【21】使用预训练的目标检测与语义分割网络
今天简单测试一下pytorch提供的模型
文章目录
- 1. 使用训练好的目标检测网络
-
- 1.1 完整代码
- 2. 使用训练好的语义分割网络
-
- 2.1 完整代码
1. 使用训练好的目标检测网络
import numpy as np
import torchvision
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
加载已经训练好的ResNet-50-FPN结构的Fast RCNN模型
model = torchvision.models.detection.fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
查看网络结构
# 切换为测试模式
model.eval()
model.modules
dataroot = 'E:\学习\机器学习\数据集\VOC2012\VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages\\2007_001526.jpg' # 这是一张五个黑人图像
image = Image.open(dataroot)
# image.show() # 会弹出图像
transform = transforms.Compose([ # 对图像进行变换
transforms.ToTensor()
])
image_t = transform(image) # 格式转换
image_t.shape
torch.Size([3, 298, 500])
# 一般来说,需要增加维度,第0维度为batchsize
image_t = image_t.unsqueeze(0)
image_t.shape, image.size
(torch.Size([1, 3, 298, 500]), (500, 298))
pred = model(image_t)
pred
[{'boxes': tensor([[377.9250, 13.7037, 493.1622, 297.6194],
[287.2326, 23.5087, 387.5676, 298.0000],
[208.0055, 36.3203, 316.6268, 298.0000],
[ 99.1883, 42.3514, 215.3772, 293.5994],
[ 0.0000, 18.5004, 113.6753, 293.4090],
[103.1641, 89.9698, 120.0527, 106.6798],
[377.6761, 83.7355, 389.9832, 99.6203],
[186.2982, 87.3854, 227.7398, 111.3254],
[369.1582, 81.4083, 384.1546, 104.8596],
[104.1660, 80.9660, 192.0679, 223.8538],
[489.6611, 87.0265, 500.0000, 115.7063],
[205.3504, 81.7290, 227.3066, 88.7337],
[ 12.9033, 70.3410, 100.9079, 232.6088],
[334.8049, 16.4304, 448.6866, 298.0000],
[ 0.0000, 68.2807, 56.2474, 295.7907],
[359.0639, 79.0281, 378.9404, 104.2661],
[263.1891, 91.6502, 285.9006, 207.0223],
[488.7800, 83.5604, 498.6758, 93.8575],
[397.8902, 69.1296, 475.0887, 158.1689],
[213.1082, 83.5962, 296.4767, 203.5594],
[192.5514, 103.8455, 214.0233, 234.5641],
[108.1454, 83.0643, 165.9468, 166.2449],
[ 2.8212, 71.0566, 42.2922, 203.3171],
[186.8724, 90.9442, 209.4068, 106.2018],
[306.5388, 75.2656, 372.6170, 110.4899],
[312.3708, 70.4173, 364.8932, 133.3953],
[114.6884, 88.3139, 196.6803, 227.3148],
[272.4024, 96.7587, 287.4213, 188.5823],
[264.7156, 95.0346, 280.7938, 172.3812],
[372.4721, 175.0065, 388.3729, 199.5335],
[357.0051, 79.2724, 373.7537, 102.6262],
[ 87.1951, 80.9814, 104.0062, 114.8614],
[250.1311, 89.9769, 279.9026, 200.7932],
[206.3279, 81.9413, 227.7696, 88.9331],
[298.3614, 71.8469, 370.1693, 184.6290],
[348.6332, 79.9749, 387.5624, 105.4334],
[ 13.1942, 98.4261, 100.7580, 229.2718],
[486.5149, 94.5922, 495.3294, 116.6954],
[185.4654, 85.1627, 228.6101, 112.0963],
[193.6432, 107.3661, 213.1962, 234.7787],
[374.9436, 81.5935, 388.6273, 93.4102],
[369.7113, 81.8386, 386.0195, 105.9965],
[ 99.3100, 87.0634, 106.2750, 112.2665],
[194.8513, 108.2166, 212.0829, 232.3898],
[201.1373, 81.8559, 229.3789, 94.0905],
[ 19.8349, 185.0172, 90.2345, 237.0425],
[461.9336, 72.3364, 497.9980, 185.3475],
[ 90.3956, 112.8333, 111.5753, 243.3585]], grad_fn=),
