100天精通Python(数据分析篇)——第55天:Pandas之DataFrame对象大总结
![]()
文章目录
- 每篇前言
- 一、什么是DataFrame?
- 二、创建DataFrame对象
-
- 1. list列表构建DataFrame
- 2. dict字典构建DataFrame
- 3. ndarray创建DataFrame
- 4. Series创建DataFrame
- 三、列索引操作
-
- 1. 读取单列
- 2. 读取不连续索引
- 3. 添加新列
- 4. 删除列
- 四、索引读取数据操作
-
- 1. 标签索引
- 2. 位置索引
- 3. 切片索引
- 4. 添加行
- 5. 删除行
- 五、书籍推荐
每篇前言
作者介绍:Python领域优质创作者、华为云享专家、阿里云专家博主、2021年CSDN博客新星Top6
- 本文已收录于Python全栈系列专栏:《100天精通Python从入门到就业》
- 此专栏文章是专门针对Python零基础小白所准备的一套完整教学,从0到100的不断进阶深入的学习,各知识点环环相扣
- 订阅专栏后续可以阅读Python从入门到就业100篇文章;还可私聊进两百人Python全栈交流群(手把手教学,问题解答); 进群可领取80GPython全栈教程视频 + 300本计算机书籍:基础、Web、爬虫、数据分析、可视化、机器学习、深度学习、人工智能、算法、面试题等。
- 加入我一起学习进步,一个人可以走的很快,一群人才能走的更远!
一、什么是DataFrame?
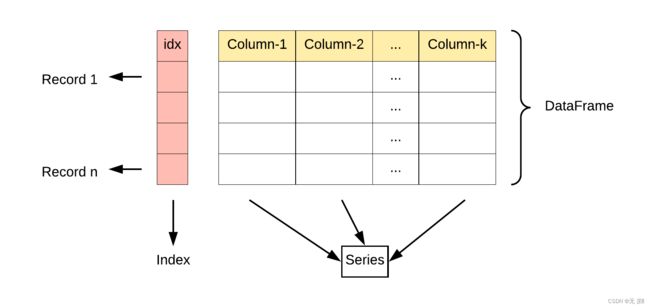
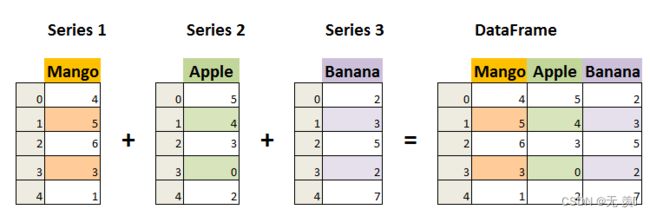
DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,它含有一组有序的列,每列可以是不同类型的值。DataFrame既有行索引也有列索引,它可以被看做是由Series组成的字典(共用同一个索引),数据是以二维结构存放的。
二、创建DataFrame对象
DataFrame 构造方法如下:
pandas.DataFrame( data, index, columns, dtype, copy)
参数说明:
-
data:一组数据(ndarray、series, map, lists, dict 等类型)。
-
index:索引值,或者可以称为行标签。
-
columns:列标签,默认为 RangeIndex (0, 1, 2, …, n) 。
-
dtype:数据类型。
-
copy:拷贝数据,默认为 False。
1. list列表构建DataFrame
1)通过单列表创建
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> print(df)
0
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2)通过嵌套列表创建
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = [['小明', 20], ['小红', 10]]
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['name', 'age'], dtype=float)
sys:1: FutureWarning: Could not cast to float64, falling back to object. This behavior is deprecated. In a future version, when a dtype is passed to 'DataFrame', either all columns will be cast to that dtype, or a TypeError will be raised
>>> print(df)
name age
0 小明 20.0
1 小红 10.0
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
3)列表中嵌套字典(字典的键被用作列名,缺失则赋值为NaN):
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = [{'A': 1, 'B': 2}, {'A': 3, 'B': 4, 'C': 5}]
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> print(df)
A B C
0 1 2 NaN
1 3 4 5.0
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2. dict字典构建DataFrame
使用 dict 创建,dict中列表的长度必须相同, 如果传递了index,则索引的长度应等于数组的长度。如果没有传递索引,则默认情况下,索引将是range(n),其中n是数组长度。
1)普通创建:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = {'name': ['小红', '小明', '小白'], 'age': [10, 20, 30]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> print(df)
name age
0 小红 10
1 小明 20
2 小白 30
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2)设置index创建:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = {'name': ['小红', '小明', '小白'], 'age': [10, 20, 30]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['老三', '老二', '老大'])
>>> print(df)
name age
老三 小红 10
老二 小明 20
老大 小白 30
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
