x5>;
status = "okay";
nand,tacls = <0xa>;
nand,twrph0 = <0x19>;
nand,twrph1 = <0xa>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partitions {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
nr-chips = <0x1>;
set-name = "jz2440-0";
partition@0 {
label = "bootloader";
reg = <0x0 0x40000>;
read-only;
};
partition@40000 {
label = "device_tree";
reg = <0x40000 0x20000>;
read-only;
};
partition@60000 {
label = "params";
reg = <0x60000 0x20000>;
read-only;
};
partition@80000 {
label = "kernel";
reg = <0x80000 0x400000>;
read-only;
};
partition@480000 {
label = "rootfs";
reg = <0x480000 0x0>;
};
};
};
usb_ohci@49000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-ohci";
reg = <0x49000000 0x60>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1a 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x21 0x2 0x7>;
clock-names = "usb-host", "usb-bus-host";
status = "okay";
};
memory {
device_type = "memory";
reg = <0x30000000 0x4000000>;
};
chosen {
bootargs = "noinitrd root=/dev/mtdblock4 rw init=/linuxrc console=ttySAC0,115200";
};
srom-cs4@20000000 {
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
reg = <0x20000000 0x8000000>;
ranges;
ethernet@20000000 {
compatible = "davicom,dm9000";
reg = <0x20000000 0x2 0x20000004 0x2>;
interrupt-parent = <0x6>;
interrupts = <0x7 0x1>;
local-mac-address = [00 00 de ad be ef];
davicom,no-eeprom;
};
};
i2c-gpio-1 {
compatible = "i2c-gpio";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
gpios = <0x7 0xf 0x0 0x7 0xe 0x0>;
i2c-gpio,delay-us = <0x5>;
status = "disabled";
eeprom@50 {
compatible = "24c02";
reg = <0x50>;
pagesize = <0x20>;
status = "okay";
};
};
fb@4d000000 {
compatible = "jz2440,lcd";
reg = <0x4d000000 0x60>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x10 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x20>;
clock-names = "lcd";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x8 0x9>;
status = "okay";
lcdcon5 = <0xb09>;
type = <0x60>;
width = [01 e0];
height = [01 10];
pixclock = <0x186a0>;
xres = [01 e0];
yres = [01 10];
bpp = [00 10];
left_margin = [00 02];
right_margin = [00 02];
hsync_len = [00 29];
upper_margin = [00 02];
lower_margin = [00 02];
vsync_len = [00 0a];
};
jz2440ts@5800000 {
compatible = "jz2440,ts";
reg = <0x58000000 0x100>;
reg-names = "adc_ts_physical";
interrupts = <0x1 0x1f 0x9 0x3 0x1 0x1f 0xa 0x3>;
interrupt-names = "int_ts", "int_adc_s";
clocks = <0x2 0x16>;
clock-names = "adc";
};
s3c2410-dma@4B000000 {
compatible = "s3c2440-dma";
reg = <0x4b000000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x11 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x12 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x13 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x14 0x3>;
#dma-cells = <0x1>;
phandle = <0xb>;
};
s3c2440_iis@55000000 {
compatible = "s3c24xx-iis";
reg = <0x55000000 0x100>;
clocks = <0x2 0x18>;
clock-names = "iis";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0xa>;
dmas = <0xb 0x9 0xb 0xa>;
dma-names = "rx", "tx";
};
s3c24xx_uda134x {
compatible = "s3c24xx_uda134x";
clocks = <0x2 0x2 0x2 0x18>;
clock-names = "mpll", "iis";
};
uda134x-codec {
compatible = "uda134x-codec";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0xc>;
uda,clk_gpio = <0xd 0x4 0x1>;
uda,data_gpio = <0xd 0x3 0x1>;
uda,mode_gpio = <0xd 0x2 0x1>;
uda,use_gpios;
uda,data_hold;
uda,data_setup;
uda,clock_high;
uda,mode_hold;
uda,mode;
uda,mode_setup;
uda,model = <0x2>;
};
buttons {
compatible = "jz2440_button";
eint-pins = <0x6 0x0 0x0 0x6 0x2 0x0 0xe 0x3 0x0 0xe 0xb 0x0>;
interrupts-extended = <0x1 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x3 0x1 0x0 0x0 0x2 0x3 0xe 0x3 0x3 0xe 0xb 0x3>;
};
};
按键驱动应用层测试程序:
#include 五、内核对设备树中断信息的处理过程
从硬件结构上看, 处理过程分上下两个层面: 中断控制器, 使用中断的设备;
从软件结构上看, 处理过程分左右两个部分: 在设备树中描述信息, 在驱动中处理设备树;
(1) 中断控制器
这又分为root irq controller, gpf/gpg irq controller
a. root irq controller
a.1 在设备树中的描述
a.2 在内核中的驱动
b. 对于S3C2440, 还有: gpf/gpg irq controller
b.1 在设备树中的描述(在pinctrl节点里)
b.2 在内核中的驱动 (在pinctrl驱动中)
(2) 设备的中断
a.1 在设备节点中描述(表明使用"哪一个中断控制器里的哪一个中断, 及中断触发方式")
a.2 在内核中的驱动 (在platform_driver.probe中获得IRQ资源, 即中断号)
irq_domain是核心:
a. 每一个中断控制器都有一个irq_domain
b. 对设备中断信息的解析,
b.1 需要调用 irq_domain->ops->xlate (即从设备树中获得hwirq, type)
b.2 获取未使用的virq, 保存: irq_domain->linear_revmap[hwirq] = virq;
b.3 在hwirq和virq之间建立联系:
要调用 irq_domain->ops->map, 比如根据hwirq的属性设置virq的中断处理函数(是一
个分发函数还是可以直接处理中断)
irq_desc[virq].handle_irq = 常规函数;
如果这个hwirq有上一级中断, 假设它的中断号为virq', 还要设置:
irq_desc[virq'].handle_irq = 中断分发函数;
(1) 中断处理过程如何触发?