'labels': tensor([ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 27, 3, 3, 27, 1, 1, 3, 32, 3,
27, 27, 27, 27, 27, 3, 27, 27, 31, 32, 32, 31, 27, 3, 32, 8, 27, 3,
31, 3, 8, 31, 3, 8, 3, 32, 3, 31, 1, 27]),
'scores': tensor([0.9997, 0.9993, 0.9991, 0.9985, 0.9982, 0.9747, 0.9662, 0.9459, 0.9411,
0.7976, 0.7688, 0.7279, 0.7057, 0.6844, 0.6773, 0.6273, 0.5956, 0.4991,
0.4626, 0.3882, 0.3289, 0.3165, 0.2188, 0.1812, 0.1696, 0.1556, 0.1480,
0.1438, 0.1274, 0.1183, 0.1129, 0.1031, 0.0971, 0.0957, 0.0954, 0.0909,
0.0851, 0.0842, 0.0730, 0.0724, 0.0651, 0.0647, 0.0623, 0.0598, 0.0563,
0.0551, 0.0546, 0.0518], grad_fn=)}]
这里的输出包含了3种值,分别是检测到每个目标的边界框(boxes)、目标的所属类别(labels)、以及属于相应类别的得分(scores)。
print(" boxes.shape:{},\n labels.shape:{},\n scores.shape:{}\n".format(pred[0]['boxes'].shape, pred[0]['labels'].shape, pred[0]['scores'].shape))
boxes.shape:torch.Size([48, 4]),
labels.shape:torch.Size([48]),
scores.shape:torch.Size([48])
这张图像可以看出有48个结果输出,但是只有前9个结果的预测置信度大于90%
# 首先定义每个类别所对应的标签
COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES = [
'__background__', 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus',
'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light', 'fire hydrant', 'N/A', 'stop sign',
'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'N/A', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'N/A', 'N/A',
'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee', 'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball',
'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard', 'tennis racket',
'bottle', 'N/A', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl',
'banana', 'apple', 'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza',
'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed', 'N/A', 'dining table',
'N/A', 'N/A', 'toilet', 'N/A', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'N/A', 'book',
'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier', 'toothbrush'
]
len(COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES)
91
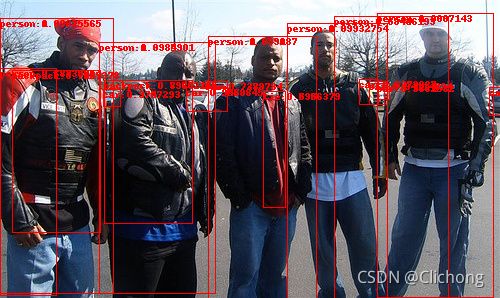
针对上述pred的预测结果,需要提取出有效数据。提取的信息又每个目标的位置、类别、得分,然后将得分大于0.5的目标作为检测到的有效目标,并将检测到的目标在图像上显示出来
# 使用name2label列表COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES,提取labels对于的类别名称
pred_class = [COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES[i] for i in list(pred[0]['labels'].numpy())]
# 获取对应的置信度分数
pred_score = list(pred[0]['scores'].detach().numpy())
# 获取对应的目标预测检测框
pred_boxes = [[box[0],box[1],box[2],box[3]] for box in list(pred[0]['boxes'].detach().numpy())]
# 提取置信度大于0.5的结果
pred_index = [pred_score.index(x) for x in pred_score if x > 0.5]
# 获取到了对应索引:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]
# 设置图像显示字体
fontsize = np.int16(image.size[1]/30)
# 可视化图像.表示在原图上添加一些元素
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
for index in pred_index:
# 依次回去边界框的坐标信息
box = pred_boxes[index]
# 添加矩形框
draw.rectangle(box, outline="red")