3. ndarray创建DataFrame
1)普通方式创建:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>>
>>> data = np.random.randn(3, 3)
>>> print(data)
[[-1.9332579 0.70876382 -0.44291914]
[-0.26228642 -1.05200338 0.57390067]
[-0.49433001 0.70472595 -0.50749279]]
>>> print(type(data))
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> print(df)
0 1 2
0 -1.933258 0.708764 -0.442919
1 -0.262286 -1.052003 0.573901
2 -0.494330 0.704726 -0.507493
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2)设置列名创建:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>>
>>> data = np.random.randn(3, 3)
>>> print(data)
[[-0.22028147 0.62374794 -0.66210282]
[-0.71785439 -1.21004547 1.15663811]
[ 1.47843923 0.4385811 0.31931312]]
>>> print(type(data))
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=list("ABC"))
>>> print(df)
A B C
0 -0.220281 0.623748 -0.662103
1 -0.717854 -1.210045 1.156638
2 1.478439 0.438581 0.319313
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
4. Series创建DataFrame
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> data = {'A': pd.Series(1, index=list(range(4)), dtype='float32'),
... 'B': pd.Series(2, index=list(range(4)), dtype='float32'),
... 'C': pd.Series(3, index=list(range(4)), dtype='float32')
... }
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> print(df)
A B C
0 1.0 2.0 3.0
1 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 1.0 2.0 3.0
3 1.0 2.0 3.0
>>> print(type(df))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
三、列索引操作
创建DataFrame对象:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> df_obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 4), columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
>>> print(df_obj.head())
a b c d
0 0.781380 -1.074496 -1.448204 -0.313385
1 -0.568288 2.011669 0.955440 1.617713
2 0.222755 -1.507924 -0.903779 1.301956
3 0.706442 -0.503069 -1.561416 -0.290718
4 -1.071889 -0.280071 -2.033153 1.618598
1. 读取单列
>>> # 列索引
>>> print(df_obj['a'])
0 0.781380
1 -0.568288
2 0.222755
3 0.706442
4 -1.071889
Name: a, dtype: float64
>>> print(type(df_obj['a'])) # 返回Series类型
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
2. 读取不连续索引
>>> # 不连续索引
>>> print(df_obj[['a', 'c']])
a c
0 0.237575 -1.931997
1 0.294029 -0.513547
2 0.151643 -0.397062
3 0.481416 0.717808
4 -0.139943 -0.221828
3. 添加新列
1)直接赋值操作:
>>> df_obj['e'] = pd.Series([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
>>> print(df_obj)
a b c d e
0 0.237575 0.396866 -1.931997 -0.821513 10
1 0.294029 -0.943375 -0.513547 0.186539 20
2 0.151643 0.900406 -0.397062 -1.136502 30
3 0.481416 -0.004957 0.717808 -1.020731 40
4 -0.139943 -0.844997 -0.221828 2.186861 50
2) insert(索引位置,column='列名',value='值') 方法插入新列:
>>> df_obj.insert(1, column='f', value=[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]) # 插入一列为不同数据