a. 内核启动时初始化中断的入口:
start_kernel // init/main.c
init_IRQ();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF) && !machine_desc->init_irq)
irqchip_init(); // 一般使用它
else
machine_desc->init_irq();
b. 设备树中的中断控制器的处理入口:
irqchip_init // drivers/irqchip/irqchip.c
of_irq_init(__irqchip_of_table); // 对设备树文件中每一个中断控制器节点, 调用对应的处理函数
为每一个符合的"interrupt-controller"节点,
分配一个of_intc_desc结构体, desc->irq_init_cb = match->data; // = IRQCHIP_DECLARE中传入的函数
并调用处理函数
(先调用root irq controller对应的函数, 再调用子控制器的函数, 再调用更下一级控制器的函数...)
(2) root irq controller的驱动调用过程:
a. 为root irq controller定义处理函数:
IRQCHIP_DECLARE(s3c2410_irq, "samsung,s3c2410-irq", s3c2410_init_intc_of); //drivers/irqchip/irq-s3c24xx.c
其中:
#define IRQCHIP_DECLARE(name, compat, fn) OF_DECLARE_2(irqchip, name, compat, fn)
#define OF_DECLARE_2(table, name, compat, fn) \
_OF_DECLARE(table, name, compat, fn, of_init_fn_2)
#define _OF_DECLARE(table, name, compat, fn, fn_type) \
static const struct of_device_id __of_table_##name \
__used __section(__##table##_of_table) \
= { .compatible = compat, \
.data = (fn == (fn_type)NULL) ? fn : fn }
展开为:
static const struct of_device_id __of_table_s3c2410_irq \
__used __section("__irqchip_of_table") \
= { .compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-irq", \
.data = s3c2410_init_intc_of }
它定义了一个of_device_id结构体, 段属性为"__irqchip_of_table", 在编译内核时
这些段被放在__irqchip_of_table地址处。即__irqchip_of_table起始地址处,放置
了一个或多个 of_device_id, 它含有compatible成员;
设备树中的设备节点含有compatible属性,如果双方的compatible相同, 并且设备节点
含有"interrupt-controller"属性,则调用of_device_id中的函数来处理该设备节点。
所以: IRQCHIP_DECLARE 是用来声明设备树中的中断控制器的处理函数。
b. root irq controller处理函数的执行过程:
s3c2410_init_intc_of // drivers/irqchip/irq-s3c24xx.c
// 初始化中断控制器: intc, subintc
s3c_init_intc_of(np, interrupt_parent, s3c2410_ctrl, ARRAY_SIZE(s3c2410_ctrl));
// 为中断控制器创建irq_domain
domain = irq_domain_add_linear(np, num_ctrl * 32,
&s3c24xx_irq_ops_of, NULL);
intc->domain = domain;
// 设置handle_arch_irq, 即中断处理的C语言总入口函数
set_handle_irq(s3c24xx_handle_irq);
(3) pinctrl系统中gpf/gpg irq controller的驱动调用过程:
a. pinctrl系统的驱动程序:
a.1 源代码: drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-samsung.c
static struct platform_driver samsung_pinctrl_driver = {
.probe = samsung_pinctrl_probe,
.driver = {
.name = "samsung-pinctrl",
.of_match_table = samsung_pinctrl_dt_match, // 含有 { .compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl", .data = &s3c2440_of_data },
.suppress_bind_attrs = true,
.pm = &samsung_pinctrl_pm_ops,
},
};
a.2 设备树中:
pinctrl@56000000 {
reg = <0x56000000 0x1000>;
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl"; // 据此找到驱动
a.3 驱动中的操作:
samsung_pinctrl_probe // drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-samsung.c