# 矩阵框中标上: class:score的形式
texts = pred_class[index] + ":" + str(np.round(pred_score[index], 4))
# texts = pred_class[index] + ":" + str(format(pred_score[index], '.4f'))
# 在图像上的指定位置添加文本
draw.text((box[0], box[1]), texts, fill="red")
image
1.1 完整代码
import numpy as np
import torchvision
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 首先定义每个类别所对应的标签
COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES = [
'__background__', 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus',
'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light', 'fire hydrant', 'N/A', 'stop sign',
'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'N/A', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'N/A', 'N/A',
'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee', 'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball',
'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard', 'tennis racket',
'bottle', 'N/A', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl',
'banana', 'apple', 'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza',
'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed', 'N/A', 'dining table',
'N/A', 'N/A', 'toilet', 'N/A', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'N/A', 'book',
'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier', 'toothbrush'
]
# 现在将其包装成一个函数
def Object_Dection(model, imagepath, COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES):
# 打卡图像
image = Image.open(imagepath)
# image.show() # 会弹出图像
transform = transforms.Compose([ # 对图像进行变换
transforms.ToTensor()
])
image_t = transform(image) # 格式转换
# 增维
image_t = image_t.unsqueeze(0)
pred = model(image_t)
# 使用name2label列表COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES,提取labels对于的类别名称
pred_class = [COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES[i] for i in list(pred[0]['labels'].numpy())]
# 获取对应的置信度分数
pred_score = list(pred[0]['scores'].detach().numpy())
# 获取对应的目标预测检测框
pred_boxes = [[box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]] for box in list(pred[0]['boxes'].detach().numpy())]
# 提取置信度大于0.8的结果
pred_index = [pred_score.index(x) for x in pred_score if x > 0.8]
# 设置图像显示字体
# fontsize = np.int16(image.size[1]/30)
# font = ImageFont.truetype("/Library/Fonts/华文细黑.ttf", fontsize)
# 在原图上添加信息
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
for index in pred_index:
# 依次回去边界框的坐标信息
box = pred_boxes[index]
# 添加矩形框
draw.rectangle(box, outline="red", width=3)
# 矩阵框中标上: class:score的形式
texts = pred_class[index] + ":" + str(np.round(pred_score[index], 4))
# texts = pred_class[index] + ":" + str(format(pred_score[index], '.4f'))
# 在图像上的指定位置添加文本
draw.text((box[0], box[1]), texts, fill="red")
return image
# 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
model = torchvision.models.detection.fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
# 切换为测试模式
model.eval()