>>> print(df_obj)
a f b c d e
0 1.520003 10 0.375014 0.059027 1.171379 10
1 0.099122 20 0.096940 -0.189679 -0.046981 20
2 -2.270308 30 -0.759622 0.660129 -1.017288 30
3 2.010634 40 1.456483 -0.741796 -0.280938 40
4 2.120968 50 1.077172 -1.616609 -1.069243 50
>>> df_obj.insert(1, column='g', value=111) # 插入一列为相同数据
>>> print(df_obj)
a g f b c d e
0 1.520003 111 10 0.375014 0.059027 1.171379 10
1 0.099122 111 20 0.096940 -0.189679 -0.046981 20
2 -2.270308 111 30 -0.759622 0.660129 -1.017288 30
3 2.010634 111 40 1.456483 -0.741796 -0.280938 40
4 2.120968 111 50 1.077172 -1.616609 -1.069243 50
4. 删除列
del() 和 pop()方法都可以删除列
>>> del df_obj['f']
>>> print(df_obj)
a g b c d e
0 1.520003 111 0.375014 0.059027 1.171379 10
1 0.099122 111 0.096940 -0.189679 -0.046981 20
2 -2.270308 111 -0.759622 0.660129 -1.017288 30
3 2.010634 111 1.456483 -0.741796 -0.280938 40
4 2.120968 111 1.077172 -1.616609 -1.069243 50
>>> df_obj.pop('g')
0 111
1 111
2 111
3 111
4 111
Name: g, dtype: int64
>>> print(df_obj)
a b c d e
0 1.520003 0.375014 0.059027 1.171379 10
1 0.099122 0.096940 -0.189679 -0.046981 20
2 -2.270308 -0.759622 0.660129 -1.017288 30
3 2.010634 1.456483 -0.741796 -0.280938 40
4 2.120968 1.077172 -1.616609 -1.069243 50
四、索引读取数据操作
1. 标签索引
DataFrame 不能直接切片,可以通过loc来做切片。 loc是基于标签名的索引,也就是我们自定义的索引名
>>> # 第一个参数索引行,第二个参数是列
>>> print(df_obj.loc[0:2, 'a'])
0 0.237575
1 0.294029
2 0.151643
Name: a, dtype: float64
2. 位置索引
作用和loc一样,不过是基于索引编号来索引
>>> print(df_obj.iloc[0:2, 0])
0 0.237575
1 0.294029
Name: a, dtype: float64
注意:和df_obj.loc[0:2, ‘a’]的区别,iloc是左闭右开
3. 切片索引
>>> print(df_obj[0:2]) # 左闭右开
a b c d
0 -0.008962 -1.440611 -0.241749 -0.328990
1 0.722666 -0.968137 0.752607 0.060432
4. 添加行
append() 函数可以将新的DataFrame 对象追加到原对象后面
>>> df_obj1 = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3, 4]], columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
>>> print(df_obj1)
a b c d
0 1 2 3 4
>>> df_obj = df_obj.append(df_obj1)
>>> print(df_obj)
a b c d
0 -0.214975 -1.574176 0.005630 0.372708
1 0.951436 0.725618 1.275498 2.072770
2 -1.739804 -0.375916 -0.588529 -0.045825
3 1.048349 -0.015041 0.953475 1.369060
4 1.515951 -1.453001 0.921479 -0.338588
0 1.000000 2.000000 3.000000 4.000000
5. 删除行
使用drop(索引)即可删除指定行
>>> df_obj = df_obj.drop(0)
>>> df_obj = df_obj.drop(1)
>>> print(df_obj)
a b c d
2 -1.739804 -0.375916 -0.588529 -0.045825
3 1.048349 -0.015041 0.953475 1.369060
4 1.515951 -1.453001 0.921479 -0.338588
五、书籍推荐
【书籍内容简介】
- 本书介绍了数据分析的方法和步骤,并分别通过Excel和Python实施和对比。通过本书一方面可以拓宽对Excel功能的认识,另一方面可以学习和掌握Python的基础操作。
本书分为 11 章,涵盖的主要内容有Excel和Python在数据分析领域的定位与核心功能对比、统计量介绍、Excel与Python实践环境搭建、数据处理与分析的基本方法、ETL方法、数据建模理论、数据挖掘基础、数据可视化的基本方法、分析报告的制作方法。
- 京东自营:https://item.jd.com/13350513.html