最终会调用到 s3c24xx_eint_init // drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-s3c24xx.c
// eint0,1,2,3的处理函数在处理root irq controller时已经设置;
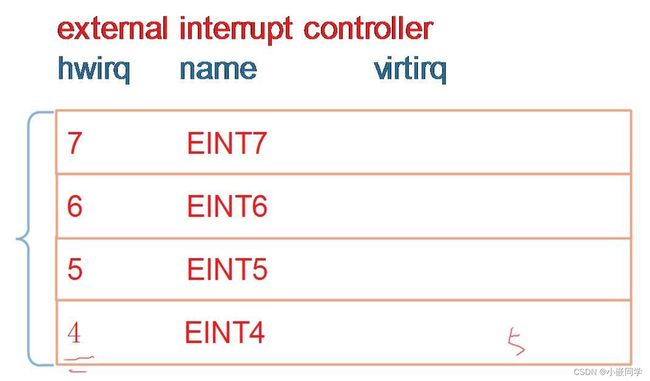
// 设置eint4_7, eint8_23的处理函数(它们是分发函数)
for (i = 0; i < NUM_EINT_IRQ; ++i) {
unsigned int irq;
if (handlers[i]) /* add by [email protected], 不再设置eint0,1,2,3的处理函数 */
{
irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(eint_np, i);
if (!irq) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to get wakeup EINT IRQ %d\n", i);
return -ENXIO;
}
eint_data->parents[i] = irq;
irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(irq, handlers[i], eint_data);
}
}
// 为GPF、GPG设置irq_domain
for (i = 0; i < d->nr_banks; ++i, ++bank) {
ops = (bank->eint_offset == 0) ? &s3c24xx_gpf_irq_ops
: &s3c24xx_gpg_irq_ops;
bank->irq_domain = irq_domain_add_linear(bank->of_node, bank->nr_pins, ops, ddata);
}
(4) 使用中断的驱动调用过程:
a. 在设备节点中描述(表明使用"哪一个中断控制器里的哪一个中断, 及中断触发方式")
比如:
buttons {
compatible = "jz2440_button";
eint-pins = <&gpf 0 0>, <&gpf 2 0>, <&gpg 3 0>, <&gpg 11 0>;
interrupts-extended = <&intc 0 0 0 3>,
<&intc 0 0 2 3>,
<&gpg 3 3>,
<&gpg 11 3>;
};
b. 设备节点会被转换为 platform_device
"中断的硬件信息" 会转换为"中断号",
保存在platform_device的"中断资源"里
在之前讲解了设备树中设备节点转换为 platform_device 的过程;
我们只关心里面对中断信息的处理:
of_device_alloc (drivers/of/platform.c)
dev = platform_device_alloc("", PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE); // 分配 platform_device
num_irq = of_irq_count(np); // 计算中断数
of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) // drivers/of/irq.c, 根据设备节点中的中断信息, 构造中断资源
of_irq_to_resource
int irq = of_irq_get(dev, index); // 获得virq, 中断号
rc = of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq); // drivers/of/irq.c, 解析设备树中的中断信息, 保存在of_phandle_args结构体中
domain = irq_find_host(oirq.np); // 查找irq_domain, 每一个中断控制器都对应一个irq_domain
irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq); // kernel/irq/irqdomain.c, 创建virq和中断信息的映射
irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
irq_domain_translate(domain, fwspec, &hwirq, &type) // 调用irq_domain->ops->xlate, 把设备节点里的中断信息解析为hwirq, type
virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 看看这个hwirq是否已经映射, 如果virq非0就直接返回
virq = irq_create_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 否则创建映射
virq = irq_domain_alloc_descs(-1, 1, hwirq, of_node_to_nid(of_node), NULL); // 返回未占用的virq
irq_domain_associate(domain, virq, hwirq) // 调用irq_domain->ops->map(domain, virq, hwirq), 做必要的硬件设置
c. 驱动程序从platform_device的"中断资源"取出中断号, 就可以request_irq了
注:本文章参考了《韦东山老师嵌入式课程》笔记、《朱有鹏老师嵌入式课程》笔记、《郭天祥老师51单片机书籍》,并结合了自己的实际开发经历以及网上他人的技术文章,综合整理得到。如有侵权,联系删除!水平有限,欢迎各位在评论区交流