imagepath = 'E:\学习\机器学习\数据集\VOC2012\VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages\\2007_001526.jpg'
image = Object_Dection(model, imagepath, COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES)
# 显示图像
image.show()
结果展示:
2. 使用训练好的语义分割网络
# 加载模型
model = torchvision.models.segmentation.fcn_resnet101(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
imagepath = 'E:\学习\机器学习\数据集\VOC2012\VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages\\2007_001526.jpg'
image = Image.open(imagepath)
# 对图像进行变换
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
image_t = transform(image)
image_t = image_t.unsqueeze(0)
pred = model(image_t)
image_t.shape
torch.Size([1, 3, 298, 500])
pred
OrderedDict([('out',
tensor([[[[10.7415, 10.7415, 10.7415, ..., 9.5000, 9.5000, 9.5000],
[10.7415, 10.7415, 10.7415, ..., 9.5000, 9.5000, 9.5000],
[10.7415, 10.7415, 10.7415, ..., 9.5000, 9.5000, 9.5000],
...,
[ 7.4524, 7.4524, 7.4524, ..., 9.5723, 9.5723, 9.5723],
[ 7.4524, 7.4524, 7.4524, ..., 9.5723, 9.5723, 9.5723],
[ 7.4524, 7.4524, 7.4524, ..., 9.5723, 9.5723, 9.5723]],
[[-1.6881, -1.6881, -1.6881, ..., -0.0993, -0.0993, -0.0993],
[-1.6881, -1.6881, -1.6881, ..., -0.0993, -0.0993, -0.0993],
[-1.6881, -1.6881, -1.6881, ..., -0.0993, -0.0993, -0.0993],
...,
[-1.4228, -1.4228, -1.4228, ..., -0.1377, -0.1377, -0.1377],
[-1.4228, -1.4228, -1.4228, ..., -0.1377, -0.1377, -0.1377],
[-1.4228, -1.4228, -1.4228, ..., -0.1377, -0.1377, -0.1377]],
[[-2.3719, -2.3719, -2.3719, ..., -1.8977, -1.8977, -1.8977],
[-2.3719, -2.3719, -2.3719, ..., -1.8977, -1.8977, -1.8977],
[-2.3719, -2.3719, -2.3719, ..., -1.8977, -1.8977, -1.8977],
...,
[-0.8262, -0.8262, -0.8262, ..., -1.6540, -1.6540, -1.6540],
[-0.8262, -0.8262, -0.8262, ..., -1.6540, -1.6540, -1.6540],
[-0.8262, -0.8262, -0.8262, ..., -1.6540, -1.6540, -1.6540]],
...,
[[-0.5688, -0.5688, -0.5688, ..., -0.9008, -0.9008, -0.9008],
[-0.5688, -0.5688, -0.5688, ..., -0.9008, -0.9008, -0.9008],
[-0.5688, -0.5688, -0.5688, ..., -0.9008, -0.9008, -0.9008],
...,
[ 0.4994, 0.4994, 0.4994, ..., 1.4651, 1.4651, 1.4651],
[ 0.4994, 0.4994, 0.4994, ..., 1.4651, 1.4651, 1.4651],
[ 0.4994, 0.4994, 0.4994, ..., 1.4651, 1.4651, 1.4651]],
[[-0.4391, -0.4391, -0.4391, ..., 2.3527, 2.3527, 2.3527],
[-0.4391, -0.4391, -0.4391, ..., 2.3527, 2.3527, 2.3527],
[-0.4391, -0.4391, -0.4391, ..., 2.3527, 2.3527, 2.3527],
...,
[ 0.1844, 0.1844, 0.1844, ..., 1.2322, 1.2322, 1.2322],
[ 0.1844, 0.1844, 0.1844, ..., 1.2322, 1.2322, 1.2322],
[ 0.1844, 0.1844, 0.1844, ..., 1.2322, 1.2322, 1.2322]],
[[ 1.3879, 1.3879, 1.3879, ..., 0.9153, 0.9153, 0.9153],
[ 1.3879, 1.3879, 1.3879, ..., 0.9153, 0.9153, 0.9153],
[ 1.3879, 1.3879, 1.3879, ..., 0.9153, 0.9153, 0.9153],
...,
[-0.0281, -0.0281, -0.0281, ..., 0.4544, 0.4544, 0.4544],
[-0.0281, -0.0281, -0.0281, ..., 0.4544, 0.4544, 0.4544],
[-0.0281, -0.0281, -0.0281, ..., 0.4544, 0.4544, 0.4544]]]],
grad_fn=)),
('aux',
tensor([[[[ 9.7964, 9.7964, 9.7964, ..., 8.7053, 8.7053, 8.7053],
[ 9.7964, 9.7964, 9.7964, ..., 8.7053, 8.7053, 8.7053],
[ 9.7964, 9.7964, 9.7964, ..., 8.7053, 8.7053, 8.7053],
...,
[ 6.6633, 6.6633, 6.6633, ..., 8.1096, 8.1096, 8.1096],
[ 6.6633, 6.6633, 6.6633, ..., 8.1096, 8.1096, 8.1096],
[ 6.6633, 6.6633, 6.6633, ..., 8.1096, 8.1096, 8.1096]],
[[-1.0417, -1.0417, -1.0417, ..., -0.4245, -0.4245, -0.4245],
[-1.0417, -1.0417, -1.0417, ..., -0.4245, -0.4245, -0.4245],
[-1.0417, -1.0417, -1.0417, ..., -0.4245, -0.4245, -0.4245],
...,
[-1.3747, -1.3747, -1.3747, ..., -0.0461, -0.0461, -0.0461],
[-1.3747, -1.3747, -1.3747, ..., -0.0461, -0.0461, -0.0461],
[-1.3747, -1.3747, -1.3747, ..., -0.0461, -0.0461, -0.0461]],
[[-1.8145, -1.8145, -1.8145, ..., -1.1215, -1.1215, -1.1215],
[-1.8145, -1.8145, -1.8145, ..., -1.1215, -1.1215, -1.1215],
[-1.8145, -1.8145, -1.8145, ..., -1.1215, -1.1215, -1.1215],
...,
[-0.3710, -0.3710, -0.3710, ..., -0.8807, -0.8807, -0.8807],
[-0.3710, -0.3710, -0.3710, ..., -0.8807, -0.8807, -0.8807],
[-0.3710, -0.3710, -0.3710, ..., -0.8807, -0.8807, -0.8807]],
...,
[[ 0.6499, 0.6499, 0.6499, ..., -0.0127, -0.0127, -0.0127],
[ 0.6499, 0.6499, 0.6499, ..., -0.0127, -0.0127, -0.0127],
[ 0.6499, 0.6499, 0.6499, ..., -0.0127, -0.0127, -0.0127],
...,
[ 0.6200, 0.6200, 0.6200, ..., 0.3854, 0.3854, 0.3854],
[ 0.6200, 0.6200, 0.6200, ..., 0.3854, 0.3854, 0.3854],
[ 0.6200, 0.6200, 0.6200, ..., 0.3854, 0.3854, 0.3854]],
[[-0.6026, -0.6026, -0.6026, ..., 1.1884, 1.1884, 1.1884],
[-0.6026, -0.6026, -0.6026, ..., 1.1884, 1.1884, 1.1884],
[-0.6026, -0.6026, -0.6026, ..., 1.1884, 1.1884, 1.1884],
...,
[-0.8764, -0.8764, -0.8764, ..., 0.7393, 0.7393, 0.7393],
[-0.8764, -0.8764, -0.8764, ..., 0.7393, 0.7393, 0.7393],
[-0.8764, -0.8764, -0.8764, ..., 0.7393, 0.7393, 0.7393]],
[[ 1.3283, 1.3283, 1.3283, ..., 1.2738, 1.2738, 1.2738],
[ 1.3283, 1.3283, 1.3283, ..., 1.2738, 1.2738, 1.2738],
[ 1.3283, 1.3283, 1.3283, ..., 1.2738, 1.2738, 1.2738],
...,
[-0.7884, -0.7884, -0.7884, ..., -0.2274, -0.2274, -0.2274],
[-0.7884, -0.7884, -0.7884, ..., -0.2274, -0.2274, -0.2274],
[-0.7884, -0.7884, -0.7884, ..., -0.2274, -0.2274, -0.2274]]]],
grad_fn=))])
pred['out'].shape, pred['aux'].shape
(torch.Size([1, 21, 298, 500]), torch.Size([1, 21, 298, 500]))
output = pred['out'].squeeze()
output.shape
torch.Size([21, 298, 500])
# 获取21类中自信度最高的哪一类,作为像素点的类; 从而实现将3维矩阵变换为二维矩阵
# 现在该二维矩阵中每个取值均代表图像中对应位置像素点的预测类别
outputarg = torch.argmax(output, dim=0).numpy()
outputarg.shape
(298, 500)
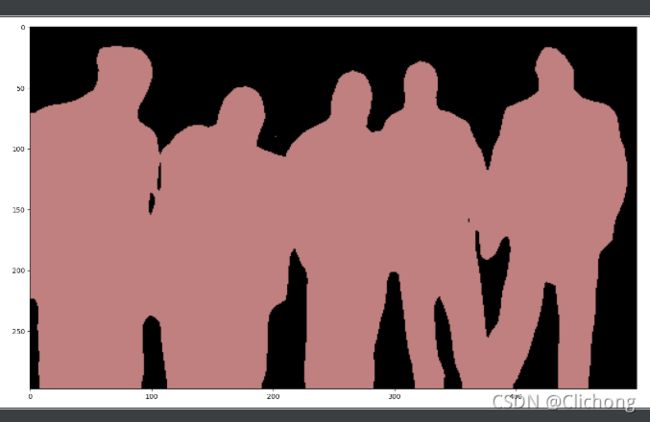
# 将像素值的每个预测类别分别编码为不同的颜色,然后将图像可视化
def decode_segmaps(image, label_colors, nc=21):
# 函数将输出的2D图像,会将不同类编码为不同的颜色
r = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
g = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
b = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
print(r.shape, g.shape, b.shape) # (298, 500) (298, 500) (298, 500)
for cls in range(0, nc):
idx = (image==cls)
print("cls:{}, idx.shape:{}".format(cls, idx.shape))
r[idx] = label_colors[cls][0]
g[idx] = label_colors[cls][1]
b[idx] = label_colors[cls][2]
rgbimage = np.stack([r,g,b], axis=2)
return rgbimage
# 指定颜色编码
label_colors = np.array([
(0,0,0),
(128,0,0),(0,128,0),(128,128,0),(0,0,128),(128,0,128),
(0,128,128),(128,128,128),(64,0,0),(192,0,0),(64,128,0),
(192,128,0),(64,0,128),(192,0,128),(64,128,128),(192,128,128),
(0,64,64),(128,64,0),(0,192,0),(128,192,0),(0,64,128)
])
outputrgb = decode_segmaps(outputarg, label_colors)
outputrgb.shape
(298, 500) (298, 500) (298, 500)
(298, 500, 3)
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8))
plt.subplot(1,1,1)
plt.imshow(outputrgb)
2.1 完整代码
import numpy as np
import torchvision
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 指定颜色编码:一共21类,每一类对应一个颜色编码
label_colors = np.array([
(0,0,0),
(128,0,0),(0,128,0),(128,128,0),(0,0,128),(128,0,128),
(0,128,128),(128,128,128),(64,0,0),(192,0,0),(64,128,0),
(192,128,0),(64,0,128),(192,0,128),(64,128,128),(192,128,128),
(0,64,64),(128,64,0),(0,192,0),(128,192,0),(0,64,128)
])
# 将像素值的每个预测类别分别编码为不同的颜色,然后将图像可视化
def decode_segmaps(image, label_colors, nc=21):
# 函数将输出的2D图像,会将不同类编码为不同的颜色
r = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
g = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
b = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
# print(r.shape, g.shape, b.shape) # (298, 500) (298, 500) (298, 500)
# 循环遍历每一层(一共21层),当第cls类出现在image的某些像素值时,这些点索引为idx
for cls in range(0, nc):
idx = (image == cls)
# print("cls:{}, idx.shape:{}".format(cls, idx.shape))
# 构造rgb三通道:本来是一个类别点变成一个像素(3通道)
r[idx] = label_colors[cls][0]
g[idx] = label_colors[cls][1]
b[idx] = label_colors[cls][2]
# 三个通道拼接获取彩色图像
rgbimage = np.stack([r, g, b], axis=2)
return rgbimage
# 功能: 输入图像路径,输出分割图像
def Semantic_Segmentation(model, imagepath, label_colors):
# 获取图片
image = Image.open(imagepath)
# 对图像进行变换
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
image_t = transform(image)
# 增维
image_t = image_t.unsqueeze(0)
pred = model(image_t)
# pred['out'].shape, pred['aux'].shape
# (torch.Size([1, 21, 298, 500]), torch.Size([1, 21, 298, 500]))
# 获取像素点值并降维
output = pred['out'].squeeze()
# 获取21类中自信度最高的哪一类,作为像素点的类; 从而实现将3维矩阵变换为二维矩阵
# 现在该二维矩阵中每个取值均代表图像中对应位置像素点的预测类别
outputarg = torch.argmax(output, dim=0).numpy()
# 类别通道转换成颜色通道,转换成一张rgb图像
outputrgb = decode_segmaps(outputarg, label_colors)
# 绘制图像
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8))
plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
plt.imshow(outputrgb)
plt.show()
# 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
model = torchvision.models.segmentation.fcn_resnet101(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
imagepath = 'E:\学习\机器学习\数据集\VOC2012\VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages\\2007_001526.jpg'
Semantic_Segmentation(model, imagepath, label_colors)